Recently, during an academic discussion, the topic of Charcot Marie Tooth disease came up. It’s a very important disease to a podiatrist, so it makes sense that we were discussing its effect on a patient. During this discussion, my mind started wandering a bit (yes, I’ll admit it), and I thought, “I know who Charcot was, but who were Marie and Tooth?” After growing up in the medical world, I knew the prevalence of eponyms (in fact, it’s one of my favorite topics to read about), so I knew that Marie and Tooth were people. But who were they? It’s easy to forget that there were actual people behind these eponyms, people with lives, loves, adventures, passions and failures. So, let’s take a digression away from things clinical and look into a window on the past … read more
Month: September 2021
Patient Engagement, Diabetes and Diabetic Foot Ulcers | EWMA Podcast
In this episode, you can listen to a conversation between the EWMA Podcast Host Samantha Holloway and Dr Athanasios Hassoulas, director of the MSc in Psychiatry programme and Senior Lecturer in Psychological Medicine at Cardiff University. They will talk about the meaning and impact of patient engagement and empowerment in relation to diabetes and diabetic foot ulcer management. The podcast provides reflections on the topic as well as recommendations on how to implement these person-centred tools in your meetings with diabetic foot ulcer patients in you daily clinical practice … listen
Turkish scientist’s work shows spinach can speed up wound healing
Spinach does not give you instant muscles as it did to Popeye, though its healthy properties are highly valued. Now, a Turkish researcher has added a new one to them. According to assistant professor Serkan Dikici, baby spinach, in its decellularized form, can accelerate the healing of wounds.
Dikici, who works at the bioengineering department of Izmir Institute of Technology, won a doctoral researcher award in the United Kingdom for his study.
The young scientist attended Sheffield University as a Ph.D. student in tissue engineering and for his Ph.D. study, he chose the development of biomaterials for healing of chronic wounds, to replace or reduce the use of guinea pigs in this field … read more
Organizations Join Forces to Boost Wound Healing Care and Research
HMP Global’s Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC) Fall has established partnerships with the Wound Healing Foundation and debra of America to boost their research and improve care of patients with chronic wounds, such as those with epidermolysis bullosa (EB).
The SAWC Fall is scheduled to take place as an in-person meeting Oct. 29–31 in Las Vegas. For every registration, a donation will be made to each organization, according to HMP Global’s press release. To register, go here.
Established in 1999, the Wound Healing Foundation is a nonprofit dedicated to boosting scientific research and care of wound healing patients by funding research and promoting education and outreach.
debra of America works to improve the quality life of people with EB. Launched in 1980 to fill the gaps in knowledge about EB, the organization offers free services to U.S.-based EB patients and their families, and funds innovative research ultimately aimed at finding a cure for the disease … read more
As an Active Cleanser, Nexodyn(R) AOS Shows Superior Wound Healing Performance Compared to Standard of Care
Relief’s Subsidiary, APR Applied Pharma Research, Reports Data Published in Journal of Wound Care, Indicating Nexodyn(R) AOS Highly Effective Treatment to Support Healing of Hard-to-Heal Leg Ulcers … RELIEF THERAPEUTICS Holding SA (SIX:RLF)(OTCQB:RLFTF) (“Relief”), a biopharmaceutical company seeking to provide patients therapeutic relief from serious diseases with high unmet need, today announced that its wholly owned subsidiary, APR Applied Pharma Research SA (“APR”), reported data published in the peer reviewed Journal of Wound Care, indicating that the company’s Nexodyn(R) acid-oxidizing solution (AOS), developed with APR’s proprietary Tehclo(R) technology, was found to be a highly effective treatment to support wound healing in infected or non-infected hard-to-heal leg ulcers. The data also confirmed the safety and tolerability of Nexodyn(R) … Conducted by Robert Strohal, M.D., Professor and Department Head, Department of Dermatology, Federal Academic Teaching Hospital of Feldkirch, Austria, and colleagues, the open-label, randomized controlled MACAN study was conducted at two centers is Austria. A total of 50 patients were enrolled, with either infected or non-infected hard-to-heal leg ulcers of different etiology. Patients were treated for six weeks either with Nexodyn(R) AOS or standard of care (SOC) wound dressings … In the patient group treated with Nexodyn(R) AOS, wounds exhibited a faster and more pronounced wound size reduction compared with wounds in the SOC group. Additionally, compared to SOC, the treatment group showed a markedly greater percentage of complete healing of hard-to-heal ulcers by the end of the study period (32% versus 8%, respectively). Furthermore, Nexodyn(R) demonstrated its ability to significantly reduce the wound pH (p<0.0001) and thus promote a faster healing process. In all patients with infected leg ulcers, local infection was overcome more rapidly with Nexodyn(R) AOS treatment. Overall, the efficacy of Nexodyn(R) AOS was found to be not only non-inferior but superior to SOC wound dressings … read more
RETHINK Talks: An Interview with ReNew Wound Care
This interview is brought to you by ReNew Wound Care. This interview took place during a live Q&A session with ReNew Wound Care CMO Dr. Rekha Bhandari at the SNN RETHINK event in Chicago held on September 1, 2021. The interview has been edited for clarity … read more
Study shows how management of serious diabetic foot ulcers was possible during the COVID-19 lockdown
New research being presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), held online this year (27 Sept-1 Oct), reveals how Belgium’s efforts to maintain a diabetic foot care programme during the COVID-19 pandemic can offer valuable lessons to the rest of the world.
“Thanks to the great efforts of diabetic foot clinics, continued availability of diabetic foot ulcer services during lockdown, although in a limited capacity, were really helpful, and may be the reason why we didn’t see late presentation and the impact on the severity of ulcers was limited to slightly larger wounds”, says lead author Dr An-Sofie Vanherwegen from Sciensano, Brussels, Belgium. “Our findings will hopefully guide diabetic foot clinics in serving their patients using innovative strategies … read more
Expanding horizons to upskill wound practice and research
With our horizons limited by Covid-related travel restrictions, it is more important than ever to experience and learn about our multicultural world through reading about wound-related research and practice in other jurisdictions and countries. Two such articles provide this important international insight and are included in this issue of the journal. The first by Obilor and colleagues describes the assessment of nurses’ knowledge, attitude and competence in wound assessment in a tertiary healthcare facility in southwest Nigeria. Here they found that many of the nurses surveyed were lacking in wound assessment competence … read more
The HealSource™ Clinical Practice Guidelines
The HealSource™ Clinical Practice Guidelines provide a standardized method for the delivery of care, treatment and services to patients with wounds or ulcers.
These clinical practice guidelines are a useful guide when caring for patients, providing general guidelines for the treatment of chronic wounds and the application of hyperbaric oxygen treatment. The data relies heavily on three significant and highly respected contributions to the fields of wound care and hyperbaric medicine:
The Wound Healing Society guidelines for the best care of chronic wounds
The Wound Ostomy Continence Nurses Society clinical practice guidelines
The Oxygen Therapy Committee Report of the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medicine Society
The Fairy Tale is Over in the Wound Center
Once upon a time there was a happy land where at least half the patients seen in a hospital-based outpatient wound center (HOPD) were Medicare Fee for Service (FFS) beneficiaries. Their treatments were covered and we got paid for providing them. The most the patient had to worry about was the 20% “patient responsible portion.” In that kingdom, only private payers required prior authorization for services like hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), or “skin substitutes,” but at least they actually authorized those treatments upon request … read more
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for paediatric patients: an unintended consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a useful adjunctive treatment for selected complicated wounds, including severe diabetic lower extremity ulcerations and compromised skin grafts or flaps. The Sars-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic has disrupted healthcare delivery, with its effects extending to delivery of HBOT. During the pandemic, paediatric patients in our geographic region who were referred for HBOT faced challenges as centres temporarily closed or were unprepared to treat younger patients. Our monoplace HBOT centre modified existing practices to allow for treatment of these patients. This study aims to outline the steps necessary to adapting a pre-existing HBOT centre for the safe treatment of paediatric patients … read more
Strategies and Techniques for Transitioning NPWT Patients to the Post-Acute Care Setting
Join Dr. Klein as he shares his experience transitioning NPWT patients to the post-acute care setting.
