Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have identified a mechanism that can explain the impaired wound healing in diabetes which can lead to diabetic foot ulcers. The study is published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In diabetic mice, wound healing improved when the identified signalling pathway was blocked … Diabetic foot ulcerations are a common complication of diabetes that constitute a major medical, social and economic issue. The lifetime risk of a person with type 1 or type 2 diabetes developing a foot ulcer is around fifteen percent. The treatment options are currently … read more
Category: Articles
Bacteria partners with virus to cause chronic wounds
A virus that infects a dangerous bacteria helps it thrive in wounds, according to a study by Stanford researchers. But a vaccine against the virus dramatically cuts the bacteria’s infectivity … A common bacterial pathogen called Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces a virus that substantially increases the pathogen’s ability to infect us, according to a study by investigators at the Stanford University School of Medicine … P. aeruginosa weaponizes its resident virus to exploit the immune system’s distinct responses to bacterial versus viral infections … read more
Janssen Submits Supplemental New Drug Application to U.S.
FDA for INVOKANA® (canagliflozin) for the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
The Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson announced today the submission of a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) seeking a new indication for INVOKANA® (canagliflozin) to reduce the risk of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), the doubling of serum creatinine, which is a key predictor of ESKD, and renal or cardiovascular (CV) death in adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). The submission is based on results from the Phase 3 CREDENCE (Canagliflozin and Renal Events in Diabetes with Established Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation) study, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of INVOKANA® versus placebo in this high-risk patient population when used in addition to standard of care.
Primary investigators will present the CREDENCE data during a late-breaking clinical trials session at the International Society of Nephrology (ISN) World Congress of Nephrology (WCN) Annual Meeting in Melbourne, Australia on April 15 at 8:30 am AEST (April 14 at 6:30 pm EDT in the U.S.). An open access live-stream of the late-breaking presentation can be accessed here (registration is required).
“Today, millions of people living with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease are at high risk of experiencing kidney failure, and unfortunately, we have not seen treatment innovation for these patients in almost 20 years. Janssen’s application is a significant step toward bringing a much-needed, new standard of care for those living with these serious conditions,” said James List, M.D., Ph.D., Global Therapeutic Area Head, Cardiovascular & Metabolism, Janssen Research & Development, LLC. “We look forward to presenting the CREDENCE data at the ISN World Congress of Nephrology and working closely with the FDA to bring this important medicine as quickly as possible to people living with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.” … read more
Diabetic Limb Salvage Conference
Highly regarded as one of the world’s finest limb salvage events, MedStar Georgetown University Hospital’s DLS conference brings together the most eminent lower limb specialists for an unforgettable meeting. It is a multidisciplinary team approach meeting that provides each member of the healthcare team with the education and resources needed to heal wounds and prevent amputations. It features a prominent international faculty that promotes the importance of a multispecialty approach in limb salvage. The course highlights evidence-based approach with emphasis on take-home points, techniques, and functional outcomes …. read more
Advanced Therapies in Wound Management
With this initiative EWMA will investigate the barriers and possibilities of advanced therapies in the next generation wound management … The primary deliverable is a document including an introduction to the available technologies based on cellular therapies, tissue engineering and tissue substitutes, which are all technologies associated with the clinical discipline of regenerative medicine. The document also describes new treatments based on physical therapies and the potential of sensors and software … read more
Integra LifeSciences reveals FDA warning letter over chronic wound treatment
Integra LifeSciences (NSDQ:IART) today revealed its receipt of a warning letter sent by the FDA last week about quality system issues at a Boston-area plant that makes products to treat chronic wounds … Plainsboro, N.J.-based Integra said the FDA inspected the plant last October and November, resulting in a Form 483 covering the problems found there. The facility makes extracellular bovine matrix products that accounted for less than 4% of Integra’s sales last year, the company said … read more
Efficacy of Maggot Therapy on Staphylococcus aureus
and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Diabetic Foot Ulcers
This study was conducted to evaluate the antimicrobial effects of medicinal maggots of Lucilia sericata on Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa on diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) … The sample comprised 50 adult patients from the clinic of the Academic Center for Education, Culture and Research of Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran. All participants who had at least 1 DFU present for at least 12 weeks, an arterial brachial index value of more than 0.6, and a hemoglobin A1c value of less than 8% were included in this study … read more
New interactive foot screening assessment now available online
Managing the growing incidence of diabetes in England is set to be one of the major clinical challenges of the 21st century. Estimates suggest that the number of people with diabetes is expected to rise to 4.2 million by 2030, affecting almost 9% of the population. More than 64 000 people with diabetes in England and Wales are thought to have foot ulcers at any given time. Around 7000 leg, foot or toe amputations are carried out each year in people with diabetes, with an estimated cost in 2014/15 at around £1 billion … read more
Identification and management of infection in diabetic foot ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are rising in prevalence globally, and particularly in the Gulf region. Infection remains a common and serious complication in managing DFUs. A need was identified for local guidelines that considered cultural and religious practices in the Gulf region, as well as clinical issues. This consensus document aims to provide practitioners with guidance on identifying and managing DFUs, which can be directly applied to local practice … download (pdf)
A Guide To Emerging Antibiotics For Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria
The rise of bacteria that are resistant to multiple drugs highlights the urgency of developing new antibiotics to combat lower extremity infection. Accordingly, this author explores the potential of new pharmacological agents such as tedizolid, oritavancin, dalbavancin and delafloxacin, and discusses other agents in the pipeline … read more
Calculating The Benefits Of An Annual Diabetic Foot Exam
The benefits of having an annual comprehensive diabetic foot exam are too numerous to mention. If a patient sees his or her podiatrist along with one other member of the diabetic foot team, the relative risk reduction of a high level amputation will decrease, with some studies showing a reduction of as much as 80 percent … It’s a simple thing. Just the patient getting into see his or her foot doctor can yield significant benefits down the road. We outlined with the American Diabetes Association many years ago what goes into a good quality diabetic foot exam … read more
Peripheral arterial disease and the diabetic foot
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a term used to describe atherosclerotic vessels in the periphery, mostly affecting the lower extremities. The blocked vessels impair blood and oxygen perfusion to the lower limbs and may lead to increased risk of ulceration, wounds and amputations. PAD is also associated with increased risk of coronary and cerebrovascular incidents. More than 50% of people living with PAD may not have any clinical symptoms, posing a challenge to diagnosis and management. This article will discuss the aetiology, presentation, risk factors, and management of PAD as related to the lower extremities … read more
Point-Counterpoint: Is Total Contact Casting Better Than
The CAM Walker Boot For Plantar Diabetic Wounds?
This author says total contact casts offer key biomechanical benefits, have extensive literature support and facilitate quicker healing of plantar diabetic foot ulcers … Offloading is one of the central concepts to healing the diabetic foot ulcer.1,2It is usually pressure (combined with neuropathy) that leads to an ulcer. Therefore, we must relieve the pressure in order to achieve wound healing … read more
MTF Biologics’ AmnioBand® Now Covered by Anthem
“We are pleased that Anthem is now covering our AmnioBand allograft solutions,” said Kim Rounds, Vice President of Wound Care at MTF Biologics. “As a nonprofit and the nation’s leading tissue bank, we are extremely pleased by Anthem’s decision to include AmnioBand for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Our expanding portfolio, including viable cryopreserved placental membranes, ambient storage placental tissues, and AlloPatch® Pliable (a human derived reticular dermal matrix), provides wound care professionals and their patients with some of the most safe, clinically proven and cost effective treatment options for chronic wounds.”
Houston’s Third Annual Amputation Prevention Summit Scheduled for March 23rd
The third annual Amputation Prevention Summit will be held on Saturday, March 23, 2019 at Memorial Hermann Greater Heights, 1635 North Loop West, South Tower, First Floor, Houston, Texas, drawing clinicians from Houston and surrounding region. Memorial Hermann is the only health system in the Houston area that is part of the Amputation Prevention Centers of America® network … This CME event aims to highlight the urgent nature of the diabetes epidemic, the prevalence of peripheral arterial disease and diabetic foot ulcers, and how healthcare professionals can change and improve their practice in order to reduce lower extremity amputations … Diabetes is among the top 10 leading causes of death in Texas and the leading cause of non-traumatic lower extremity amputation. The risk of leg amputation for people with diabetes is 15 to 40 times greater than for a person without diabetes. Within two to four years of unilateral limb loss, one-third of all patients lose the other leg. Sadly, only about 50 percent of amputees survive within five years following a leg amputation due to ongoing complications of the chronic disease. With the future incidence of diabetes projected to rise to 550 million people worldwide by the year 2030, limb salvage is becoming a viable alternative, often producing better outcomes than amputation … read more
Vomaris Announces Launch of New Microcurrent-Generating Wound Care Product
Vomaris Innovations, Inc. reports the U.S. launch and first uses of a revolutionary new post-surgical wound dressing. Procellera® FlexEFit™ Antibacterial Wound Dressing employs a novel ‘Link & Build’ design that enables it to be ‘built’ during application to seamlessly cover incisions of virtually any length or curvature with just one product configuration. It is an important addition to Vomaris’s line of wound care products powered by V.Dox™ Technology. The only technology of its kind in the world, it employs embedded moisture-activated microcell batteries that wirelessly generate microcurrents designed to mimic the skin’s electrical energy … Procellera FlexEFit was first used by Orthopedic Surgeons Dr. Jimmy Chow and Dr. Brandon Gough, co-founders of the Orthopedic Institute of the West at Abrazo Scottsdale Campus in Phoenix, AZ … read more
Is Diabetic Footcare in the UK Still a ‘Cinderella’ Service?
Editor’s note. While this pertains to Great Britain and Whales, the concerns are universal.
We’ve got the background problem of foot ulcers and diabetes, which is a major problem and one which has been traditionally, perhaps, neglected by people, health care professionals. But we know it obviously causes tremendous suffering to the people who’ve got a foot ulcer, whether or not they go on to amputation, which is always the major threat … But it also is enormously expensive. And people don’t think of diabetic foot ulcers as being a major health care issue. And yet, care of diabetic foot ulcers we know costs at least a billion pounds each year to the NHS. That’s just about 1% of the total NHS budget, so it is an enormous problem, we know that … read more
Mobile bedside bioprinter can heal wounds
Imagine a day when a bioprinter filled with a patient’s own cells can be wheeled right to the bedside to treat large wounds or burns by printing skin, layer by layer, to begin the healing process. That day is not far off … Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) scientists have created such a mobile skin bioprinting system — the first of its kind — that allows bi-layered skin to be printed directly into a wound … read more
Electrifying wound care: Better bandages to destroy bacteria
Bandages infused with electricity can help heal wounds faster than typical bandages or antibiotics—but for years, researchers have not really understood why … A recent study by a team at The Ohio State University is offering new clues about the science behind those bandages, and researchers say the findings could help lead to better wound treatment … The bandages belong to a class of therapies called electroceuticals, which are devices that use electrical impulses to treat medical issues such as wounds … read more
What Caused This Man’s Weakness and Hematuria?
A 52-year-old black man with type 2 insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus presents to hospital suffering from significant weakness and nausea; he says he has had no appetite for the past week, but has not been vomiting. He reports seeing blood in his urine, and that his urinary output has decreased … He looks very ill but shows no signs of distress – he is mentally alert and aware of his surroundings. He does not use over-the-counter medications or herbal remedies, nor does he smoke, drink alcohol, or use any illicit drugs … read more
Australian study shows specialist clinics are cost-effective
for chronic wound care
Average saving of $3,947 per patient, and increased patient quality of life also reported … A study published in PLOS ONE by academics in Australia and the UK, shows that specialist wound management clinics are the most cost-effective route for the care of chronic wounds with better results for patients … The research team includes Dr Rosana Pacella, Head of Research at the University of Chichester, West Sussex, UK as part of an international health economics collaboration including Dr David Brain, and other researchers at the Queensland University of Technology … read more
Mobile bedside bioprinter can heal wounds
Imagine a day when a bioprinter filled with a patient’s own cells can be wheeled right to the bedside to treat large wounds or burns by printing skin, layer by layer, to begin the healing process. That day is not far off … Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) scientists have created such a mobile skin bioprinting system — the first of its kind — that allows bi-layered skin to be printed directly into a wound … read more
Maggots: Hong Kong reports two human myiasis cases
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), myiasis is infection with a fly larva, usually occurring in tropical and subtropical areas … There are a number of ways to contract it–getting an infection from accidentally ingesting larvae, from having an open wound or sore, or through your nose or ears. People can also be bitten by mosquitoes, ticks, or other flies that harbor larvae. In tropical areas, where the infection is most likely to occur, some flies lay their eggs on drying clothes that are hung outside … read more
Negative pressure wound therapy promoted wound healing
by suppressing inflammation via down-regulating MAPK-JNK signaling pathway in diabetic foot patients
Negative pressure wound therapy displayed significant clinical benefits in the healing of diabetic foot wounds. In the present study, we investigated the mechanism of regulation of MAPK-JNK (Mitogen-activated protein kinase- c-Jun N-terminal kinase) signaling pathway by negative pressure wound therapy on these wounds …
Read the full article on Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice
Randomized Clinical Study Assessing NuShield Versus
Standard of Care in Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFUs)
This prospective, multi-center, randomized, controlled clinical study compares NuShield® plus SOC to SOC alone in subjects with chronic DFUs. NuShield® will be used along with standard of care on diabetic foot ulcers of greater than 6 weeks which have not adequately responded to conventional ulcer therapy … One hundred and twenty five (125) subjects with a chronic DFU ranging in size from 0.5cm2 and 25 cm2 will be randomized 1:1 to either NuShield® and SOC or SOC alone following the 14 day screening period. Following screening and randomization, subjects shall be seen weekly for up to 24 weeks. For subjects that heal prior to week 24, a healing confirmation visit shall occur two weeks later to confirm maintenance of complete wound closure … read more
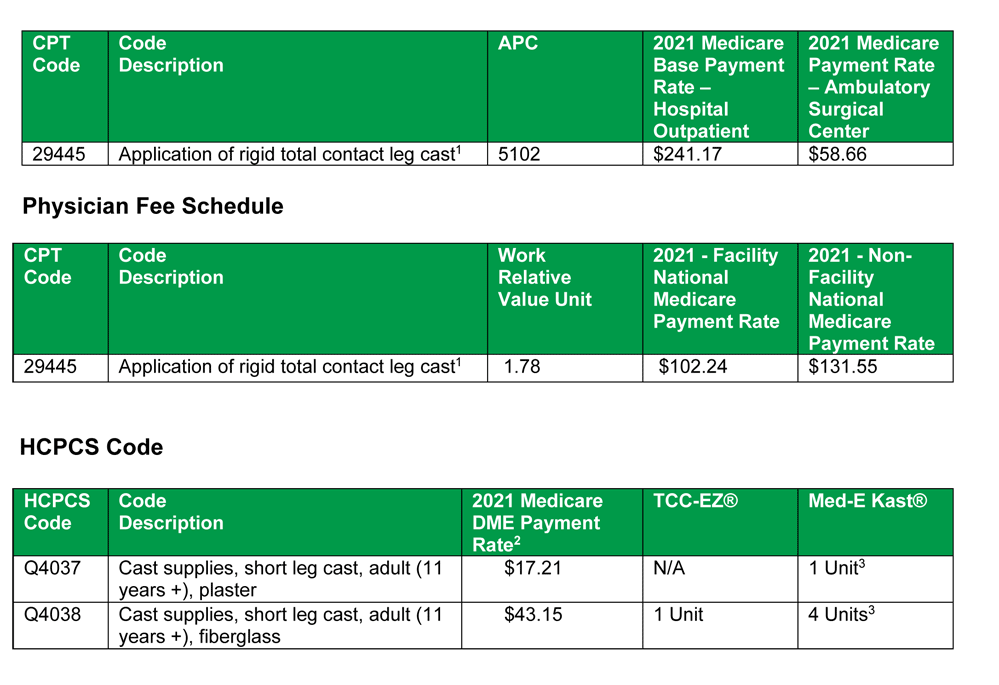
Reimbursement for Total Contact Casting and Debridement
Few things in life are more complicated than medical reimbursements, we believe this (table below) to be accurate for TCC based on how current clients are billing. Also this is from SuperCoder on debridement:
As per NCCI edits total contact cast application (29445) cannot be billed separately from a debridement (97597) when treating the same ulceration/same anatomical location for medicare as of above scenario. However, Commercial payers may consider separate payment with appropriate modifier.
Also from SuperCoder on CPT codes for debridement:
CPT code 97602 can be used for removal of devitalized tissue from wounds when non selective debridement (chemical method, hydrogen peroxide, iodine, Pulsed lavage method etc.) method is performed.
CPT codes from wound debridement series (11042 – 11047) can be used if active debridement is performed with surgical instruments (forceps and scissors to remove infected or dead tissue material from the wound). Here code selection depends on the depth of the tissue removed e.g. for debridement up to level of subcutaneous tissue – CPT code 11042 is the correct CPT code.
This from medicarepaymentandreimbursement.com on reimbursement fees:
11042-Debridement, subcutaneous tissue (includes epidermis and dermis, if performed); first 20 square cm or less. – average fee payment- $120 – $130
From Integra Life Sciences:
- Coding/Billing Notes:
According to the National Correct Coding Initiative (CCI) Policy Manual for Medicare Services (Revision
Date: 01/01/2017), casting/splinting/strapping should not be reported separately if a restorative treatment
or procedure to stabilize or protect a fracture, injury, or dislocation and/or afford comfort to the patient is
also performed. Several examples follow: (1) If a provider injects an anesthetic agent into a peripheral
nerve or branch (CPT code 64450), the provider should not report CPT codes such as 29515, 29540, or
29580 for that anatomic area; (2) A provider should not report a casting/splinting/strapping CPT code for
the same site as an injection or aspiration (e.g., CPT codes 20526-20615); (3) Debridement CPT codes
(e.g., 11042-11047, 97597) and grafting CPT codes (e.g., 15040-15776) should not be reported with a
casting/splinting/strapping CPT code (e.g., 29445, 29580, 29581) for the same anatomic area. - If the cast is supplied by the physician in his/her office, the physician may bill the Medicare for the
application of the cast as well as the supply of wrap itself, not the actual boot, during instances where just
an application of TCC is occurring and the physician is enrolled in Medicare as a licensed DME Supplier.
Reference: CPT® Code Book 2021. Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) copyright 2020 American
Medical Association (AMA). All rights reserved. CPT is a registered trademark of the AMA. Fee
Schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
AMA, are not part of CPT, and the AMA is not recommending their use. The AMA does not directly or
indirectly practice medicine or dispense medical services. The AMA assumes no liability for data
contained or not contained herein.
The use of topical analgesics in the management of painful diabetic neuropathy
Painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN) affects up to half of patients with diabetes and is a major cause of functional impairment and increased mortality. Its clinical manifestations include sensations such as burning, stabbing and tingling and/or loss of sensation, and it increases the risk for injuries and foot ulceration. Oral pharmacological therapy is the standard approach to management. It is effective in some patients, but its use is limited due to unfavourable side-effect profiles, limited response rates and drug interactions. Increasing evidence of the localized, non-systemic treatment approach of topical analgesics aims to overcome these obstacles and provide valuable, efficacious and safe management of PDN. This article reviews the rapidly expanding field of topical analgesia in managing PDN … read more
Acelity’s KCI launches Abthera NPWT system in Japan
Acelity subsidiary KCI said today that it launched its Abthera open abdomen negative pressure therapy system in Japan … The San Antonio-based company’s Abthera is a temporary abdominal closure system intended to allow surgeons to manage challenging abdominal wall openings where primary closure is not possible and to manage repeat abdominal entries … KCI said that the system has be validated in clinical studies, showing increased patient survival, improved primary fascial closure rates, shorter intensive care unit stays and improved outcomes … read more
Proactive Approaches to Help Prevent and Treat Chronic Wounds
There are many risk factors associated with chronic wound development, with age being an unchangeable one. The good news is, there are also changeable risk factors. Understanding how to prevent and treat a chronic wound is crucial when caring for older adults. To help older adults, caregivers, and the professionals working with them, below are answers to some common questions about chronic wounds and tips for how to educate on risk factors … There is no true definition for a chronic wound, but it is typically a wound that does not progress normally through stages of healing and has not healed within four weeks. There are many different types of chronic wounds, examples include diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure injuries … read more
Factors associated with foot ulcer self-management behaviors
among hospitalized patients with diabetes
In this cross-sectional design, researchers have identified self-management behaviors related to pre-hospitalized diabetes-related foot ulcers (DFUs) and examined the factors associated with these behaviors. A survey questionnaire was given to 199 hospitalized patients with DFU at a medical center in Northern Taiwan from June 2015 to June 2016. According to findings, 62.8% of participants never monitored their blood glucose level when they had foot ulcers, and 63.8% did not seek treatment for their wounds when their wounds were not painful. Data reported that DFU self-management behaviors were not enough. Following the control of demographic and medical variables, multiple stepwise regression analysis showed that the following 8 significant variables were related to DFU self-management behaviors: two DFU self-management barrier beliefs, foot self-care behavior, no treatment for diabetes, poor financial status, employment, knowledge regarding the warning signs of DFU deterioration, and number of DFU hospitalizations. They concluded that some modifiable factors and high-risk groups have been identified for inadequate DFU self-management behavior.
Read the full article on Journal of Clinical Nursing
Revolutionary wound care: Local men off to Iceland to learn about new procedure
A member of East Liverpool City Hospital management and a production team from EM-Media are flying to Iceland today to learn more about using cod skin in the treatment of wounds … Kerecis Omega3 is intact fish skin rich in naturally occurring Omega3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. When grafted onto damaged human tissue, such as a burn or a diabetic wound, the material recruits the body’s own cells and is ultimately converted into living tissue, significantly speeding the time needed to close an open wound, hospital officials said … read more
Factors associated with wearing inadequate outdoor footwear
in populations at risk of foot ulceration: A cross-sectional study
Researchers performed a secondary analysis of a multi-site cross-sectional study examining foot conditions in a large inpatient population admitted into the hospital for any medical reason on one day, to assess, in those with diabetes or peripheral neuropathy, the prevalence of wearing inadequate outdoor footwear, as well as the related factors. Inadequate outdoor footwear wearing was reported in 47% of 726 inpatients–49% of the 171 in the diabetes subgroup and 43% of 159 in the neuropathy subgroup. Women were identified wearing inadequate footwear more frequently. They identified the necessity for more efforts to enhance the adherence to footwear recommendations in these populations to prevent foot ulceration.
Exercise and Chronic Wound Healing
The calf muscles have been called the body’s “second heart,” improving blood circulation when exercised, usually by walking. Structured exercise training (SET) increases calf muscle pump function, lower limb circulation, and walking capacity for those with limited ambulation due to peripheral arterial disease (PAD)1 or venous insufficiency.2 This resulted in the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) decision to reimburse up to thirty-six 30- to 60-minute, properly supervised hospital outpatient or office-based SET sessions over 12 weeks to treat intermittent claudication for patients with PAD. Exercise improves acute wound healing in diabetic mice3 and healthy elderly humans …. read more
Enhancement of wound healing by single-wall/multi-wall carbon
nanotubes complexed with chitosan
Impaired wound healing is commonly associated with many health problems, including diabetes, bedsores and extensive burns. In such cases, healing often takes a long time, which subjects patients to various complications. This study aims to investigate whether single-wall or multi-wall carbon nanotubes complexed with chitosan hydrogel can improve wound healing … read more
Reduction of 50% in Diabetic Foot Ulcers With Stem Cells
Local injection of mesenchymal stem cells derived from autologous bone marrow shows promise in healing recalcitrant neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers, a novel study from Egypt shows … Presenting the results at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2016 Annual Meeting, Ahmed Albehairy, MD, from Mansoura University, Egypt, said: “In patients who received the mesenchymal stem cells, ulcer reduction was found to be significantly higher compared with patients on conventional treatment after both 6 weeks and 12 weeks of follow-up. This is despite the fact that initial ulcer size was larger in the stem-cell–treated group.” … read more
Cura Surgical Receives Innovative Technology Designation
from Vizient for Silverlon Antimicrobial Surgical Dressings
Cura Surgical announced its Silverlon Antimicrobial Surgical Dressings have received a 2018 Innovative Technology designation from Vizient, Inc., the largest member-driven health care performance improvement company in the country. The designation was based on the recommendations of health care experts serving on a member-led council who interacted with the product shown at the Vizient Innovative Technology Exchange held on Oct. 4, 2018. The council determined the technology had the potential to enhance clinical care, patient safety, health care worker safety or improves business operations of health care organizations … Containing more metallic silver than any other silver-based dressing, Silverlon Antimicrobial Surgical Dressings are supported by multiple, peer-reviewed clinical studies demonstrating the effectiveness of Silverlon technology across multiple specialties. When activated by moisture, silver ions are released in the dressing, providing immediate antimicrobial activity and a protective barrier against a broad spectrum of pathogens including MRSA and pseudomonas … read more
Study Demonstrates Cook Biotech’s OASIS® Wound Matrix
Has Higher Rates of Healing in Pressure Ulcers Than Standard of Care
A recently published multi-center, randomized, controlled trial (RCT) demonstrated higher rates of healing when using OASIS® Wound Matrix with standard of care (SOC) for the treatment of full-thickness Stage III or Stage IV pressure ulcers than when using SOC alone … Pressure ulcers are open wounds caused by pressure. They often occur when an individual remains in one position for an extended period … read more
Corstrata Sponsors National Post-Acute Care Wound Nurse Excellence Award
Corstrata, a provider of digital healthcare IT solutions and services for wound prevention and care management, announced today that it will sponsor the nation’s first Post-Acute Care Wound Nurse Excellence Award. The Post-Acute Care Wound Nurse Excellence Award sponsored by Corstrata is a new annual program designed to recognize and honor the individual contributions of wound care nurses for their knowledge and expertise in providing exceptional patient care using evidence-based best practices to accelerate patient wound healing, improve patient outcomes and instill excellence in his/her overall practice of wound management … Sponsored by CORSTRATA and hosted by the Post-Acute Care Symposium (PACS): Advancing Quality Outcomes Through Wound & Incontinence Education, the Post-Acute Care Wound Nurse Excellence Award is open to all nurses working in post-acute care settings. The first annual award will recognize one individual for his/her direct contribution to overall wound care excellence in a post-acute care setting … read more
The use of topical analgesics in the management of painful diabetic neuropathy
Painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN) affects up to half of patients with diabetes and is a major cause of functional impairment and increased mortality. Its clinical manifestations include sensations such as burning, stabbing and tingling and/or loss of sensation, and it increases the risk for injuries and foot ulceration. Oral pharmacological therapy is the standard approach to management. It is effective in some patients, but its use is limited due to unfavourable side-effect profiles, limited response rates and drug interactions. Increasing evidence of the localized, non-systemic treatment approach of topical analgesics aims to overcome these obstacles and provide valuable, efficacious and safe management of PDN. This article reviews the rapidly expanding field of topical analgesia in managing PDN … read more
Silverlon® Antimicrobial Dressing Line Receives Contract Extension from Vizient, Inc.
Cura Surgical announced that their existing Vizient Contract (number MS11396) has been extended through January 31, 2021. This contract allows a comprehensive line of unique silver-plated nylon dressings in both Silverlon® and TheraBond® product ranges to be available to Vizient members across the nation. Vizient represents a diverse membership base that includes academic medical centers, pediatric facilities, community hospitals, integrated health delivery networks and non-acute health care providers representing more than $100 billion in annual purchasing volume … “We are thrilled to extend enhanced savings on our Silverlon® product line through this contract to Vizient members,” said Raul Brizuela, president and CEO of Cura Surgical and Argentum Medical, provider of Silverlon. “Combating hospital acquired infections, including surgical site infections, remains a top priority to healthcare facilities, and we are proud make a positive impact in this field.” … Silverlon® antimicrobial silver-plated dressings provide 50-100xs more silver than other silver-based antimicrobial dressings, and Silverlon’s efficacy is supported by multiple independent, peer-reviewed and published clinical studies. These studies suggest Silverlon® Dressings can be an important element in wound care and that control of wound bacteria within the dressing may help reduce the risk of infection … read more
Smartphone-based infrared camera accurately detects diabetic foot ulcers
medwireNews: A low-cost, smartphone-based infrared (IR) camera works as well as a high-end IR camera for the detection of diabetic foot ulcers (DFU), study findings indicate … “An advanced home assessment tool to monitor the foot in people with diabetes is desirable, and for this measurement of foot skin temperature is a promising modality,” Rob van Doremalen (University of Twente, Enschede, the Netherlands) and co-authors explain … They acquired plantar images of both feet from 32 participants (mean age 67 years, 75% men) with a current (n=28) or recently healed (n=4) DFU using the FLIR-One IR camera (FLIR Systems, Wilsonville, Oregon, USA) attached to a Motorola XT1642 Moto G4 Plus smartphone (Motorola Mobility LLC, Chicago, Illinois, USA) … read more
Can Smarter Technology Have An Impact In Diabetic Foot Remission?
With the dangerous complications diabetes can cause, including amputation and mortality, could smarter technology reduce the risk for complications?