– Examine the prevalence of hospital readmissions, the economic impact, and the importance of preventing readmissions to improve wound healing.
– Discuss common challenges associated with discharging a NPWT patient to the post-acute care setting and the steps to develop a comprehensive discharge plan.
– Review strategies for educating patients and empowering them to be an active participant in their treatment plan as they transition from the acute to post-acute care setting.
– View case studies utilizing negative pressure wound therapy to optimize wound healing.
Read more and register
Improving Vascular Access Dressing Integrity in the Acute Care Setting
Hospitals have a major focus on improving healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) with intense scrutiny on central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs) and other hospital-onset bacteremias. Efforts at prevention have long targeted the skin of the patient and healthcare worker processes such as hand hygiene, maximum sterile barrier precautions, antiseptic skin preparation, use of chlorhexidine-impregnated dressings, and other interventions.1–3 Maintaining the health and integrity of the patient’s skin receives considerable attention; however, less common are efforts to establish partnerships between wound/ostomy and infection prevention and/or vascular access teams to improve and promote HAI prevention processes … read more
Partial calcanectomy with antibiotic biocomposite injection for diabetes patients with heel ulcers and calcaneal osteomyelitis
a single stage treatment
Heel ulcers with calcaneal infection are difficult to treat, with frequent relapses. The authors report a series of four patients who presented with a heel ulcer and calcaneal osteomyelitis. The results show that using a single stage partial resection of calcaneum with primary closure of wound and an antibiotic biocomposite injection (Cerament®, Bonesupport) injection is a viable and useful technique in managing calcaneal osteomyelitis … read more
ACFAS 2022 – Austin Convention Center Feb. 24-27
Whether you come for the captivating sessions, hands-on workshops, or reconnecting with colleagues, ACFAS offers four days of learning as unique and as vibrant as the city of Austin itself! The ACFAS Annual Scientific Conference offers a wide range of topics so there is something for everyone, highly respected faculty, and the opportunity to enhance your knowledge and skills. Don’t miss out on this once-a-year learning experience … REGISTRATION IS NOW OPEN! REGISTER BY 2/9 BEFORE ONSITE FEES APPLY … read more
Podiatry Management’s annual Buyers’ Desk Reference
Podiatry Management’s annual Buyers’ Desk Reference is a user-friendly guide to products and services currently being offered to the podiatric community … read more
Study provides new tool to assess amputation risk following popliteal vascular injury
A large, multicentre cohort study provides a simple, practical method to effectively stratify patients preoperatively into low- and high-risk major amputation categories.
According to lead author Leigh Ann O’Banion (University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, USA), “traumatic popliteal artery injuries present a serious clinical challenge because they are associated with the greatest risk of limb loss of all peripheral vascular injuries, with major amputation rates of 14–25%.” … read more
Principles of Wound Healing
A wound is a break in the continuity of a bodily tissue, such as the skin or mucous membrane. Wounds can be caused by events that are external to the organism – such as trauma, burns, or surgical incisions; and wounds can also be of endogenous origin – such as a distal ischemic event involving the toes due to embolism or arterial stenosis … Wound attributes, such as its causative mechanism, size, depth and location are useful for characterizing its type. When a wound is being assessed, it is also important to determine the stage of wound healing, extent of tissue repair, presence of any obvious elements preventing complete wound closure, and the patient’s psychological status. Complete restoration of tissue integrity requires multidisciplinary care and patient adherence to the recommended treatment …The patient’s baseline clinical condition greatly influences the wound healing process. Healthy individuals tend to recover quickly, with restoration of skin integrity and scars that have a better appearance as well as fewer complications. Patients with chronic diseases (e.g. diabetes mellitus and hypertension, malnutrition or obesity) tend to present delayed wound healing and have greater risk of complications such as infection, and functional and psychological sequelae … read more
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease (LEAD) Awareness and Discussion
By Holly Hovan, MSN, GERO-BC, APRN, CWOCN-AP
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is also known as lower extremity arterial disease (LEAD), peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD), or arteriosclerosis obliterans.1 LEAD is a disease that impacts the circulatory system, specifically the arteries (narrowing, which can result in a decreased supply of blood flow to the limb), and can eventually lead to limb loss or amputations. It is important to bring awareness to LEAD and its diagnosis, treatment, and prevention to improve access to care and screenings and ultimately to prevent limb loss … read more
Negative pressure wound therapy for surgical wounds healing by primary closure
Indications for the use of negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) are broad and include prophylaxis for surgical site infections (SSIs). Existing evidence for the effectiveness of NPWT on postoperative wounds healing by primary closure remains uncertain … To assess the effects of NPWT for preventing SSI in wounds healing through primary closure, and to assess the cost‐effectiveness of NPWT in wounds healing through primary closure … read more
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Prevention Strategies
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) may affect up to 25% of people with diabetes at some point in their lifetime. Once a person has developed a DFU, there is a 50% chance the ulcer will become infected.1 DFUs are also among the leading causes of amputation.2
Wound care specialists encounter DFUs regularly in the clinic, and these wounds can be very difficult to treat because of the underlying metabolic insufficiency. This blog provides a guide to current best practices with regard to DFUs and prevention … read more
Effect of Flap Selection on the Postoperative Success of Sacral Pressure Injuries: A Retrospective Analysis
Pressure injuries (PIs) continue to be a substantial problem and burden for the present-day health care system and are the leading cause of chronic wounds worldwide. There is no current consensus on the long-term results of the use of flaps in sacral PI reconstruction and optimal flap choice. Objective. This study aimed to evaluate whether flap selection influences postoperative results in sacral PI reconstruction. Materials and Methods. Patients who underwent surgery for PIs in the authors’ clinic between 2002 and 2016 were retrospectively analyzed. A total of 63 patients with stage 3/stage 4 sacral PIs and who underwent reconstruction with fasciocutaneous (FC) flaps (group 1), musculocutaneous (MC) flaps (group 2), or perforator (P) flaps (group 3) were included in the study. The mean duration of the follow-up period was 14.4 months, and patients were evaluated in terms of their demographic data … read more
Evidence Summaries for Improved Wound Care Practice
This month’s issue includes three important review articles related to alternative/local wound care, support surface evaluation testing, and skin failure. The “alternative” medicine review was originally submitted by three colleagues from Nanavati College of Pharmacy in India. The editorial team connected the investigators with Dr Laura Bolton, a collaboration that resulted in an excellent scoping review summarizing 50 years of literature.
Natural and synthetic agents have been used to optimize local wound care for centuries. The authors reviewed 281 abstracts outlining 274 studies with 28,315 participants … read more
The Use of an Antimicrobial Moisture Management Dressing Paired With a Gellable Fiber Technology under a Two-layer Compression System
in the Treatment of Heavily Exudating VLUs Improves Clinical Outcomes and Cost Savings
Introduction: Chronic venous insufficiency is the 7th most common chronic disease and is the underlying cause of 95% of leg ulcers1. Venous leg ulcers (VLUs) are difficult to treat and even with proper care can take a minimum of 12 weeks to heal2. VLUs are a clinical challenge because they are notoriously heavily draining wounds. This drainage contributes to the formation of excessive bioburden, devitalized tissue, and microorganisms, all which prolong wound healing. In order to effectively manage VLU exudate it is not uncommon to change dressings 3 or more times weekly. More frequent dressing changes increase the overall cost of care and may further contribute to delayed wound healing … read more
MolecuLight i:X® Receives FDA 510(k) Clearance for the Device’s Ability to Detect Wounds Likely to Contain Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA)
New FDA Clearance Illustrates the Utility of the i:X to Reliably Predict Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a Bacterial Pathogen that Precludes Wound Healing and Often Evades Conventional Treatment Methods
TORONTO, CANADA – (September 23 2021) MolecuLight Inc., the leader in point-of-care fluorescence imaging for real-time detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial loads, announces that it has received FDA 510(k) clearance for the detection of wounds containing clinically significant levels (>104 CFU/g) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) for the previously cleared MolecuLight i:X imaging device. The i:X device visualizes fluorescence, enabling the point-of-care detection of wounds containing elevated levels of bacteria. This new FDA clearance supports the ability of the i:X device to increase the clinician’s ability to detect the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in wounds using the cyan fluorescence signal. This augmented labeling is based on a detailed retrospective statistical analysis of over 350 patients.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) is a common bacterial pathogen that precludes wound healing. PA is notorious for its intrinsic resistance to many antibiotics and its tendency to form biofilm matrices that evade antibiotics and other conventional treatment methods1. The presence of PA in wounds is associated with rapid deterioration and more severe wound outcomes 2,3. The MolecuLight i:X is the only imaging device that provides real-time information on whether a wound is likely to contain elevated levels of PA (>104 CFU/g). The i:X is becoming an essential tool for assisting in clinician decision-making regarding the assessment and treatment of wounds.
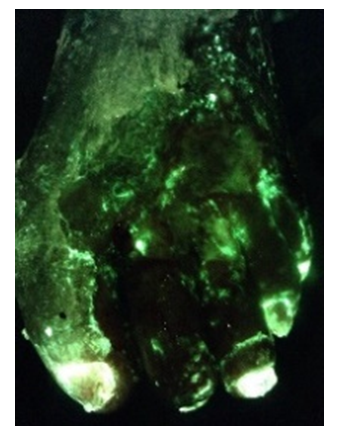
Image and video courtesy of Dot Weir
“Bacterial removal is a critical component of wound care and wound healing. The ability of the MolecuLight i:X to detect and visualize wounds containing elevated bacterial burden while we are with the patient enables a proactive and objective approach to wound management”, says Dot Weir, RN, CWON, CWS, Clinician at Saratoga Hospital Center for Wound Healing and Hyperbaric Medicine, Saratoga Springs, New York and Co-Chair of SAWC, the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care. “Wounds harboring Pseudomonas often require unique treatments. This new FDA clearance recognizes the added benefit of the i:X in visualizing and differentiating Pseudomonas aeruginosa in wounds through the cyan fluorescence signal it produces on the images. This is especially important because detecting the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at the point-of-care allows wound care professionals to act immediately to tailor our cleaning, debridement, antimicrobial strategy and treatments accordingly.”
This video showing the cleansing of a diabetic foot ulcer is an example of the MolecuLight i:X’s cyan fluorescence signal indicating the likely presence of PA. The cyan is clearly visible on the patient’s foot (see image) as well as on the gauze after cleansing, indicating that the wound contains clinically significant (>104 CFU/g) levels of PA:
Video link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5YiT4zTUL8
References
1 Raizman et al., “Rapid Diagnosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Wounds with Point-of-Care Fluorescence Imaging“, Diagnostics 2021, 11(2), 280
2Turner et al., “Requirements for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acute Burn and Chronic Surgical Wound Infection”, PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004518
3McManus et al., “Twenty-five-year review of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia in a burn center”, Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 4, 219–223
About MolecuLight Inc.
MolecuLight Inc., a privately-owned medical imaging company that has developed and is commercializing its proprietary fluorescent imaging platform technology in multiple clinical markets. MolecuLight’s first commercially released device, the MolecuLight i:X fluorescence imaging system and its accessories provide a point-of-care handheld imaging device for the global wound care market for the detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial burden (when used with clinical signs and symptoms) and for digital wound measurement. The company is also commercializing its unique fluorescence imaging platform technology for other markets with globally relevant, unmet needs including food safety, consumer cosmetics and other key industrial markets.
For more information, contact:
Rob Sandler
Chief Marketing Officer
MolecuLight Inc.
T. +1.647.362.4684
Image: Download at: https://moleculight.box.com/s/b4d44tv25dq5wr834ilx7ldiqzl1orxi
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5YiT4zTUL8
Advances in Wound Care Technology: What We See Is What We Get … and More
The science of wound care dressings has progressed a long way over the years, especially during the not-too-distant past. As recently as the early 1990s, the main dressings available to patients included transparent films, hydrocolloids, foam, and calcium alginate. Although not incredibly common, moist wound care was also utilized more than many clinicians would care to admit some 30 years later. Standard dressings at the time were wet-to-dry and betadine.
Today, dressing technology has transitioned from a passive to an active role. Yet, the sophistication of dressings that our patients enjoy today would not be possible without understanding the clinical progression that has occurred, even among those treatments that have since been abandoned … read more
Periwound Skin Management
Periwound skin management is just as important as wound bed preparation in wound healing. The goal of periwound management is to maintain an optimal moist wound healing environment while preventing skin breakdown and infection. Skin is more vulnerable in patients with certain comorbidities and conditions. Periwound skin breakdown is just one of the culprits that delay wound healing and increase pain … read more
Use of a Novel Silicone-Acrylic Drape With Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Four Patients With Periwound Skin Breakdown
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is applied using a foam dressing and an adhesive acrylic drape to create a seal. Removal of this drape can be painful and may play a role in periwound skin breakdown during dressing changes. A novel silicone-acrylic hybrid drape (HA-drape) has been developed for use with NPWT to allow for repositioning after initial placement and easier removal. Objective. This retrospective case series reports on the use of HA-drape in 4 patients who experienced periwound skin breakdown. The goal was to minimize skin breakdown while maintaining a seal on the dressing. Materials and Methods. Four patients with mild to moderate periwound skin breakdown were selected to receive NPWT with HA-drape … read more
The wound healing effect of local leukocyte platelet-rich plasma after total hip arthroplasty
A randomized controlled trial:
Rapid wound closure is important after arthroplasty procedures to prevent postoperative complications. Platelets are rich in growth factors and leukocytes contribute to innate immunity. We hypothesized that topical leukocyte platelet-rich plasma (L-PRP) derived from the blood of patients would be beneficial to wound healing. In this randomized controlled trial, patients subjected to elective total hip arthroplasty (THA) were assigned by concealed allocation either L-PRP application onto the sutured fascia or no application (control) after the THA intervention. In addition, all patients received 1.5 g protein/kg, 5 g L-arginine, 500 mg vitamin C and 44 mg zinc daily over the 4-week postoperative period to obtain optimal nutrition. The primary endpoint was complete healing of the skin incision. The secondary endpoints were blood transfusions, length of hospital stay, pain and wound infections. Sixteen patients in the L-PRP group and 17 patients in the control group completed the trial. L-PRP treatment accelerated complete wound healing after 3 weeks (seven in the L-PRP group vs. zero in the control group, p = 0.003) and after 4 weeks … read more
From PMC: Current Clinical Recommendations for Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma
The ISWCAP and ASEAN wound conference 2021
The ISWCAP and ASEAN wound conference was held online on the 19–20 June 2021. Over the two-day programme the 434 participants saw 22 lectures and plenary sessions along with sponsored lunch symposia.
The chair of the organising committee Prof. Dr. Harikrishna K.R.Nair gave the opening address for what he described as “An inspiring two days, with a wealth of knowledge shared among the wound care family”. There were updates from Gulnaz Tariq on the World Union of Wound Healing Societies (WUWHS) events and Karen Ousey on behalf of the International Wound Infection Institute (IWII), along with sessions on diabetic foot ulcers, amputation, surgical site infection, oxygen therapy and much more. It was a truly international event with both speakers and delegates from Europe, North America, South America mainly Brazil, South Africa and Asia.
Recordings of that day will be uploaded onto the Malaysian Society Of Wound Care Professionals (MSWCP) website www.mswcp.org
EWMA Journal of Wound Management
July 2021 issue of the Journal of Wound Management. Official journal of the European Wound Management Association
This issue of the Journal of Wound Management includes seven original manuscripts. the full issue can be accessed here: Journal of Wound Management. No 22, vol. 2, July 2021
One Podiatrist’s Experience With A Novel NMES Device For Patients With PAD
In previous articles, I have written about medicine having endless career opportunities. One opportunity in the medical field is that to evaluate and potential provide feedback on an array of products or medical devices, in hopes of participating in the betterment of patient care. To me, advising on new innovations is always an exciting time because I believe becoming aware of the latest and cost-efficient technology to aid my patients with pain relief, healing, or even improved quality of life is imperative.