I really think we are approaching a time when the line is completely blurred between medical devices and consumer electronics. That was really on display with the podcast I did with Davide Vigano, CEO of Sensoria, on NPR’s Tech Nation with Moira Gunn, PhD. We discussed technology and wearables for patients with diabetes … read more
The use of casting techniques in foot ulcer treatment: a literature review
Total contact casts (TCCs) continue to be considered as the gold standard offloading option for the treatment of neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). Although evidence in the literature continue to prove the efficacy of TCCs as the optimum option for offloading and expediting the healing process of ulcers, in reality they are very minimally used. This was evidenced in both Europe and the United States with a very low percentage of cast utilisation (Prompers et al., 2008 and Wu et al., 2008). As a result, several cast modalities have been developed in order to facilitate the use of this intervention for the treatment DFUs. Therefore, the aims of this critical review were to explore the literature regarding efficacy the different casting modalities alongside TCCs … read more
Efficacy of Maggot Therapy on Staphylococcus aureus
and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Subjects were randomly selected for the maggot-treated (treatment) or conventional treatment (control) group. Conventional treatments such as antibiotic therapy, debridement, and offloading were done for both groups, but maggot therapy (MT) was added to the protocol of the treatment group. Bacterial burden was monitored and compared for both groups using cultures … read more
Regenerative wound dressings created by Lithuanian scientists
will help wounds healing
Group of researchers at Kaunas University of Technology, Lithuania are developing new generation sponge-like wound dressings with hyaluronic acid. Antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory wound dressings stimulate tissue regeneration and can be especially efficient in treating deep wounds that are difficult to heal … According to data, of the total healthcare expenditure in the European Union, wound management makes up 2-4%. A single chronic wound can cost up to 10 thousand EUR to treat, and it is estimated that up to 1.5% of EU population has one or more of such wounds … read more
Nutritional Factors for Wound Healing in the Older Adult Patient
There are seemingly countless factors that contribute to increased risk for the development of pressure injuries among certain patient populations. For those who require a stay in long-term care, the incidence of pressure injuries can be a concern. Conditions that contribute to increased risk for pressure injury development include (but are not limited to) diabetes mellitus, peripheral vascular disease, malignancy, prolonged pressure on an area of the body … read more
Diabetes doubles risk for hospital-acquired foot ulcers
Patients with diabetes have at least double the risk for developing hospital-acquired foot ulcers vs. those without diabetes, according to a study published in BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care … In a prospective, multilevel regression analysis, Frances Wensley, PhD, MBBS,formerly of the Royal Free Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust in London, and colleagues analyzed data from 18,946 patients with 28,642 admissions of at least 2 days to the Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust between October 2008 and September 2010, including 3,076 individuals with diabetes with 5,043 admissions. Patients included in the analysis were aged at least 50 years and developed a hospital-acquired foot ulcer at least 48 hours after hospital admission … read more
Gemco Medical adds to wound-care line
Gemco Medical said it has added a new brand of advanced wound-care products … The Gemcore360˚ line was designed to maintain a moist wound environment, address bioburden, reduce pain, minimize friction and increase overall patient comfort, according to the Hudson Ohio-based company. It includes transparent thin films, alginate dressings, silver alginate dressings, hydrocolloid dressings, foam dressings, and PHMB foam dressings … read more
Converting antibiotic may help diabetics
Researchers are studying whether a common antibiotic used to treat everything from acne to urinary tract infections could be converted to a powerful topical treatment for diabetic lower extremity wounds … In a study published in Wounds online, a group of Canadian scientists explained their efforts to develop a stable, topical doxycycline hyclate. DOXY, a type of tetracycline, could be used to inhibit protein synthesis … read more
Urgo Medical announces NICE recommendation
of UrgoStart for diabetic and venous ulcers
The UK’s National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has published new guidance recommending UrgoStart wound dressings (Urgo Medical) for treatment of diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers. In a press release, Urgo Medical states that use of the wound dressing could prevent more than 3,000 diabetes-related amputations … The conclusion of the NICE medical technology guidance is that UrgoStart is associated with increased wound healing compared with non-interactive dressings and could result in fewer ulcer-related amputations. The committee recognised that the treatment is also associated with significant cost savings for the UK National Health Service (NHS) and improved quality of life for patients … read more
COPPER 3D RECEIVES NASA GRANT FOR 3D PRINTING OF MEDICAL DEVICES
The funding has been allotted by NASA Nebraska Space Grant, one of the 52 space grant consortiums in the U.S. Copper 3D, the Chilean/USA based 3D printing industry leader, has made it to the headlines for receiving a new grant from NASA. Reportedly, the Copper 3D has been granted the award for testing antibacterial 3D printing material properties, for medical devices used on the International Space Station … Recent reports revealed that the funding has been allotted by NASA Nebraska Space Grant, which is one of the 52 space grant consortiums in the USA. The group is currently highlighting its innovative faculty research projects in 2019, one of which is its collaboration with Copper 3D. This work is focused towards validating new antimicrobial 3D printing materials to develop medical devices and help reduce microbial risks during long-duration spaceflight missions … read more
The combination of high bacterial count and positive biofilm
formation is associated with the inflammation of pressure ulcers
Evaluating the bacterial bioburden of pressure ulcers through bacterial count and pathogenicity is important but is currently difficult to perform in the clinical setting. In order to address this problem, we proposed two methods: 1) measurement of bacterial count using a quantitative device and 2) detection of biofilm formation by wound blotting. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between the bacterial bioburden, assessed by combining these two methods, and the presence of wound inflammation … The participants of this cross-sectional study were patients aged >20years with category II, III, IV, or unstageable pressure ulcers examined during a routine round in an interdisciplinary pressure ulcer team between July 2014 and April 2018. Relevant clinical information, including bacterial count, biofilm formation … read more
GEMCO Medical Introduces the GEMCORE360˚™
Brand of Advanced Wound Care Products
HUDSON, Ohio, Feb. 5, 2019 /PRNewswire/ — GEMCO Medical, a national distributor of medical products, is pleased to announce the addition of the GEMCORE360˚ brand of advanced wound care products. GEMCORE360˚ Advanced Wound Care offers healthcare professionals a simple, clear and cost-effective wound care range while ensuring excellent clinical outcomes for their patients … The product line includes transparent thin films, alginate dressings, silver alginate dressings, hydrocolloid dressings, foam dressings and PHMB foam dressings – all designed to maintain a moist wound environment, address bioburden, reduce pain and increase overall patient comfort … It is estimated that approximately 15 to 25 percent of individuals with diabetes will develop a foot ulcer at some point in their lifetime. GEMCO Medical was a pioneer in the diabetes supply industry over 27 years ago and has continued to evolve bringing on new product categories. The GEMCORE360˚ Advanced Wound Care product line is a logical addition to offer their healthcare professionals, so patients can receive the necessary treatment and find relief … read more
American College of Wound Healing & Tissue Repair Needs ….
WE NEED YOUR HELP IN ESTABLISHING WOUND CARE AS AN ACGME-APPROVED SPECIALTY!
– Reminder – Comments Due By February 20, 2019! –
Dear Wound Care Providers,
As you are aware, The American College of Wound Healing and Tissue Repair (ACWHTR) was founded almost a decade ago, with the sole purpose of helping to promote wound care towards specialty status. The ACWHTR submitted a proposal to the ACGME seeking formal acceptance and approval of this specialty at the highest level of medical education in the US. The ACWHTR has created a balanced educational fellowship program which, if approved, can be adopted by many academic centers and help drive innovation and improve the lives of many patients over the years.
Here’s How You Can Help
Please see Dr William Ennis’ letter inviting you to participate by reviewing the proposal and providing your feedback and comment to the ACGME. The enclosed PDF provides an explanation of the proposal and a link to the ACGME website to access both the proposal and comment document. The deadline for comment is February 20, 2019, so time is of the essence in getting your input on this important and historic proposal.
We appreciate your time and attention and willingness to participate.
StimLabs enrolls first patient in Revita trial for diabetic foot ulcers
StimLabs, a provider of regenerative technologies and products, has enrolled first patient in its trial designed to assess the safety and efficacy of Revita human placental graft in diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) … Revita is said to be the first amniotic placental membrane allograft to capture the complete intact membrane in a shelf-stable format … The multi-center randomized, comparative and controlled trial will assess the efficacy of Revita full thickness placental allograft in improving wound closure rates and mean closure time in DFUs compared against current standards of wound care treatment … StimLabs is carrying out the trial at primary institutions/centers in the US. The trial includes patients who suffer from type 1 or 2 diabetes … read more
Southeastern Wound Healing Center raises awareness
about impact of heart health on wound healing
An alarming 33 percent of Americans currently suffer from cardiovascular disease …Throughout Heart Health Awareness Month, Southeastern Health’s Southeastern Wound Healing Center, a member of the Healogics network, will work to spread awareness about how cardiovascular diseases can affect the wound-healing process. Cardiovascular diseases and other issues with the heart and vessels can cause blockages that obstruct the flow of blood needed for proper wound healing … Chronic wounds affect about 6.7 million people in the United States and, if left untreated, an unhealed wound on the foot or leg can lead to a diminished quality of life and possible amputation. As many as 82 percent of leg amputations are the result of poor circulation of the affected limb … read more
The DFU Dilemma: Is the Total Contact Cast a True “Gold Standard”?
McGuire and Sebag wrote: “Early diagnosis and intervention for diabetic foot wounds is essential for the prevention of complications associated with these ulcers. We are all familiar with the term ‘the golden hour’ with respect to the first 60 minutes after the onset of a stroke or cardiac arrest. The rapid initiation of aggressive care is the key to positive outcomes for the patient. In this way, the diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) also has a golden hour. The 4-week period following the onset of a diabetic ulcer is a critical time for treatments aimed at preventing the development of a chronic wound, staving off infection, and allowing for early closure of the skin. Wounds that have not achieved 50% closure within the first 4 weeks are destined to become difficult-to-heal chronic wounds. A fundamental component of early intervention and resolution of diabetic foot ulcers is the use of an array of offloading devices that includes everything from total contact casting to depth shoes with molded inserts.”1 However, as they go on to document, there is no consensus among practitioners … read more
Novel nitric oxide technologies pave way for new diabetic foot ulcer treatments
Researchers in Michigan have developed a novel nitric oxide sensing device, providing new insight into the causes of diabetic foot ulcers and possible avenues for treatment … Approximately 9 to 26 million diabetic patients around the world develop foot ulcers every year. These ulcers can double the risk of death for diabetic patients and may take up to 120 days to heal. Previous research has suggested that the impaired healing associated with diabetic foot ulcers is caused by unregulated levels of nitric oxide. Measuring live concentrations of this compound has posed a significant challenge due to its highly reactive nature. Previous studies have used nitrite, a stable byproduct, to measure nitric oxide levels indirectly … read more
Applied Tissue Technologies’ negative-pressure dressing gets FDA nod
Wound-care company Applied Tissue Technologies said it has won FDA clearance of its negative-pressure wound therapy product, the Platform Wound Dressing (PWD). The class II device represents the first-of-its-kind embossed negative pressure wound therapy device to be used without foam or gauze, according to the Hingham, Mass. company.
The PWD is a transparent dressing with an integral adhesive base and a permanently embossed, impermeable membrane that combines the traditional functions of the negative-pressure wound therapy membrane and foam/gauze in currently marketed negative-pressure devices. When the negative-pressure pump is switched on, the embossed membrane is pulled into direct contact with all geometries of the wound, eliminating the need for foam or gauze. The space created between the embossments provides primary channels for air and fluid, while folds in the membrane create secondary channels that provide an even distribution of negative pressure across the wound … read more
HMP Announces Multiple Endorsements for SAWC Spring
HMP, a leader in healthcare events and education, today announced that its annual Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC) Spring, taking place in San Antonio, Texas, May 7-11, 2019, and serving as the annual meeting of the Wound Healing Society (WHS), has received endorsements from the following prominent organizations:
- American Physical Therapy Association’s Academy of Clinical Electrophysiology and Wound Management:
“The Wound Management Special Interest Group of the American Physical Therapy Association’s Academy of Clinical Electrophysiology and Wound Management endorses the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care,” says Melissa Johnson, Chair, Wound Management Special Interest Group. “SAWC promotes interdisciplinary wound management and provides robust continuing education for physical therapists and other healthcare providers enabling optimal care for patients with wounds.”
- Critical Limb Ischemia (CLI) Global Society, the only organization solely dedicated to patients and the public health aspect of CLI:
“The Critical Limb Ischemia Global Society is endorsing the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care, an important conference that brings together the latest technologies, best practices, and research in all areas of wound care,” says founding board member, Jihad A. Mustapha, MD. “In our efforts to further share information and educate practitioners, we are especially proud to take part in this year’s Spring meeting by organizing a session on CLI awareness, diagnosis, and treatment.”
- National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP), the nation’s leading scientific expert group on pressure injury prevention and treatment, is endorsing and organizing three sessions at the meeting:
“The National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel is proud to endorse and support the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care, an important medical conference for those of us who rely on the latest technologies to remain up to date on wound care and prevention,” says Dr. Nancy Munoz, DCN, MHA, FAND, Assistant Chief, Nutrition and Food Services, Southern Nevada VA System. “As part of our support and engagement, we are delighted to present three sessions during this conference, sharing expertise and best practices in areas of pressure injury prevention and treatment.”
- American Venous Forum (AVF), which fosters cutting-edge research and clinical innovation and educates healthcare professionals, patients, and policy makers about venous and lymphatic diseases, is endorsing SAWC Spring and coordinating a session at the meeting:
“The American Venous Forum proudly supports the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and its role in furthering education, particularly in the areas of venous and lymphatic disease,” says William Marston, MD, Professor of Surgery University of North Carolina; and Secretary of the Board of Directors of the American Venous Forum. “The cutting-edge topics and emerging therapies presented at this meeting are important as we all continue to strive for improvements in the prevention and treatment of patients with chronic nonhealing wounds.” … read more
Lakewood-Amedex Prepares To Launch A Phase 2 cDFU
Clinical Trial for Its Nu-3 Antimicrobial In The Bahamas
SARASOTA, Fla., Jan. 17, 2019 /PRNewswire/ — Lakewood-Amedex Inc., a leading developer of novel anti-infective pharmaceuticals, announced today it had entered into a collaboration agreement with Nassau based Foot and Ankle International (Bahamas) to conduct two Phase 2 cDFU clinical trial for its topically applied Nu-3 antimicrobial used to eliminate infection and promote wound healing in patients with chronic diabetic foot ulcers (cDFU). The trial will be under the direction of the prominent Bahamian surgeon, Dr. Daniel Johnson, who is the principal and chief researcher of Foot and Ankle International (Bahamas). He is an acknowledged expert on the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers.
Nu-3, which belongs to a proprietary class of antimicrobials called Bisphosphocins™, was first used as a solution to treat infected diabetic foot ulcers for seven days in a Phase 1/2 a clinical trial completed late 2017, when it was well-tolerated with no reported adverse events related to treatment. Results showed promising trends with median wound area reduction (change from baseline) of 65.5% in the 2% Nu-3 treatment arm, versus 29.9% in the placebo arm.
Lakewood-Amedex, based in Sarasota, Florida, has developed a proprietary gel formulation of Nu-3, said they intend to conduct a Phase 2 clinical trial commencing early 2019 using this compound to treat chronic diabetic foot ulcers (cDFU), with a 28-day treatment period using escalating concentrations of Nu-3. The company believes this longer treatment with increased Nu-3 concentration will improve the potential to reach a point of healing or partial healing of the patient’s ulcers. Lake-Amedex also intends to conduct an ‘adaptive arm’ of this clinical trial which will involve treating an increased number of patients with the most effective concentration of the gel formulation to achieve robust clinical data.
Steve Parkinson, President and CEO of Lakewood-Amedex, said the company will seek to recruit up to 120 patients for the entire clinical trial and has identified the Bahamas as not only an up and coming location for medical specialty in DFU in the treatment of diabetic foot wounds and ulcers, but also a potential source of large numbers of patients … read more
Medscape National Physician Burnout, Depression & Suicide Report 2019
More than 15,000 physicians told Medscape how they feel about burnout, depression, and suicidal thoughts, and also how they attain happiness … read more
Balance of biomolecular signals stimulates healing by setting skin cells into motion
After a flesh wound, skin cells march forward to close the gap and repair the injury. Findings from a team led by Leah Vardy at A*STAR’s Skin Research Institute of Singapore now demonstrate how a carefully regulated set of molecular cues helps coordinate this healing migration … Vardy was particularly interested in a trio of organic molecules known as polyamines, which play a role in cellular proliferation. “They are well studied in cancer, but much less is known about how changes in their levels can drive normal … read more
medi USA introduces the new circaid® juxtalite® hd
WHITSETT, N.C., Jan. 15, 2019 /PRNewswire/ — Medical device manufacturer medi USA announced the launch of its new ready-to-wear circaid® juxtalite® hd. The juxtalite hd is an inelastic compression wrap for the management of venous disease and venous leg ulcers for patients with moderate to severe edema … Designed with patented, juxtaposing band technology and made with a soft but strong fabric, the juxtalite hd applies graduated compression over the entire lower leg. The effortless juxtaposing bands promote patient self-management and improve quality of life, enabling patients to easily adjust their compression wrap throughout the day and expedite the wound healing process. The juxtalite hd comes with a pair of new circaid compressive undersocks, which apply compression to the foot and ankle areas to effectively manage foot and ankle swelling. circaid products are designed with a patented, Built-In-Pressure System™ (BPS™) that enables multiple, measurable, targeted compression ranges in a single product … read more
HMP’s Wound Certification Prep Course Announces 12 New Locations for 2019
HMP, a leader in healthcare events and education, today announced twelve new course locations for the 2019 Wound Certification Prep Course (WCPC), the leading comprehensive wound care training program. Based upon the ongoing demand for clinicians to possess increased specialized knowledge in wound management, WCPC will be expanding its course to 12 cities nationwide, including San Francisco, Philadelphia, Nashville, and Chicago. Furthermore, three of the 12 programs will be co-located with HMP’s leading medical conferences: the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC) Spring and Fall meetings, the world’s largest wound care educational events; and the Amputation Prevention Symposium (AMP) … read more
Orpyx partners with alphabet subsidiary for virtual diabetes program
Orpyx’s foot sensor technology is installed in foot insoles and monitors foot pressure on diabetic patients and those with foot numbness. The tech will then send alerts to smartphones or smartwatches when a person is at risk for a foot injury, so preventative actions can be taken. The company indicated that 25 percent of people with diabetes develop foot ulcers over their lifetime, with one in five of those people experiencing complications that lead to amputation … read more
‘Bio-scaffold’ that could speed by the healing of wounds has been created by scientists
Scientists have created a ‘bio-scaffold’ that could speed up the healing of wounds.
In a world first, the researchers designed materials that ‘talk’ to the body’s injured tissue to support its repair through every stage of the healing process.
Known as traction force-activated payloads (TrAPs), the scientists believe the technique will have ‘far-reaching uses’ on everything from broken bones to diabetic foot ulcers.
TrAPs were designed by scientists at Imperial College London in a study led by Dr Ben Almquist from the department of bioengineering.
While collagen sponges are already used on burns and scaffold-like implants help to strengthen broken bones, the researchers felt a material should be created that met the changing needs of damaged tissue as it goes through the healing process … read more
Scientists design ‘smart’ wound healing technique
New research, published in the journal Advanced Materials, paves the way for “a new generation of materials that actively work with tissues to drive [wound] healing.” … As more and more surgical procedures are performed in the United States, the number of surgical site infections is also on the rise … Chronic wounds that do not heal — such as those that occur in diabetes — often host a wide range of bacteria in the form of a biofilm … Such biofilm bacteria are often very resilient to treatment, and antimicrobial resistance only increases the possibility that these wounds become infected … read more
The long-term outcomes following the application
of intralesional epidermal growth factor in patients with diabetic foot ulcers
Authors assessed 36 feet of 34 candidates (mean age 61 ± 13.7 years) to examine the long-term consequences of intralesional epidermal growth factor injections in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. They observed participants’ demographics, Wagner classifications, recurrence and amputation rates, 55.40 ± 12.15 of Foot Function Index, Short Form 36, and 65.92 ± 17.56 of American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons Foot and Ankle Module scores at the final follow-up review. They noted a complete response of wound closure in 87.9% of lesions with granulation tissue greater than 75%. The meantime of wound closure was recorded from 25 to 72 days. Toe amputation was performed in only 2 participants due to ischemic necrosis, suggesting a low recurrence and concise amputation rate with complete wound healing …. read more
Mortality in patients with diabetic foot ulcer
A retrospective study of 513 cases from a single Centre in the Northern Territory of Australia
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) are a common problem in longstanding diabetes. However, mortality outcomes in Australian patients with DFU are still unclear … All patients with DFU presenting for the first time to the Multi-Disciplinary Foot Clinic (MDFC) at Royal Darwin Hospital, Northern Territory Australia, between January 2003 and June 2015 were included in this study … read more
Four Patients Treated in Phase 2 Trial Testing Topical Gene Therapy
KB103, for Wound Healing
All four patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) enrolled in a Phase 2 study testing the safety and efficacy of Krystal Biotech’s topical gene therapy candidate KB103 have received the treatment.
Results are expected to be known by mid-year.
The protein type 7 collagen (Col7) binds the two top layers of the skin, and its deficit results in blisters and wounds. Mutations in the Col7A1 gene encoding Col7 results in either non-working or insufficient levels of Col7, causing the skin blistering observed in DEB patients.
KB103 is a gene therapy candidate designed to deliver functional Col7 directly to the impacted cells with the help of a modified herpes simplex virus (HSV-1; this modified virus is unable to cause disease).
In the ongoing six-month study (NCT03536143; GEM-1), underway at Stanford University, KB103 or placebo were applied directly to skin wounds (topical administration) of four DEB patients, two adults and two children (age 5 or older) … read more
Experimental Stem Cell Therapy Speeds Up Wound Healing in Diabetes
The healing of wounded skin in diabetes can be sped up by more than 50 percent using injections of stem cells taken from bone marrow, a new study in mice shows.
The research, led by scientists at NYU School of Medicine, focused on a chain of events in diabetes that makes skin sores more likely to form and less likely to heal.
Namely, the body’s failure in diabetes to break down dietary sugar creates molecules called free radicals that can wreak havoc on cells and damage their DNA. These free radicals also trigger an inrush of immune cells and chemicals meant to fight infection that, researchers say, instead kill normal cells and cause diabetic skin ulcers. These wounds, they note, can take twice as long to heal as in healthy mammals and are prone to infection.
Published in the January issue of the journal Diabetes, the study showed that the injected stem cells restore a cell signaling pathway called Nrf2/Keap1, recently shown by the NYU team to be disrupted in diabetes. The rebalancing brought on by stem cell therapy, the researchers say, decreased wound healing time to 21 days in treated diabetic mice compared with 32 days in untreated diabetic mice. By contrast, normal mouse skin wounds usually heal in 14 days.
“Our study shows that in mice, stem-cell-based therapies can stimulate the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway to counteract … read more
An Electrifying Way To Heal Skin Wounds
Using electricity to treat skin wounds may sound unconventional, but scientists in China and the US have developed a self-powered bandage that accelerated wound healing in rats. The findings are published in the journal ACS Nano. Skin has a remarkable ability to heal itself, but in some people, such as those suffering from diabetes, wounds heal very slowly or not at all. Such patients are thus at risk of chronic pain, infection and scarring. Doctors have explored various approaches to help chronic wounds heal, including bandaging, dressing, exposure to oxygen and growth-factor therapy, but these methods often show limited effectiveness. Meanwhile, as early as the 1960s, researchers have observed that electrical stimulation could help skin wounds heal. However, the equipment for generating an electric field is often large and may require patient hospitalization … Read more
RFID, GPS Technology Automate Wound Therapy Pump Management
DeRoyal’s Continuum solution consists of RFID tags and GPS units attached to negative pressure wound pumps, so that each pump can be tracked from the time it is assigned to a patient until that individual is finished using the pump at home, following discharge … Health-care technology company DeRoyal has released a solution for hospitals employing its Continuum UHF RFID-based platform, for use in tracking pumps that are utilized for negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT). The system leverages RFID technology built into cabinets, as well as tags and GPS technology—along with cellular and satellite connections—built into pump units to identify where they are located in real time. The solution enables the pumps to be used at hospitals, and to travel with patients after they are discharged, with insurance companies billed accordingly … read more
Updated Federal Physical Activity Guidelines: Do They Apply to People with Diabetes?
In mid-November 2018, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services finally released new physical activity guidelines (as a 2nd edition) to update their previous set from a decade before. Various activity guidelines for adults with diabetes have been updated several times in the interim, including a 2010 position statement on exercising with type 2 diabetes published jointly by the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Diabetes Association; a 2016 ADA position statement on exercise and physical activity for all types of diabetes ; and a consensus statement on being active with type 1 diabetes published in The Lancet in 2017 … In those three sets of recommendations specific to diabetes, it was clear that everyone with diabetes can benefit from being more regularly active … read more
Breaking the Biofilm Cycle: Strategies for Evaluating and Managing Wound Bioburden
Advancements in molecular microbiology, microscopy technology, and techniques for study of bacteria have increased the ability to identify the existence of biofilms, but there still remains the unknown, such as differentiating between planktonic bacteria and biofilm.1 Chronic non-healing wounds harbor bacteria across the wound etiology classification.2–4 Malone et al. determined that the prevalence of biofilms in chronic wounds was 78.2% (confidence interval, 61.6–89, P < 0.002).2 The development of biofilms moves through a common pattern: attachment, microcolony formation, maturation, and dispersion. The initial attachment is reversible, but the attachment becomes stronger as cells multiply and change their gene expressions. This cell communication process is referred to as quorum sensing, allowing cells to survive … read more
Point-of-care wound visioning technology
Reproducibility and accuracy of a wound measurement app
The wounds of 87 patients were measured using the Swift Wound app and a ruler. The skin surface temperature of 37 patients was also measured using an infrared FLIR™ camera integrated with the Swift Wound app and using the clinically accepted reference thermometer Exergen DermaTemp 1001. Accuracy measurements were determined by assessing differences in surface area measurements of 15 plastic wounds between a digital planimeter of known accuracy and the Swift Wound app. To evaluate the impact of training on the reproducibility of the Swift Wound app measurements, three novice raters with no wound care training, measured the length, width and area of 12 plastic model wounds using the app. High inter-rater reliabilities (ICC = 0.97–1.00) and high accuracies were obtained using the Swift Wound app across raters of different levels of training in wound care. The ruler method also yielded reliable wound measurements (ICC = 0.92–0.97), albeit lower than that of the Swift Wound app. Furthermore, there was no statistical difference between the temperature differences measured using the infrared camera and the clinically tested reference thermometer … read more
Breaking the Biofilm Cycle: Strategies for Evaluating
and Managing Wound Bioburden
Advancements in molecular microbiology, microscopy technology, and techniques for study of bacteria have increased the ability to identify the existence of biofilms, but there still remains the unknown, such as differentiating between planktonic bacteria and biofilm.1 Chronic non-healing wounds harbor bacteria across the wound etiology classification.2–4 Malone et al. determined that the prevalence of biofilms in chronic wounds was 78.2% (confidence interval, 61.6–89, P < 0.002).2 The development of biofilms moves through a common pattern: attachment, microcolony formation, maturation, and dispersion. The initial attachment is reversible, but the attachment becomes stronger as cells multiply and change their gene expressions. This cell communication process is referred to as quorum sensing, allowing cells to survive … read more
Maxwell Healthcare teams up with Swift for digital wound care management
SHOREVIEW, Minn., and TORONTO, On, Nov 30 2018. Maxwell Healthcare Associates (MHA), a post-acute operational, financial, technological and regulatory consulting firm, today announced Swift Skin and Wound as its exclusive digital wound care management solution of choice for MHA home health clients.
The partnership comes just a few weeks before the January 2019 rollout of new Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services rules surrounding pressure ulcer prevention and management.
“At Maxwell we believe technology is key to not only surviving but thriving amid constant regulatory changes and reimbursement cuts,” said MHA CEO Tom Maxwell. “We began searching for a wound care technology for our clients and found it in Swift. More than 1,000 facilities are already successfully leveraging Swift Skin and Wound for better clinical outcomes. It’s the only one with a home health-specific focus build that allows home health clinicians to document in and out of the home.”
Swift Skin and Wound significantly improves clinical and administrative wound care management workflows through: the Swift app, which captures wound care information as easily as taking a picture; the Swift HealX, an FDA-registered adhesive marker applied to calibrate wound images for size, color and lighting; and Swift Dashboards that display real-time healing and treatment to help clinicians and administrators identify risks immediately and improve care … read more
E-bandage generates electricity, speeds wound healing in rats
Skin has a remarkable ability to heal itself. But in some cases, wounds heal very slowly or not at all, putting a person at risk for chronic pain, infection and scarring. Now, researchers have developed a self-powered bandage that generates an electric field over an injury, dramatically reducing the healing time for skin wounds in rats. They report their results in ACS Nano … read more
Study: Socks with sensors could help continuously monitor diabetic neuropathy
A pair of washable and reuseable socks with a special sensor could be key to continuously monitoring foot temperature in patients with diabetic neuropathy, according to a study in JMIR sponsored by Siren, maker of the socks. Researchers found that the socks were able to report temperature within 0.2 degrees Celcius of the reference standard, and that patients found the technology useable.
“The temperature studies conducted show that the sensors used in the socks are reliable and accurate at detecting temperature and the findings matched clinical observations,” the researchers of the study wrote. “Continuous temperature monitoring is a promising approach as an early warning system for foot ulcers, Charcot foot, and reulceration.” … read more
Healogics Newest Service Line Drives Competitive Advantage with Data
Healogics Research ServicesSM provides comprehensive market and clinical analytics that enable access to the largest database of wounded patients in the world. Healogics Research Services team analyzes comprehensive patient-level data to guide population identification, aid in study protocol development and identify patients for potential enrollment in late phase studies. JACKSONVILLE, Fla.–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Healogics®, the nation’s largest provider of advanced chronic wound care services, today announced the debut of their newest service: Healogics Research ServicesSM. With robust clinical data on treatments and outcomes of over 1.8 million patients with 5.2 million wounds, Healogics has the largest repository of wound care-specific clinical encounter data in the industry. This data enables Healogics Research Services to generate real world insights that drive patient outcomes, product effectiveness and appropriate utilization.
“With our nationwide network of nearly 700 Wound Care Centers®, we care for more than 330,000 patients living with non-healing wounds each year,” said David Bassin, Chief Executive Officer at Healogics. “These numbers translate into meaningful data that enables us to better reach and improve healing for more people living with chronic wounds. We are excited about the unlimited opportunities and insights this new service offers us, our partners and, most importantly, our industry.” … read more
KCI Announces First-of-its-Kind Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Agreement with Highmark to Improve Patient Engagement, Raise Adherence and Lower Costs
SAN ANTONIO–(BUSINESS WIRE)–KCI, an Acelity Company, a global leader in advanced wound management, and Highmark Inc., a national diversified health care insurance provider, today announced they have entered into a performance-based agreement for the KCI iOn PROGRESS™ Remote Therapy Monitoring Program which aims to improve overall patient experience, while lowering costs through increased engagement and adherence. Used in conjunction with the ACTIV.A.C.™ Therapy System, iOn PROGRESS™ Remote Therapy Monitoring Program consists of 3 key components:
- Monitoring: A proprietary remote monitoring module attached to the ACTIV.A.C.™ Therapy device enables secure transmission of therapy data to KCI.
- Engagement: A highly trained team of KCI Virtual Therapy Specialists (VTS) analyze the data and interact directly with patients and healthcare professionals to support adherence.
- Adherence: 73% of patients demonstrated an increase in hours of NPWT use per day following an adherence call from a Virtual Therapy Specialist. A lower average 90-day wound-related cost was associated with those receiving remote therapy monitoring.1
The agreement is the first-of-its-kind for negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) and creates a performance-based payment structure for reducing total wound care costs. The partnership is a result of a diligent evaluation process by Highmark to understand how the iOn PROGRESS™ Remote Therapy Monitoring Program impacts its members in alignment with their commitment to improve quality while lowering total cost of care …. read more
Medical device player outlines wound care industry aims after government commitment
Medical products and technologies company ConvaTec has welcomed the government’s support for the wound care industry as part of the Life Sciences Sector Deal, and has outlined its own objectives to supporting the government’s actions.
The company has been working with the Association of British HealthTech Industries, healthcare providers and UK academia to identify ways of improving patient outcomes and maximise financial efficiency in the wound care industry. This will include the use of new digital clinical decision support tools to try and support health professionals and patients.
Simon Whitfield, vice president & UK general manager of ConvaTec said: “We are proud to be contributing to the Wound Care Sector Deal, which brings key stakeholders across the NHS, government and industry together to reduce variation in wound assessments and deliver better outcomes for patients and healthcare professionals … read more
Wound care revolution: Put away your rulers and reach for your phone
Monitoring a wound is critical, especially in diabetic patients, whose lack of sensation due to nerve damage can lead to infection of a lesion and, ultimately, amputation. Clinicians and healthcare professionals at the McGill University Health Centre (MUHC) and other hospitals believe that the use of a new app, Swift Skin and Wound, which accurately measures and charts the progression of skin wounds, could potentially have a significant impact on clinical management and patient outcomes.
“Many of my patients are diabetic and are dealing with slow-healing foot ulcers; this app offers a way to clearly document and quantify the size of the ulcer to ensure it is actually healing, and if it is not healing, I can change strategies,” says Dr. Greg Berry, Chief of Orthopaedic Surgery at the Montreal General Hospital of the MUHC and Chief and Mueller Chair of the Division of Orthopaedic Surgery at McGill University. “I can concretely show them that what we are doing is working. They get on board and are more devoted to the treatment plan because they see it is successful,” he adds.