In recent months, I had the unique opportunity to trial a circulation booster device for the legs and feet … read more
Innosphere re-ups with diabetic ulcer gel developer
Innosphere Ventures Fund bought in again on GelSana Therapeutics Inc. An earlier backing funded product development for the start-up’s therapeutic gels … This second seed-stage buy-in will accelerate research work, prepare a U.S. Food and Drug Administration submission and begin to build a pipeline of products … GelSana’s hydrogels aim to improve healing of diabetic ulcers and other wounds: closing cuts and sores faster, growing stronger skin and enabling controlled delivery of healing therapies … A product prototype was aimed at diabetic foot ulcers but “we believe the unique properties of GelSana’s hydrogels may have much larger applicability in wound healing,” founder and CEO Melissa Krebs said … read more
Wound Care Advantage and Swift Medical Announce Partnership
Wound Care Advantage, the nation’s leading wound care consulting firm and Swift Medical, the global leader in digital wound care, announces a new strategic partnership.
Wound Care Advantage (WCA) , the nation’s leading wound care consulting firm and Swift Medical, the global leader in digital wound care, announces a new strategic partnership that brings Swift Medical’s advanced wound imaging platform to WCA’s Network hospitals to enhance their collective impact on the wound care industry.
Swift Medical’s technology platform will be integrated into the WCA network of tools and resources that empower hospitals to run successful wound care programs. Swift Medical’s technology connects directly with hospital EHR systems to enable seamless clinical workflows, such as advanced wound imaging, documentation and analytics.
“We are very pleased to partner with Swift Medical to bring their wound imaging technology to our wound centers,” says Melissa Bailey, President of Wound Care Advantage. “Our hospital partners are looking for continuum solutions and the introduction of Swift’s wound imaging platform into the WCA Network is an effective tool that compliments the operational expertise we provide.”
Expert EWMA group highlight need for investment in maternity services research
“Investment in maternity services research is essential for our understanding of the extent of wound-related complications for the postpartum mother and improved clinical pathways for wound management,” write Charmaine Childs (Sheffield Hallam University, Sheffield, UK), Kylie Sandy-Hodgetts (University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia), and colleagues in an evidence-based consensus document for healthcare workers published by the European Wound Management Association … read more
Bacterial Biofilm Destruction: A Focused Review On The Recent Use of Phage-Based Strategies With Other Antibiofilm Agents
Biofilms are bacterial communities that live in association with biotic or abiotic surfaces and enclosed in an extracellular polymeric substance. Their formation on both biotic and abiotic surfaces, including human tissue and medical device surfaces, pose a major threat causing chronic infections. In addition, current antibiotics and antiseptic agents have shown limited ability to completely remove biofilms. In this review, the authors provide an overview on the formation of bacterial biofilms and its characteristics, burden and evolution with phages. Moreover, the most recent possible use of phages and phage-derived enzymes to combat bacteria in biofilm structures is elucidated. From the emerging results, it can be concluded that despite successful use of phages and phage-derived products in destroying biofilms, they are mostly not adequate to eradicate all bacterial cells. Nevertheless, a combined therapy with the use of phages and/or phage-derived products with other antimicrobial agents including antibiotics, nanoparticles, and antimicrobial peptides may be effective approaches to remove biofilms from medical device surfaces and to treat their associated infections in humans … read more
Managing the Surge: Delayed Chronic Wound Care During COVID-19
A growing body of research, as well as first-hand accounts from clinicians on the ground, indicate that a significant percentage of patients with chronic wounds have delayed preventative and emergent wound care during the COVID-19 pandemic.1 While it will take time to assess the full impact of these trends, existing evidence suggests delayed wound care can result in more severe infections, increased hospital admissions, and lead to more amputations.2 Therefore, it will be critical for providers, hospitals, outpatient departments, payers and policymakers to understand and plan for a surge in patients with untreated and unmanaged non-healing wounds and related acute-on-chronic complications as a result of delayed care during the COVID-19 pandemic … read more
Examining the Science of Chronic Wounds and the Leading-Edge Approach to Elevating Early Wound Care
Drs. Randall Wolcott and Andrew Rader host a discussion on the persistence of wound chronicity without early combination treatment strategies and review recent compelling data to support the need to change the status quo of early wound care … Register
Medical Device-related Pressure Injuries Associated With Electroencephalogram Leads in a Tertiary Care Children’s Hospital
Medical device-related pressure injuries (MDRPIs) present a substantial safety risk for children who are hospitalized. PURPOSE: This study aimed to describe patient and clinical characteristics of children who develop MDRPIs related to electroencephalogram (EEG) leads, determine risk factors associated with their development, and determine if there are common risk factors that can lead to actionable strategies to reduce MDRPIs related to EEG leads. METHODS: A retrospective review was completed of the electronic health records of all 3136 children who had EEG lead placements between January 1, 2014, and April 16, 2018, at a large tertiary care children’s hospital. Data abstracted included demographic variables, patient and pressure injury characteristics, as well as length of stay. RESULTS: Twenty-four (24) of the 3136 children (0.8%) developed an MDRPI. Most were stage 2 pressure injuries. Patients who developed a pressure injury were significantly younger than patients who did not (median age, 0.9 and 5.2 years … read more
Closure of a Difficult-to-Manage Chronic Pressure Injury with the Use of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma
Pressure injury (PI) corresponds to a skin damage of ischemic aetiology that affects the integrity of the skin and is produced by prolonged pressure or friction between a hard internal and external surface. Treatment can be challenging when there is no resolution with usual care. The use of autologous platelet-rich plasma (APRP) gel arises as a therapeutic possibility in the presence of chronic pressure injuries. The case of a patient with chronic PI who has been treated with APRP is presented, achieving resolution of the lesion … read more
Improving patient outcomes with medical technology
An ideal healthcare system cures every type of medical condition an individual may have. However, healthcare professionals have always had to judge whether they can cure a patient or simply manage their condition to provide a better quality of life.
Many pharmaceutical interventions and treatment options are designed to manage people’s illnesses, not necessarily cure them. This increases the cost of healthcare – particularly as people live longer and the proportion of illnesses that are manageable rather than curable increases – as do the requirements for long-term care.
Some conditions have proven particularly hard to cure, such as diabetes and high blood pressure, leaving no choice but to manage and monitor a condition across an extended period. However, this is costly and poses many challenges to medical and clinical resources … read more
Use of social media in medicine: the future – Webinar
This free-to-attend CPD webinar has been organised by British Journal of Hospital Medicine, supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Cook Biotech, Inc, West Lafayette, IN, USA.
In this webinar, the presenters will share their tips and insights into how healthcare professionals can make the most of social media platforms to share and learn new skills. They will also provide guidenace on the potential risks and how to avoid pitfalls.
*** This webinar is CPD certified and all attendees will receive a personalised CPD certificate sent by email after the session.***
The Frank & Lizzie Show: Episode 007, Dr. Marc “Dutch” Matthews
On this episode, Frank & Lizzie sit down with Dr. Marc “Dutch” Matthews from the Arizona Burn Center to discuss his experience with Vashe, a hypochlorous acid preserved wound cleanser solution. Dutch explains how this pH skin neutral wound solution has helped changed his practice for the better, but more importantly the lives of his patients.
A NOVEL APPROACH TO TREATING HARD-TO-HEAL WOUNDS
OUR INNOVATIVE WOUND THERAPY IS DESIGNED FOR OUTPATIENT SETTINGS
Stiehl Tech is a medical device company focused on creating innovative surgical products for both outpatient and inpatient settings.
Selective Mechanical Debridement
Our Perilav wound irrigation system adapts time-tested surgical debridement methods for the outpatient setting. We make it easier for nursing home staff or home health providers to treat wounds in a more comfortable patient setting. Our unique treatment enclosure bags make a standard treatment safer and simpler by containing fluid and wound debris in an easily disposable bag … read more
UA Surgeon Armstrong Urges New Focus on Diabetic Ulcers
Remission — rather than repair — needs to be the goal of treatment, according to Dr. David Armstrong, whose report on diabetic foot ulcers appears in the New England Journal of Medicine … Foot ulcers are a prevalent complication for millions of people with diabetes. Estimates indicate that as many as one-third of people with the disease will develop at least one foot ulcer over the course of their lifetime. These wounds can lead to further complications such as strokes, heart attacks, infections, loss of limbs and premature death … read more
Lipodystrophy, a Common Risk in Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Patients with lipodystrophy have a high risk of diabetic foot ulcers, especially in the younger population.