The app was the idea of Dr. Sheila Wang, a resident in dermatology in the Department of Medicine at McGill University and a scientist at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC). Early in her medical career, she saw that there was a problem with the way that wounds were measured and went on to co-found the company, Swift Medical, which developed the smartphone software … read more
URGO Group Receives the ‘Prix Galien France 2018’ for UrgoStart®
an Innovative Treatment for Diabetic Foot Wound Healing
URGO Group, through its Urgo Medical division, received the Prix Galien France 2018 in the medical device category for UrgoStart®, the first dressing to have demonstrated clinical efficacy in the treatment of chronic wounds, especially in diabetic foot ulcers. This prestigious award recognizes URGO’s work and investment in R&D and its ongoing commitment to innovating for patients.
Urgo Medical: innovation as part of its DNA. URGO Group invests €25 million a year in R&D, in particular on medical technologies related to chronic wound healing.
“The prestigious Prix Galien rewards six years of collective hard work. Our R&D teams have spared no effort in developing the innovative UrgoStart® wound dressing,” said a beaming Hervé Le Lous, Chairman of URGO Group. “Our goal is to enable many more people to heal much faster, which will be a major benefit for patients, doctors and nurses, and society as a whole.”
UrgoStart®: a breakthrough in diabetic foot wound healing
With close to 425 million people affected worldwide, diabetes has become an epidemic that is growing steadily [1]. Nearly one out of every four patients with diabetes will suffer from a diabetic foot ulcer at least once in their lifetime[2].
Such wounds are also a major risk of infection which can lead to amputation and even death.
With one amputation carried out every 20 seconds, diabetes is the world’s leading cause of amputation[2]. In light of this finding, Urgo Medical launched the Explorer clinical study[3] in France, Spain, Italy, Germany and the UK, with the outcomes published in March 2018 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. The results demonstrated the efficacy of UrgoStart® which led to a 60% increase in wound closure compared with standard care and reduced wound closure time by 60 days from an average period of 180 days.
The first dressing to be deemed a local treatment, UrgoStart® is a French innovation recognized at the international level and now honoured by the Prix Galien.
URGO Group: https://www.urgo-group.com/
Prix Galien France: https://www.prixgalien.fr/
1. International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes atlas. 8th ed. 2017. Brussels: International, International Diabetes Federation https://www.idf.org/e-library/epidemiology-research/diabestes-atlas.html
2. Whiting, D. R., Guariguata, L., Weil, C., and Shax, J. 23011. “IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global Estimates of the Prevalence of Diabetes for 2011 and 2030.” Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 94 (3):311-21
3. Michael Edmonds, José Luis Lázaro-Martínez, Jesus Manuel Alfayate-García, Jacques Martini, Jean-Michel Petit, Gerry Rayman, Ralf Lobmann, Luigi Uccioli, Anne Sauvadet, Serge Bohbot, Jean-Charles Kerihuel, Alberto Piaggesi. Sucrose octasulfate dressing versus control dressing in patients with neuroischaemic diabetic foot ulcers (Explorer): an international, multicentre, double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018;6 (3) :186-196
Siren Announces Publication of Foundational Data for Novel Approach
to Skin Temperature Monitoring in Journal of Medical Internet Research (JMIR)
— Paper details results of first at-home, continuous, wireless temperature monitoring system to detect onset of diabetic foot ulcers caused by neuropathy
— Temperatures measured by standalone sensors were within 0.2℃ of the reference standard
–Data demonstrates potential as promising approach for early warning of foot ulcers, Charcot foot, and re-ulceration
SAN FRANCISCO–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Siren, the health technology company that developed Neurofabric™, a machine-washable, machine-dryable smart textile with built-in sensors, today announced publication of a foundational paper supporting its approach in Journal of Medical Internet Research (JMIR), the leading peer-reviewed journal for digital medicine, and health & healthcare in the Internet age. In the paper, a team of international researchers led by Ran Ma, co-founder and CEO, and Alexander M Reyzelman, DPM; Samuel Merritt University, detail the role of Siren’s Diabetic Sock and Foot Monitoring System in maintaining continuous, wireless skin temperature monitoring for users at-home, demonstrating the potential for the reduction of foot ulceration for diabetic patients.
“Diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) result in considerable cost to the healthcare system when immediate ulcers, social services, home care, and subsequent ulcers are taken into consideration,” said Alexander M Reyzelman, DPM; Samuel Merritt University and lead author on the paper. “The cost per ulcer is over $33,000 per year and the cost per leg amputation is more than $100,000 per year. Over 100,000 legs are lost to diabetes each year. In diabetic foot complications such as foot ulcers, elevated temperatures in regions of the foot have been shown to be a precursor for ulceration.”
The JMIR publication details Siren’s pilot study of its Diabetic Sock and Foot Monitoring System to assess how comfortable their sensor-embedded socks were for daily use, and whether observed temperatures correlated with clinical observations.
In the study, patients wore the socks at home for a median of 7 hours, reporting that they felt just like their normal, everyday socks. Their stated willingness to wear the socks every day underscores the socks’ suitability for home use, suggesting that Neurofabric can seamlessly integrate into the life of the wearer.
“Several tools have been developed to measure plantar temperatures and the progression of foot ulcers, but they only measure temperature once a day which can lead to false-positives, or are only available for in-clinic use and not at home,” said Ran Ma, co-founder and CEO of Siren. “Now, for the first time, we highlight the striking connection between our Neurofabric’s powerful ability to capture data at home, every single second. The data is incredibly meaningful—it’s the largest amount of patient data that physicians have had wireless access to in real-time. This solidifies the potential for Neurofabric to change the trajectory of diabetic foot ulcerations and the many complications that can occur from it—including sepsis, and lower limb amputations.”
Patients also reported that Siren’s mobile app was easy to use and navigate. Through the mobile app, wearers can view the current temperature as measured at six points on the user’s foot. While the app was not set up to generate alerts in this study, users can receive a notification on their phone when a temperature increase is detected between contralateral positions.
“Digital health is a vast and burgeoning field and spans several aspects of health management—Neurofabric can facilitate the management of chronic conditions at home, including the effective and timely management of DFUs,” said Henk Jan Scholten, co-founder and COO of Siren. “The JMIR publication sheds light on both the ability of these Neurofabrics to improve quality of life for diabetes patients, and Siren’s first use-case to empowering people to take their health into their own hands.”
Siren is initiating a large-scale patient study in 2019.
Read the JMIR paper in full here: Continuous Temperature-Monitoring Socks for Home Use in Patients With Diabetes: Observational Study
About Siren
Founded in August 2016, Siren is a health technology company and the maker of Neurofabric™, machine-washable, machine-dryable smart textiles. Siren’s first product, Siren Diabetic Socks, are designed to help people with diabetes avoid amputations. Siren was previously named AARP Consumer’s Choice Award winner, 2017 CES TechCrunch Hardware Battlefield, 2018 CES Best of Innovation, Fast Co.’s 2018 Innovation by Design Award Honorable Mention, and 2018 ADA Healthtech Showcase winner. Siren’s investors include DCM, Khosla Ventures and Founders Fund.
Maxwell Healthcare teams up with Swift for digital wound care management
SHOREVIEW, Minn., and TORONTO, On, Nov 30 2018. Maxwell Healthcare Associates (MHA), a post-acute operational, financial, technological and regulatory consulting firm, today announced Swift Skin and Wound as its exclusive digital wound care management solution of choice for MHA home health clients.
The partnership comes just a few weeks before the January 2019 rollout of new Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services rules surrounding pressure ulcer prevention and management.
“At Maxwell we believe technology is key to not only surviving but thriving amid constant regulatory changes and reimbursement cuts,” said MHA CEO Tom Maxwell. “We began searching for a wound care technology for our clients and found it in Swift. More than 1,000 facilities are already successfully leveraging Swift Skin and Wound for better clinical outcomes. It’s the only one with a home health-specific focus build that allows home health clinicians to document in and out of the home.”
Swift Skin and Wound significantly improves clinical and administrative wound care management workflows through: the Swift app, which captures wound care information as easily as taking a picture; the Swift HealX, an FDA-registered adhesive marker applied to calibrate wound images for size, color and lighting; and Swift Dashboards that display real-time healing and treatment to help clinicians and administrators identify risks immediately and improve care … read more
Record 169 UK patients a week get diabetes-related amputations
A record 169 people a week are having to undergo an amputation procedure as a result of diabetes, a study has found.
Analysis by the charity Diabetes UK found that 26,378 people had lower limb amputations linked to diabetes between 2014 and 2017, a 19.4% rise from 2010 to 2013. Unhealed ulcers and foot infections are the main cause of diabetes-related amputations. Diabetes affects almost 3.7 million people in the UK … read more
Tissue Regenix’s Decellularized Human Dermis Product, DermaPure
Demonstrated Substantial Clinical and Cost Benefits in Case Series Presented at Cleveland Clinic Accredited VEITH Symposium
SAN ANTONIO–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Tissue Regenix Group (AIM:TRX) (“Tissue Regenix” or “The Group”), a regenerative medical devices company, recently shared findings from a case series that concluded DermaPure, a decellularized human dermis product, was more cost effective, prompted faster healing times and improved quality of life versus other available options.
Undertaken by David Naar, MD, founder of Premier Vein Clinic, LLC. in collaboration with the Cleveland Clinic, the case series was shared at the 45th annual VEITH symposium and included six patients presenting with acute or chronic wounds, including necrotizing fasciitis and venous leg ulcers. Through the retrospective and prospective collection of data, the investigation showed a 65% mean surface area reduction in wound size at six weeks following an average of 1 DermaPure application per patient. One patient in the series, presented with a wound duration of over 10 years and had previously failed with multiple different graft options. Dr. Naar therefore concluded that DermaPure offers a significant health economic benefit to both patients and physicians in addition to its proven clinical advantage over current standard treatments … read more
Clinical Evidence for and Cost-Effectiveness of Advanced Cellular
Tissue Products for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
In its recently released research compendium Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot Complications, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) provides a comprehensive overview of the latest approaches for the manage- ment and treatment of DFUs and their complications. Produced by leading international DFU authorities, the compendium includes information about the use of adjunctive therapies, such as hyperbaric oxygen and negative pressure wound therapy, in instances in which DFUs do not respond to standard treatment.5 Among the treatments highlighted in the compendium that garnered the most attention were advanced cellular tissue products (CTPs). These are bioengineered cell-based therapies that supply the wound with the cells, tissues, proteins, and growth factors needed to support the healing process … read more (registration required)
Neem Biotech, Welsh Wound Innovation Centre
and Sheffield Collaboratorium for Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilms Awarded NBIC Grant to Advance Development of Neem’s First-in-Class Treatments for Wound Infections
Neem Biotech, a company focused on developing novel solutions to address antimicrobial resistance, together with the Welsh Wound Innovation Centre and Sheffield Collaboratorium for Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilms (SCARAB) announced today the receipt of a £50,000 inaugural National Biofilms Innovation Centre (NBIC) Proof of Concept grant. This inaugural grant has been awarded to expand the development and testing of effective anti-biofilm interventions, in this case based on the pioneering research conducted by Neem Biotech. Biofilms are formed by many bacteria as a protective mechanisms for colonies of bacteria in a range of metabolic states. In humans, biofilms protect bacteria from the human immune system and antibiotics and also exude virulence factors which allow the colonies of bacteria to invade local tissues and spread infection. Products that inhibit the spread of infection in biofilms are called quorum sensing inhibitors.
Specifically, the collaborators will expand data on the biological activity of Neem’s candidate compounds for managing bacterial infections in wounds. The research is aimed at advancing rational drug design and accelerating translation of basic research into the clinic …. read more
Verily, Sanofi-backed diabetes management program to offer Orpyx’s foot ulcer sensors
Onduo, a Verily-Sanofi joint venture focused on digitally-driven diabetes management, is looking to further protect its members from foot ulcers and limb loss. Orpyx Medical Technologies’ diabetic foot ulcer sensors for its members.
Thanks to a newly announced deal struck between the companies, Orpyx Medical Technologies’ FDA-cleared SurroSense Rx system will be available to “select members” of Onduo’s diabetes management program in 2019. The system consists of a thin sensor that is placed in a patient’s shoes and a wirelessly connected smartwatch, which displays readings and alerts to the user when dangerous pressure levels are detected.
“Orpyx helps people with diabetes to prevent foot ulcers by providing insight that protects foot health and mobility and reduces the risk of complications that can lead to limb loss,” Breanne Everett, CEO of Orpyx Medical Technologies, said in a statement. “We are pleased to extend access to our foot sensor technology to the Onduo member community and to invite Orpyx US patients to take advantage of Onduo services.” … read more
Patterns and Predictors of Medication Initiation in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
quality and cost implications
Adults with a new principal DPN diagnosis were categorized as initially untreated if they had no newly initiated DPNrelated medication within the fi rst 14 days after diagnosis. Bivariate logistic regression evaluated predictors for newly initiating medication versus being initially untreated. Multinomial logistic regression evaluated predictors for each medication category (antidepressants, anticonvulsants, or multiple medications versus opioids) … read more
Resurgence of diabetes-related nontraumatic lower extremity amputation
in the young and middle-aged adult U.S. population
We are grateful to Linda Geiss and her coworkers at CDC for their always intriguing efforts at revealing the big picture to us. These data– which certainly aren’t welcome news– are supremely important. Do they signal what we’ve posited for some time? Did the increase in the “denominator” of people with diabetes in the mid-1990s initially reduced the proportionate pool of high risk patients (and thereby reduced amputation rates)? Was it better team care? Whatever the explanation, we have yet more data on which to ruminate … read more
Diabetic Amputations May Be Rising in the United States
Lower-limb amputations may be rising in the United States after decades of decline, according to data published in Diabetes Care, the official journal of the American Diabetes Association.
The study, which evaluated hospitalization rates for nontraumatic lower extremity amputation in the years 2000 to 2015 using data from the National Health Interview Survey, evaluated estimates for populations with and without diabetes.
Poorly controlled blood sugar that occurs in diabetes can limit blood flow to the lower legs and toes, causing nerve damage that people with the disease may not sense until problems have already developed. People with advanced diabetes may develop wounds or sores that do not heal and eventually result in loss of the damaged toe or portion of the foot or leg … read more
Researchers Coax Leftover Pancreatic Cells to Morph Into Insulin-Producing Cells
Using a growth factor produced naturally by the human body—and used in spinal-fusion surgeries—scientists from the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have coaxed “leftover” cells from the pancreas to morph into insulin-producing islet cells. In a study set for publication in the December issue of the journal Diabetes, the reprogrammed cells churned out about as much insulin as healthy human islet cells.
 Transplanted into lab mice and rats, the new islets released their blood sugar-lowering hormone in response to increases in blood glucose levels—just like the real thing. “That’s the hallmark of functioning islet cells, the ability to sense and respond to blood glucose levels,” notes the study’s co-lead investigator Juan Dominguez-Bendala, Ph.D., director of stem cell development for translational research at the DRI … read more
Transplanted into lab mice and rats, the new islets released their blood sugar-lowering hormone in response to increases in blood glucose levels—just like the real thing. “That’s the hallmark of functioning islet cells, the ability to sense and respond to blood glucose levels,” notes the study’s co-lead investigator Juan Dominguez-Bendala, Ph.D., director of stem cell development for translational research at the DRI … read more
September is Diabetic Foot Ulcers Month
Well September has passed but this is a wealth of information on DFUs from WoundSource:
A photonic band aid using the healing power of blue light
A smart dressing that uses blue-light therapy for wound healing and which can also monitor and treat infections has been developed by an EU-funded consortium … Blue light is already known for its anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, but now the EU-funded MEDILIGHT consortium has harnessed it to aid the healing of chronic wounds such as those suffered by patients with diabetes … “The aim is to have a non-chemical solution for chronic wounds,” says project coordinator Dionysios Manessis of the System Integration and Interconnection Technologies Department, Technical University Berlin. “We found that blue light originally thought to be good for disinfection also produces good results for proliferation of keratinocytes and fibroblasts—the types of skin cells needed for wound closure.” … With EUR 3 million of EU funding for just over three years, the research team was able to produce a smart wearable device from scratch. The prototype consists of a soft, flexible foil with blue LEDs (light emitting diodes) and sensors. This is inserted into a transparent pocket over the wound dressing … read more
HMP Announces Launch of Post-Acute Care Symposium for Nurses
HMP, a leader in healthcare events and education, today announced the launch of the Post-Acute Care Symposium (PACS). The meeting will take place May 9–10, 2019, and will be co-located with the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC) Spring/Wound Healing Society meeting in San Antonio, Texas.
PACS is uniquely designed to provide nurses with the important tools they need through a curriculum that focuses on practical, evidence-based strategies for implementing clinical practice guidelines, protocols, and care pathways for wound and incontinence interventions. The PACS Steering Committee is comprised of many of the same experts who guide the programming for the established SAWC Spring and Fall meetings.
“With the post-acute care setting now central to our healthcare delivery system, the time has come to provide a practical conference for nursing professionals that focuses on the day-to-day realities of patients with wound and incontinence issues,” said Catherine T. Milne, MSN, APRN, CWOCN-AP, Advanced Practice Nurse and Co-Chair for the meeting.
The two-day event, expected to draw approximately 250 nursing professionals, will provide a unique experience for attendees. The meeting will include a curriculum based on the nursing process method, interactive panel and case-based discussion, and “Rapid-Fire” and “Ask the Experts” sessions led by a diverse faculty that includes post-acute care educators with broad experience and practical insight. Attendees will have the opportunity to earn up to 10 CNE credits.
By co-locating the meeting with SAWC Spring, PACS attendees will also gain access to the world’s largest wound care exhibit hall and networking receptions as part of their registration.
“HMP saw an unmet need in the marketplace,” said Peter Norris, Executive Vice President, HMP. “The idea for PACS came in light of statistics showing the majority of wounds in the U.S. are being treated within the post-acute care setting by skilled nursing facility (SNF), home health (HH), and hospice providers. The educational agenda aims to provide post-acute care nursing professionals with real-world tools and strategies fit for the setting in which they care for patients on a daily basis.”
To learn more about the meeting, visit pacsymposium.com.
About HMP
HMP is the force behind Healthcare Made Practical—and is a multichannel leader in healthcare events and education, with a mission to improve patient care. The company produces accredited medical education events and clinically relevant, evidence-based content for the global healthcare community across a range of therapeutic areas. Its brands include Consultant360, the year-round, award-winning platform relied upon by healthcare providers across 21 specialties; Psych Congress, the largest independent mental health meeting in the U.S.; EMS World Expo, the world’s largest EMS-dedicated event; and the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC), the largest wound care meeting in the world. For more information, visit hmpglobal.com.
‘Magic powder’ heals wounds nothing else can
FORT LAUDERDALE, Fla. (Ivanhoe Newswire) – More than 5.7 million Americans suffer from chronic wounds that won’t heal. Now, a new, easy to use treatment some are calling a “magic powder” is helping patients heal much faster.
Plastic surgeon Tracey Stokes, MD, FACS, Board Certified Plastic Surgeon is used to being in the operating room, but not as a patient.
“I underwent bilateral mastectomy and reconstruction,” said Dr. Stokes.
Dr. Stokes made the decision after she and her mother tested positive for the gene that causes breast cancer. Unfortunately, she developed a wound on her left breast that would not heal.
“I think in today’s day and age wound care and wound care problems have almost become an epidemic,” said Laura Sudarsky, MD, FACS, Board Certified Plastic Surgeon & Wound Care Specialist at Esse Plastic Surgery … read more
Meet The First Wound-Care Certified LPN aka “WOuNDER Woman”
By Portia Wofford
Have you ever been the first to achieve a great feat? Do you remember all the naysayers and those “encouraging” you to pursue other avenues? The self-doubt, that nagging lump at the bottom of your throat, the second-guessing you plagued yourself with? Despite it all, you kept swimming and here you are, a badass!
I thought of these things when I met Cheryl Carver or as her friends and colleagues call her- ‘WOuNder WOMAN!’ Cheryl is a nationally renowned wound care specialist and expert, published writer, educator, and LPN!
Life Doesn’t Always Go As Planned
Cheryl’s nursing career began when she served in the Army, while stationed in Germany. She received a life-changing phone call that her mother had a stroke. She rushed home to be her mother’s caregiver. After a year, her mother died in Cheryl’s arms due to complications of diabetes and pressure ulcers/osteomyelitis/sepsis … read more
Healogics Wound Science Initiative Addresses Social Determinants of Health
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines social determinants of health as the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work and age, that shape health. These factors include characteristics such as socioeconomic status, education, neighborhood and physical environment, employment and social support networks. Surprisingly, these social and environmental conditions account for 80 percent of health outcomes while only 20 percent are the result of care delivery.
“Over the next year, we will release a series of findings based on surveys of clinicians, interviews with patients and secondary data analysis,” said Hanna Gordon, PhD, Healogics Executive Director, Research and Informatics. “Our goal is to ensure that all patients can access high quality care and heal their chronic ulcers. We will begin our series with an introduction to the social determinants and how they impact health outcomes, followed by the findings of a survey on clinician perspectives on social barriers to care, and original research on the sociogeographic patterning of chronic wounds.”
Chronic wound patients face a number of challenges to their health and well-being. The presence of ulcers is an indication of broader physical systems failures. However, with education, many wounds could be prevented or treated when they are less severe resulting in improved outcomes. The association between chronic conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease and social conditions is well established, yet none of the previous studies have addressed chronic ulcers. Healogics Wound Science Initiative is partnering with hospitals … read more
Multiphoton Microscopy Monitors Chronic Wound Healing
Chronic skin wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure wounds and other chronic skin wounds affect more than 6 million people in the U.S. alone, with the cost of treatments mounting to $25 billion each year. The current standard of care requires removing a small piece of the wound tissue for laboratory analysis under a microscope, but disturbing tissue around the wound can be disruptive to the healing process.
Recognizing a lack of non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers to monitor such wounds, University of Arkansas 
Diabetic foot care providers’ perspectives on barriers and facilitators
to delivering patient-focused foot care services: A qualitative descriptive study.
A qualitative descriptive study design was used (Sandelowski, 2000). Participants were health-care professionals providing foot care, foot wear, and wound care services in a Canadian province. Professionals voluntarily completed 48 open-ended surveys. Survey data was thematically analyzed to identify meaning and leading themes (nVivo10). The lead researcher kept field notes to support auditability and trustworthiness. Ethical approval was from the Research Ethics Board at St. Lawrence College, Cornwall, Ontario. Informed participant consent was obtained. Workshop attendees did not have to participate, and they did not have to return the survey if they did not choose to do so … read more
PolarityTE to Present SkinTE Clinical Outcomes
at Innovations in Wound Healing Conference
SALT LAKE CITY, Dec. 4, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — PolarityTE, Inc. (Nasdaq: PTE), a commercial stage biotechnology company focused on transforming the lives of patients by discovering, designing and developing a range of regenerative tissue products and biomaterials for the fields of medicine, biomedical engineering and material sciences, announced today that it will present SkinTE™ clinical outcomes at the Innovations in Wound Healing Conference held in Key West, FL December 6-9, 2018.
During a presentation entitled, Regeneration of Functional Skin, Stephen Milner, MD, DDS, DSc, FRCSE, FACS and Chief Clinical Officer of PolarityTE, who practiced medicine for more than 20 years and served as former Professor of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and former Director of Johns Hopkins Burn Center, will discuss SkinTE clinical outcomes data. Dr. Milner will highlight utilization of the autologous SkinTE cell-tissue product in chronic, burn and acute traumatic wounds. The presentation is scheduled during Scientific Session 8 on Sunday, December 9, 2018.
This unique conference is led by a group of experienced educators, scientists and clinicians interested in communicating new approaches to the repair of tissues throughout the human body. The program will focus on the science of tissue repair, the implementation of new findings and the exchange of the latest advances and thinking in the field. Participants, who include clinicians, developers, students and scientists from government, academia and industry, all share an interest in innovative ideas and novel therapies of tissue regeneration and the treatment of chronic wounds. Attendees come from the country’s foremost academic institutions and high-volume medical centers and include notable individuals from the wound care field like leaders from the nation’s largest provider of advanced wound healing services … read more
Outcomes of an Esterified Hyaluronic Acid Matrix in the Treatment
of Chronic Lower Extremity Wounds: A Case Series
This case series evaluates the outcomes of persons with chronic lower extremity wounds treated with an esterified hyaluronic acid matrix (EHAM). Materials and Methods.Data were abstracted from 12 consecutive patients with a total of 14 evaluated chronic wounds (12 [100%] men, mean age 58.72 years) presenting for care at a multidisciplinary wound care center. Nine of the 12 patients had diabetes. The mean wound duration was 39.2 weeks. All patients received surgical wound debridement and were started on therapy consisting of weekly to biweekly applications of the EHAM with a nonadherent, moisture-retentive dressing until complete epithelialization was achieved. Outcomes evaluated included time to complete wound closure and proportion of patients achieving wound closure in 20 weeks. Results. In total, 85.7% of wounds measuring a mean of 2.32 cm2healed in the 20-week evaluation period … read more
Ask the wound care expert about … arterial ulcers
They’re less frequent than diabetic ulcers, but how concerned should we be about arterial ulcers (ischemic ulcers)?… Atherosclerosis is the major cause of peripheral arterial disease. This reduces the arterial blood flow to the lower extremities. The lumen of the arteries become occluded and the extremity becomes ischemic. Most ulcers develop due to a traumatic event to the ischemic leg or foot. However, skin breakdown can occur spontaneously … Risk factors for arterial ulcers include hyperlipidemia, smoking, hypertension, diabetes, advanced age and post trauma to the foot or leg … Arterial ulcers are usually located on the top of the toes, over the phalangeal heads … read more
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Heal Quickly with Nitric Oxide Technology
Editors Note: This article starts by claiming that “15% of 425 million people in the U.S. living with diabetes develop foot ulcers”. So ….
15% of the 425 million people in the U.S. living with diabetes develop foot ulcers. This is called diabetic foot ulcers, and it is said to increase the risk of death on a person by up to 2.5 times. Treating the ulcer with current means takes around 120 days … Now, with a nitric oxide-releasing technology, a team of biometric engineers say they can reduce the healing time of this diabetic foot ulcer by 99 days – that is from 120 to only 21 days … In the quest to lower these expenses, experts from Michigan Technological University have created what they call a nitric oxide-laden bandage that monitors, adjusts and releases the chemical, based on the need or depending on the state of the cells … To arrive at that, they first investigated what goes inside the skin cells when nitric oxide was introduced. In this case, the focus was on dermal fibroblast cells, which they analyzed on both normal and diabetic human cells … read more
NIBIB-funded researchers use non-invasive imaging technique
to diagnose, monitor chronic wounds
A team of NIH-funded researchers at the University of Arkansas have demonstrated the novel use of multiphoton microscopy to monitor wound healing in live animals. The scientists measured metabolic changes that occur during healing at the wounds’ surface using autofluorescence imaging. In the future, doctors could use the images to non-invasively diagnose the type of chronic wound and determine the best treatment strategy.
Chronic skin wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure wounds affect more than 6 million people in the United States, with the cost of treatments mounting to $25 billion each year … read more
TWC Video Series: Reimbursement Tips for Success
In this new video series, TWC editorial advisory board member Kathleen D. Schaum, MS, shares eight poignant reimbursement tips for today’s outpatient wound care clinics.
Tip No. 1: Research
Tip No. 2: Learn Payment Systems
Tip No. 3: Itemizing
Tip No. 4: Identify Pertinent Codes
Tip No. 5: Establish Appropriate Charges
Tip No. 6: NCDs, LCDs, Payer Contracts & Medical Policies
Tip No. 7: Insurance Benefits & Coverage Verification
Tip No. 8: Auditing Claims
It’s not a shock: Better bandage promotes powerful healing
A new, low-cost wound dressing developed by University of Wisconsin-Madison engineers could dramatically speed up healing in a surprising way … The method leverages energy generated from a patient’s own body motions to apply gentle electrical pulses at the site of an injury … In rodent tests, the dressings reduced healing times to a mere three days compared to nearly two weeks for the normal healing process …”We were surprised to see such a fast recovery rate,” says Xudong Wang, a professor of materials science and engineering at UW-Madison … “We suspected that the devices would produce some effect, but the magnitude was much more than we expected” … Wang and collaborators described their wound dressing method today (Nov … 29, 2018) in the journal ACS Nano … read more
Organogenesis Supports ADA Scientific Compendium
Highlighting Latest Treatments for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
CANTON, Mass., Nov. 29, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — Organogenesis Inc., a leading regenerative medicine company committed to empowering healing, is proud to support the American Diabetes Association (ADA)’s publication of a new scientific compendium reviewing the latest methods for diagnosing and treating diabetic foot complications.
“We are proud to support the production of the compendium, which will be an invaluable resource for both clinicians and patients,” said Shabnam Vaezzadeh, Vice President of Global Medical & Clinical Affairs for Organogenesis. “Diabetic foot ulcers represent a significant and ongoing public health challenge and we applaud the ADA for this rigorous, independent and timely review of evidence-based interventions.”
The ADA compendium, Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot Complications, is a comprehensive review of the latest scientific evidence related to the treatment of DFUs, including best practices for early screening and diagnosis, prevention strategies, and wound care and treatment options. The content for the compendium was developed by a respected team of independent researchers and clinicians and is solely the responsibility of the ADA and ADA leadership.
DFUs are the leading cause of diabetes-related amputations in the United States. Nearly 100,000 non-traumatic amputations are performed each year, a number which includes 1 in 6 patients with a DFU, according to the ADA. Proper foot care and access to advanced wound care treatment options are critical to prevent amputation or premature death due to diabetic foot ulcers.
Amputation-free survival in 17,353 people at high risk for foot ulceration in diabetes
a national observational study
Diabetic foot ulcers and amputations are devastating and much feared complications of diabetes. Between 15% and 34% of people with diabetes develop a foot ulcer during their lifetime, with more than half acquiring infections that may result in lower extremity amputations causing disability, extensive periods of hospitalisation, and premature mortality. The incidence of major amputation ranges from 0·2 to 2·0 per 1000 people in those with diabetes [4, 5]. Major or minor amputation also increases the risk of additional subsequent amputations [6]. Foot ulcers are the costliest microvascular complication of diabetes …Amputations in people with diabetes have a significant impact on ambulation, body care, movement and mobility, resulting in an inability to perform daily tasks and often a loss of employment [6] impacting on the wider family. Clinical epidemiology studies suggest that foot ulcers precede around 85% of non-traumatic lower extremity amputations in individuals with diabetes and hence ulcer prevention is important. Previous studies have reported that apart from severity of ulcer … read more
Shoe Insole May be a Help for Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic ulcers commonly result from high blood sugar damaging nerves, which takes away feeling from the toes or feet … Without the ability to feel pain, hits and bumps tend to go unnoticed and skin tissue breaks down, forming ulcers … A lot of sugar in the bloodstream, along with dried skin as a consequence of diabetes, further slow the ulcer healing process … Recently, Purdue researchers developed a shoe insole that could help make the healing process more portable for the 15% of Americans who develop ulcers as a result of diabetes … The researchers used lasers to shape silicone-based rubber into insoles, and then create reservoirs that release oxygen only at the part of the foot where the ulcer is located … read more
Choosing compression to heal venous leg ulceration
There is a robust evidence base to support the use of compression therapy for healing venous leg ulceration and for preventing ulcer recurrence. The most recent version of the Cochrane Review on the effectiveness of compression and the relative effectiveness of different compression systems on venous leg ulcer healing included 48 randomised controlled trials (RCTs) reporting 59 comparisons. Although the methodological quality of the evidence is variable, there is overwhelming evidence that multi-layer high compression systems greatly increase the chances of healing compared to no compression. A more recent review and update of the evidence came to the same conclusion. Similarly, although there is very little evidence on the use of compression to prevent recurrence of venous ulcers, the overwhelming evidence of effectiveness for healing makes it highly likely that compression is also highly effective at preventing recurrence … read more
How Israel is transforming diabetes worldwide
Israeli companies are tackling medical issues that are impacting people across the world, and diabetes is one of the key areas that these companies are tackling. Improved approaches, treatments and management are helping these companies transform diabetes across the world … A chronic disease of the pancreas, diabetes occurs when a person cannot make enough insulin to regulate their blood sugar … Betalin Therapeutics, a startup, is leading the way for diabetic treatment advancement. The company, still a relatively young company, has been able to cure type-1 diabetes in mice. And while the transition from mice to humans is drastically different, the company hopes that they’ll be able to one day cure humans of diabetes … read more
Quick Guide: Using IODOSORB in practice
This Quick Guide outlines the use of IODOSORB as part of a biofilm-based wound care approach and provides helpful tips for it’s implementation in practice … download pdf
Researchers develop portable 3-D skin printer to repair deep wounds
University of Toronto researchers have developed a handheld 3-D skin printer that deposits even layers of skin tissue to cover and heal deep wounds. The team believes it to be the first device that forms tissue in situ, depositing and setting in place, within two minutes or less … The research, led by Ph.D. student Navid Hakimi under the supervision of Associate Professor Axel Guenther of the Faculty of Applied Science & Engineering, and in collaboration with Dr. Marc Jeschke, director of the Ross Tilley Burn Centre at Sunnybrook Hospital and professor of immunology at the Faculty of Medicine, was recently published in the journal Lab on a Chip … read more
Moldable Hyaluronan Hydrogel Enabled by Dynamic Metal–Bisphosphonate
Coordination Chemistry for Wound Healing
Biomaterial‐based regenerative approaches would allow for cost‐effective off‐the‐shelf solution for the treatment of wounds. Hyaluronan (HA)‐based hydrogel is one attractive biomaterial candidate because it is involved in natural healing processes, including inflammation, granulation, and reepithelialization. Herein, dynamic metal–ligand coordination bonds are used to fabricate moldable supramolecular HA hydrogels with self‐healing properties. To achieve reversible crosslinking of HA chains, the biopolymer is modified with pendant bisphosphonate (BP) ligands using carbodiimide coupling and chemoselective “click” reactions. Hydrogel is formed immediately after simple addition of silver (Ag+) ions to the solution of HA containing BP groups (HA‐BP). Compared with previous HA‐based wound healing hydrogels, the HA‐BP·Ag+ hydrogel is highly suitable for clinical use as it can fill irregularly shaped wound defects without the need for premolding. The HA‐BP·Ag+ hydrogel shows antimicrobial properties to both Gram‐positive and Gram‐negative bacterial strains, enabling prevention of infections in wound care. In vivo evaluation using a rat full‐thickness skin wound model shows significantly lower wound remaining rate and a thicker layer of regenerated epidermis as compared with the group left without treatment. The presented moldable and self‐healing supramolecular HA hydrogel with “ready‐to‐use” properties possesses a great potential for regenerative wound treatment … read more
Nexodyn Wound Care Solution Launched in the U.S.
The new Nexodyn AOS wound care solution, cleared for sale by the FDA, is now starting to be available in the USA, promoted and commercialized by the Italian pharmaceutical company Angelini, as a result of an exclusive partnership with the Swiss company APR Applied Pharma Research, the owner and developer of the proprietary, patented technology TEHCLO, for the production of acidic super-oxidizing solutions … Nexodyn helps cleanse and moisten the wound environment by removing dirt, debris and foreign material by flushing across the wound … Nexodyn is intended for use, under the supervision of healthcare professionals, to treat acute and chronic dermal lesions (such as leg ulcers, post-surgical wounds or 1st and 2nd degree burns) and minor cuts, burns, skin irritations and superficial abrasions … The solution, characterized by an acidic pH between 2 … 5 and 3 … 0, has cell viability preservation features, so as not to negatively interfere with the natural physiological healing process and epthelialization … Its antimicrobial preservative effectiveness has been demonstrated by in vitro testing … read more
The Effect of Foot Exercises on Wound Healing in Type 2
Diabetic Patients With a Foot Ulcer
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of foot exercises on wound healing in type 2 diabetic patients with a diabetic foot ulcer … Sixty-five patients from an outpatient clinic with grade 1 or 2 ulcers (Wagner classification) who met study criteria agreed to participate; 60 patients completed the study and were included in the final analysis … Subjects were followed up between February 2014 and June 2015 … Subjects were recruited by the researchers in the clinics where they received treatment … Subjects were randomly allocated to either the control or intervention group … Data were collected using investigator-developed forms: patient information form and the diabetic foot exercises log … Patients in the intervention group received standard wound care and performed daily foot exercises for 12 weeks; the control group received standard wound care but no exercises … The ulcers of the patients in both the intervention and control groups were examined and measured at the 4th, 8th, and 12th weeks … The groups were compared in terms of the ulcer size and depth … To analyze and compare the data, frequency distribution, mean (standard deviation), variance analysis, and the independent samples t test and the χ test were used … read more
New healing hydrogel is full of holes
Although we’ve already heard about hydrogels that help to heal chronic wounds, the University of New Hampshire’s Asst … Prof … Kyung Jae Jeong states that most of them have a shortcoming – they’re not porous enough … An inexpensive micro-hole-filled gel made by his team, however, is claimed to perform much better … The idea behind most hydrogels is that they get applied to “difficult” wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers, either being injected into them or put on as a dressing … The gels then create a form-fitting matrix across the surface of those injuries, promoting healing by keeping the wounds moist, preventing bacteria from entering them, and in some cases releasing medication … According to Jeong, though, cells from adjacent tissue often have difficulty growing through these relatively non-porous hydrogels and into the wound, resulting in a slow healing process … read more
Non-invasive Ozone Therapy Shows Effectiveness in Treating Digital Ulcers
Non-invasive, local treatment of digital ulcers with ozone for 20 days showed clinical effectiveness in systemic sclerosis patients, according to a new study …The study, “Non-invasive Oxygen-Ozone Therapy in Treating Digital Ulcers of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis,” was published in the journal Acta Reumatológica Portuguesa, and was conducted by researchers at Asyut University and Suez Canal University, in Egypt …Systemic sclerosis (SSc), or systemic scleroderma, is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects connective tissue (the tissue that supports and holds other tissues or organs together), and is characterized by excessive production of collagen protein, leading to fibrosis of the skin and internal organs …Excessive collagen deposition can also narrow small blood vessels in the fingers and toes, resulting in Raynaud’s phenomenon … read more
A guide to wound care
In this table, we cover the basics of wound care, such as reducing bioburden, reducing edema and maintaining a moist wound environment. This information was gathered from a 2014 article from the journal, Plastic Surgical Nursing, in which Marcia Spear, DNP, ACNP-BC, CWS, CPSN, addressed the “Principles of Wound Care – Back to Basics.” … view pdf
Researchers Develop New Method to Diagnose, Monitor Chronic Wounds
Researchers at the University of Arkansas have developed a new approach to diagnosing and monitoring chronic skin wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure wounds … Chronic skin wounds affect more than 150 million people worldwide and cost approximately $25 billion in health care annually in the United States alone. These non-healing wounds are characterized by inflamed tissue, poor blood circulation, callus formation or infection … Current clinical approaches for diagnosing and monitoring these wounds do not provide critical diagnostic information about how they develop or why they do not heal … read more
Wound healing in psoriasis, multiple sclerosis
Wound healing is impaired in both psoriasis and multiple sclerosis, raising the prospect that a better understanding of the process could improve our understanding of the pathophysiology of these two chronic conditions and generate targets for treating them … The two conditions share a number of characteristics … For example, both diseases demonstrate slight itching, symmetry of the lesions, exacerbation after stopping corticosteroid treatment, and the Koebner phenomenon – provocation of the condition by stress … The Koebner phenomenon (isomorphic response) was first described in 1876 by the German dermatologist Heinrich Koebner who noted that patients developed psoriasis at sites of excoriations, horse bites, and tattoos … Koebner famously saw a psoriatic plaque develop on the skin of a farmer where his horse … read more
What can be revealed when you listen to your patients
You may wonder, “What in the world does this man know about type 2 diabetes (T2D) and toe injuries?” Well, I have had a very lengthy and lived experience with T2D. I was diagnosed 19 years ago, and I was very likely one of the worst patients with T2D ever.
How did I get here? How did it come to this? What is this? This is a problem with my feet that I will battle with for the rest of my life. This is an ongoing wound on my left large toe that a dear friend and I caused nearly 9 years ago that has never completely healed and now causes me to visit the diabetic foot clinic at the local hospital every 2–3 months.
Nearly 8.5 years ago, I did not know that this clinic even existed. I learned this fact, literally, by accident. Actually, it wasn’t an accident; I learned through what some might consider performing a really stupid act … read more
Considering Function When Evaluating Threatened Limbs
At the Southwestern Academic Limb Salvage Alliance (SALSA), we have long nicknamed our program “Toe and Flow,” highlighting the central nature of podiatric and vascular surgery to the interdisciplinary team. However, this may be inadequate to describe what we actually do. “Toe, Flow and Go” might better describe what we are doing in clinic, on the hospital wards, and on our research team … As we get more and more adept at technique and technology for limb preservation and limb salvage, what we’re faced with often is a much more fundamental question, which is just because we can do something to preserve a limb, should we? I know people have discussed and talked about this over the years but we are really doing our best to live at it SALSA and USC … read more
Victory on E/M Codes: Medicare Physician Fee Schedule Final Rule Released
APMA celebrated another major advocacy win today as CMS released the 2019 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule final rule. The final rule did not include the originally proposed podiatry-specific E/M codes, which would have reimbursed at a significantly lower rate than codes for the same care provided by other physicians … APMA extends its sincere gratitude to the thousands of members, colleagues, patients, family, and friends who joined APMA’s grassroots campaign and submitted comments to CMS about this punitive proposal. We also thank our allies at other medical societies and in the halls of Congress, who strongly opposed the proposed rule.“Today we saw proof that when APMA members work together … toward a common goal, we can do great things,” said APMA President Dennis R. Frisch, DPM …. read more
Diabetes Mellitus ‘Fifth Leading Cause Of Death’ In The Bahamas
DIABETES mellitus is the fifth leading cause of death in The Bahamas, according to Health Minister Dr Duane Sands …The Bahamas Podiatric Medical Association underscored the devastating impact of diabetes on feet during a conference at the University of the Bahamas yesterday …“Foot complications are the source of major patient suffering, high emotion and financial costs to the individual and health care system,” Dr Sands told the conference …“We have seen the prevalence of diabetes increase from 6.7% to 9.2% in 2005 now to epidemic proportions of 13.6% in 2017. 37.9 deaths per 100,000 persons are due to diabetes …Dr Sands continued: “Foot ulcers are the most prevalent problem, with a yearly incidence of around 2 – 4% and a lifetime incidence between 15 and 25%. The most important factors underlying the development of foot ulcers are peripheral sensory neuropathy, foot deformities related to motor neuropathy, minor foot trauma, and peripheral artery disease … “Once the skin is ulcerated, it is susceptible to becoming infected, an urgent medical problem that can result in amputation or even death … read more
Some Diabetes Drugs, Higher Amputation Risk Linked
A specific class of diabetes medication appears to double the risk of losing a leg or foot to amputation, a new study reports … People on sodium-glucose cotransporter2 (SGLT2) inhibitors were twice as likely to require a lower limb amputation as people taking another type of diabetes medication, Scandinavian researchers found … Patients also had a doubled risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening complication in which acids called ketones build up in the bloodstream … “Patients at high risk of amputation, for example those with peripheral artery disease or foot ulcers, might be monitored more closely if SGLT2 inhibitors are used, and the risk of this adverse event may be considered when deciding on which drugs to use,” said lead researcher Dr. Peter Ueda, a postdoctoral researcher with Karolinska University Hospital in Stockholm, Sweden … read more
Oxygen-dispensing insole designed to treat diabetic ulcers
Developed at Indiana’s Purdue University, the prototype two-layered insole is made of polydimethylsiloxane, which is a type of silicone. Its bottom layer is actually a chamber that contains oxygen gas, while the top layer is laser-ablated to be particularly oxygen-permeable right at the point where the ulcer is located … The idea is that as the wearer walks throughout the day, placing pressure upon the insole, oxygen is continuously forced out of the bottom layer, up through the top layer and into the oxygen-deprived tissue of the ulcer – there, it helps accelerate healing. Even when they’re sitting, the patient’s foot will still exert enough pressure to deliver some oxygen to the wound … read more
Wound Fluid in Diabetic Foot Ulceration
Valid and reproducible sampling techniques as well as processing protocols are required for the assessment of biomarkers and mediators contained in wound exudate. Moreover, the ideal technique should be easy to use even in daily clinical routine. This is challenging since wound fluid represents an inhomogeneous mixture of different exogenous and endogenous sources. Analyzing wound fluid, however, may facilitate clinical decision making. Many techniques for obtaining wound fluid have been described. There is very little validation data, and the array of different techniques appears confusing. Structuring and new standards are needed to avoid wound fluid sampling yielding an “undefined soup.” A lot of wound fluid parameters have been analyzed, although none of them have made its way into clinical practice. Nevertheless, basic principles of wound healing have been established from wound fluid analysis. With adequate techniques suitable for daily practice, basic research might foster our clinical understanding of wound healing with implications for new therapies. So far, research has mainly concentrated on analyzing available sample material with respect to … read more
Role of protease targets in wound healing uncertain
Protease modulating therapies are used to assist in venous leg ulcer closure. However, a recent systematic review of the evidence1 suggests a need to question the biomarker’s importance and further role in the future of targeted chronic wound healing therapies … Earlier research reported in the literature has suggested that reducing protease levels can improve venous leg ulcer healing beyond the use of first-line treatments, such as compression, according to Maggie Westby, Ph.D., research fellow in the School of Health Sciences at the University
of Manchester, UK … read more
Diabetic foot ulcers heal quickly with nitric oxide technology
Diabetic foot ulcers can take up to 150 days to heal. A biomedical engineering team wants to reduce it to 21 days … They’re planning to drop the healing time by amplifying what the body already does naturally: build layers of new tissue pumped up by nitric oxide. In patients with diabetes, impaired nitric oxide production lessens the healing power of skin cells and the Centers for Disease Control reports that 15 percent of Americans living with type II diabetes struggle with hard-to-heal foot ulcers. However, simply pumping up nitric oxide is not necessarily better. The long-term plan of Michigan Technological University …. read more
Leg ulcers that require punch biopsies
Leg ulcers can be caused by vasculitis, pressure sores, inflammatory diseases, traumatic injuries and cutaneous neoplasms―which are often misdiagnosed as skin ulcers, write Lidia Sacchelli and colleagues in the September 19 online issue of the Journal Dermatopathology … “We believe that clinicians should be aware of the importance of an early and correct diagnosis of cutaneous neoplasms underlying chronic leg ulcers. This could avoid diagnostic delay and guarantee the best therapeutic approach to each patient,” they wrote … Lesions that grow, spread or are pigmented may require a biopsy and histologic study … read more
An Aussie Researcher Insists Maggots Are the Best Way to Heal Wounds
“Maggots are fantastic,” he says. “They eat all the dead and decaying tissue in the wound… [and] remove bacteria by eating them and digesting them, and through their excretions and secretions that they place into the wound.” … Frank explains that these “anti-microbial” properties of the humble maggot keep the infection under control and allow the body to properly heal the wound. The process is known as “debridement”: the removal of dead or infected tissue that in turn improves the healing potential of the healthy tissue. The maggot then disinfects the wound by secreting anti-bacterial substances, and stimulates the production of new, fresh capillaries over the top … read more
Bayer VP Alan Westwood to lead antimicrobial firm Matoke Pharma
Former Bayer VP Alan Westwood has taken the reins of British antimicrobial biotech Matoke Pharma … Westwood spent 35 years at Bayer Health Care, becoming its VP of global strategic marketing for anti-infectives. As managing director of Matoke Pharma, he will oversee development of its lead candidate, RO-101, based on the company’s “reactive oxygen” platform …The platform uses naturally occurring compounds and molecules, such as hydrogen peroxide, to kill bacteria by physically disrupting their cell structures and membranes. Such oxygen-containing compounds are also used in the body’s normal wound-healing processes … read more
Amputation-free survival in 17,353 people at high risk for foot ulceration
in diabetes: A national observational study
Diabetic foot ulcers and amputations are devastating and much feared complications of diabetes. Between 15% and 34% of people with diabetes develop a foot ulcer during their lifetime, with more than half acquiring infections that may result in lower extremity amputations causing disability, extensive periods of hospitalisation, and premature mortality. The incidence of major amputation ranges from 0·2 to 2·0 per 1000 people in those with diabetes. Major or minor amputation also increases the risk of additional subsequent amputations. Foot ulcers are the costliest microvascular complication of diabetes … Amputations in people with diabetes have a significant impact on ambulation, body care, movement and mobility, resulting in an inability to perform daily tasks and often a loss of employment impacting on the wider family. Clinical epidemiology studies suggest that foot ulcers precede around 85% of non-traumatic lower extremity amputations in individuals with diabetes [8] and hence ulcer prevention is important. Previous studies have reported that apart from severity of ulcer, age [9], low socioeconomic status, smoking, sex, renal impairment, ischaemic heart disease, diabetic neuropathy, glucose levels and peripheral arterial disease are some of the important factors associated with the risk of amputation. Identifying a person’s risk of foot ulceration helps in directing scarce resources to those most at need. Assessment of individual risk factors … read more
London-developed tool zeros in on diabetic foot ulcers
A new screening tool developed by St. Joseph’s Health Care London could reduce the number of diabetes-related amputations across the region … The primary care diabetes support program (PCDSP) at St. Joseph’s partnered with the South West Local Health Integration Network (LHIN) to come up with a standardized screening, assessment and referral tool for family doctors. The tool helps to identify red flags in patients that could lead to devastating foot ulcers … “The end game is early identification and effective intervention of those at risk of diabetes-related foot ulcers,” said Betty Harvey, a nurse practitioner and clinical nurse specialist with the PCDSP. “Once a person has a foot ulcer … read more
Evaluation of fluorescence biomodulation in the real-life management
of chronic wounds: the EUREKA trial
Fluorescence biomodulation (FB), a form of photobiomodulation (PBM) that is also known as low energy level light (LELL), has become an increasingly used clinical tool to induce wound healing in wounds that remain recalcitrant to treatment. In a real-life clinical setting, the aim of the EUREKA (EvalUation of Real-lifE use of Klox biophotonic system in chronic wound mAnagement) study was to confirm the efficacy and safety of LumiHeal, a system based on FB, in the treatment of chronic wounds such as venous leg ulcers (VLUs), diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) and pressure ulcers (PUs). The effects of this FB system on the modulation of wound healing in chronic ulcers through FB induction were previously examined in an interim analysis of this study … read more
Healogics Unveils Patient Engagement Program
Healogics®, the nation’s leading provider of advanced chronic wound care services, today unveiled their Patient Engagement program. Through this program, patients will receive text message reminders for their appointments as well as links to educational videos, relevant articles and instructions related to wound and ostomy care … “Wound care as a specialty relies heavily on patients’ willingness and ability to adhere to their prescribed plan of care,” says Dr. William Ennis, DO, MBA, MMM, Healogics Chief Medical Officer. “By engaging patients where they are, and encouraging appointment attendance, the Patient Engagement program has reduced appointment cancellations supporting care plan adherence.” … The new program has two-way engagement, meaning Healogics team members can see patients’ responses in real time. If a patient has to cancel, a team member will proactively call the patient to reschedule the appointment to avoid any delays in care. During the program’s pilot, Healogics saw an eight percent reduction in appointment cancellations, which means eight percent more people received the life-changing care … read more
Silverlon’s New Wound Care Website Gives Surgeons
Healthcare Professionals Searchable Access to Clinical Studies and Silverlon Products by Specialty
Argentum Medical, LLC and Cura Surgical launched its new website for its Silverlon® antimicrobial wound care technology (https://www.silverlon.com). The robust website gives surgeons and other healthcare professionals — both in civilian and in military settings — convenient access to the science and clinical research supporting the most evidence-based silver-based dressings available today.
Users of the new Silverlon website can quickly find Silverlon wound care products by specialty, including surgical, wound care, burn, catheter and negative pressure contact dressings. The site includes educational videos to explain the antimicrobial advantage of silver ions as well as instructional videos on the proper use of Silverlon dressings in a number of clinical settings.
The website also features a searchable index of independent, peer-reviewed, clinical studies that demonstrate the effectiveness of Silverlon technology across multiple specialties including surgical, venous catheter, wound and burn care. Recent clinical studies include research conducted by the Harvard Combined Orthopaedic Residency Program published in the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons and the University of South Florida/Tampa General Hospital’s central line catheter-related infection (CLABSI) study published in the Journal of Intensive Care Medicine.
“Our new website is designed to give surgeons and other medical professionals an efficient resource to explore the science and robust body of clinical research supporting the advantages of Silverlon dressings as part of a comprehensive infection prevention bundle,” said Raul Brizuela, president and CEO of Cura Surgical and Argentum Medical … read more
Amputation-free survival in 17,353 people at high risk for foot ulceration
in diabetes: a national observational study
Using data from the Scottish Care Information-Diabetes register (N=247,278), researchers analyzed 17,353 individuals with diabetes and at high risk for foot ulceration (“high-risk foot”) from January 2008 to December 2011 to determine amputation-free survival and to compare different subcategories of high-risk foot. According to findings, for those with diabetes and at high risk for foot ulceration, the risk of death was up to nine times the risk of amputation. In addition, those with diabetes who had healed ulcers displayed higher death rates than those with active ulcers. However, the highest risk of amputation was noted for people with active ulcers.
Read the full article on Diabetologia – Clinical and Experimental Diabetes and Metabolism
LeucoPatch system for the management of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers
in the UK, Denmark, and Sweden: An observer-masked, randomised controlled trial
The LeucoPatch device uses bedside centrifugation without additional reagents to generate a disc comprising autologous leucocytes, platelets, and fibrin, which is applied to the surface of the wound. We aimed to test the effectiveness of LeucoPatch on the healing of hard-to-heal foot ulcers in people with diabetes … This was a multicentre, international, observer-masked, randomised controlled trial of people with diabetes and a hard-to-heal foot ulcer done in 32 specialist diabetic foot clinics in three countries (UK, Denmark, and Sweden). After a 4-week run-in period, those with a reduction in ulcer area of less than 50% were randomly allocated (1:1) by computer-generated, web-based randomisation … read more
Read the full article on The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology
MiMedx To Present Clinical And Scientific Studies At Desert Foot Conference
MARIETTA, Ga. /PRNewswire/ —MiMedx (NASDAQ: MDXG), a leading developer and marketer of regenerative and therapeutic biologics, today announced that five poster abstracts reporting on the Company’s EpiFix® dehydrated Human Amnion/Chorion Membrane (dHACM) allograft and EpiCord® dehydrated human umbilical cord (dHUC) allograft will be presented at the Desert Foot 15th Annual Multi-Disciplinary Limb Salvage Conference in Phoenix, Arizona. The conference begins Wednesday, November 7, 2018, and concludes on Saturday, November 10, 2018.
MiMedx will sponsor a symposium entitled, “Clinical Efficacy of EpiFix and AmnioFix dehydrated human amnion/chorion membrane allografts in Surgical and Wound Care Applications” on Wednesday, November 7th in the Phoenix Ballroom main lecture hall. The symposium faculty and presenters include Ray Ortega, MD, MiMedx Medical Director, and Jeremy Lim, PhD, Senior R&D Engineer at MiMedx.
Dr. Ortega, a former Army Special Forces Officer (Green Beret) and Medical Corps plastic surgeon, will review two recent EpiFix and EpiCord multicenter DFU randomized control trial (RCTs) studies … read more
Ending Avoidable Amputations Within A Generation
Diabetic Foot Australia (DFA) was established in 2015 with the goal of ending avoidable amputations within a generation in Australia. As a key initiative of the Wound Management Innovation CRC, we engaged the expertise of multiple partner organisations across Australia to create a national diabetes-related foot disease (DFD) body for Australia. On the 1st July 2018, Diabetic Foot Australia joined the Australian Diabetes Society’s (ADS) stable of national diabetes clinical and research programs …. download Australian Diabetes-Related Foot Disease Strategy (PDF)
MTF Biologics and Academy Medical Partner to Advance Care for Veterans
EDISON, N.J., Nov. 1, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — MTF Biologics, the world’s largest tissue bank, and Academy Medical, a certified Service-Disabled, Veteran-Owned Small Business (SDVOSB) that specializes in providing medical products, tissues and devices to government agencies, have joined forces to bring advanced human allograft tissues to the Department of Veteran’s Affairs (VA) medical centers across the country. MTF Biologics has joined Academy Medical’s supplier network, ensuring that MTF Biologics’ portfolio of tissue innovations, used to treat a variety of acute and chronic wounds, orthopedic conditions, and plastic and reconstructive surgery needs, are available to healthcare providers serving veterans at VA facilities.
As a result of this partnership with Academy Medical, MTF Biologics tissues have been added to Academy Medical’s Strategic Acquisition Center (SAC) Biologics and Biological Implants Contract and their National Acquisition Center (NAC) Federal Supply Schedule (FSS) contract for the Department of Veterans Affairs. Together, Academy Medical and MTF Biologics now offer the broadest portfolio of bone, dermis, placenta and other tissues to address the needs of our veterans and military personnel.
“Academy Medical has a great track record of connecting government healthcare providers with medical innovations,” said Thomas Shaffer, Executive Vice President of Global Sales and Marketing at MTF Biologics. “We are excited to partner with the Academy Medical team to bring innovations in tissue transplantation to our nation’s veterans. Our organizations share a commitment to ensuring that physicians have access to the medical advances, tools and technologies they need to meet the needs of their patients. This partnership achieves this commitment while also furthering MTF Biologics’ Mission of saving and healing lives.” … read more
Mӧlnlycke® to Launch Latest Innovation, Mepilex® Border Flex, at Fall SAWC Conference
Mӧlnlycke® will launch Mepilex® Border Flex at the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care Fall meeting (SAWC Fall) 2-4 November in Las Vegas. The new Mepilex® Border Flex dressing was specifically engineered to support fewer dressing changes, reducing dressing costs and waste, while creating an optimal healing environment.
‘We believe that the Mepilex Border Flex dressing may change the way wound care experts practice because its features effectively support undisturbed wound healing,’ says Randy Schwartz, Vice President of Marketing. ‘Less frequent dressing changes benefit the patient, caregiver and the wound healing process. The product’s unique structure enhances conformability and its exudate management properties and allows it to remain in place for longer wear times. These features will positively impact cost.‘
Mӧlnlycke will feature the dressing in its booth and is sponsoring a complimentary breakfast symposium at the Fall SAWC conference, ‘Novel Technology for Advanced Wound Dressings: Early Clinical Experience.’ The session will examine the role of dressing conformability and exudate management in supporting undisturbed healing of acute and chronic wounds. The presenters will also share their experience with the new dressing and examine its impact on clinical outcomes, patient satisfaction and cost savings.
Renowned wound care expert Robert Kirsner, MD, PhD will lead the symposium which features Oscar Alvarez, PhD and Deborah Nelson RN, BSN, CWOCN who will discuss their clinical experience with the product. The symposium will take place on Sunday, 4 November at 7:30 AM – 9:00 AM … read more
Organogenesis Celebrates Launch of Advancing Healing Education
Resource Center and Highlights Latest Wound Care Research at SAWC Fall 2018
CANTON, Mass. and LAS VEGAS, Nov. 1, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — Organogenesis Inc., a leading regenerative medicine company committed to empowering healing, will celebrate the launch of the Advancing Healing Education Resource Center, a continuing medical education microsite covering the latest clinical and practical developments in wound healing, as well as showcase the company’s latest product research during the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC) Fall 2018 meeting held this week in Las Vegas.
Made possible through an educational grant from Organogenesis to the North American Center for Continuing Medical Education (NACCME), the Advancing Healing Education Resource Center will feature accredited educational activities designed to improve the care of patients with repair and regenerative needs across the continuum of care. Topics will include healing of musculoskeletal injuries, including degenerative conditions, and the treatment of chronic and acute wounds … read more
Harbor MedTech Presents the Latest Findings on its Advanced Wound-Healing
Technology at the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and Wound Healing Society Spring Conference
Harbor MedTech, a commercial-stage regenerative medicine company delivering innovative biologic wound-healing products, presented a Poster on Architect®, its advanced wound-healing product, and BriDGE®, its unique technology.
The scientific poster, “Stabilized Collagen Matrix Dressing Improves Macrophage Recruitment and Wound Epithelialization” was presented at the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care and Wound Healing Society Spring Conference, April 5 – April 9, 2017, in San Diego, California and was selected for the WHS Industrial Research & Development Poster Award Competition.
The poster was a presentation of ongoing research, led by Dr. Chandan K. Sen, Executive Director of Ohio State University’s Comprehensive Wound Center. Dr. Sen’s work involves a variety of in vitro and animal studies that initially describe the mechanism of action of Architect, a stabilized collagen matrix, for the treatment of a variety of wound types. These studies suggest that Architect may serve as a scaffold for cells within the wound microenvironment and may provide effective defenses against bacterial colonization and wound infection. In vivo, application of Architect stimulated … read more
MiMedx to Present Clinical and Scientific Studies at SAWC Fall Meeting
MARIETTA, Ga., Oct. 31, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — MiMedx Group, Inc. (NASDAQ: MDXG), a leading developer and marketer of regenerative and therapeutic biologics, today announced that five poster abstracts highlighting studies on the Company’s EpiFix® dehydrated Human Amnion/Chorion Membrane (dHACM) allograft and EpiCord® dehydrated human umbilical cord (dHUC) allograft will be presented at the 2018 Symposium on Advanced Wound Care Fall (SAWC Fall) at Caesars Palace in Las Vegas, Nevada. The SAWC, now in its 31st year, is the official meeting for members of The Association for the Advancement of Wound Care and the leading national wound healing conference.
The conference begins Friday, November 2nd and concludes on Sunday, November 4th. MiMedx will be exhibiting in booth #207 during all booth times throughout the three-day meeting.
MiMedx will also sponsor a Breakfast Symposium entitled, “PURION® Processed Placental Based Allografts – The Use of Bioactive Tissue Matrices in the Treatment of Wounds,” on Friday, November 2nd, from 7:30 a.m. to 9:00 a.m. The presenters during the breakfast symposium will include:
- Michelle Massee, Manager of Biomedical Research, MiMedx
- William Tettelbach, MD, Associate Chief Medical Officer, MiMedx
- James Stavosky, DPM
Wound Care Advantage Partners With Tissue Analytics
Combining 17 Years of Clinical Data With AI and 3D Imaging to Improve Patient Outcomes
BALTIMORE, Oct. 29, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — Wound Care Advantage, a leading provider of management and consulting services for outpatient wound care and hyperbaric medicine programs, today announced a partnership with Tissue Analytics, the world’s leading mobile imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) platform for wound management. The partnership allows for WCA to leverage its clinical expertise and 17 years of clinical data with Tissue Analytics’ imaging and AI to improve the accuracy of measurement during wound assessments and provide better insights into the efficacy of wound treatments to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs … Chronic wounds affect about 6.5 million people in the U.S., many stemming from diabetes and/or vascular insufficiency. These wounds have a slow healing process and require frequent monitoring and measurement of progress by a specialized wound care team. Research has shown that automatic smartphone measurements help to eliminate the high degree of interrater and intrarater reliability often encountered when using a traditional ruler … read more
Corstrata Shares Post-Acute Wound Care Challenges Survey Results
Corstrata, a provider of digital healthcare IT solutions and services for wound prevention and care management, announced today the results of the recently completed, Post-Acute Wound Care Challenge Survey. The survey was directed to U.S.-based home health agencies (HHAs) and hospice organizations and sought to gather industry-wide input on the state of the current challenges HHAs and hospice organizations face in providing value-based care for the growing wound patient population.