Lipodystrophy is a disorder characterized by an abnormal fat distribution in the body. It can refer to an irregular loss or accumulation of fat tissue, and can even cause macrovascular and microvascular complications. Diabetic foot ulcers are a chronic complication of diabetes that can cause loss of lower limbs from amputations. DFU is also a risk factor in diabetes-related mortality. Previous studies have not found a correlation between lipodystrophy and DFU or even a treatment to reduce these complications. Lipodystrophy is a complication caused mainly by familial partial lipodystrophy. This study used an observational retrospective cohort study to understand the correlation between these two disorders, lipodystrophy and diabetic foot ulcers, and which age was the most critical … read more
RedDress Announces Distribution Agreements in 12 European Countries
Ponte Vedra Beach, Sept. 20, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — RedDress, a privately held U.S. and Israel-based wound care company, announced today strategic agreements in 12 European countries to distribute its innovative CE-marked wound care solution for exuding cutaneous wounds, ActiGraft® system, throughout Europe.
“We are proud to announce our expansion into Europe,” said Alon Kushnir, CEO of RedDress. “Our distribution partnerships in these key areas enable us to deliver our innovative solution in one of the world’s leading wound care markets and will accelerate our growth globally. We are looking forward to providing Europeans with an effective alternative treatment modality as a solution for their hard-to-heal chronic wounds.”
These strategic distribution agreements support RedDress’ global mission to improve the health and lives of patients around the world living with chronic wounds by expanding access to ActiGraft in several European countries:
Austria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Germany, Greece, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Switzerland, Turkey, and Ukraine
Measurement properties of quality of life instruments for adults with active venous leg ulcers: a systematic review protocol
Objectives The primary objective is to identify instruments used to measure quality of life (QoL) in studies of people with active venous leg ulcers (VLUs). The secondary objective is to map the qualities of each instrument to make recommendations for clinical practice and future research.
Introduction VLUs have a negative impact on patients’ QoL. Prolonged healing and frequent recurrence leads to pain, prolonged disability and psychosocial morbidity. Accurate measurement of QoL can optimise the evaluation of VLU treatments and guide clinician and patient decision-making … read more
Researchers explore promising treatment for MRSA ‘superbug’
A new Cornell study has found the antimicrobial properties of certain stem cell proteins could offer a potential treatment to reduce infection in skin wounds.
Treating wounds with the secretion of a type of stem cell effectively reduced the viability of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus – better known as MRSA – according to a new study from researchers at the Baker Institute for Animal Health, part of the College of Veterinary Medicine (CVM). Moreover, the secretion stimulated the surrounding skin cells to build up a defense against the bacterial invader, the researchers found … read more
The History and Effectiveness of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy – Part One
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) uses controlled negative pressure to remove fluid from open wounds. This is done through a sealed or foam dressing connected to a vacuum pump and canister1. Closed-system negative pressure is relatively new in modern medicine and will continue to evolve for better patient outcomes.
Although NPWT has increased in utilization over the past decade due to positive results and data showing its effectiveness in healing many acute and chronic wounds, it has potential for even more growth and innovation … read more
Microneedle patch penetrates biofilms to treat chronic wounds
Chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers can be very difficult to treat, partially because of antibiotic-resistant “biofilms” that form over the affected tissue. A new type of microneedle patch, however, has been shown to deliver medication through such films … Bacterial bioflms are made up of colonies of bacteria that stick together by building up a slimy polymer matrix. Unfortunately, topically applied antibiotics and other medications have difficulty penetrating that matrix, so they can’t reach the infected tissue underneath … read more
Next Science: Products that help treat wounds
Founded by scientist Matthew Myntti, the company develops products to reduce biofilm-based infections, which can be fatal.
As a scientist at Medtronic’s Jacksonville office working on chronic infections, Matthew Myntti said he began to understand the life-threatening nature of chronic wounds, and the infections that come with them.
He left the medical technology company in 2012 to start his own research focused on treating chronic wounds and keeping them from becoming infected … read more
“Elephant-trunk” negative pressure wound therapy for fixing artificial dermis with basic fibroblast growth factor for critical limb ischemia
INTRODUCTION: The treatment of intractable toe ulcer with critical limb ischemia (CLI) is a challenge because of its poor blood flow and the wound. Here, a novel fixation technique for artificial dermis with negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) was reported.
METHOD: After the amputation of toe, artificial dermis made of collagen-gelatin sponge (CGS) was grafted onto the wound where human recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) was sprayed. The foot was put on adhesive iodine-impregnated drape, the artificial-dermis area was covered with a sponge dressing of which another end reached to the drape, and the vacuum port was applied on the dressing sponge sandwiched with two drapes … read more
Rates of T1D-Related Amputations Decline in Sweden
Results of a Swedish retrospective cohort study showed reduced rates of type 1 diabetes-related amputations over the past 2 decades.
In recent years, Sweden has seen a sharp decline in incidence of lower-level extremity amputations among individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D), according to results of an observational cohort study. Findings were published in Diabetologia.
Because diabetes-related foot ulcers are common and healing is often delayed, limb loss through amputation “is not an infrequent final outcome,” the authors explained.
In addition, “about half of all nontraumatic amputations in the western world are attributable to diabetes … read more
The Hemostatic and Wound Healing Effect of Chitosan Following Debridement of Chronic Ulcers
Chitosan has been proven to be helpful in wound care as a hemostatic agent. The hemostatic effect is due to the positively charged chitosan interacting with negatively charged red blood cell membranes, initiating the agglutination of red blood cells and platelets. This promotes the activation of thrombin, which activates the clotting pathway, leading to thrombus formation. Objective. Based on the properties of chitosan as a rapidly acting hemostatic agent, the authors sought to determine if a chitosan gelling fiber wound dressing could control bleeding of freshly debrided wounds. The effect of the chitosan dressing on overall healing and patient and provider satisfaction was also evaluated. Materials and Methods. Wounds of any etiology requiring sharp debridement in patients older than 18 years who were capable of consent were eligible. Wounds were sharply debrided by curettage … read more
Swift Medical’s new imaging platform expands the digital wound care company into decentralized trials
Digital wound care company Swift Medical launched Swift Scientific, a digital imaging platform to support decentralized clinical trials.
The platform allows for large-scale image collection and management so researchers can monitor the effects of medical interventions at a multisite trial or from study participants’ homes.
Swift’s product, Swift Skin and Wound, is an AI-enabled platform that lets patients or providers capture high-precision images of skin conditions or injuries with a smartphone. It tracks disease progression and healing, and allows for remote communication and data sharing … read more
Wound Week 2022 | Call for abstracts
All abstracts for the Wound Week 2022 must be submitted electronically via the online platform: www.abstractscorecard.com
Hosted by the American Professional Wound Care Association (APWCA), Wound Week 2022 provides attendees with an innovative, unparalleled educational opportunity that will feature superior content delivered by multidisciplinary faculty with clinical expertise in the field of wound healing/care. Presenting your scholarly work at the APWCA Annual meeting will showcase your knowledge and dedication to discovery in wound care in front of a prestigious audience … read more
Antibacterial nanozymes: Healing chronic wounds with nanochemistry
Chronic infected wounds are often highly problematic for diabetic patients. However, a team of Chinese researchers has now developed a targeted approach to wound healing that makes use of nanomedicine, and their research has been published in the journal Angewandte Chemie. The researchers were able to deactivate wound-infecting bacteria using a solution of nanocapsules that alter the wound environment and unleash reactive oxygen species … read more
Evaluation & Management vs. Hospital Owned Outpatient Provider-Based Department Clinic Visits
If you had an opportunity to listen to the webinar entitled “2021 Mid-Year Reimbursement Reports: A Live Discussion Series,” that Jolayne Devers and this author presented on July 28, 2021, you know that the topic was Wound Care Audits Have Resumed: Are You Prepared? The attendees submitted many excellent questions during the webinar and sent many more emails to this author following the webinar. To accommodate the high volume of questions, this author promised to address the topics and questions in this and future Business Briefs columns.