Like other areas of healthcare, HHAs and hospice organizations have also historically had difficulties with hiring and retaining board-certified wound cares nurses. While nearly 80% of the 124 survey respondents believe their organization is properly staffed to handle wound care patients, 46% of CNOs/VPs Nursing/Directors of Nursing indicate their organizations do not have access to a board-certified wound care nurse. Collectively, 32% of all respondents indicate they do not have access to a board-certified wound care nurse with another 12% of respondents indicating they only have access to a part-time/contract board-certified wound care nurse.
In addition, when HHA and hospice representatives were asked to describe how their current wound care staffing model impacts their business, 9% indicate they are missing out on patients due to lack of adequate wound care staff or wound knowledge; 37% say their in-home nursing visits are high with wound patients, and 29% have low or no financial margins on wound care patients.
However, another key finding is indicative of a growing desire to change how HHAs and hospice organizations address the needs of its wound care patients. 55% of HHAs and hospice organizations believe they would benefit from increased access to board-certified wound care nurses using virtual visit technologies …. read more
Healogics to take part in campaign highlighting link between diabetes
and chronic wounds
Healogics®, the nation’s wound healing expert, is proud to participate in a national diabetes awareness campaign October 29 through November 2. This campaign will highlight the important connection between diabetes and chronic wounds and their recurrence. Throughout this week, Wound Care Centers® from across the country will dedicate their time to visiting local physician offices to provide education on the treatment of potential or existing chronic wounds for people also living with diabetes … An estimated 30.3 million people in the United States have diabetes, and the percentage of adults with diabetes increases with age, reaching a high of 25.2 percent among those aged 65 years or older. In addition to age, risk factors for diabetes also include diet, activity level, obesity and heredity. Approximately one in four people living with diabetes will develop a foot ulcer. Even more alarmingly, people with healed a diabetic foot ulcer have a recurrence rate of nearly 40 percent within the first year … read more
Cuba aims to boost exports at China’s import expo (Heberprot-P)
Cuba plans to put on a big show at the upcoming China International Import Expo (CIIE) in a bid to expand its export market, Vice President of Cuba’s Chamber of Commerce Ruben Ramos told Xinhua in a recent interview … While Cuba plans to tout its traditional strengths at the expo, it also intends to introduce its ground-breaking biotechnology products such as CIMAvax-EGF, a therapeutic vaccine against lung cancer and Heberprot-P, a unique treatment for diabetic foot ulcers.
Frank Bures: Diabetic foot ulcers: A story, and a lesson
Here’s a story about a foot ulcer and it’s tragic result in a diabetic with several other health problems. This is an attempt to inform people with diabetes about the vital necessity of foot inspection and care. It goes like this … Someone familiar, who will be Uncle Al for this yarn, had his left foot and lower leg amputated because of a diabetic foot ulcer he didn’t even know he had, because he never looked. Uncle Al has been a very happy fellow throughout his life. He had known he has diabetes for quite a while. He also has had a heart attack, and more lately congestive heart failure of controllable nature — if he watches it … read more
Transcutaneous oxygen – not abi or toe pressure – is a predictor for
short-term survival in people with diabetic foot ulcers (study)
Ankle-brachial index (ABI) is the most commonly used test when diagnosing peripheral vascular disease and is considered a marker for cardiovascular risk. Transcutaneous oxygen pressure (TcPO2), a test associated with microvascular function, has in several studies shown better correlation with diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) healing. Whether a low TcPO2 could be a marker for mortality in the high-risk population of DFU patients has not been evaluated before. The aim of this study was to evaluate the predictive value of TcPO2 in comparison with ABI and toe blood pressure (TBP) on 1-year mortality in type 2 diabetes patients with DFU …. read more
Financial burden of diabetic foot ulcers to world: a progressive topic to discuss always
Diabetic foot complications are the most common occurring problems throughout the globe, resulting in devastating economic crises for the patients, families and society. Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) have a neuropathic origin with a progressive prevalence rate in developing countries compared with developed countries among diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetic patients that are of greatest risk of ulcers may easily be diagnosed with foot examination. Economic burden may be carefully examined. The budget costing must include both the clinical and social impact of the patients … Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder imparting loss in health and economic burden on patients and healthcare machinery around the globe. As the present world is facing an epidemic of both type 1 and type 2 DM, the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) has focused on the micro and macrovascular complications associated with DM. In 2005, the IDF committed to execute the management approach for diabetic foot diseases. The risk for developing foot ulcers is 25% high in patients with diabetes and it is also reported that every 30 seconds, one lower limb amputation in diabetes patients occurred around the world. The IDF has now become proactive and declared in its mandate that now is the time to increase awareness about the foot complications associated with DM in scenarios of social, personal, clinical and economic costs … read more
25 MUST Know Statistics About Amputation Due to Diabetes
There are some surprising statistics about how common diabetic foot ulcers are, how often they can lead to amputation and the ultimate cost of having a foot ulcer that results in an amputation …. read more
Novel combination therapy promotes wound healing
October 25, 2018–(BRONX, NY)–By incorporating a gene-suppressing drug into an over-the-counter gel, researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine and their colleagues cut healing time by half and significantly improved healing outcomes compared to control treatments. Results from the combination therapy, which was tested in mice, were published online today in Advances in Wound Care …”Not only did wound healing occur more rapidly and completely, but actual regeneration occurred, with hair follicles and the skin’s supportive collagen network restored in wounded skin–clinically important improvements that are unprecedented in wound care,” says senior author David J. Sharp, Ph.D, professor of physiology & biophysics at Einstein. “We foresee this therapy having broad application for all sorts of wounds … read more
Efficacy of negative pressure wound therapy using vacuum-assisted
closure combined with photon therapy for management of diabetic foot ulcers
Background: Diabetes mellitus, one of the most prevalent chronic metabolic diseases, causes many complications. Among the complications, one of the most common chronic complications is diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs).
Objective: This study was conducted to investigate the efficacy of negative pressure wound therapy using vacuum-assisted closure (VAC) combined with photon therapy for the management of DFUs … Patients and methods: The study included a total of 69 patients with DFUs during the period from January 2014 to December 2015. All patients were diagnosed with DFUs with Wagner’s stage 2 or 3 and were divided into two groups – the VAC group in which patients received only VAC and the combined group in which patients received both VAC and photon therapy. Data on duration of the treatment, pre- and postoperative wound surface areas, dressing changing times, pain conditions assessed using visual analog scale scores, recurrence rate and amputation rate were collected … Results: Among all patients, 35 patients were divided into the VAC group and 34 patients into the …. read more
New Clinical Research Program Takes Steps to Predict
and Prevent Diabetic Foot Ulcers
More than 100 million adults in the United States live with diabetes or prediabetes, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Most people know that common complications of the disease include increased thirst, weight loss and fatigue … But fewer may know about another side effect: diabetic foot ulcers, which affect nearly 25 percent of individuals and are one of the disease’s most prevalent complications. Patients with ulcers can’t put weight on the affected area in order to facilitate healing (and avoid infection) … Still, those ulcers are responsible for about 80,000 nontraumatic amputations nationwide each year — surgery that comes with a five-year mortality rate of up to 40 percent … read more
Podiatry Billing Firm Announces Partnership with iRemedy
to Dispense Wound Care Supplies
Hippocratic Solutions, an outsourced podiatry billing firm, has announced a partnership with iRemedy, a leading ecommerce medical supplies provider. The partnership will allow podiatrists to prescribe, bill for, and dispense advanced wound care supplies through their DME license … iRemedy, an industry leader in ecommerce medical supplies and medical business consulting, has recently partnered with Hippocratic Solutions … “Integrating iRemedy with Hippocratic Solutions is a real breakthrough that is going to take our Advanced Wound Care Program to the next level,” said Tony Paquin, CEO of iRemedy Healthcare. “We’re excited to work with Peter Koukounasand the Hippocratic Solutions team.” … Alongside outsourced podiatry billing services, Hippocratic Solutions clients will now have instant online access to iRemedy’s online platform with the ability to submit and manage prescriptions for their patients with chronic wounds. Podiatrists will be able to file and bill for wound care prescriptions directly through iRemedy, who will audit the prescription for the podiatrist and handle insurance preauthorization and any insurance denials …”Most podiatrists don’t think they can dispense and profit from wound care supplies through their license, but this just isn’t true,” said Peter Koukounas, CEO of Hippocratic Solutions. “By partnering with iRemedy, we’re helping podiatrists earn greater profits while drastically improving patient outcomes.”
Arizona-based biotech startup BioLab Sciences announces patent
for regenerative tissue therapy, MyOwn Skin™
SCOTTSDALE, Ariz., Oct. 24, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — BioLab Sciences, an innovator in regenerative medicine technologies, today announced its exclusively licensed technology for MyOwn SkinTM, a painless, non-surgical procedure, which leverages a patient’s own skin to produce full-thickness skin grafts in 5-7 days.
MyOwn SkinTM is a revolutionary approach that uses a patient’s own skin to accelerate healing of chronic wounds, burns, diabetic foot ulcers and other difficult-to-heal wounds. By utilizing a small skin sample, this regenerative approach allows the body to heal itself and is less likely to face infection or rejection.
“In the United States alone, chronic wounds affect 6.5 million patients,” said Bob Maguire, BioLab Sciences CEO. “Our advanced, tissue-biomanufacturing approach offers a viable, effective solution for skin regeneration and repair. This innovative strategy has shown to accelerate the healing of damaged soft tissue and improve wound-care outcomes.”
This autologous strategy to wound care is non-invasive, improves recovery time, and eliminates potential rejection. BioLab’s impressive portfolio of regenerative products includes its amnion-derived fluid products, Fluid FlowTM and Amnio RestoreTM and its amniotic allograft membrane product Membrane PatchTM, an amnion membrane allograft …
View original content to download multimedia: http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/arizona-based-biotech-startup-biolab-sciences-announces-patent-for-regenerative-tissue-therapy-myown-skin-300736690.html
Smoking e-cigarettes could significantly slow healing of wounds
Researchers have found that smoking electronic cigarettes could slow the healing of skin wounds as much as regular cigarettes, according to a new study on rats – but admit that further studies are warranted … Smoking electronic cigarettes could slow the healing of skin wounds as much as regular cigarettes, according to a new study on rats … “Based on our findings, e-cigarettes are not a safe alternative to traditional cigarettes as it relates to timely wound healing,” said study corresponding author Dr Jeffrey Spiegel. He’s chief of facial plastic surgery at Boston Medical Center … It’s long been known that smoking regular cigarettes impairs wound healing, and surgery patients are advised to avoid smoking for several months before an elective operation … read more
Study: Antiobitics, probiotics together eradicate bacteria that infect wounds
By combining antibiotics and probiotics, researchers have developed a one-two punch to eradicate two strains of drug-resistant bacteria that often infect wounds, according to a preclinical study … MIT researchers encapsulated probiotic bacteria in a protective shell of alginate, which is a biocompatible material that prevents the probiotics from being killed by the antibiotic. The findings were published Wednesday in the journal Advanced Materials … Probiotics, which are good live bacteria and yeasts, help send food through the digestive system by affecting nerves that control gut movement. Probiotics come from supplements, as well as foods that are prepared by bacterial fermentation, including yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, tempeh and kimchi … read more
related: Probiotics and antibiotics create a killer combination
Acelity Acquires Crawford Healthcare to Create the World’s
Most Expansive Wound Care Portfolio
Acelity L.P. Inc., the world’s largest wound care company, and Crawford Healthcare, a rapidly growing UK-based advanced wound care and dermatology company, today announced an agreement for Acelity to acquire Crawford and all of its assets. Terms of the agreement were not disclosed.
With the acquisition of Crawford, Acelity expands its portfolio of advanced wound dressings (AWD), further strengthening its position as the global leader in advanced wound healing.
Crawford Healthcare is a recognized leader in developing and commercializing innovative treatments for the care and repair of skin. Crawford’s wound dressing portfolio includes the market-leading superabsorbent KerraMax Care® range and KerraFoam and KerraCel in the foam and antimicrobial gelling fiber AWD categories, respectively.
Crawford’s advanced wound dressing lines complement Acelity’s existing AWD portfolio, which includes the market-leading collagen dressing PROMOGRAN PRISMA™ Matrix, as well as the TIELLE™ Dressing Family and ADAPTIC™ Dressings. This expanded line of advanced wound dressings combined with Acelity’s industry-leading negative pressure wound therapy platforms forms the world’s most expansive wound care portfolio. In addition to its commercial products, Acelity will acquire Crawford’s innovative R&D capabilities and manufacturing operations based in Cheshire, UK … read more
Healogics Provides Unrestricted Educational Grant to Support an American Diabetes
Association Compendium: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot Complications
JACKSONVILLE, Fla., Oct. 17, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — Healogics Inc., the nation’s largest provider of advanced wound care services, today announced their support of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Compendium Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcer Complications through an unrestricted educational grant1. More than 30 million people across the U.S. are living with diabetes, and foot problems including foot ulcers are common complications that, without proper treatment, can lead to hospital admissions and even amputations. The ADA Compendium was compiled by a panel of contributing authors and distributed this month to health care professionals who subscribe to the ADA’s peer-reviewed journals Diabetes Care and Diabetes. Healogics is passionate about providing wound care for the 25 percent of diabetics who will experience a foot ulcer at some point in their life2 … “We are proud to support the ADA in their efforts to better understand the latest evidence for treating diabetic foot ulcers,” said David Bassin, Healogics Chief Executive Officer. “We are thrilled that through our unrestricted grant to the ADA, the Compendium was published with a focus on diabetic foot complications.” … read more
Developing a foot ulcer risk model
what is needed to do this in a real‐world primary care setting?
To determine how routinely collected data can inform a risk model to predict de novofoot ulcer presentation in the primary care setting … Data were available on 15 727 individuals without foot ulcers and 1125 individuals with new foot ulcers over a 12‐year follow‐up in UK primary care. We examined known risk factors and added putative risk factors in our logistic model … read more
Arizona-based biotech startup BioLab Sciences
announces patent for regenerative tissue therapy, MyOwn Skin™
SCOTTSDALE, Ariz., Oct. 24, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — BioLab Sciences, an innovator in regenerative medicine technologies, today announced its exclusively licensed technology for MyOwn SkinTM, a painless, non-surgical procedure, which leverages a patient’s own skin to produce full-thickness skin grafts in 5-7 days.
MyOwn SkinTM is a revolutionary approach that uses a patient’s own skin to accelerate healing of chronic wounds, burns, diabetic foot ulcers and other difficult-to-heal wounds. By utilizing a small skin sample, this regenerative approach allows the body to heal itself and is less likely to face infection or rejection.
“In the United States alone, chronic wounds affect 6.5 million patients,” said Bob Maguire, BioLab Sciences CEO. “Our advanced, tissue-biomanufacturing approach offers a viable, effective solution for skin regeneration and repair. This innovative strategy has shown to accelerate the healing of damaged soft tissue and improve wound-care outcomes.”
This autologous strategy to wound care is non-invasive, improves recovery time, and eliminates potential rejection. BioLab’s impressive portfolio of regenerative products includes its amnion-derived fluid products, Fluid FlowTM and Amnio RestoreTM and its amniotic allograft membrane product Membrane PatchTM, an amnion membrane allograft composed of a connective tissue matrix that regenerates soft tissue while inhibiting inflammation and scarring. BioLab Sciences also offers a comprehensive wound care kit that provides physicians with the necessary tools to help patients recover quickly from diabetic ulcers, burns and other traumatic external wounds, as well as its Amnio Breathe Nebulizer bundled package designed to deliver a topical treatment directly onto a patient’s respiratory system …
View original content to download multimedia: http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/arizona-based-biotech-startup-biolab-sciences-announces-patent-for-regenerative-tissue-therapy-myown-skin-300736690.html
Change in Circulating Monocyte Profile with Foot Ulcer Healing in Diabetic Patients
Poor wound healing in diabetes is associated with increased chronic inflammation and alterations in macrophage accumulation. Chronic inflammation can alter the phenotype of macrophage precursors, monocytes but whether their phenotype is changed in association with wound healing is not known. Blood was obtained from 21 patients (14 male: 7 female) attending the High Risk Foot Clinic at RPA Hospital at their initial visit (V1), week 4 (V2) and week 8 (V3). Wound area was measured and wound type was assessed by a podiatrist. Monocyte number (CD14+), phenotype as classical (CD16−), non-classical (CD16++), and intermediate (CD16+), anti-inflammatory (CD163+) subset and expression of receptors CCR2, CCR5 and TLR2, TLR4 were determined by flow cytometry. The MMPs and TIMP-1 were measured in plasma by zymography and ELISA. Over the 8 weeks, 6 ulcers healed (H) and 15 failed to heal (NH). The age, duration of diabetes, HbA1c, wound size and duration at V1 were not different between the groups but the % CD16++ monocytes was higher in H vs. NH at V1 (23.5 vs. 8.3) and V3 (17.4 vs. 7.2) and monocyte CCR2+ was lower in H at V3 … read more
Bioelectrical impedance assessment of wound healing
Objective assessment of wound healing is fundamental to evaluate therapeutic and nutritional interventions and to identify complications. Despite availability of many techniques to monitor wounds, there is a need for a safe, practical, accurate, and effective method. A new method is localized bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) that noninvasively provides information describing cellular changes that occur during healing and signal complications to wound healing. This article describes the theory and application of localized BIA and provides examples of its use among patients with lower leg wounds. This promising method may afford clinicians a novel technique for routine monitoring of interventions and surveillance of wounds … read more
Legal Perils and Pitfalls of Wound Care
How to Keep Yourself out of Court: Part 1
No matter the setting in which we practice, as health care providers we constantly are under the threat of a malpractice lawsuit. In nursing homes the top targets for litigation are pressure ulcers, malnutrition, and dehydration. Up to 20% of all U.S. legal medical claims and more than 10% of settlements are wound related,1 and there are more than 17,000 pressure ulcer-related lawsuits filed annually in the United States … So, it behooves us to take the necessary measures to avoid being sued! What are the perils and pitfalls of wound care that we may encounter in our practice, and how can we best avoid them? This blog explores the various elements that can make or break a case … read more
TWO2 Randomized Controlled Trial Chosen
as One of the Best Abstracts Presented at the Leading Diabetic Foot Global Conference
The number of biotech companies completing an IPO has swelled this year and Adynxx aims to join their ranks—but through an alternate path. The pain drug developer has agreed to combine operations with publicly traded Alliqua Biomedical … Under the merger agreement announced Friday, shares of Adynxx will convert into Alliqua (NASDAQ: ALQA) stock, leaving former Adynxx shareholders owning approximately 86 percent of the combined company. That company will have the Adynxx name and will be led by the current Adynnx management team. It will be headquartered in San Francisco, where Adynxx is currently based … read more
Be ‘Smart’ With New Technology for Diabetic Foot Monitoring
Diabetic foot ulcers are a major health and economic global burden, but ultimately, at least in theory, they’re preventable. The re-ulceration rate is as high as 65% within 5 years, and among persons who initially present with a diabetic foot ulcer, up to 25% may require amputation … One of the most important risk factors for diabetic foot ulceration is diabetic peripheral neuropathy. This involves loss of sensory perception, haptic feedback, and pain perception, so patients can’t self-regulate their foot pressures. It’s thought that these high foot pressures over time cumulatively contribute to the development of diabetic foot ulcers … read more
Common Inadequacies in Wound Management
Throughout my career I have been lucky enough to be part of several nursing branches: home health, long-term care, acute care, long-term acute care hospital, hospice, and even a tuberculosis hospital; wounds have no limitations on where they will appear. As a passionate clinician, teaching, coaching, and mentoring have become a huge part of what I do, as is true for most clinicians. We are teachers, coaches, and mentors driven by passion and wanting to help and put in our “two clinical cents” or “stamp” on the industry … I frequently converse with clinicians in my area, all part of SWAT (skin and wound assessment team), and talk about how it takes a village. I especially enjoy talking with my good friend and mentor Jesse Cantu, RN, BSN, CWS, FACCWS, who is a passionate clinician with a fire that gets you all excited—those who know him know what I am talking about. We share stories of what we do, we give each other constructive criticism, and we often share with each other some of the most common inadequacies we see out there. We always get after each other, in a good way: are we doing enough? and how can we help educate, empower, increase awareness … read more
Tissue Analytics Launches 3D Wound Imaging for Smartphones
Digital health company delivers mobile depth imaging with submillimeter resolution and no need for specialty hardware. The product will be showcased at Cerner Health Conference, October 8-11, Kansas City, Missouri … “Tissue Analytics uses sophisticated algorithms that allow clinicians to generate and securely transfer clinical data from Android or iOS devices into the electronic medical record (EMR). Now, for the first time ever, I’m very excited and honored to present our 3D measurement feature that requires no external device attachments,” announced Joshua Budman, CTO. “From a very simple five-second video, we can now generate a true 3D rendering of any wound, to provide clients with volume and depth measurements at a submillimeter resolution.” … read more
AmpliPhi Biosciences Announces Presentation of Positive Clinical
Data From its Expanded Access Program for Serious S. aureus Infections at IDWeek 2018 Conference
AmpliPhi Biosciences Corporation (NYSE American:APHB), a clinical-stage biotechnology company focused on precisely targeted bacteriophage therapeutics for antibiotic-resistant infections, today announced the presentation of clinical case series data from the company’s ongoing expanded access program for its investigational bacteriophage therapeutic, AB-SA01 targeting Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), at the IDWeek 2018 conference in San Francisco … Prof. Jonathan Iredell, Senior Staff Infectious Diseases Physician at the Westmead Hospital in Sydney, Director of Centre for Infectious Diseases and Microbiology at the Westmead Institute of Medical Research and Professor of Medicine and Microbiology at the University of Sydney, gave a presentation “Adjunctive bacteriophage therapy for severe Staphylococcal sepsis,” including data on 13 patients suffering from severe S. aureus infections, who were treated with AB-SA01 as an adjunct to antibiotics at the Westmead Hospital in 2017-2018. The potential treatment of S. aureus bacteremia with AB-SA01 was also the subject of the Company’s recent Type B meeting with the FDA. The treatment was conducted under emergency protocols per the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration’s (TGA) Special Access Scheme (SAS) … read more
Researcher Looks To Curb Rate Of Diabetic Amputations In NL
A local researcher is hoping to change the alarming rate of amputation due to diabetes in the province … Newfoundland and Labrador has the highest rate of diabetes in the country, and the highest rate of lower limb amputation due to diabetes … Kathleen Stevens is a Registered Nurse and PhD candidate at Memorial University’s School of Nursing … read more
Windsor’s Scapa completes acquisition
Windsor skin care products provider Scapa Healthcare says it has completed its acquisition of an England-based maker of wound care products … Scapa is adding Systagenix and its 335,000-square-foot manufacturing facility in Gargrave, England to its wound care footprint. Financial terms were not disclosed … read more
Malnutrition in type 2 diabetic patients does not affect healing of foot ulcers
Protein–energy malnutrition is known to be involved in wound healing. While wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) is a complex and multifactorial process, the role of malnutrition in this case has rarely been explored. The objective of this study was to determine whether the nutritional status of diabetic patients influences the healing of DFU … 48 patients were included in this prospective, single-center study. All patients with comorbidities or factors involving malnutrition or influencing biological measurements were excluded. Patients were followed up for 24 weeks … read more at Acta Diabetologica (purchase required)
Increasing SBP variability is associated with an increased risk of
developing incident diabetic foot ulcers
Researchers assessed the link between increased SBP variability and incident diabetic foot ulceration risk in 51,111 cases and 129,247 controls. Cases were patients diagnosed with diabetes and treated by the US Department of Veterans Affairs Healthcare system for development of a diabetic foot ulcer (event) between 2006 and 2010; on the basis of age, sex, race/ethnicity, and calendar time, each case was randomly matched to up to five controls. Higher adjusted odds ratios for diabetic foot ulcer development were observed in patients in quartiles 2-4 vs those in quartile 1 (lowest variability). In adjusted subgroup analyses, reduced risks of ulceration were observed in association with calcium channel blockers for those without peripheral vascular disease or neuropathy. Overall, a graded link between SBP variability and diabetic foot ulceration risk was shown.
Read the full article on Journal of Hypertension (subscription required)
‘Smart’ Insoles Reduce Diabetic Foot Ulcer Recurrence
BERLIN — Wearing pressure-sensing smart insoles (SurroSense Rx, Orpyx Medical Technologies) reduced diabetic foot ulcer recurrence by up to 86% in compliant patients in a randomized single-blinded trial in high-risk individuals with type 1 and 2 diabetes … Neil Reeves, PhD, professor of musculoskeletal biomechanics, Manchester Metropolitan University, UK, presented the results here today at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2018 Annual Meeting …“By using a plantar pressure-sensing smart insole device, the feedback of pressure information in the intervention arm reduces ulcer recurrence by 71%, and furthermore in the compliant patients, this further increased benefit, with an 86% reduction in ulcer recurrence [compared with controls],” he reported … read more
Bioactive Glass Implants and Wound Care
Bioactive glass implants are commonly used in orthopedics and dentistry as they can form strong and direct bonds with bone. The capability of bioactive glass to stimulate the growth of new blood vessels also makes them ideal for wound healing …Bioactive glasses are a group of surface-reactive glass-ceramic biomaterials. The first bioactive glass was developed in 1969 by Larry L. Hench at the University of Florida … This material was formed using silicate glass in order to enhance the mechanical and bioactive properties needed for applications in bone regeneration … read more
MTF Biologics Adds New Recovery Partner: Regenerative Biologics, Inc.
MTF Biologics today announced that it has formed a new tissue recovery relationship with Regenerative Biologics, Inc. (RBI). Together, the organizations will seek to provide expanded birth tissue donation opportunities for expectant mothers and their families and enhance patients’ access to high-quality placental tissues for wound care applications … Joe Yaccarino, President and CEO of MTF Biologics added, “MTF Biologics is pleased to partner with RBI again as it combines the key strengths of each of our organizations and expands donation opportunities. We’ve known many of the senior staff at RBI for years and are excited to be collaborating with them again.” … read more
As obesity rate rises, ‘double diabetes’ looms large
An October report from the CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics revealed a startling increase in the prevalence of obesity in the U.S., with rates now approaching 20% in children and 40% in adults for 2015-2016 … The growing epidemic has not spared those with type 1 diabetes. Today, obesity prevalence is as high or higher among patients with type 1 diabetes as in the general population. According to 2015 data from the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry, nearly 40% of children and adolescents with the disease also have overweight or obesity, putting them at increased risk for insulin resistance, hypertension and dyslipidemia — all the hallmarks of not type 1, but type 2 diabetes … read more
Osiris Therapeutics, Inc. Announces Peer-Reviewed Publication
Demonstrating That Lyopreservation Method Developed for Living Tissues is an Alternative to Cryopreservation with the Convenience of Ambient Storage
COLUMBIA, Md., Oct. 02, 2018 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Osiris Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ: OSIR), a regenerative medicine company focused on developing and marketing products for wound care, orthopedics, and sports medicine, announced today that a new peer-reviewed manuscript entitled “Properties of Viable Lyopreserved Amnion Are Equivalent to Viable Cryopreserved Amnion with the Convenience of Ambient Storage” has been published in PLOS ONE and is available online https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0204060 … In the published study the structural, molecular, and wound relevant properties of a lyopreserved human amniotic membrane were compared with the properties of a cryopreserved human amniotic membrane. Results showed that the structure, growth factors, and cell viability of the lyopreserved amnion are comparable to that of cryopreserved and fresh amnions. Properties of lyopreserved and cryopreserved amniotic membranes were tested in vivo in a diabetic mouse chronic wound model, which mimics impaired wound healing reported in diabetic patients. Both lyopreserved and cryopreserved amnion weekly applications resulted in wound closure by day 35 whereas in the saline gel control group of animals wounds became larger … read more
Thermal imaging improves diabetes-related foot ulcer assessment
Thermal imaging can better predict a diabetes related foot ulcer’s size and the healing trajectory than conventional methods, Melbourne-led research has found. It could also possibly save money through better targeted treatment … The study, which was the first of its kind, was a collaboration between RMIT University, the University of Melbourne and Austin Health. It used thermal imaging to quantify the size and predict the healing status of recently developed ulcers … based on their work, the RMIT researchers want to see thermal imaging, which is suitable for most clinical settings, used as an inexpensive and real-time option to identify wounds that may have delayed healing … read more
Calcipotriol Ointment Seen to Improve Wound Healing in RDEB Patient, Study Finds
A low dose of calcipotriol, which is already approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may improve healing and prevent wound infections in patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB), a study showed … treatment with calcipotriol ointment helped close a chronic wound in one patient and eliminated harmful bacteria growing inside it. The compound was also able to enhance skin cells’ defenses against microbial growth and reduce cancer proliferation in skin cells of RDEB patients … read more
Surgical Wounds 101
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate approximately 30 million surgical procedures are performed annually in the United States.1 Advances in technology have afforded patients options such as minimally invasive surgery, commonly known as laparoscopic or arthroscopic surgery, which tend to result in much smaller (1cm–2cm) incisions … However, some procedures necessitate larger incisions of varying size, potentially 10cm–20cm or greater, depending on type of procedure, body habitus, and anatomic area involved. These longer incisions create larger surgical wounds with greater potential for chronicity and complications … read more
Aquacel Extra dressing in practice: Quick Guide
This Quick Guide outlines how using a partnership of tried and tested AQUACEL dressings can provide effective wound management. The focus is on AQUACEL Extra dressing, which is designed to lock in harmful bacteria, micro-contour to the wound bed to maintain optimal moisture balance and reduce ‘dead space’ where bacteria can grow, and respond to wound conditions by forming a cohesive gel when in contact with exudate … read more
Intraoperative oxygen monitoring predicts wound healing
in critical limb ischaemia patients after endovascular intervention
Preliminary findings from an initial study with 25 patients have shown that measuring the changes in oxygen concentration at baseline, during, and after endovascular revascularisation, can predict wound healing and functional improvement in critical limb ischaemia patients … Marianne Brodmann, Medical University Graz, Austria, presented the initial OMNIA study results that used the Lumee oxygen platform (Profusa) as a unique tool to assess and clinical management of critical limb ischaemia patients at the Leipzig Interventional Course (LINC; 30 January–2 February 2018, Leipzig, Germany). The platform is designed to provide immediate feedback on the quality of revascularisation and along the entire course of the patient’s recovery. It uses hydrogel sensors that are injected into the skin of the patient that measure the oxygen concentration in the tissue … read more
The use of topical analgesics in the management of diabetic neuropathy
Painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN) affects up to half of patients with diabetes and is a major cause of functional impairment and increased mortality. Its clinical manifestations include sensations such as burning, stabbing and tingling and/or loss of sensation, and it increases the risk for injuries and foot ulceration. Oral pharmacological therapy is the standard approach to management. It is effective in some patients, but its use is limited due to unfavourable side-effect profiles, limited response rates and drug interactions. Increasing evidence of the localized, non-systemic treatment approach of topical analgesics aims to overcome these obstacles and provide valuable, efficacious and safe management of PDN. This article reviews the rapidly expanding field of topical analgesia in managing PDN … read more
Clean vs. Sterile Dressing Techniques for Management of Chronic Wounds
This document originated in 2001 as a joint position statement from a collaborative effort of the Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nurses Society and the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology, Inc.1,2 Its purpose was to review the evidence about clean vs. sterile technique and present approaches for chronic wound care management. Then as now, areas of controversy exist due to a lack of agreement on the definitions of “clean” and “sterile” technique, lack of consensus as to when each is indicated in the management of chronic wounds, and lack of research to serve as a guide. Wound care practices are extremely variable and are frequently based on rituals and traditions as opposed to a scientific foundation … read more
Joint EPUAP & EWMA Pressure Ulcer prevention & patient safety
advocacy project
The European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (EPUAP) and EWMA are collaborating on a joint engagement in the PU prevention and patient safety agendas at the European level as well as at the national level in selected European countries.