One of the topics that generated many questions and follow-up emails was “Physician/qualified healthcare professional (QHP) evaluation & management (E/M) services are different than hospital owned outpatient wound/ulcer management provider-based department … read more
Abstracts from the Amputation Prevention Symposium (AMP) August 11-14, 2021
An Endovascular Approach as a Backup for Open Surgery After Corynebacterium striatum Vascular Graft Infection
Gabriel C. Inaraja-Pérez, MD, PhD, FEBVS; Manoela Oliveira Brito, MD; Alejandra Bartolomé Sánchez, MD; Daniela Acuña Paz y Miño, MD; Eva María Martin Herrero, MD, PhD; Jose-Manuel Buisán-Bardají, Prof. MD; Jorge Coghi Granados, MD
A Hybrid Approach to ALI Utilizing Penumbra Aspiration Thrombectomy in Conjunction With Catheter-directed Thrombolysis
Emily M. Rey, DO; Ganesh Arun, DO; Kristian O. Hochberg, MD; Sang Lee, MD
Cost-Effectiveness of Office-Based Labs for Treating Peripheral Arterial Disease
Morish Shah; Ashish Chaturvedi, BS; Paramjit S. Chopra, MD; Manasvi Paudel, BS; Kashish Shah
Hybrid Approach for Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia: A Case Report
Vincent Demesmaker, MD; Arnaud Kerzmann, MD; Evelyne Boesmans, MD; Vlad Alexandrescu; Jean-Olivier Defraigne
Observations Regarding the Effect of COVID-19 on Amputations Performed in a Tertiary Referral Health System
Dayle K. Colpitts, DO; Richard F. Neville, MD, FACS, DFSVS; Arkadii Sipok, PhD; Anthony Comerota, MD, FACS
Salvage of Popliteal-Dorsalis Pedis Bypass: A Case Series
Crystal James, MD; Denise Alabi, BA; Mabel Chan, MD; So Park, MD; John C. Lantis, II, MD
PRELUDE BTK vs. POBA Analysis: Serration Angioplasty and POBA
Marianne Brodmann, MD
Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Pressure Injuries: How Do You Tell the Difference?
In evaluating a patient with a wound on the foot, a question that often comes to mind is whether that wound is caused by pressure, diabetes mellitus (DM), ischemia, trauma, or a combination. For example, a patient with DM who happens to have an ulcer on the foot may have a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) or possibly something else. One of the bigger challenges that many clinicians face is trying to determine the etiology of a foot ulcer. There has been a great deal of debate about DFUs and pressure injuries (PIs) on the feet of patients in terms of how to appropriately assess, classify, and treat them. The confusion and lack of evidence in differentiating between these two types of foot ulcers, particularly on the heel, can lead to misdiagnosis, which can increase both financial and patient-related costs … read more
AOFAS Annual Meeting, September 22-25 Charlotte, North Carolina
AOFAS President, Bruce E. Cohen, MD, invites you to AOFAS Annual Meeting, September 22-25, for the premier meeting for foot and ankle education that gives you the choice between attending in person in Charlotte, North Carolina, or virtually. Learn more: https://aofas.org/annualmeeting
World Union of Wound Healing Societies (WUWHS) announces Congress Postponement
Professor Marco Romanelli and Gulnaz Tariq, President and President Elect of WUWHS have announced the postponement of the forthcoming Congress to 1-5 March 2022. With concerns around the availability of travel and the wish for the organisers not to divert attention of busy HCPs from their own local facilities during the Covid-19 pandemic, they have taken the difficult decision to postpone … read more
Enhancing Pressure Injury Prevention Strategies Based on New Technology: From Learning More to Doing Better
he med-surg health care environment is constantly changing, driving complexity in care. The most recent findings from the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services state that pressure injuries develop in nearly 2.5 million patients annually, representing 8.3% of hospital admissions; the resulting financial burden for care is estimated to be between $3.3 and $11 billion annually.1 Although most occurrences of hospital-acquired conditions sharply decreased between 2010 and 2017, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality reported that pressure injuries increased by 6%.2
Pressure injuries develop when there is localized damage to the skin or underlying tissues due to pressure—and sometimes combined with shear—that impacts the skin’s ability to provide oxygen and nutrients and remove waste byproducts … read more
Koya Medical and Essity Sponsor Forum for Physicians, Lymphedema Therapists and Researchers to Discuss Health Effects of Space Travel
Koya Medical, a transformative healthcare company focused on developing breakthrough treatments for lymphedema and venous diseases, and Essity, a leading global hygiene and health company that has as history of supporting space travel through the manufacturing of compression suits for astronauts, are sponsoring a forum to highlight the importance of venous and lymphatic health for space travel. The event takes place October 8, 2021 at the 35th annual congress for the American Vein & Lymphatic Society (AVLS).
The unique environment of space travel – reduced gravity, radiation exposure, varying atmospheric conditions, and the mental and physical stresses – imposes many challenges to human physiology and adaptability. The current goal is to create “nominal human function,” to extended safe habitation and exploration in space, and to ensure that humans thrive and quickly recover upon returning to Earth’s “1G” environment. For more than 50 years, NASA’s Human Research Programs have studied the intricacies of the human body in the weightlessness of space. Understanding the effects of spaceflight on humans is essential, and NASA and its European, Japanese, Russian and Australian colleagues have been particularly interested in investigating how the body reacts to long-duration spaceflight as the agency plans for extended missions on the Moon and Mars … read more
Predictors of Foot Ulcers Among Diabetic Patients at a Tertiary Care Center, Egypt
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a major public health problem worldwide and is considered one of the main global health emergencies of the 21st century.1 The prevalence of DM is increasing in both developed and developing countries, recent estimates indicate that there were 463 million adults living with diabetes in 2019 which is projected to increase to 642 million in 2040.2,3 In the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region, the number of patients with diabetes is expected to increase from 34.6 million in 2013 to 67.9 million by 2035.2 The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) classified Egypt among the top 10 countries in the world with the highest prevalence of diabetes, where about 9 million adults between 20 and 79 years of age were living with DM in 2019. The number of patients with DM in Egypt has increased rapidly from about 4.5 million in 2007 to 7.5 million in 2013, and is expected to increase to 13.1 million by 2035.4 … read more
Wound Management of Venous Leg Ulcers in the Right Lower Extremity Limb
A 68-year-old male presented for care with lymphedema and multiple, copiously draining ulcerations on the right lower extremity (Figure 1). Symptoms were present for years and failed to respond to compression, foam dressings, or abdominal pads. Previous medical history included hypertension requiring use of anti-hypertensive medication … read more
Challenges faced by doctors and nurses in wound care management during the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey and their views on telehealth
AIM: This study aimed to determine the problems faced by physicians and nurses dealing with chronic wound care during the COVID-19 pandemic and their views on telehealth.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A descriptive and cross-sectional design was used in this study. The sample comprised physicians (n = 74) and nurses (n = 271) interested in chronic wound care. Data were collected through a questionnaire form consisting of open- and closed-ended questions … read more
Wounds UK Annual Conference | 8–10th November
this year’s Wounds UK Annual Conference will take place from 8–10th November with the ultimate goal to embrace the opportunity to connect, collaborate and learn in person. The sessions over the 3 days have been especially developed to have a greater emphasis on interaction and networking.
The programme will be diverse and will include updates from the National Wound Care Strategy Programme, tools for learning, patient engagement and shared care planning, and updates on the current science and terminology of healing. After the conference, you will return to your clinical settings armed with solutions to problems and campaigns for improving delivery of care … read more
The Analgesic Benefits of Ketorolac to Local Anesthetic Wound Infiltration Is Statistically Significant But Clinically Unimportant
A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Objective: Even though ketorolac-infiltration is said to provide superior postoperative analgesic benefits in different surgical procedures, its safety and efficacy remain to be validated because of the lack of high-quality evidence. We aimed to summarize the efficacy and safety of ketorolac-infiltration based on published randomized-controlled trials (RCTs) … read more
Surgical wound dehiscence Improving prevention and outcomes
Surgical wound dehiscence (SWD) is a significant issue that affects large numbers of patients and
is almost certainly under-reported. The impact of SWD can be considerable: increased mortality,
delayed hospital discharge, readmission, further surgery, delayed adjuvant treatment, suboptimal
aesthetic outcome and impaired psychosocial wellbeing … download PDF
Combined Regenerative Approach for a Complex Lower Extremity Wound
More than 400 million patients worldwide are affected by diabetes; over their lifetime, at least 25% will develop foot ulcers that often result in high rates of nonhealing wounds and amputation. The authors present the case of a 43-year-old female patient with multiple comorbidities who presented with a large (8 cm x 4 cm), noninfected, hindfoot plantar ulcer that extended down to the bone and calcaneus. Over 2 weeks, the patient was successfully treated using a combination of an acellular dermal matrix, nanofat grafting, and negative pressure wound therapy, lessening the effects of the ulcer on the patient’s quality of life and achieving limb salvage. Utilizing the regenerative procedures described herein may improve patient care and decrease costs … read more
History and Physical as the Best Diagnostic Tool for the Wound Care Clinician
This chapter is an excerpt from Chapter 8: Wound Assessment by Monica Stout and Jayesh Shah, Wound Care Certification Study Guide 3rd Edition, (Best Publishing Company, 3rd quarter, 2021), and Chapter 8: Wound Assessment by Dr. Jayesh Shah, Wound Care Certification Study Guide 2nd edition, Best Publishing Company, 2016. Reprinted with permission of Best Publishing Company.
Even with the technological innovations of the 21st century, history taking still remains the best diagnostic tool and least expensive tool to make a good diagnosis. Recognizing clues from a patient’s history can give important information about the patient’s wound … read more
COVID-19 Skin Manifestations | A Guide for WOC Nursing Practice
The COVID-19 pandemic has created unique challenges for WOC nursing practice. Clinicians have identified skin manifestations on or near the bony prominence that are atypical of classic pressure injury among persons diagnosed with COVID-19. In some cases it may be difficult for the clinician to initially discern COVID-19 related skin manifestations from other etiologies … read more
Reducing the incidence and severity of pressure injuries in a high level care residential aged facility: a quality improvement project
Aims Reduce pressure injuries (PIs) in residents of a high level care facility by increasing staff knowledge and skills through clinical support and a skin integrity education package.
Method This project was a quality improvement (QI) activity and data were de-identified and reported in aggregate. Pre- and post-implementation data included staff knowledge testing and PI prevalence and severity.
Results Pre-implementation data indicated that staff knowledge was very limited, skin inspections and PI risk assessment were not performed, and use of pressure redistribution devices was low, with point prevalence at 64% of mainly severe PIs. Despite ongoing external clinical … read more
New Insights on Wound Healing Unraveled
Despite advancements in treating wounds, the molecular mechanisms behind wound healing is not fully understood. Now, researchers at the University of California, Irvine (UCI), have identified a new molecular pathway that promotes wound healing in the skin. Their findings could even play a role in nonhealing wounds.
Their findings are published in the journal JCI Insight in a paper titled, “GRHL3 activates FSCN1 to relax cell-cell adhesions between migrating keratinocytes during wound reepithelialization.”
“The migrating keratinocyte wound front is required for skin wound closure. Despite significant advances in wound healing research, we do not fully understand the molecular mechanisms that orchestrate collective keratinocyte migration,” the researchers wrote. “Here, we show that, in the wound front, the epidermal transcription factor Grainyhead like-3 (GRHL3) mediates decreased expression of the adherens junction protein E-cadherin; this results in relaxed adhesions between suprabasal keratinocytes, thus promoting collective cell migration and wound closure.” … read more
EZ Debride is Now Available in Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, and Bruni
SAN ANTONIO, Sept. 2, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — EZ Debride, a registered and patented brand of MDM Wound Ventures Inc. developed and manufactured out of San Antonio and Kerrville, Texas, is announcing the distribution agreement with UCT Medical Co Ltd. Seoul, South Korea.
“At Intega Healthcare, we are excited to partner with MDM Ventures to introduce EZ Debride to our customers. EZ Debride is an innovative product that will offer clinicians an option to safely remove non-viable tissues with precision and minimal discomfort for patients. EZ Debride complements our innovative Wound Care Portfolio that comprises cellular-therapy & regenerative-tissue treatments, advanced wound care, surgical, and wound closure range. The partnership with MDM is allowing us to offer our clinicians a complete set of products and services which expands their patient treatment options.” Rebecca Ng, Business Development and Operations Director at Intega Healthcare … read more
The Clinical Role in Antimicrobial Resistance and Best Practices for Prescribing Antibiotics Podcast
In this podcast, Laura Swoboda, DNP, APNP, FNP-C, CWOCN-AP, discusses how clinicians should be mindful of their role in antimicrobial resistance and commit to responsible prescribing practices … listen
Surgical treatment of pressure injuries in children: A multicentre experience
Pressure injuries (PI) are infrequent in paediatric patients, prevalence estimates ranging from 1.4% to 8.2%, and reaching values as high as 43.1% in critical care areas. They can be associated with congenital neurological or metabolic disorders that cause reduced mobility or require the need for medical devices. In children, most pressure injuries heal spontaneously. However, a small percentage of ulcers that is refractory to conservative management or is too severe at presentation (Stage 3 or 4) will be candidates for surgery. We retrospectively reviewed the clinical history of paediatric patients affected by pressure injuries from four European Plastic Surgery Centres. Information was collected from clinical and radiology records, and laboratory reports. An accurate search of the literature revealed only two articles reporting on the surgical treatment of pressure injuries in children. After debridement, we performed surgical coverage of the pressure injuries. We report here our experience with 18 children aged 1–17 years, affected by pressure injury Stages 3 and 4. They were successfully treated with pedicled (17 patients) or free flaps (1 patient). The injuries involved the sacrum … read more
Physical activity, sleep and wound healing in adults with venous leg ulcers: a prospective observational cohort pilot study protocol
Background Adults with venous leg ulcers (VLUs) are less likely to be physically active and show greater sleep disturbances than the general population. Limited evidence suggests these issues contribute to VLU healing delays.
Objectives The primary objective is to determine if physical activity (PA) and sleep levels are associated with VLU healing. The secondary objectives are to: 1) evaluate the feasibility and acceptability of a wrist-worn accelerometer device, wActiSleep-BT device wear (ActiGraph); 2) evaluate the utility of self-reported PA instruments to measure PA for people with VLU; and 3) determine whether PA and sleep levels are associated with i) delayed healing, ii) self-reported quality of life (QoL) and/or iii) self-reported VLU pain … –
The Biomechanics of Diabetic Foot Amputation
According to the International Diabetes Federation, approximately 463 million adults live with diabetes mellitus (DM), a number projected to increase to 700 million by 2045; a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) will occur in about 15% of that population. Multiple factors contribute to the development of those wounds including diabetic peripheral neuropathy, biomechanical imbalances, trauma, and peripheral vascular disease. In addition, 85% of all lower limb amputations in patients with diabetes are preceded by a DFU resulting in significant biomechanical challenges for these patients, many of who never become ambulatory again. Prior to surgical intervention, patients come with inherited and acquired biomechanical imbalances or weaknesses such as equinus, severe pronation/supination, mid and forefoot deformities, and muscle weakness unrelated to their other diseases. Surgeons may not take these into consideration when making decisions about amputation level … read more
A Few Notes on Caring for the Diabetic Foot
Monique Abner, MD, CWSP, shares a song she wrote to help patients with diabetes care for their feet and prevent complications.
watch video
Low-cost sensors rapidly detect infections in wounds
Low-cost, screen-printed carbon sensors have been used to rapidly detect bacteria commonly found in wounds, which could pave the way for a real time medical device.
A study carried out by the University of Strathclyde and NHS Ayrshire & Arran used sensitive portable electrochemical sensors, which detected infections in clinical samples within half an hour, much quicker than current hospital laboratory testing.
The detection of infection in clinical practice can be expensive and … read more
The Healing Power of Oxygen, by Dr. Joseph P. Cavorsi
Oxygen is an abundant chemical within our atmosphere that is essential for most living things. Everyone associates oxygen with breathing and the lungs, but the process goes far beyond. All cells in the body need oxygen to create energy to live. Inadequate oxygen delivery to the cells can lead to dysfunction of the cells, contributing to many disease states, and in severe cases may lead to cell death … read more
Innovation Medical Group Selects SnapshotNIR to Visualize Wound Healing in Advanced Wound Care
ent Imaging is pleased to announce that Innovation Medical Group (formerly Utah Foot and Ankle), in Salt Lake City, Utah, has selected SnapshotNIR as a standard of care throughout their clinical network.