Five articles by the joint EPUAP-EWMA initiative have now been published. The articles are available for download here:
The role of pressure ulcer prevention in the fight against antimicrobial resistance
EWMA & EPUAP added-value to OECD efforts
Diabetic Control & Pressure Ulcers: fighting fatal complications and
improving quality of life
Patient safety across Europe: the perspective of pressure ulcers.
The time to invest in patient safety and pressure ulcer prevention is now!
Patient safety has for some years been high on the European Commission health care agenda. At the EU level as well as at national levels of many European nations, considerable investments have been made by health care authorities to establish organisations and programmes addressing the patient safety agenda.
Looking at the patient safety agenda from a wound care perspective, the topic of Pressure Ulcer (PU) prevention has always been central due to the fact that most PU’s are preventable if the patient is managed correctly by health care staff … read more
‘Amputated limb every two hours’: Experts warn Aussies against health risk
For a health issue that has cost the Australian health care system $1.6 billion every year and has a mortality rate worse than many cancers, diabetic foot disease is one of the country’s least known major health problems … The condition typically develops from trauma caused by peripheral neuropathy or peripheral arterial disease, which is complicated by infection. Neuropathy is a nerve condition that can lead to pain, numbness and tingling and is one of the major factors in diabetic foot disease … read more
Effect of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide Solution on Bacterial
Load and Biofilm in Venous Leg Ulcers: A Randomized Controlled Trial
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB) solution as a wound cleanser on bacterial load and bacterial biofilm in venous leg ulcers … The target population was adults attending the dermatology outpatient clinic of the Clinical Hospital of the Federal University of Minas Gerais, Brazil. The sample comprised 44 patients with venous leg ulcers recruited over a 6-month period … read more
Liraglutide Lowers Risk for Amputation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and CV Risk
Liraglutide lowers risk for amputation: investigators find patients treated with GLP-1 drug had significantly lower number of amputations compared to placebo group.
The word may still be out on whether certain oral diabetes medications puts patients at risk for lower limb complications, but a new study has shown that liraglutide is not one of them. A post hoc review analysis of the LEADER trial published in Diabetes Care examined the effects of Liraglutide on rates of foot ulceration and amputation in patients at high risk for cardiovascular (CV) events.
Liraglutide, a GLP-1 agonist, is an injectable glucose-lowering medication used in patients with type 2 diabetes. GLP-1 agonists act by mimicking the effects of the hormone GLP-1, which increases insulin secretion and lowers glucagon release. This, in effect, causes increased satiety and slowed gastric emptying, with one of the main benefits of GLP-1 agonists being weight loss in patients with diabetes … read more
Advanced Wound Care Technologies to Manage Wound Infections
BOSTON, Sept. 26, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — Recently, research undertaken by the UK’s House of Commons library at the request of the UK’s Labour Party revealed that diabetic foot and toe amputations performed by the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) has risen by 26 percent. Between April 2010 and March 2013, minor amputations due to diabetes numbered 15,075. This has risen to 19,073 in the same 3-year period of 2014 – 2017. Though the Department of Health and Social Care acknowledge that the rate of minor amputations has increased, it is also important to note that they state that the number of major amputations (above the ankle) has decreased. Regardless, diabetic foot amputations are estimated to cost the NHS over £44 million just in the year 2016.
Patients typically arrive at the point of requiring a lower limb amputation due to tissue necrosis resulting from an infected diabetic foot ulcer (DFU). DFUs are hard to heal wounds that remain open for extended time. Thus, extra care is required in keeping the wound clean and in preventing infection. DFUs are formed in the first place due to ischemia and neuropathy, two side effects of poor blood glucose management.
Clearly, the best intervention is to prevent the formation of DFUs in the first place. This may begin in good management of blood glucose to prevent ischemia and neuropathy, though sensor technologies can also be used for the express purpose of preventing DFUs. Once the wound is formed, preventing and treating any wound infection is critical. However, there are many factors that healthcare providers have to contend with during the treatment of DFUs … read more
Early-stage company offering the novel drug ND-336 as a topical therapy
SalvePeds: An early-stage pharmaceutical company offering the novel drug ND-336 as a topical therapy for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. SalvePeds’ goal is to provide an effective, safe and convenient therapeutic treatment for DFUs to improve the quality of life for patients and ultimately decrease the number of ulcer related amputations. (University of Notre Dame) … from Inside Indiana Business
Following the Evidence for Total Contact Casting
as First-Line Treatment of DFUs in the Wound Clinic
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are a major concern in the outpatient wound clinic due to the growing diabetes epidemic, the significant morbidity and mortality associated with DFUs, and the economic burden on the healthcare system. Despite a well-established standard of care for DFUs, which includes effective offloading as a cornerstone, there are gaps in practice with regard to clinical implementation of appropriate offloading. This article will provide a discussion of the evidence supporting the use of offloading as a standard of care for DFUs with a focus on total contact casting (TCC). In addition, we will discuss barriers to using TCC in clinical practice followed by an example of how one heavily trafficked wound clinic located in Texas has successfully implemented TCC and has experienced a positive impact on wound healing rates as well as clinic efficiency … read more
Support Surfaces Do Not Replace the Need for Good Pressure Ulcer Care
Support surfaces alone neither prevent nor heal pressure ulcers. They are to be used as part of a total program of prevention and treatment. When pressure ulcers deteriorate or fail to heal, the professional should consider replacing the existing support surface with one that will improve pressure redistribution and microclimate (heat and moisture control) for the individual. Changing the support surface is only one of several strategies to consider. The individual and his or her pressure ulcer should be re-evaluated. Preventive interventions and local wound care should also be intensified as needed. A significant increase in risk status may also prompt such re-evaluation of the individual and the support surface … read more
Factors associated with acute and chronic wound complications
in patients with soft tissue sarcoma with long-term follow-up
In a cohort of patients treated for soft tissue sarcoma (STS) with modern radiotherapy (RT) and surgical techniques, experts assessed the rates of acute and chronic wound complications and related factors. They identified all adult nonmetastatic patients treated for STS at a single institution between 2006 and 2015 with a minimum 1-year follow-up. In these patients, the rate of acute wound complications was 22.1%. In STS patients, numerous factors linked to acute and chronic wound complications, including the timing of RT, tumor site, and reconstruction use, were found. Results demonstrated the probable correlation between development of acute wound complications with a higher risk of chronic wound complications … read more
Corstrata to Launch Next Gen Virtual Wound Clinic Powered by Citus Health
Corstrata, a provider of digital healthcare IT solutions and services for wound prevention and care management, announced today a partnership with Citus Health, a digital health solutions provider for the post-acute care industry, to power its next-generation virtual clinic. Corstrata will leverage Citus Health’s state-of-the-art patient and provider engagement platform to enable enhanced remote access to wound and ostomy care experts for wound and ostomy patients everywhere … Corstrata will utilize the Citus Health platform to serve its wound and ostomy customers, provider customers, and Diabetic Foot Ulcer Prevention members. Citus provides a versatile, leading-edge, patient and provider engagement architecture for enhanced care coordination and communication to improve clinical and financial outcomes. The Corstrata branded app powered by Citus Health will integrate key technologies, including wound image capture, video, patient engagement, and with the flexibility of the platform, streamline the capability to add third-party IoT data sources in the future … read more
Advanced Wound Care Technologies to Manage Wound Infections
BOSTON, Sept. 26, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — Recently, research undertaken by the UK’s House of Commons library at the request of the UK’s Labour Party revealed that diabetic foot and toe amputations performed by the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) has risen by 26 percent. Between April 2010 and March 2013, minor amputations due to diabetes numbered 15,075. This has risen to 19,073 in the same 3-year period of 2014 – 2017. Though the Department of Health and Social Care acknowledge that the rate of minor amputations has increased, it is also important to note that they state that the number of major amputations (above the ankle) has decreased. Regardless, diabetic foot amputations are estimated to cost the NHS over £44 million just in the year 2016 … read more
LeucoPatch helps heal diabetic foot ulcers faster
A new system that uses a multilayer patch made with a patient’s own leukocytes, platelets, and fibrin can speed the healing of diabetic foot ulcers, according to new findings … “The use of LeucoPatch is associated with significant enhancement of healing of hard-to-heal foot ulcers in people with diabetes,” Dr. Frances Game of Derby Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust in the UK and colleagues conclude in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology online September 19 report … read more
New study reveals potential therapeutic approach to enhance keratinocyte
Researchers have identified a new mechanism involving ginsenoside Rb1, which has the ability to stimulate keratinocyte migration and promote cutaneous wound healing. They report the results of a study showing that Rb1 enhances keratinocyte migration in an article published in Journal of Medicinal Food, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The researchers demonstrated that Rb1 significantly increases the production of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), which is a signaling factor in keratinocytes known to stimulate wound repair through greater keratinocyte migration … read more
Preventive Care: Reducing the Recurrence of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Comprehensive treatment of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) includes moist local or topical wound care, serial sharp debridement, treatment of infection, mechanical offloading, glycemic control, nutritional management, and overall chronic disease management. These facets of therapy are best addressed by an interdisciplinary approach.
If we understand the principles of healing, what can we do to prevent the pathologic process of DFUs? Instituting measures to prevent development of DFUs can decrease morbidity and mortality. There are several organizations with guidelines for prevention of DFU and subsequent complications including amputation, infection, and loss of independence. This article will review the highlights of some of the most recent guidelines for DFU prevention … read more
Healogics Joins the Epic App Orchard
JACKSONVILLE, Fla.–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Healogics Inc., the nation’s largest provider of advanced wound care services, today announced they have joined the App Orchard to begin working on an integration to improve interoperability within their nationwide network of Wound Care Centers®. Currently, this integration is set to deploy in the fall of 2019.
This integration will allow discrete data flow between systems with a goal to reduce errors for hospital compliance and audits, eliminate redundant double entry work for Wound Care Centers and foster better partnerships with hospital systems. Additionally, these updates will allow for integration with Healogics applications, and Epic creating a more streamlined user experience.
“This integration is a major step forward for Healogics’ hospital partners that are looking to use Epic in their Wound Care Center,” said Ty Smith, Chief Information Officer at Healogics. “This level of integration will bring the best of Healogics applications into the Epic ecosystem and supports our Centers with the best technology available. We are looking forward to all the ways in which these updates will improve the patient experience and save time for clinicians and physicians, all while increasing the quality and consistency of patient care.” … read more
MiMedx up 6% premarket on positive data on dHUC in diabetic foot ulcers
MiMedx Group (NASDAQ:MDXG) is up 6% premarket on light volume on the heels of the publication of a study evaluating its dehydrated human umbilical cord (dHUC) for the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers in the International Wound Journal … In the intent-to-treat group, 70% of patients receiving weekly dHUC allograft achieved complete healing by week 12 compared to 48% of those receiving standard-of-care (SOC) treatment for 12 weeks (p=0.0089) … read more
Decompression nerve surgery for diabetic neuropathy
a structured review of published clinical trials
MEDLINE, PubMed, and related registries were searched through December 2017 to identify randomized, quasi-randomized or observational trials that evaluated the efficacy of lower extremity DNS on pain relief (primary outcome) or other secondary outcomes. Observational studies were included, given investigators’ reluctance to use sham surgery controls. Outcome effect size was estimated, and a weighted average was calculated.
Results: Eight of 23 studies evaluated pain relief, including a double-blind randomized controlled trial (with a sham surgery leg), an unblinded trial with a nonsurgical control leg, and 6 observational studies. All reported substantial pain relief post-DNS with average effect sizes between two and five. Unexpectedly, the double-blind trial showed improvement in the sham leg comparable to the DNS leg … read more
Principles of Clean Dressing Technique Versus Asepsis
Having read a recent article on clean versus sterile dressing technique, commenting again on this issue seems highly appropriate. The conclusion of the paper essentially is that a clean technique for acute wound care does not affect the incidence of infection.1 There is insufficient evidence in the literature relating to chronic wound care. I particularly appreciated the comment that nurses need to decide which approach to have by using critical thinking skills. I was reminded of a visit to a patient to utilize a fancy new dressing that I had never used before … read more
NuVasive launches expanded biologics in US
NuVasive (NSDQ:NUVA) said today it launched three new products as part of its biologics portfolio, including its Traditional Bone Allograft, Amniotic Membrate DS and Propel DBM …The San Diego-based company’s Traditional Bone Allograft includes cancellous chips, demineralized cancellous chips, cortical cancellous chips and cancellous crushed, which the company claims the has osteoconductive properties intended to provide a scaffold for bone growth … The newly launched Amniotic Membrane DS is a dual-sided layer of human amniotic membrane intended to act as a biologic barrier to prevent adhesions and reduce scar tissue formation near adjacent muscle, nerve and fascia layer tissues … read more
Key Considerations With Dressing Selection In Wound Care
With the plethora of wound dressings available, how can you choose the right dressing for your patients? Assessing the merits and drawbacks of current and emerging dressings, these authors share their experience with multi-layer dressings, wound cleansers, dressings that facilitate wound debridement and others … In our wound care practice, we diagnose and treat various etiologies of lower extremity wounds including diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, pressure ulcers and other wounds. As there are hundreds of wound dressings and topical treatments available in the United States today … read more
Peripheral arterial disease and the diabetic foot
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a term used to describe atherosclerotic vessels in the periphery, mostly affecting the lower extremities. The blocked vessels impair blood and oxygen perfusion to the lower limbs and may lead to increased risk of ulceration, wounds and amputations. PAD is also associated with increased risk of coronary and cerebrovascular incidents. More than 50% of people living with PAD may not have any clinical symptoms, posing a challenge to diagnosis and management. This article will discuss the aetiology, presentation, risk factors, and management of PAD as related to the lower extremities … read more
Why Do Promising Wound Therapies Fail?
Is a histologically hostile environment causing promising treatments for chronic wounds to fail? My coauthor and I tackle this question in a recent review for Nature Reviews Endocrinology.
As we say in the review, “As with so many other areas in medicine, the field of tissue repair and wound healing is littered with early-stage promise in preclinical models followed by late-stage disappointment in human trials.”1 If we understand that the wound environment is histologically hostile, many of the types of treatments we have endeavored to use in this area come into question … read more
UK nurses carry out 180 wound dressing changes a year
on each chronic wound patient
- Chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers and venous leg ulcers, take more than 8 months to heal for the average patient and some will be affected for decades1
- Despite advancements in wound care, patients report dressings are changed on average 5 times a week1
- This poses a huge burden on UK nurses and impacts the quality of life for nearly all (90%) of patients1
Higher proportion of limb salvage and lower amputation rates
The impact of a wound centre on a vascular surgery practice
The opening of an outpatient wound centre has been associated with a significant increase in peripheral vascular practice and a significant decrease in amputation rate. Venita Chandra and colleagues Alyssa M Flores, Matthew W Mell and Ronald L Dalman (Stanford University, Stanford, USA) believe that such centres result in synergistic systems that promote more aggressive and effective limb salvage strategies. Chandra presented the findings of a recent study analysing the clinical impact of a wound care centre on a vascular surgery practice, at the Society for Vascular Surgery’s Vascular Annual Meeting (VAM; 20–23 June, Boston, USA) … read more
Reduction of 50% in Diabetic Foot Ulcers With Stem Cells
MUNICH — Local injection of mesenchymal stem cells derived from autologous bone marrow shows promise in healing recalcitrant neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers, a novel study from Egypt shows.
Presenting the results at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2016 Annual Meeting, Ahmed Albehairy, MD, from Mansoura University, Egypt, said: “In patients who received the mesenchymal stem cells, ulcer reduction was found to be significantly higher compared with patients on conventional treatment after both 6 weeks and 12 weeks of follow-up. This is despite the fact that initial ulcer size was larger in the stem-cell–treated group.”
After 6 weeks, median ulcer reductions were 49.9% and 7.67% (P = .001) in stem-cell–treated and control groups, respectively, and after 12 weeks, median ulcer reductions were 68.24% and 5.27% (P = .0001). Complete healing was achieved in one case in the mesenchymal stem cell–treated group.
“The healing mechanism may be due to the pure effect of injected mesenchymal stem cells … read more
The Rise Of The Bio-Inks: 3D Skin Printing
May Solve Problems For Patients With Chronic Wounds
Bio-inks are becoming an increasingly common feature of next-generation medicine. These inks consist of living cells from donor tissues that may be suspended in bio-compatible solutions or polymers. The bio-inks are laid down or deposited using techniques much like medical-grade 3D printing … A recent project that incorporates bio-inks is intended to address deep skin wounds and the issues that affect their treatment and ultimate healing. The scientists behind it hope that their innovative solution can improve outcomes for these patients while overcoming the problems they face as a result of current medical practice … read more
An Observational, Prospective Cohort Pilot Study to Compare the Use of …
Subepidermal Moisture Measurements Versus Ultrasound and Visual Skin Assessments for Early Detection of Pressure Injury
Pressure ulcers (PUs) are detected by visual skin assessment (VSA). Evidence suggests ultrasound (US) and subepidermal moisture (SEM) scanner technology can measure tissue damage before it is visible … A pilot study was conducted to evaluate consistency between SEM and US examinations of suspected deep tissue injury (sDTI) … Using an observational, prospective cohort study design, patients >55 years of age were recruited. VSA, SEM, and US assessments were performed daily for a minimum of 3 and maximum of 10 consecutive days following enrollment. US results were considered indicative of sDTI if hypoechoic lesions were present. SEM readings were considered abnormal when ∆ ≥0.6 was noted for at least 2 consecutive days. Boolean analysis was utilized to systematically determine consistency between US and SEM where sDTI was the clinical judgment … read more
Effective Wound Bed Preparation Using Maggot Debridement Therapy
for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia
An important factor in wound healing is adequate blood flow; thus patients with critical limb ischemia (CLI) and complex wounds are poor healers. Primary treatment for CLI is revascularization. Wound healing can be prolonged as a consequence of cyclical protease production by necrotic tissue during the inflammatory phase of healing. Debridement of necrotic tissue is therefore necessary to reduce inflammation and progress the healing cycle, as well as to promote epithelialization and reduce risk of infection. Conventional debridement therapy can be difficult in patients with CLI because of limitations in visualizing wound margins and time effectiveness. Maggot debridement therapy (MDT) is a traditional debridement therapy using live, sterilized fly larvae. This study investigated MDT in patients with CLI after midfoot amputation following revascularization by endovascular therapy. The outcomes of wound bed preparation were compared with the outcomes in patients receiving conventional therapy … read more
LeucoPatch system for the management of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers in
the UK, Denmark, and Sweden: an observer-masked, randomised controlled trial
The LeucoPatch device uses bedside centrifugation without additional reagents to generate a disc comprising autologous leucocytes, platelets, and fibrin, which is applied to the surface of the wound. We aimed to test the effectiveness of LeucoPatch on the healing of hard-to-heal foot ulcers in people with diabetes … Methods … This was a multicentre, international, observer-masked, randomised controlled trial of people with diabetes and a hard-to-heal foot ulcer done in 32 specialist diabetic foot clinics in three countries (UK, Denmark, and Sweden). After a 4-week run-in period, those with a reduction in ulcer area of less than 50% were randomly allocated … read more
R&D Remains the “Heartbeat” of 3M
While 3M is 116 years old, the company continues to churn out new products like a young startup. Research and development remains the heartbeat of 3M with the company spending $1.9 billion or 6% of sales in 2017 on research and development to drive organic growth and new products … Top priorities for growth today include automotive electrification, advanced wound care, connected safety, data centers, structural adhesives, filtration, air quality and population health … read more
OnCourse Learning to be acquired for reported $500 million
Brookfield-based professional training webinar provider OnCourse Learning is set to be acquired by German company Bertelsmann for a reported $500 million. The transaction is expected to close this fall, pending regulatory approval … OnCourse was sold by New York private equity firm CIP Capital, which acquired the company in 2014 from Cleveland private equity firm The Riverside Co. The transaction was described by Bertelsmann as “in the mid-nine-digit euro range.” Reuters pegged the deal at around $500 million … The company, which was founded in 2007, has grown steadily via acquisition. In January, it announced the acquisition of Lake Geneva-based Wound Care Education Institute Inc., … read more
3D Printing Advances are Changing Medicine and Military Safety
3D–printed objects are no longer a novelty and are paving the way for incredible scientific innovation. For example, a large 3D–printed engine part was successfully tested and could be used in the next generation SLS rocket that will send humans to the moon and Mars, NASA reported … The road to recovery for any individual with deep skin wounds, which affect all three layers of the skin, can be as painful and traumatic as the incident itself … Researchers at the University of Toronto have developed a handheld 3D printer filled with “bio ink” — essentially an ink cartridge containing biological materials. The bio ink contains strips of biomaterial that include the proteins collagen and fibrin, which are used to promote wound healing … read more
Wounds Asia: Current issue: Vol 1, No 2
- Wound care management in Indonesia: issues and challenges in diabetic foot ulceration
There are 415 million people aged 20–79 years with diabetes worldwide, almost 153 million of them live in the Western Pacific region (Ogurtsova et al, 2017). The number of people with diabetes is predicted to rise to 642 million worldwide by 2040 (Ogurtsova et al, 2017). Indonesia has approximately 258 million citizens, making it the world’s fourth most populated country. It is one of 21 countries and territories in the International Diabetes Federation Western Pacific region. According to the International Diabetes Federation (2017), about 10.3 million Indonesians have diabetes - Optimising quality of life for people with non-healing wounds
Some wounds persist for months or years (Krasner et al, 2014). Non-healing wounds may be a result of host factors, such as inadequate vasculature, medications that interfere with the healing process, immunocompromised status or critically-ill status with non-modifiable risk factors (terminal disease, end-stage organ failure and other life-threatening health conditions). Among patients who are dying, receiving hospice or palliative care, non-healing or palliative wounds can be associated with complications - Reconstruction of a soft tissue defect of the big toe by pedicled perforator flap
Treatment of soft tissue defect on the distal of the big toe is challenging due to the lack of reliable options that can be used to create a local flap to cover the injured area. Following injury, soft tissue defects expose the structures, joints, tendons and bone. Even a small defect will become problematic if it is not managed appropriately - Natrox® — Let the topical oxygen flow for healing complex wounds
The presence of a wound increases the body’s requirement for oxygen by 20% for a patient with a clean wound and by 50% for an infected wound (Dernling, 2009). Oxygen is critical to many of the processes required in wound healing including the production of energy to fuel cell function and metabolism, angiogenesis, collagen synthesis and cross-linking
AmpliPhi receives positive feedback from FDA for its …
AB-PA01 product targeting P.aeruginosa infections
AmpliPhi Biosciences Corporation, a clinical-stage biotechnology company focused on precisely targeted bacteriophage therapeutics for antibiotic-resistant infections, today announced that the company has received positive feedback, via written response, from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regarding its development plans for AB-PA01, without the need for a Type B Pre-IND meeting … “We are delighted with the FDA’s response to our development plans for AB-PA01, AmpliPhi’s bacteriophage product candidate targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, and the FDA’s concurrence on the proposed design of two randomized controlled clinical trials, in hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia and P. aeruginosabacteremia,” said Paul C. Grint, M.D., CEO … read more
Beverly Hospital Hosts Amputation Prevention Summit
Beverly Hospital will be hosting its first Amputation Prevention Summit on Saturday, September 29, 2018 on the hospital campus at 309 West Beverly Boulevard, Montebello, California, drawing clinicians from the greater Los Angeles area.
This educational event will highlight the urgent nature of the diabetes epidemic— diabetes being among one of the top ten leading causes of death in California and the leading cause of non-traumatic lower extremity amputation. Guest speakers will share important data, current trends in limb salvage and best-practices in the battle against diabetes-related complications. They will also discuss ways healthcare professionals can improve their practices in order to reduce lower extremity amputations.
A person with diabetes has a risk of leg amputation that is 15-40 times greater than a person without diabetes. Within two to four years of unilateral limb loss, one-third of all patients lose the other leg. Only about 50% survive more than five years following a leg amputation. With the future incidence of diabetes projected to rise to 550 million people worldwide by the year 2030, limb salvage is becoming a viable alternative, often producing better outcomes than amputation … read more
Negative pressure wound therapy in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers
may be mediated through differential gene expression
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) has been successfully used as a treatment for diabetic foot ulceration (DFU). Its mechanism of action on the molecular level, however, is not fully understood. We assessed the effect of NPWT on gene expression in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and DFU … The final cohort encompassed 21 patients treated with NPWT and 8 with standard therapy. The groups were similar in terms of age (69.0 versus 67.5 years) and duration of T2DM (14.5 versus 14.4 years). We identified four genes differentially expressed between the two study arms post-treatment, but not pre-treatment: GFRA2 (GDNF family receptor alpha-2), C1QBP (complement C1q binding protein), RAB35 (member of RAS oncogene family) and SYNJ1 (synaptic inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase 1) … read more
One Call Announces New Wound Resource Program with Broadspire®
One Call, the nation’s leading provider of workers’ compensation care management services, and Broadspire®, a subsidiary of Crawford & Company® and a leading global third-party administrator, today announced a partnership to develop a customized patient-centric wound resource program to improve wound healing of injured workers.
The primary goal of wound care is to provide optimal conditions for the natural reparative processes to take place on their own. One Call’s new wound resource program, in partnership with Broadspire, utilizes evidence-based protocols to proactively identify injured workers who either have a non-healing wound or may be at risk for developing wounds.
Wounds that have continued for more than 30 days are 36-69 percent less likely to heal. Chronic wounds affect 5.7 million people in the U.S. at an annual cost of $20 billion.[1] Pressure ulcers are among the most common chronic wounds. According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), pressure ulcers account for more than 17,000 lawsuits annually and are the second most common claim after wrongful death. Sadly, about 60,000 patients die as a direct result of a pressure ulcer each year.
“Pressure ulcers and other chronic wounds have an enormously detrimental impact on function and overall healing,” said Dr. Marcos Iglesias, chief medical officer at Broadspire … read more
Osiris Therapeutics, Inc. Announces GrafixPL PRIME™
Launches October 1, 2018
COLUMBIA, Md., Sept. 17, 2018 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Osiris Therapeutics, Inc.(NASDAQ: OSIR), a regenerative medicine company focused on developing and marketing products for wound care, orthopedics, and sports medicine, announces that GrafixPL PRIME™, a human placental membrane that can be stored at ambient temperatures, launches for sale on October 1, 2018. The structural matrix, growth factors, and cell viability of GrafixPL PRIME is equivalent to those of Grafix®, a cryopreserved placental membrane, but without the constraints of ultra-low temperature storage.
GrafixPL PRIME is processed using Prestige LyotechnologySM, which is Osiris’s preservation technique for ambient storage of living tissues. GrafixPL PRIME is flexible and conforming and designed as a wound cover/barrier for application directly to hard-to-treat acute and chronic wounds, including but not limited to diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers and thermal burns.
Jason Keefer, Interim President and CEO said: “I am pleased to announce that our ambient temperature stable GrafixPL PRIME product will be available in all settings of care, in addition to our cryopreserved Grafix products … read more
The role of bacteria and biofilms in non-healing wounds
Broadcast times available: 8:00 AM (UK), 11:00 AM (UK), 15:00 PM (UK)
Evidence has proven the positive effects of topical oxygen therapy on chronic, hard-to-heal wounds. It is becoming widely accepted that hard-to-heal wounds contain biofilm and that the presence of biofilm delays and/or prevents healing. This webcast will inform practitioners about the issue of biofilm and how it affects wound chronicity, as well as how topical oxygen therapy may help to kickstart stalled healing. The NATROX study has shown that topical oxygen therapy has a positive effect on biofilm in chronic wounds, and this webcast will provide practical guidance so this can be applied in practice to improve healing outcomes ….. read more
Solsys Medical’s TheraSkin Regenerative Wound Healing
Product Chosen to be a Part of Healogics New iSupply(SM) Program
NEWPORT NEWS, Va., Sept. 10, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — Solsys Medical, LLC (“Solsys”) (formerly known and doing business as Soluble Systems, LLC) (“Solsys Medical”), which markets TheraSkin®, a cellular and tissue-based product for regenerative wound healing, announced today that it has partnered with Healogics, the nations largest provider of advanced chronic wound care services, to be a part of the new Healogics iSupply program, offering TheraSkin to Healogics facilities. Through the partnership with Healogics, Solsys furthers its mission to improve quality outcomes while reducing the total cost of care. TheraSkin is a living human split-thickness skin allograft that is cryopreserved to preserve living cells and growth factors while maintaining a mature native human dermal architecture. The versatility in applications and sizes of TheraSkin reduces product waste and helps to drive operational efficiencies in the wound care center to better manage total cost of care and quality outcomes related to wound care.
“We are very excited to be working with Healogics and have TheraSkin included in its iSupply initiative,” stated Allan Staley, CEO of Solsys Medical. “The iSupply program enables Healogics’ hospital partners improved access to TheraSkin in order to improve wound healing outcomes at a lower cost.” … read more
Supporting Closure: Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are arguably among the most difficult types of wounds to manage; the etiology of these wounds poses some of the greatest clinical challenges for healing, considering the multifaceted nature of diabetes mellitus (DM). Multiple patient-related factors must be addressed and controlled through faithful adherence to the prescribed plan of care, which is developed by both the patient and clinicians to ensure success … Treatment of DFUs requires multidisciplinary provider involvement (podiatry, vascular, infectious disease, internal medicine or family practice, endocrinology, cardiology, nephrology, and physical therapy). The standard of care for patients with DFUs includes medical management of chronic disease, including nutrition and glucose control, routine wound assessments with ulcer grading and risk stratification, topical wound management with attention to serial debridements and moist wound healing … read more
The Diabetic Foot in Remission: Strategies to Make Prevention Pay
Because neuroischemic complications are associated with a high rate of recurrence, this presentation proposes a slight shift in how health care providers counsel and communicate risk to their patients. If the epidemiology of this problem is comparable with that of cancer, and recurrences are common, then perhaps language commensurate with such risks should follow.
After initial healing of an index wound, patients are referred to not as being cured but rather as being “in remission.” This concept is easy for the patient and the rest of the team to understand, and it powerfully connotes the necessity for frequent follow-up and rapid intervention for inevitable minor and sometimes major complications.
This program will review tried-and-true as well as up-to-the-minute advances in biologics, consumer electronics, mechanics, medicine, and surgery that are “pushing the envelope” in extending ulcer-free, hospital-free, and activity-rich days in efforts to make prevention pay.
Registrants will learn how to:
- Identify risk factors for ulceration
- Identify risk factors for amputation
- Understand the impact of diabetes on the health care system
- Understand the impact of diabetic foot complications on the health care system
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Classification and Assessment
Classification of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Historically, classification and subsequent treatment of DFUs do not adequately include management of concomitant ischemia of peripheral arterial disease (PAD). The Wagner Diabetic Foot Ulcer Grade Classification System, which has been in use since its inception in the 1970s, did not have the capacity to describe ischemic components of DFU. The University of Texas Diabetic Foot Ulcer Classification System, PEDIS (perfusion, extent, depth, infection, and sensation), WIfI Threatened Limb (Wound/Ischemia/Foot Infection), and SINBAD (Site, Ischemia, Neuropathy, Bacterial infection, And Depth) are classification systems that utilize degrees of ischemia as a contributing factor.
At present, subclassification of DFUs can be divided into three categories: neuropathic, ischemic, and neuroischemic. The most prevalent of the three is the neuroischemic DFU, which comprises approximately 50% of such ulcerations. Organization and reproducibility of the assessment process are crucial to success. Workups should include identification of intrinsic and extrinsic factors, both modifiable and non-modifiable. We will review appropriate assessments by using a typical history and physical examination format … read more
Scientists Trial An Unexpected Source To Help Heal Hard-To-Treat Injuries
Scientists have revealed how proteins in menstrual blood can be used to stimulate skin repair, including wounds that otherwise recover poorly. Today, tens of billions of dollars are spent on chronic skin injuries, and increasing rates of diabetes are adding to this demand, so utilizing the womb’s incredible ability to repair itself quickly could be the way forward … “The lining of the uterus, the endometrium, is an amazing tissue which undergoes ‘self-destruction’ each month at menstruation, followed by repair and regeneration of the tissue in preparation for pregnancy. This occurs, on average, 450 times in each woman’s reproductive life,” said Dr Jemma Evans of Melbourne’s Hudson Institute of Medical Research in a statement … read more
Treating Diabetes with GLP-1 Reduces Heart Disease, Fewer Foot Ulcers
Two analyses from the LEADER Trial show reduced risks of deaths and better outcomes in both heart health and diabetes-related foot ulcers and associated complications in patients with type 2 diabetes who are at increased risk for cardiovascular disease … GLP-1 Proves Effective in Lessening Risks of 2 Common Diabetes-Related Risks … Patients with type 2 diabetes who were at heightened risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and received liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1) saw a reduction in CVD events and cardiovascular death … read more
3Minute Exam + Offloading Algorithm
Wound Care Weekly Creative Services
We have a full creative / marketing department that offers everything from Animation to Web. Our digital marketing services actually pay for themselves …. guaranteed.
- Web Design
- Digital Marketing
- Brochure Design and Printing
- Illustration and Animation
- Forms and Checks
- Social Media
Call (336) 645-5121 or message us today to see how we can assist your practice.
Car crashes and chronic wounds
The health epidemic no one is talking about
Chronic wounds impact the lives of millions of Americans, yet the stories of those suffering are rarely told. As a result, chronic wounds have turned into a silent epidemic that remains largely invisible to the general public. Twenty-five years ago, Kevin Fontenot was one of those people, living his life generally unaware of this horrible condition, which is often caused by other diseases such as renal failure, diabetes, circulatory problems or malnutrition. That is, until he himself fell victim to it … read more
Natural product-based nanomedicines for wound healing purposes:
therapeutic targets and drug delivery systems
Wound healing process is an intricate sequence of well-orchestrated biochemical and cellular phenomena to restore the integrity of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Several plant extracts and their phytoconstituents are known as a promising alternative for wound healing agents due to the presence of diverse active components, ease of access, and their limited side effects. The development of nanotechnological methods can help to improve the efficacy of different therapeutics as well as herbal-based products. Here, we present a review of the efficacy of the plant based-nanomaterials in the management of wounds and discuss the involved therapeutic targets. For this purpose, a profound search has been conducted on in vitro, in vivo, and/or clinical evidences evaluating the efficacy and pharmacological mechanisms of natural product-based nanostructures on different types of wounds … read more
Using AutoCAD software to measure venous leg ulcers:
a reproducibility assessment study
To assess the reproducibility of using AutoCAD software to measure the area of venous leg ulcers (VLUs) … Data from patients with VLUs were collected between March and July 2015, using data collection forms and photographing the different ulcers. A researcher and five nurses collected the data. The wounds were measured using AutoCAD software. Data were analysed using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) and Bland-Altman analysis … read more (login required)
US military explores microbiology of combat wounds
To help improve the care of troops injured in combat, the United States military has been exploring the complex microbiology of combat wounds … The goal of the initiative “is to expand the understanding of the complex microbiology inherent within combat-related extremity wounds,” according to Katrin Mende, PhD … Biofilm formation in 376 Enterococcus wound isolates was found to be generally weak — 8.8% in the presence of human plasma and 1.9% in the absence of human plasma, Mende and colleagues reported … read more
Electrical Stimulation for Pressure Injuries: A Health Technology Assessment
Pressure injuries (bedsores) are common and reduce quality of life. They are also costly and difficult to treat. This health technology assessment evaluates the effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, budget impact, and lived experience of adding electrical stimulation to standard wound care for pressure injuries … We conducted a systematic search for studies published to December 7, 2016, limited to randomized and non–randomized controlled trials examining the effectiveness of electrical stimulation plus standard wound care versus standard wound care alone for patients with pressure injuries. We assessed the quality of evidence through Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE). In addition, we conducted an economic literature review and a budget impact analysis to assess the cost-effectiveness and affordability of electrical stimulation for treatment of pressure ulcers in Ontario. Given uncertainties in clinical evidence and resource use, we did not conduct … read more
Transitioning wound care patients to post-acute care
When discharging patients from acute care facilities, consider cognitive and functional status; the home environment; family or caregiver support; access to services, medications, and transportation; and follow-up care.
Depending on the patient’s situation, the three goals of wound care are healing, maintenance, and comfort.
After discharge from an acute-care facility, patient medication management, diet, and lifestyle can help support wound healing … read more
Greater concentration on wound care will save NHS millions
argues prof of vascular surgery
Former Head of Vascular Surgery at Bradford’s Royal Infirmary Professor Peter Vowden gave the opening address at the 3rd International Skin Integrity and Tissue Viability Conference which explored advances in and the management of all aspects wound care.
IT is estimated that annually the NHS treats over two million wounds at a cost of £5.3 billion and with tougher financial constraints being announced every year, there needs to be ongoing research to ensure the lack of finances doesn’t affect the quality of wound care available.
This was the topic of the opening lecture at the 3rd International Skin Integrity and Tissue Viability Conference hosted by the University of Huddersfield’s Institute of Skin Integrity and Infection Prevention (ISIaIP), in conjunction with the Journal of Wound Care … read more
Scientists Create a Surgical Sealant for Closing Major Wounds
Closing a wound usually requires a needle going through your skin, or staples. Just imagine having to sit there watching staples sticking into your flesh, not a pretty sight, right? Well, researchers have found an easier way to get things done.
One of the primary reasons the ways as mentioned above to close wounds are not perfect is the fact that they do not completely seal the entrance area. OK then, maybe doctors should use sealants to get the job done, but you know what? None of the ones available today meet the requirements of being a useful surgical tool … read more
BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE Prevention and
Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
The best practice recommendation articles are special publications of Wound Care Canada. Together they form the Foundations of Best Practice for Skin and Wound Management, an online resource available for free download from the Wounds Canada website (woundscanada.ca). These 2017 updates build on the work of previous author teams and incorporate the latest research and expert opinion. We would like to thank everyone involved in the production of past and present versions of these articles for their hard work, diligence and rigour in researching, writing and producing these valuable resources … read more
Hemoglobin A1c levels not tied to wound outcomes
There does not appear to be a clinically meaningful association between baseline or prospective hemoglobin A1c (A1C) and wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), according to a study published online April 16 in Diabetes Care.
The researchers found that baseline A1C was not associated with wound healing in univariate or in fully adjusted models. In the participants with baseline A1C <7.5 percent (hazard ratio [HR], 2.07; 95 percent CI, 1.08 to 4.00), no association with wound healing was seen with the mean A1C change from baseline. A nadir A1C change of 0.09 to 2.4 (tertile 3) was positively associated with long-term wound healing versus those with a nadir A1C … read more
Nexodyn Wound Care Solution Launched in the U.S.
Angelini and APR Applied Pharma Research strengthen their partnership in wound care with the launch of Nexodyn in the USA.
The new Nexodyn AOS wound care solution, cleared for sale by the FDA, is now starting to be available in the USA, promoted and commercialized by the Italian pharmaceutical company Angelini, as a result of an exclusive partnership with the Swiss company APR Applied Pharma Research, the owner and developer of the proprietary, patented technology TEHCLO, for the production of acidic super-oxidizing solutions.
Nexodyn helps cleanse and moisten the wound environment by removing dirt, debris and foreign material by flushing across the wound. Nexodyn is intended for use, under the supervision of healthcare … read more
Researchers invent ‘smart’ thread that collects diagnostic data
when sutured into tissue
For the first time, researchers led by Tufts University engineers have integrated nano-scale sensors, electronics and microfluidics into threads – ranging from simple cotton to sophisticated synthetics – that can be sutured through multiple layers of tissue to gather diagnostic data wirelessly in real time, according to a paper published online July 18 in Microsystems & Nanoengineering. The research suggests that the thread-based diagnostic platform could be an effective substrate for a new generation of implantable diagnostic devices and smart wearable systems … read more
International Conference on Wound Care, Tissue Repair and Regenerative Medicine
With Immense pleasure, Wound Care 2018 along with the Organizing Committee Members invites all the participants from all across the globe to attend “International Conference on Wound Care, Tissue Repair and Regenerative Medicine” which is slated on October 29-30, 2018 at Amsterdam, Netherlands with the theme Advanced wound healing techniques for the cure and care of wounded patients. This year Wound Care Conferences anticipated as two days interactive, stimulating discussion with 10+ keynote lectures, 50+ plenary lectures, 10+ Young Research Forum Lectures, 20 + Poster Sessions. Besides, there will be 3+ workshops and 2+ Symposiums. We also expect to provide technical demonstrations and numerous opportunities for informal networking.
Mission, Vision and Values:
Wound Care conferences mission is to provide the exclusive research topics where all the participants can be up to date with the Latest developments in the wound care. Conference on Wound Care ultimate vision is to be the Premier and Exclusive healthcare conference in the worldwide regions. The values of Wound Care 2018 are Innovation, Quality, Integrity, Knowledge and Patient care.
Why Amsterdam?
Amsterdam is the capital of the Netherlands. These days the city has a population of just over 790.000 inhabitants and is the largest city in the country. Amsterdam is located in the province ‘Noord-Holland’, situated in the west. It is one of the most popular destinations in Europe, receiving more than 4.5 million tourists annually … read more
A new platform for gaining insight and knowledge in managing wounds
Wounds can cover diabetic foot ulcers, pressure injury, vascular ulcers or wounds, immunopathic wounds and traumatic wounds. Chronic, hard-to-heal wounds also have an adverse effect on health-related quality of life. Wounds are a global problem, with increasing incidence due in part to the increase in diabetes mellitus. In Asia, there are more than 4 billion people, and this is where diabetes and its complications, namely diabetic foot, are increasing at an alarming rate … read more
Moldable Hyaluronan Hydrogel Enabled by Dynamic
Metal–Bisphosphonate Coordination Chemistry for Wound Healing
Biomaterial‐based regenerative approaches would allow for cost‐effective off‐the‐shelf solution for the treatment of wounds. Hyaluronan (HA)‐based hydrogel is one attractive biomaterial candidate because it is involved in natural healing processes, including inflammation, granulation, and reepithelialization. Herein, dynamic metal–ligand coordination bonds are used to fabricate moldable supramolecular HA hydrogels with self‐healing properties. To achieve reversible crosslinking of HA chains, the biopolymer is modified with pendant bisphosphonate (BP) ligands using carbodiimide coupling and chemoselective “click” reactions. Hydrogel is formed immediately after simple addition of silver (Ag+) ions to the solution of HA containing BP groups (HA‐BP). Compared with previous HA‐based wound healing hydrogels, the HA‐BP·Ag+ hydrogel is highly suitable … read more
Oxygen therapies for wound healing: EWMA findings and recommendations
For wounds to heal, it is essential that macro- and microcirculation is restored in the surrounding tissue (Niinikoski et al, 1991; Gottrup, 2004a). One of the most urgent requirements is oxygen, as it is critically important for the reconstruction of new vessels and connective tissue, and also enables resistance to infection … View PDF
Diabetes causes more than 120 foot and toe amputations a WEEK in England
More than 120 foot and toe amputations are carried out every week in England as a result of diabetes.
Shocking figures reveal the number of amputations linked to the disease have risen by over a quarter since 2013.
Type 2 diabetes’ prevalence has more than doubled over the past decade due to rising rates of obesity, inactivity and unhealthy eating.
The disease can lead to amputations if it causes nerve damage that lead to infected wounds that do not heal. These infections can then spread to a person’s bones and even result in gangrene … read more
Windsor’s Scapa to expand wound care footprint with acquisition
Windsor skin care products provider Scapa Healthcare said Thursday it has agreed to acquire an England-based maker of wound care products.
Scapa said acquiring Systagenix, and its 335,000-square-foot manufacturing facility, will “significantly” add to the Windsor company’s wound care footprint. Financial terms were not disclosed for the deal expected to be completed in October …. read more
Methodological considerations of investigating adherence
to using offloading devices among people with diabetes
Foot ulcers are a diabetic complication associated with significant morbidity, mortality, and amputation risk. Offloading devices prevent and heal foot ulcers, but adherence to using these devices is low. The reasons for nonadherence are unclear, and study results are difficult to compare due to methodological heterogeneity. This paper explores aspects of investigating adherence to using offloading devices among people with diabetes and provides recommendations for future studies, focusing on study designs, definitions of adherence, measurement methods, and conceptual frameworks. Most studies use a cross-sectional observational study design, limiting the potential to establish the temporal sequence between predictors and adherence, rule out confounding factors, and establish causality. Studies defining adherence as the length of time the device is worn have often used self-report to measure adherence, which may be unreliable. Studies using activity monitors to … read more
SMARTPORE Technology Made Easy
Download:
Cell reprogramming converts open wounds into healthy skin
The work focuses on a type of wound known as cutaneous ulcers, which are long-lasting lesions commonly found on sufferers of severe burns, bedsores and diabetes. These complex wounds run deep, through several layers of skin, which often means that they need to be treated surgically by taking grafts of existing skin and layering them over the top.
With expertise in plastic surgery, Salk scientists Izpisua Belmonte and Masakazu Kurita started to explore advanced regenerative techniques that could avoid the need for these procedures. Key to their mission were cells called basal keratinocytes, which resemble stem cells in that they serve as a precursor to various types of skin cells … read more
UIC to lead study of negative pressure wound
therapy in obese and diabetic patients
Surgical site infections are a significant complication that can prevent proper wound healing, require expensive treatment and may even lead to death in severe cases. Patients with higher body mass indices and with diabetes have an increased risk of developing incision infections.
With a $1.7 million, two-year grant from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, researchers in the University of Illinois at Chicago Epicenter for Prevention of Healthcare Associated Infections — one of six such centers funded by the CDC — will determine whether negative pressure wound therapy can help reduce the incidents of surgical site infections in obese and diabetic patients.
“Obese patients are more prone to develop surgical site infections because incisions tend to be larger and need to be deeper to allow surgeons to access the areas they need to work,” said Dr. Susan Bleasdale, associate professor of clinical medicine in the UIC College of Medicine and principal investigator on the grant … read more
Wilmington-based company creates smartphone app for wound care
A smartphone application called MyWoundDoctor can help people needing wound care get quick access and treatment from a certified healthcare provider.
Here’s a simple version of how it can work: You snap a picture of the wound, select where on your body it’s located, and share a few more details about your condition. Then 30 minutes to four hours later, you’ll receive a doctor’s assessment, treatment instructions, and personalized supplies mailed to your home in a few days.
“It’s sort of a self-serve model,” said Dan Heneghan, the CEO of MyWoundDoctor, LLC which is based in Wilmington.
MyWoundDoctor was founded in 2015 by Heneghan and Dr. Nick Sieveking, a board-certified plastic surgeon.
Heneghan said he was talking with Sieveking, who said his patients had been sending pictures of wounds to him through his smartphone … read more
Scientists find way of treating skin wounds without surgery
Researchers trick wound cells in mice into becoming healing surface skin cells
Scientists have discovered a new way of treating skin wounds in mice by tricking the cells in the wound into becoming healing surface skin cells.
The findings raise the prospect of being able to develop simple, non-surgical treatments for human wounds in the future.
Large skin wounds and ulcers are painful and occasionally life-threatening. When the surface of the skin is ruptured, epithelial cells, which make up the outer layer of the skin, migrate towards the wound in an effort to seal up the injury. But this healing process becomes more difficult in larger wounds and is impaired in older people, making the need for simple, effective treatments all the greater … read more
Chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol nanoscale liquid film-forming system
facilitates MRSA-infected wound healing by enhancing antibacterial and antibiofilm properties
Sha Yang,* Yun Yang,* Sixin Cui, Ziqi Feng, Yuzhi Du, Zhen Song, Yanan Tong, Liuyang Yang, Zelin Wang, Hao Zeng, Quanming Zou, Hongwu Sun
National Engineering Research Center of Immunological Products & Department of Microbiology and Biochemical Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, Third Military Medical University of Chinese PLA, Chongqing, 400038, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Introduction: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is one of the most predominant and fatal pathogens at wound infection sites. MRSA is difficult to treat because of its antibiotic resistance and ability to form biofilms at the wound site.
Methods: In this study, a novel nanoscale liquid film-forming system (LFFS) loaded with benzalkonium bromide was produced based on polyvinyl alcohol and chitosan.
Results: This LFFS showed a faster and more potent effect against MRSA252 than benzalkonium bromide aqueous solution both in vitro and in vivo. Additionally, the LFFS had a stronger ability to destroy biofilms (5 mg/mL) and inhibit their formation (1.33 µg/mL). The LFFS inflicted obvious damage to the structure and integrity of MRSA cell membranes and caused increases in the release of alkaline phosphate and lactate dehydrogenase in the relative electrical conductivity and in K+ and Mg2+ concentrations due to changes in the MRSA cell membrane permeability.
Conclusion: The novel LFFS is promising as an effective system for disinfectant delivery and for application in the treatment of MRSA wound infections.
Antibiotic Resistance Influence on Wound Care
Antibiotic resistance is one of the factors which causes delay in wound healing and a corresponding spike in medical and healthcare expenses.
The primary reason for the emergence of resistance is the inappropriate use of antimicrobials. To use antibiotics wisely, it is necessary to understand the principles of diagnosing wound infection, what organisms are likely to be responsible, and to what antimicrobial agents they respond.
This knowledge will help to ensure that antibiotics are used only when essential, and in a manner that does not cause more resistance to be generated … read more
Role of oxygen in wound healing (webcast)
13 Sep 2018
Broadcast times available: 8:30 AM (UK), 12:30 PM (UK), 16:30 PM (UK)
This Wounds International webcast focuses on the role of oxygen in wound healing and how topical oxygen therapy can improve oxygenation and, therefore, healing.
In the first presentation, Breda Cullen, Research and Development Director, UK, outlines the vital role that oxygen plays throughout the healing process and the impact that lack of oxygen (hypoxia) can have on the wound. Breda explores the factors that can cause compromised healing and how these can be addressed.
In the next presentation, Hanna Kaufman, Orthopaedic Surgeon, Israel, looks in depth at the clinical evidence and how this can be applied to practice. Hanna identifies the wounds that are suitable for topical oxygen therapy and shares tips for use in practice, drawing on clinical evidence and experience.
In the final presentation, Tjun Tang, Vascular Surgeon, Singapore, looks at the role of topical oxygen therapy in limb salvage.
Complex Wound Management: Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Background and Prevalence of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetes-related foot complications, including diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), are leading causes of non-traumatic lower extremity amputation. Of the approximately 420 million adults in the United States with diabetes mellitus, one fourth will develop at least one DFU. DFUs are preceded by a compendium of risk factors, including the presence of neuropathy, external trauma, infection, effects of ischemia from concomitant peripheral arterial disease, malnutrition, and poor hygiene or self-care, among others. In 80% of patients, DFU is a precursor to some degree of lower extremity amputation. And, for these patients who have undergone amputation, their risk for further amputation becomes double that of a patient without diabetes. The mortality rate following a diagnosis of diabetic foot ulceration is 5% in the first year. The five-year mortality rate is 50% and rises to 70% after amputation. Once healed, 40% of DFUs will recur within 12 months, nearly 70% at three years, and nearly 75% at five years … read more
Wound Management Tech spins CellerateRX collagen asset into JV with Catalyst Group
Wound Management Technologies (OTC:WNDM), operating under WNDM Medical, said last week it inked a deal to spin out its CellerateRX activated collagen assets into a new joint venture with The Catalyst Group.
Fort Worth, Texas-based Wound Management Tech will maintain a 50% ownership interest in the new joint venture, with The Catalyst Group taking up the other half, according to an SEC filing.
The newly formed Cellerate JV will maintain an exclusive sublicense to distribute the CellerateRX activated collagen adjuvant into the wound care markets in the US, Canada and Mexico, according to an SEC filing.
As part of the agreement, Wound Management Tech issued a 30-month promissory note to The Catalyst Group’s newly formed CellerateRX subsidiary in the princpal amount of $1.5 million with a 5% interest rate, convertible into shares of WNDM Medical at a conversion price of 9¢ per share, according to an SEC filing … read more
Turning wound cells into skin cells may help doctors heal ulcers
Sept. 6 (UPI) — Scientists have developed a technique to convert cells in open wounds into skin cells as an alternative to plastic surgery for treatment of large cutaneous ulcers.
The method involves reprogramming the cells into a stem-cell-like state for healing skin damage, including severe burns, bedsores or chronic diseases such as diabetes. The researchers at the Salk Institute also see this process as a way to counter the effects of aging and better understanding skin cancer.
Their findings were published Wednesday in the journal Nature.
“This knowledge might not only be useful for enhancing skin repair but could also serve to guide in vivo regenerative strategies in other human pathological situations, as well as during aging, in which tissue repair is impaired,” senior author Dr. Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte, a professor at he Salk Institute, said in a press release … read more
Telehealth technology utilized at Signature HealthCARE
GLASGOW — Residents at Signature HealthCARE of Glasgow can avoid trips to a doctor’s office or to the hospital for treatment of some medical conditions thanks to telehealth technology through YourDoc2U.
With telehealth technology, health care providers can talk face-to-face with residents, as well as the staff at the nursing facility via computer screen that sits atop a cart enabling it to be moved from location to location as needed.
Psychiatric and wound care evaluations are the medical services available to the nursing facility residents through telehealth technology.
“If we identify a need with any of our elders, we call the primary physician and ask for a consult with telewound,” said Kim Poynter, director of nursing at Signature HealthCare of Glasgow. “It’s all online. They have nurse practitioners and physicians available. If it’s an emergency situation, like if we have an elder who is having a crisis and needs psych services, we either call in or get online and make an appointment. They are available 24/7.” read more
Wound Care Patient Outcomes: Establishing Trust to
Improve Wound Healing Results
Last spring, I encountered that specific type of patient we sometimes meet, the one who has been through the chronic wound care revolving door so many times that he or she sets out on his or her own path and refuses any byways diverting from it.
Ms. A had stage 3 lymphedema after a left knee replacement opened the hidden trap door of undiagnosed lymphedema several years before her admission to our inpatient rehab facility. Her reason for admission was debility from urinary tract infection (UTI). Comorbidities of obesity, severe arthritis of the right knee, diabetes, and chronic lymphedema wounds on both legs were exacerbating factors making discharge home difficult from the acute hospital … read more
Intravenous Ketamine as an adjunct to procedural sedation
during burn wound care and dressing changes
Little has been published regarding intravenous (IV) ketamine for burn wound care in adult patients. Ketamine may serve as a safe alternative to provide conscious sedation and limit opioid administration to patients. The purpose of this study was to characterize IV ketamine use during burn wound care and establish its potential role as a safe adjunct to opioid and benzodiazepine medications. This is a retrospective review of adult patients admitted to a regional burn center who received IV ketamine for burn wound care. Patient demographics, medications, and ketamine-related side effects including hypertension and dysphoric reactions were recorded. Cardiopulmonary complications were also tracked. Thirty-six patients met inclusion criteria; 50 total cases were performed. The median patient age was 37 [IQR 28 – 55] years with a median burn size of 9.5 [IQR 4.0 – 52] %TBSA. The median ketamine dose administered was 1.2 [IQR 0.8 – 2.1] mg/kg. IV midazolam was administered in almost all cases (98%) at a median dose of 3.0 [IQR 2.0 – 5.0] mg. Opioids were administered in 13 of 50 cases (26%) at a median morphine … read more
The Diabetic Foot in Remission: Strategies to Make Prevention Pay
Tuesday, September 25, 2018
Because neuroischemic complications are associated with a high rate of recurrence, this presentation proposes a slight shift in how health care providers counsel and communicate risk to their patients. If the epidemiology of this problem is comparable with that of cancer, and recurrences are common, then perhaps language commensurate with such risks should follow.
After initial healing of an index wound, patients are referred to not as being cured but rather as being “in remission.” This concept is easy for the patient and the rest of the team to understand, and it powerfully connotes the necessity for frequent follow-up and rapid intervention for inevitable minor and sometimes major complications.
This program will review tried-and-true as well as up-to-the-minute advances in biologics, consumer electronics, mechanics, medicine, and surgery that are “pushing the envelope” in extending ulcer-free, hospital-free, and activity-rich days in efforts to make prevention pay.

DPM, MD, PhD
University of Southern California
Phase 2 Clinical Trial for Venous Leg Ulcers Nears Completion
BRISBANE, Australia, Sept. 05, 2018 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Factor Therapeutics Limited (ASX: FTT, the “Company”), an Australian biomedical company developing therapeutics for advanced wound care, is pleased to announce that the Company’s Phase 2 clinical trial VF00102, for the treatment of venous leg ulcers (VLU), is approaching the end of its treatment phase.
“Since finalising recruitment in July, the study has progressed to schedule and there are now only eight patients left to complete treatment. We expect the last patient to have their final treatment visit in the first week of October, a key milestone for the study as it then triggers a final round of data cleaning and quality checks before top-line results can be analysed in November,” said Dr Ros Wilson, CEO of Factor Therapeutics … read more
Know-how: Canadian hospital first to сure patients with virtual reality
Graydon Cuthbertson, a patient at Rockyview General Hospital, nearly lost his legs from compartment syndrome. Following multiple surgeries on his calf muscle, the 47-year old experienced pain ranging from discomfort to excruciating during wound-dressing changes.
Cuthbertson found that utilizing the VR technology helped him to escape his grim hospital surroundings and take in a calming virtual lakeside campground, a prehistoric landscape with dinosaurs, or a tranquil ocean to swim with dolphins.
“It’s a godsend,” he said. “Even with painkillers, the first time I had wound care after my surgery, the pain was excruciating. But with virtual reality, I got through the next treatment with flying colors. I was focused on what I was seeing and hearing, and not thinking at all about how painful it might be. All of the sudden, one-and-a-half hours go by and it’s all over. It was awesome.” read more
When and When Not to Use An SGLT-2
After reviewing evidence, a tool to evaluate benefit and risk has been developed showing when and when not to use an SGLT-2 inhibitor.
The management of type 2 diabetes has significantly diversified over recent years, producing a data-rich environment. SGLT2 inhibitors are a more recent agent that work by reabsorbing glucose in the kidney and cause an increase in glucose excretion in the urine. There have been misconceptions concerning the efficacy, safety and appropriate use of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetes management. In order to address these concerns, the UK created The Improving Diabetes Steering Committee, consisting of diabetes specialists.
The Improving Diabetes Steering Committee used multiple trials to developed a quick reference guide that aims to clarify common areas in type 2 diabetes management, with a focus on SGLT2 inhibitors … read more
Is it a Pressure Injury?
Factors to Consider When Determining Wound Etiology
As specialists in wound, continence and ostomy care, we are forever in a role of wearing many hats. We are educators to patients, staff, and providers… we are patient advocates and supporters of our bedside nurses… we are liaisons in many aspects of care and help to coordinate care and services for our patient population. We are often referred to as the specialist and are called upon when there is a patient with a wound, skin, ostomy, or continence concern. Our peers trust us, and it is important that we possess the knowledge and skills to share with others when determining etiology and treatment of wounds and skin issues.
Determining Wound Etiology
An issue we are often faced with as skin specialists is determining the etiology of wounds and skin concerns. When determining the etiology of wounds, it is important to look at the entire picture…and, when doing so, understand that many variables can and do make wounds better or worse, but there is usually an isolated variable that caused the wound.
Medical Device-Related Pressure Injuries
Some things to keep in mind: Pressure injuries are usually round, can appear punched out, may be partial- or full-thickness, may have slough or necrotic tissue, and are usually over a bony prominence. In terms of shape, pressure injuries related to devices usually take the shape of that device (think of a linear, fluid-filled blister from Foley catheter tubing on the thigh… a stage 2 medical device-related pressure injury, or a purple or discolored, non-blanchable area on the lip from an endotracheal tube… a mucosal pressure injury). Other devices that may be responsible for pressure injuries are prosthetic devices … read more
Cold Atmospheric Plasmas Used In Wound Healing and Cancer Treatment
Cold atmospheric plasmas (CAPs) are investigated for several medical applications; major research effort is devoted to the promotion of wound healing in of chronic wounds. These wounds, typically associated with diabetes, are a major health concern due to their high occurrence in the population, long healing time, and associated high costs. Cell culture studies and clinical trials show promising results towards wound reduction or closure using relatively short plasma treatment times between 45 s and 2 min. Another growing application of CAPs is the inactivation of cancer cells. While short treatment times associated with wound healing seem to induce no permanent damage, cancer treatments are performed at significantly higher plasma exposure times.
Due to the complex nature of both wound healing and cancer, investigating the effect of plasma is challenging. One system that seems highly interesting in both wound healing and cancer is the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and one of its ligands, the epidermal growth factor (EGF). EGFR is known to be involved in several cancer types, because an overproduction or overstimulation of EGFR has a severe impact on the cell cycle by inducing proliferation … read more
The skill behind skilled
So many times, we get questions about how to “skill” a resident. Is she skilled if she’s getting IVs? Is he skilled because he’s getting wound care? What about the resident whose trach is capped? Is she skilled? When the rehab patient reaches the almighty “plateau”, and isn’t getting better, is he still skilled?
We need to remember what the S-word means (no, not that one.) “Skilled” in our arena is defined by the services that we are delivering to the client, not by what the client is or isn’t doing … read more
Higher proportion of limb salvage and lower amputation rates
The impact of a wound centre on a vascular surgery practice
The opening of an outpatient wound centre has been associated with a significant increase in peripheral vascular practice and a significant decrease in amputation rate. Venita Chandra and colleagues Alyssa M Flores, Matthew W Mell and Ronald L Dalman (Stanford University, Stanford, USA) believe that such centres result in synergistic systems that promote more aggressive and effective limb salvage strategies. Chandra presented the findings of a recent study analysing the clinical impact of a wound care centre on a vascular surgery practice, at the Society for Vascular Surgery’s Vascular Annual Meeting (VAM; 20–23 June, Boston, USA).
According to Chandra, chronic wounds remain a growing problem, not only in the USA but worldwide—with many patients at risk of limb loss presenting as particularly challenging. This cohort requires complex and resource-intensive medical care, reported Chandra.
World experts and leaders in this specialty have developed and described programs to attempt to improve the care of these complex patients and decrease the risk of amputation … read more
Healogics® Announces New Program Aimed at Improving Continuity of Care
JACKSONVILLE, Fla.–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Aug 30, 2018–Healogics®, the wound healing experts, today announced the launch of their newest program: Healogics Specialty Physicians Care Continuum (HSP Care Continuum). The Program is designed to support the patient experience by improving continuity of care, cost-effectiveness, patient outcomes, value and satisfaction for people with chronic wounds who are transitioning from an inpatient to an outpatient setting.
Healogics Announces New Program Aimed at Improving Continuity of Care
The HSP Care Continuum Program provides skilled wound care physicians in the hospital inpatient setting who have specialized training in the management of complex wounds. These physicians will work collaboratively with Certified Wound and Ostomy Nurses and referring specialists needing a specialty consult. Also, Healogics clinical teams educate discharge planners on post-acute options so patients with wounds receive care for this critical co-morbid condition while they are also receiving post-acute care for their primary diagnosis. Healogics has a vast library of educational content that will be made available for patients who can care for their wounds between follow up post-acute visits.
“The average hospital stay is 2.4 days longer for patients living with a chronic wound. With better inpatient consults, we believe we can have an impact on care continuity and, in turn, reducing the overall cost of care. We are excited for the launch of this new program, and the positive implications it will have on the overall patient experience,” said David Bassin, Healogics Chief Executive Officer.
This press release features multimedia. View the full release here: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20180830005777/en/
NeuroMetrix to Exhibit and Sponsor Symposium on the
Early Diagnosis of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy at the Annual Meeting of NEURODIAB
WALTHAM, Mass., Aug. 29, 2018 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — NeuroMetrix, Inc. (Nasdaq:NURO) today reported that it will be both exhibiting and sponsoring a diabetic neuropathy symposium at the 28th Annual Meeting of NEURODIAB held in Rome, Italy September 4-7.
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is the most common complication of diabetes, affecting over half of people with diabetes. It causes significant morbidity including pain, increased risk of falling in the elderly, and is the primary trigger for diabetic foot ulcers which may require lower extremity amputations. Early detection of neuropathy allows for earlier clinical intervention to help mitigate the effects of neuropathy on both patient quality of life and cost of care.
NEURODIAB is the annual meeting of the Diabetic Neuropathy Study Group of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) where thought leaders share ideas and scientific findings on diabetic neuropathy. NEURODIAB is considered the most important annual event in the field of diabetic neuropathy … read more
Caring for the diabetic foot
Patients with psoriasis have a higher risk of developing new onset diabetes mellitus. It’s a risk that’s been described as statistically significant. So, in this article, we examine dermatologic care for diabetic foot infections.
Patients with psoriasis have a higher risk of developing new onset diabetes mellitus. The increased incidence of psoriasis and diabetes mellitus was documented in a 2013 study by Usman Khalid, et al. published in Diabetes Care in which authors described the correlation as “statistically significant.” So, in this article, we examine dermatologic care for diabetic foot infections.
Dermatologists must be able to diagnose and manage mild-to-moderate infections in diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), said Warren S. Joseph, D.P.M., FIDSA, in a presentation at DERMfoot 2018 in Baltimore … read more
True multidisciplinary approach essential for limb preservation
CHICAGO — To prevent amputation, physicians must assemble a comprehensive multidisciplinary team to care for patients at risk for losing their limbs, Ramon Varcoe, MD, MBBS, MS, FRACS, PhD, said at AMP: The Amputation Prevention Symposium.
A multidisciplinary approach to limb preservation begins with recognizing the major drivers of amputation. The global public health threat posed by the “tsunami of diabetes,” for instance, is a significant problem, he said.
If a patient develops diabetes, his or her risk for amputation is 15 times as high as someone who does not, according to Varcoe.
“The impact is more than amputation itself, though; it’s a reduction in life expectancy as well,” he said, noting that studies have linked amputation to an increased risk for death and 5-year rates of death exceeding that of some cancers … read more
New smart bandages could monitor and treat chronic wounds
Researchers in the United States present their findings on research into new smart bandages capable of real-time monitoring and treating chronic wounds.
Chronic wounds develop when a wound fails to heal within the expected time, which might be a couple of weeks or up to several months. They are often caused by diabetic wounds, pressure ulcers, leg ulcers, arterial ulcers, and malignant wounds. Chronic wounds may lead to severe pain, affecting an individual’s quality of life.
Chronic wounds affect millions
Currently, chronic wounds are a major health concern in the United States as they are affecting over 25 million people. This number will likely increase owing to the aging population and the continuous increase in the number of diabetes and obesity cases. According to the American Professional Wound Care Association, chronic wounds have caused the nation over 30 billion dollars each year … read more
Liraglutide May Lower Risk for Foot Amputation in Type 2 Diabetes
Patients with type 2 diabetes who took liraglutide were at a lower risk for foot amputation, according to a study recently published in Diabetes Care.
Researchers completed a post hoc analysis on data collected during the Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome Results (LEADER) trial to determine the effect of liraglutide on rates of diabetes-related foot ulcers in patients who were also at high risk for cardiovascular events. Patients in the LEADER study were randomly assigned to either an intervention arm (n=4668), receiving 1.8 mg of liraglutide a day, or a control arm (n=4672), receiving a placebo. The study continued for 5 years with an average follow-up time of 3.8 years. A diabetes-related foot ulcer was … read more
Deferoxamine Can Prevent Pressure Ulcers and Accelerate Healing in Aged Mice
Chronic wounds are a significant medical and economic problem worldwide. Individuals over the age of 65 are particularly vulnerable to pressure ulcers and impaired wound healing. With this demographic growing rapidly there is a need for effective treatments. We have previously shown that defective hypoxia signaling through destabilization of the master hypoxia‐inducible factor 1α (HIF‐1α) underlies impairments in both aging and diabetic wound healing. To stabilize HIF‐1α, we developed a transdermal delivery system of the FDA‐approved small molecule deferoxamine (DFO) and found that transdermal DFO could both prevent and treat ulcers in diabetic mice. Here, we show that transdermal DFO can similarly prevent pressure ulcers and normalize aged wound healing. Enhanced wound healing by DFO is brought about by stabilization of HIF‐1α and improvements in neovascularization. Transdermal DFO can be rapidly translated into the clinic and may represent a new approach to prevent and treat pressure ulcers in aged patients … read more
Liraglutide May Lower Risk for Foot Amputation in Type 2 Diabetes
Patients with type 2 diabetes who took liraglutide were at a lower risk for foot amputation, according to a study recently published in Diabetes Care.
Researchers completed a post hoc analysis on data collected during the Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome Results (LEADER) trial to determine the effect of liraglutide on rates of diabetes-related foot ulcers in patients who were also at high risk for cardiovascular events. Patients in the LEADER study were randomly assigned to either an intervention arm (n=4668), receiving 1.8 mg of liraglutide a day, or a control arm (n=4672), receiving a placebo. The study continued for 5 years with an average follow-up time of 3.8 years. A diabetes-related foot ulcer was specified as a medical event of special interest, and all complications related to the ulcer were documented.
Texas A&M partnership developing biomedical ‘bandage’ for wounds
University research focusing on building stimuli-responsive material that could release, absorb antibiotics
Researchers at Texas A&M University and the Stevens Institute of Technology are working on the next generation of biomedical materials used to treat chronic wounds, including ulcers and wounds caused by diabetes.
Svetlana Sukhishvili, A&M professor and director of the soft matter facility, and her research partner at Stevens, Hongjun Wang, have conducted experiments alongside their respective teams and combined them to form one study.
“If you have diabetes, for example, your ability to heal wounds may be compromised, and ulcers may occur. What we’re trying to do is give you this bandage-like material that will be able to transform into skin that will help your body overcome the wound and to heal,” said Victoria Albright, a fourth-year doctoral student and lead researcher in the A&M Department of Materials Science and Engineering … read more
Man Bitten By Shark Develops Flesh-Eating Bacteria
A man bitten on the leg by a 7-foot shark quickly gets treatment for his wounds. A week later, he suffers from excruciating pain brought about by flesh-eating bacteria.
In early August, Blaine Shelton from Texas was swimming at Crystal Beach in Houston when he spotted a fin, which he immediately knew was not from a friendly porpoise. He was reportedly about 200 yards from the shore, so he began swimming to get away from the shark. It was then that he was bitten on the thigh, just above his knee. Shelton was able to swim ashore after the bite and was immediately taken to the hospital to be treated for his wounds. He later learns that the shark attack was likely from a 7-foot bull shark … read more
MiMedx Announces Statistically Significant Results
In New Multicenter Clinical Study Of Healing Of Diabetic Foot Ulcers Using EpiFix®
MARIETTA, Ga., Aug. 24, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — MiMedx Group, Inc. (NASDAQ : MDXG ), a leading developer and marketer of regenerative and therapeutic biologics, today announced that a new study regarding the use of EpiFix® in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) has been published in the peer-reviewed journal, International Wound Journal.
The paper is entitled “A Confirmatory Study on the Efficacy of Dehydrated Human Amnion/Chorion Membrane dHACM Allograft in the Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study of 110 Patients from 14 Wound Clinics.” The paper was authored by: William Tettelbach, MD; Shawn Cazzell, DPM; Alexander M. Reyzelman, DPM; Felix Sigal, DPM; Joseph M Caporusso, DPM; and Patrick S. Agnew, DPM. The electronic publication of the article in International Wound Journal can be found at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/iwj.12976.
This multi-center randomized and controlled trial was led by William Tettelbach, MD, principal investigator and former Executive System Medical Director of Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Services for InterMountain Healthcare. Dr. Tettelbach is now Associate Chief Medical Officer for MiMedx, a position that postdated the completion of the study.
Clinical Study Design and Results
The objective of the study was to determine the safety and effectiveness of EpiFix as compared to standard of care (SOC) therapy for the treatment of non-healing DFUs. The primary efficacy endpoint was the incidence of complete wound closure over a 12-week period. Data from 110 patients meeting study inclusion and exclusion criteria were analyzed in the Intent-to-Treat (ITT) cohort. A total of 98 patients completed the study Per Protocol (Per-Protocol cohort).
ITT analysis requires patients to be included even if they did not fully adhere to the protocol. In comparison, in a Per-Protocol analysis, only patients who completed the entire clinical trial according to the protocol are counted towards the final results.
In the current study on an ITT basis, 70% of patients who received weekly EpiFix had complete healing by 12 weeks versus 50% of patients only receiving weekly SOC (EpiFix 70% vs. SOC 50%, p=0.0338) … read more
Epidermolysis bullosa: a case report
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB), often referred to as the butterfly disease, is a group of rare genetic conditions characterized by skin that is delicate and fragile as butterfly wings. The skin blisters in response to friction, minor injury, or trauma. In certain types of EB, other organs, such as the esophagus, can also be affected, and secondary complications may require multiple interventions. While there has been significant progress in classifying the disease – identifying genes and proteins involved – there have been few advances in the treatment of the disease. The care of the EB patient focuses on management of symptoms, protecting the skin, and preventing complications. In this case report, the use of a multivalent wound-healing ointment (Terrasil®) was evaluated in a 60-year-old patient with a history of junctional EB. A polymerase chain reaction-based culturing was utilized to quantitatively test for bacteria and fungi at baseline and follow-up visits. Pain assessment and wound area were also documented at each visit. Following the application of the wound care ointment, there was a reduction in wound surface area on central (96%) and distal mid-back (92%) by treatment visit three, and there was a 96% reduction on the left shoulder blade ulcer by treatment visit four. Moreover, there was a noticeable drop in the percentage of bacteria detected by polymerase chain reaction. The wound care ointment was also effective in eliminating the fungal species and reducing pain, itching, blistering, and cracking around the wound … read more
The industry’s BEST TCC Kit is Now Available on Amazon. M-Med provides the most versatile total contact cast on the market with the TCC-Mobility Series. 60% more padding for patient comfort and safety. Click here for more information on TCC-Mobility Series.
You can order as many or as few kits based on your need- there’s no minimum order quantity. And, we have the Best Price in the marketplace allowing your practice to maximize value per procedure. M-Med’s TCC kits are fully customizable.

As an advanced wound care specialist for almost 20 years full time, I am a relentless devotee of best practices and the wound care literature. While there are many wound care practices that allow some personal latitude, there are one or two “definites”. The literature has recently become very vociferous in the use of Total Contact Casting as the “Gold Standard” for offloading plantar based Diabetic Neuropathic Foot ulcers. As a non-hospital affiliated wound care specialist, I have no deep pocket entity to support me as I trial device after device searching for ease of use, facilitated patient compliance, and more, best pricing.
I found your devices in a search for an equally efficacious TCC that had better pricing than the many on the market. Since no two patients are alike, the many components in your kit allowed me to configure the final product, controlling the height, thickness, weight and even the configuration/position of the walking gasket. More, the pricing for needed large orders made this a less painful expenditure for me. Of course, the rapid shipping came in handy when my staff opened a closet door to discover two casts and four patients on the schedule in 48 hours.
I wanted to take the time to let you know how much I appreciate the products you have available for those of us who strive to provide best care using the best products, at what I have found to be best service and pricing.
Respectfully yours
Michael S. Miller DO, FACOS, WCC
CEO and Medical Director – The Miller Care Group
Indianapolis, IN
Clay fights MRSA, other ‘superbugs’ in wounds
The use of mud or wet clay as a topical skin treatment, or poultice, is a common practice in many cultures. In fact, the concept of using mud as medicine goes back to the earliest times.
Now, Arizona State University (ASU) and Mayo Clinic researchers have found that one type of clay, Oregon blue clay, may help fight disease-causing bacteria in wounds, including treatment-resistant bacteria. Their findings appear in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.
“The study is an important advance in understanding how clays, specifically blue clay from Oregon, have shown medicinal properties by attaching to pathogenic bacteria,” says Enriqueta Barrera, a program director in the National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Division of Earth Sciences, which funded the research.
The scientists identified certain clays that kill bacteria, including many drug-resistant pathogens.
“Working with Mayo Clinic, we showed that these clays also diminish populations of bacterial biofilms, as well as bacteria common in wounds that are more resistant to drugs,” says biogeochemist Lynda Williams of ASU, a co-author of the study. “The results support our efforts to design new antibacterial drugs using natural clays.” … read more
Innovation in Wound Care
An interview with Prof. Harding, CBE, and Dr Dixon, PhD, conducted by Alina Shrourou, BSC
What is a hard-to-heal wound?
There are many definitions of hard-to-heal. More conventionally, it’s based on underlying etiology of the wound, but in practice it’s any wound that has not healed within a timely fashion. This is often due to a lack of coordinated care. Many of those patients receive multiple courses of antibiotics and antimicrobial therapy, because clinicians aren’t sure what they’re looking at.
Not all wounds are necessarily hard-to-heal from the beginning, but because of the need for improvements and coordination of care, many of those patients that are seen in clinical practice become hard-to-heal … read more
MiMedx Announces Statistically Significant Results In New
Multicenter Clinical Study Of Healing Of Diabetic Foot Ulcers Using EpiFix®
– Study Published in International Wound Journal Reported Statistically Significant Evidence of Healing Compared to Control Group
– Intent-To-Treat EpiFix Treated Patients = 70% vs Control 50%, p=0.0338
– Per-Protocol EpiFix Treated Patients = 81% vs Control 55%, p=0.0093
MARIETTA, Ga., Aug. 24, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — MiMedx Group, Inc. (NASDAQ: MDXG), a leading developer and marketer of regenerative and therapeutic biologics, today announced that a new study regarding the use of EpiFix® in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) has been published in the peer-reviewed journal, International Wound Journal.
The paper is entitled “A Confirmatory Study on the Efficacy of Dehydrated Human Amnion/Chorion Membrane dHACM Allograft in the Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study of 110 Patients from 14 Wound Clinics.” The paper was authored by: William Tettelbach, MD; Shawn Cazzell, DPM; Alexander M. Reyzelman, DPM; Felix Sigal, DPM; Joseph M Caporusso, DPM; and Patrick S. Agnew, DPM. The electronic publication of the article in International Wound Journal can be found at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/iwj.12976.
This multi-center randomized and controlled trial was led by William Tettelbach, MD, principal investigator and former Executive System Medical Director of Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Services for InterMountain Healthcare. Dr. Tettelbach is now Associate Chief Medical Officer for MiMedx, a position that postdated the completion of the study.
Type 2 diabetes: Poor sleep slows wound healing
Researchers uncovered a connection between poor sleep and wound healing in type 2 diabetes that could pave the way for new treatments.
Diabetes is one of the leading causes of death in the United States.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, and it impacts the ability of the body to produce insulin, the hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
One serious complication of diabetes are ulcers that can form from wounds. Feet are one of the most common places of injury. Small wounds that develop on feet can eventually become ulcers … read more
SGLT2 inhibitor therapies may raise risk for amputation
Adults with type 2 diabetes and established CVD prescribed SGLT2 inhibitor therapy have a twofold increased risk for lower-limb amputation and diabetic ketoacidosis compared with patients prescribed a GLP-1 receptor agonist, according to study findings presented at the European Society of Cardiology Congress.
“Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors are playing an increasingly prominent role in the treatment of diabetes, following the reduced risk of major adverse cardiovascular events and heart failure outcomes seen in the EMPA-REG Outcome trial with empagliflozin [Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim] and in the CANVAS study with canagliflozin [Invokana, Janssen],” Peter Ueda, MD, PhD, from the department of medicine at the Karolinska Institute in Solna, Sweden, said during a presentation here. “Concerns exist regarding the safety of the drugs, with signals of serious adverse events emerging from clinical trials, case reports and observational studies.” … read more
Wound healing work presented at the RCP Innovation in
Medicine Conference 2018 by Neem Biotech
Neem Biotech, a South Wales based R&D pharmaceutical biotech working in the field of novel antimicrobial drug development, and the Welsh Wound Innovation Centre recently attended the Royal College of Physicians’ Innovation in Medicine Conference 2018 where Neem presented their data around wound-relevant biofilms.
The promising laboratory data presented reinforces the role of quorum sensing inhibition in virulence factor regulation and biofilm disruption, with implications for management of antimicrobial resistance.
Dr Graham Dixon, Neem’s CEO and Prof Keith Harding … read more
Jipmer to treat wounds with marine resource
Doctors at JIPMER have begun using a marine resource sourced from shrimps for wound management. Marine resources are used to help patients with chronic wounds such as burns, diabetic foot ulcers, bed sores, infections, trauma and even surgery-related injury.
Jipmer Director, Dr. S Vivekanandam, said the protocol was initiated by the Department of Plastic Surgery. As a forerunner, a Continuing Medical Education (CME) was recently organised on ‘Wound Update-2018’ by the Department of Plastic Surgery to sensitise and to make aware of this technology in wound management.
According to the Director … read more
Wound Management Technologies, Inc. (WNDM) Reports
Publication of Clinical Trial Data from CellerateRX(R) Surgical Activated Collagen(R) Peptides
WNDM Medical Inc. (: WNDM) today announced the publication of a journal article in Orthopedics: ”The Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Activated Collagen on Wound Healing in Primary Total Joint Arthroplasty” by David Evans, BA and Bruce Evans, MD. This study examined whether two wound additives, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and activated collagen (CellerateRX Surgical), would improve postoperative wound healing and reduce complications after total knee or hip replacement surgery.
Based in Fort Worth, Texas, WNDM Medical Inc. (WNDM) has a management team in place with significant healthcare industry experience that is committed to sales growth by providing efficacious products to improve patient outcomes.
Key Points from the Publication
• This was an unsponsored, institutional review board (IRB)-approved, prospective, randomized, single-blinded, controlled study with three cohorts of 30 patients each … read more
Bedside Advanced Wound Care in Nursing Homes
As it stands now, we have 1.6 million nursing home residents in the United States; that number is expected to double by the year 2030. Bringing advanced wound care to the long-term care arena is becoming more common throughout the country. Physician-based wound groups can bring their expertise to the patient’s bedside, thereby saving the patient pain during transport to the wound center and lowering costs. However, certain procedures—such as total contact casting and bioengineered skin substitutes—cannot be performed at the bedside because of billing and reimbursement guidelines.
Physician-Based Wound Care Groups: Rationale and Challenges in the Long-Term Care Setting
Utilizing a wound care physician-based group has many advantages in long-term care. Residents build a trusting relationship with their providers who come weekly to assess and treat their wounds. Wound rounds are also the perfect opportunity for the physician and nurse to collaborate. However, providers tend to have somewhat of a learning curve, as well as culture shock stepping into the long-term care arena for the first time. Being competent in wound care is not sufficient to work as a provider in this setting. The long-term care arena is surprisingly different from the hospital. The best way to describe it is, you are on their turf. Nursing homes are under a microscope, and federal regulations must be followed accordingly or facilities are at risk for fines and penalties. Providers must be compliant with the state survey process and associated wound care federal tags … read more
Medicare update: new electronic clinical quality measure
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) recently released an announcement seeking input from stakeholders on a new electronic clinical quality measure under development titled, “Hospital Harm – Hospital-Acquired Pressure Injury.”
This measure assesses the proportion of hospitalized patients 18 years and older who develop a new stage 2-4 pressure ulcer, deep tissue injury, unstageable pressure ulcer, or experience worsening of any of the above during their hospitalization.
We read the full description of the measure and provided the following feedback on behalf of APWCA membership … read more
Skin Conditions Frequently Found in Obese Patient Populations
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention state that in the United States, “…thirty eight percent of adults, and that seventeen percent of children and teens are obese.” It is imperative that the term obesity be differentiated from overweight. Obesity refers to higher than normal body fat, whereas overweight is in reference to an individual weighing more than the standard for height and weight. Although both terms mean that a person’s weight is greater than what is considered healthy for his or her height, obesity has higher negative health-related consequences.
Health care professionals are challenged to manage increasingly complex health issues related to obesity, including complex skin conditions. The increase in stored fat associated with obesity can contribute to a variety of changes in skin physiology and is implicated in a range of dermatologic conditions.2 The skin’s ability to manage transepidermal water loss is altered in the obese population. With increased fat stores the transepidermal water loss is increased, resulting in dryness and delayed skin repair. Additionally, sebaceous channels are blocked, leading to an increase in oils and resulting in acne.2 The thick layers of subcutaneous fat in obese individuals may contribute to profuse sweating (hyperhidrosis) when overheated or with activities. Hyperhidrosis can set the stage for profuse skin damage. Moisture trapped in skin folds coupled with friction as body folds rub together … read more
Predictors of lower extremity amputation among
patients with diabetic foot ulcer in a tertiary health facility in north central Nigeria
INTRODUCTION: Diabetic foot ulcer is a complication of diabetes mellitus of great public health importance. It has the potential of leading to the dreaded sequelae of lower extremity amputation. This outcome is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, hence the need to explore its predictors among persons with diabetic foot ulcers.
METHODOLOGY: The study involved the review of the medical records of seventy (70) in-patients who had received treatment for diabetic foot ulcer at the Federal Medical Centre, Keffi, North Central Nigeria. In addition to obtaining sociodemographic and medical history, information on the Wagner grade of the ulcer, the presence of peripheral sensory neuropathy (using the 10g monofilament) and the presence of osteomyelitis (using plain X-ray of the foot) were obtained and documented. The prevalence rate of lower extremity amputation was also determined.
RESULTS: The study population comprised 52.9% males and 42.1% females. The mean age for male and female participants were 53.4±10.5 and 58.8±13.0 years respectively ( t = 2.35; p = 0.061). Majority of study subjects (37.1%) had Wagner grade 2 disease. Prevalence rate of amputation was 38.6%. Among the potential predictors of lower extremity amputation analyzed (Age, sex, foot care education, duration of diabetes, cigarette smoking, walking bare feet, impaired vision, peripheral neuropathy, hypertension, previous foot ulcer, osteomyelitis), none of them demonstrated a significant association with lower extremity amputation.
CONCLUSION: The list of potential predictors of lower extremity amputation considered in this study is by no means exhaustive. More studies involving larger study populations and other potential predictors of lower extremity amputation not considered in this work (such as peripheral artery disease and glycated haemoglobin) are encouraged.
Application of Viable Cryopreserved Human Placental Membrane
Grafts in the Treatment of Wounds of Diverse Etiologies
There is evidence in the literature that viable cryopreserved human placental membrane (vCHPM) grafts are effective in treating diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers.
Objective. This case series presents 3 cases of chronic ulcerations — 1 arterial ulcer (AU), 1 pressure ulcer (PU), and 1 recurrence of a pyoderma gangrenosum ulcer (PGU) — that had failed previous courses of standard wound care and were subsequently treated with vCHPM to determine if the treatment is an effective modality for treating wounds of these etiologies.
Materials and Methods. This retrospective review describes 3 cases in which patients with chronic wounds that had failed standard of care treatments for more than 4 weeks were subsequently treated with weekly applications of vCHPM. Each wound area was recorded and photographed on a weekly basis and wound area reduction also was charted weekly.
Results. The PU and AU both reached full closure in 4 and 5 weeks, respectively, without complication. The patient with the PGU achieved 64% closure after 9 applications of vCHPM … read more
Inlow’s 60-Second Diabetic Foot Screen Gets a New Look!
Dr. Shane Inlow wrote a two-page article, published in 2004, to help guide clinicians in assessing and planning care for patients with or at risk for diabetic foot ulcers.1 A few years later, clinicians in Northern Canada indicated that one of their problems was communicating effectively with experts in larger centres about their patients’ foot problems. The article by Dr. Inlow came to mind, and Inlow’s 60-Second Diabetic Foot Screen was created to give clinicians a common language and process to perform such an assessment.2 This tool then underwent a validation study that included interrater and intrarater reliability and predictive validity to determine consistency of risk recognition for development of ulceration independent of specific assessor and practice setting.1,3 Four years later, a growing body of work by the International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot (IWGDF) resulted in a risk-classification tool … read more
Ants care for wounded comrades by licking their wounds clean
A species of ant has become the first known non-human animal to tend the wounds of its fellows. “Nurse” ants lick the wounds of fallen comrades, and this helps them survive.
Matabele ants (Megaponera analis) live dangerous lives. Several times a day, parties of 200-600 soldier ants set out to hunt termites, dragging them from their nests and carrying them home. The termites fight back, and their powerful jaws can administer lethal bites, so Matabele ants frequently lose one or more limbs.
In 2017, Erik Frank, then at the University of Würzburg, Germany reported that Matabele ants routinely carry their wounded back to the nest. This is odd, as social insects usually treat each other as expendable … read more
Novel tissue engineering scaffolds fabricated via controlled
ice crystallization
A large number of people around the world suffer from chronic skin wounds each year. Often, chronic wounds such as skin ulcers are seen in older people suffering from circulation disorders and diabetic patients whose skin tissue has a poor capacity of regeneration. Currently, many treatment approaches focus primarily on managing the wounds.
Researchers have now taken a nanotechnology-based tissue engineering approach to accelerate the regeneration and repair of damaged tissues at the wound site by directing cells and tissues to grow towards the target site. Their hope is that this leads to the development of affordable and functional biodegradable wound dressings for accelerated healing of chronic skin wounds by promoting regeneration of local tissues.
“We show that 3D scaffolds with both aligned nanofibers and aligned interconnected macrochannels can be created with various biomacromolecules, including silk fibroin, using a facile guided ice-crystal growth and nanofiber assembly strategy,” Dr. Linpeng Fan, first author of a paper on this work (ACS Nano, “Creating Biomimetic Anisotropic Architectures with Co-Aligned Nanofibers and Macrochannels by Manipulating Ice Crystallization”), tells Nanowerk … read more
Role of oxygen in wound healing Webcast
13 Sep 2018
This Wounds International webcast focuses on the role of oxygen in wound healing and how topical oxygen therapy can improve oxygenation and, therefore, healing.
In the first presentation, Breda Cullen, Research and Development Director, UK, outlines the vital role that oxygen plays throughout the healing process and the impact that lack of oxygen (hypoxia) can have on the wound. Breda explores the factors that can cause compromised healing and how these can be addressed.
In the next presentation, Hanna Kaufman, Orthopaedic Surgeon, Israel, looks in depth at the clinical evidence and how this can be applied to practice. Hanna identifies the wounds that are suitable for topical oxygen therapy and shares tips for use in practice, drawing on clinical evidence and experience … read more
‘Really Good’ New Guidelines for T2 Diabetes
The diabetes guidelines discussed below are a draft version of a consensus statement to be issued in October at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes in Berlin, Germany.
Hi. I am Dr Anne Peters, and today I’m going to talk about the new ADA/EASD treatment guidelines for managing patients with type 2 diabetes. First off, my “headline” is that I think these are really good guidelines. Although guiding people is difficult, these guidelines actually begin to guide us in the treatment of our patients with type 2 diabetes …. read more
Agony of Britons hit by chronic wounds lasting more than three months
The devastating impact of chronic wounds has been laid bare as research reveals that hundreds of thousands of patients suffer with pain and immobility for more than a year.
One in ten sufferers is even taking antidepressants to cope, with many more unable to work or leave the house.
About a million patients are undergoing five dressing changes a week, with 90 per cent of those claiming their quality of life is severely affected.
More than 2.8 million Britons are living with a chronic wound, defined as one that does not heal within three months.
But the ‘new normal’ is that patients are affected for eight months … read more
Wounds Australia’s Five Point Plan to Reduce the Burden of Chronic Wounds
The burden of chronic wounds for the individual, the health system and the whole community is familiar to the readers of this journal. Improving lives and saving money through better wound care is a common theme across this issue, and in the broader wound care activities.
Wounds Australia recognises that to achieve our vision of Quality wound care and prevention for all requires us to inform and engage with a broad audience. During Wound Awareness Week from 15 to 21 July 2018 Wounds Australia will launch our Five Point Plan to Reduce the Burden of Chronic Wounds. Our plan outlines 5 key initiatives to drive the change for best practice wound care for all Australians and reduce the suffering as a result of chronic wounds.
1. Medicare funding for treatment of chronic wounds in primary health care. A dedicated MBS item for treatment of chronic wounds to enable GPs, nurses and allied health professionals to deliver the best practice.
2. Subsidised wound products (dressings and related products) for people experiencing long term wound care. Advanced Wound management products often attract a premium cost. Selecting low cost, modest outcome products is a false economy. Research has shown that the use of less expensive dressings actually increases costs of treating a wound … read more
Wound Care, Tissue Repair and Regenerative Medicine
The accuracy of venous leg ulcer prognostic models in a wound care system
Venous leg ulcers are among the most common chronic wounds. Treatment is commonly with a limb compression bandage. Previous small, often single‐center, studies have shown that it is possible to predict which wounds are likely to respond to compression therapy. We designed this cohort study using a dataset of over 20,000 individuals with a venous leg ulcer to investigate the accuracy of several prognostic models. Creating complex models using logistic regression, as well as simply counting prognostic factors, we show that initial measures of wound size and duration accurately predict, as measured by area under the receiver operator curve and Brier score, who will heal by the 24th week of care. For example, a wound that is less than 10 cm2 and less than 12 months old at the first visit has a 29 percent chance of not healing by the 24th week of care, while a wound greater than 10 cm2 …. read more