Innovation Medical Group provides unique, advanced wound therapy for a wide variety of foot and ankle conditions including diabetic foot and wound care. SnapshotNIR provides physicians at their clinics the ability to conduct rapid wound assessments, allowing for more accurate healing trajectory predictions, the potential to mitigate risks early and improve clinical outcomes. SnapshotNIR provides a tracked and documented assessment of tissue viability and wound healing, supporting the responsible use of appropriate advanced wound care modalities and monitoring the therapeutic benefit.
“Understanding the wound is the first step to healing,” states Dr. Doug Toole. “Tissue oxygenation values are not detectable through the unaided eye or with traditional perfusion imaging … read more

Omeza Receives FDA Clearance for Omeza® Collagen Matrix
First Drug Device Combination of Its Kind for Chronic Wound Care Sarasota, FL, September 2, 2021 — Omeza, a skin science company, announced today the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cleared Omeza® Collagen Matrix through the FDA 510(k) premarket notification process. Omeza® Collagen Matrix is Omeza’s first Rx product, and the first drug/device combination…
HMP Global Announces Keynote Speaker for October Symposium on Advanced Wound Care
HMP Global recently announced world-renowned fetal pediatric surgeon Oluyinka Olutoye, MD, PhD will deliver the Keynote Address during the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC Fall), taking place October 29-31, 2021 in Las Vegas, Nevada. In a session focused on Research, Discovery & Innovation on Friday, October 29, 2021 at 9:10 AM PDT, Dr. Olutoye’s address will combine inspiration with critical insight, and detail how his early research evolved to clinical care and brought fetal wound healing to the field … Dr. Olutoye first achieved international recognition in 2016 after successfully completing an unprecedented operation on a baby-in-utero. Under Dr. Olutoye’s leadership, a team of 21 doctors removed a sacrococcygeal teratoma from a baby’s tailbone, establishing Dr. Olutoye as an innovator and difference-maker in the surgical field. His groundbreaking work and specialized clinical expertise in fetal and neonatal surgery has yielded promising research on the role of the inflammatory response in scarless fetal wound healing and in-utero correction of severe congenital malformations.
To learn more and register for SAWC Fall visit sawcfall.com.
Study finds sharp fall in amputations among people with type 1 diabetes
Amputation in type 1 diabetes is becoming relatively less common in Sweden. The rate has fallen by just over 40 percent over an approximately 20-year period, a University of Gothenburg study shows.
The results, published in the journal Diabetologia, are based on registry data on 46,088 people with type 1 diabetes in the years 1998–2019. The study involved linking data from the Swedish National Diabetes Register, the National Patient Register, and a couple of other Swedish national registers … read more
The Benefits of Merging Medical Care and Technology
Technology is always advancing, and it is one industry that never stands still. Another industry that is constantly pushing boundaries too is the medical or healthcare industry. Merging two industries to ensure high rates of success is essential. When you look at the advantages of merging technology with medical care and medical treatment, you realize that the potential is limitless and endless … For example, wound care is an area where little has changed over recent years. However, this may be something that can change with the introduction of the silicone-covered wound dressing, which enables cleaner and faster healing for certain types of wounds. These dressings can be changed even easier and quicker, which is, of course, beneficial to those changing, and cleaning up wounds, in any healthcare setting … read more
A novel macrophage-regulating new drug has shown promise in treating diabetic foot ulcers according to the latest issue of article ….
Accumulating scientific evidence has revealed that targeting macrophage phenotypes might be a potentially effective therapy in DFUs because hyperglycemia increases the ratio of proinflammatory M1 to pro-regenerative M2 macrophages. This study is the first international Phase 3 randomized clinical trial of an investigation drug able to regulate M1/M2 macrophage activities in the patients with diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). The investigational compound has been given a research code: ON101 (trade name: Fespixon) has demonstrated the clinical superiority to the standard care (an absorbent dressing). The primary endpoint, complete healing, was found in 60.7% of the ON101 group and 35.1% of the comparison group during the treatment period (p=0.0001). Time to complete healing, the secondary endpoint, was faster in the ON101 group (p=0.002). The researchers have reported that “Topical application of ON101 with gauze … read more
Painful and Non-painful Diabetic Neuropathy, Diagnostic Challenges and Implications for Future Management
Peripheral neuropathy is one of the most common complications of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Up to half of patients with diabetes develop neuropathy during the course of their disease, which is accompanied by neuropathic pain in 30–40% of cases. Peripheral nerve injury in diabetes can manifest as progressive distal symmetric polyneuropathy, autonomic neuropathy, radiculo-plexopathies, and mononeuropathies.
The most common diabetic neuropathy is distal symmetric polyneuropathy, which we will refer to as DN, with its characteristic glove and stocking like presentation of distal sensory or motor function loss … read more
Wound Care Centers Market Expected To Reach Over USD 32.60 billion By 2028: Data Lab Forecast
The Wound Care Centers Market study comprises a comprehensive market analysis that encompasses key aspects of the industry and defines current market dynamics in detail. It assesses growth patterns, magnitudes, and specific business developments under the current Wound Care Centers market scenario. The study report shows a balanced presentation of statistical and theoretical data with an accurately estimated forecast that includes the growth prospects in the specified period. The study also determines the market share and size of the Wound Care Centers along with the metric forecast associated with its growth and development during the forecast period. The study mainly focuses on the precise growth projections contained in the report … read more
Screening for Depression in Patients with Chronic Wounds
Wounds with a duration longer than 30 days are considered chronic. For example, diabetic foot ulcers comprise a large majority of these wounds and often exceed the expected 12-week healing period because of underlying factors that cannot be fully corrected.1 Patients with chronic wounds face considerable psychological stress because they need continuous medical care and frequent visits to healthcare facilities. The presence of these wounds significantly disrupts the daily life of patients, including changes in sleeping patterns, diet, and mobility. Loss of mobility may lead to feelings of loneliness, powerlessness, and dependency, as patients rely on family or friends to help fulfill their basic needs such as commuting, activities of daily living, and personal hygiene. Further, patients may experience chronic pain, exudate, and odor, which negatively impact social interactions, relationships, sexuality, and self-confidence. All of these psychosocial factors add up and may lead to a slow onset of anxiety and depression in patients with chronic wounds … read more
Reducing Hospital-acquired Pressure Injuries Among Pediatric Patients Receiving ECMO
BACKGROUND: Pediatric patients immobilized for certain procedures, such as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), are at high risk for developing hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs). PURPOSE: To evaluate the rate of HAPI occurrence in ECMO patients before and after implementation of prevention interventions. METHODS: Patients younger than 18 years of age who were placed on ECMO from January 2012 through March 2020 were identified, and patient data … read more
Assessing the Links Between Eschar Removal and Management of Severe Burns
When treating severe burns, surgeons generally consider eschar removal to be the major factor and the top challenge in both initiating and planning for the optimal course of treatment for each patient. Before grafting, all devitalized tissue must be removed, leaving a wound bed of only healthy tissue. Some burn wounds are clearly full-thickness on initial examination, and some are clearly superficial, with relatively straightforward decision making. However, some wounds have an indeterminate depth and are more challenging. Deep partial-thickness, indeterminate-, and … read more
Webinar: Documenting Drainage Quantity
Coverage of surgical dressings by third-party payers depends, in part, on the volume of drainage of the ulcer being treated. Providers who dispense surgical dressings and expect payment from a third-party payer must document the drainage quantity of the ulcer. This webinar will review this requirement, list the options for drainage documentation, and detail exactly how drainage documentation should be documented in the medical record.
At the end of Dr. Lehrman’s presentation stay for a Question & Answer session where he will answer any questions that you might have.
What You Will Learn:
- List the keywords needed in documenting ulcer drainage when dispensing surgical dressings.
- Define different terms used to document ulcer drainage quantity.
- List the drainage volume requirements associated with commonly used surgical dressings.
Register Now!
Singapore researchers develop novel 3D model to study vascular diseases
A Singapore team of scientists and clinicians from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) and Tan Tock Seng Hospital (TTSH), have developed a three-dimensional (3D) model of the human artery blood vessel wall. Called an “arterial wall-on-a-chip”, it will help researchers study atherosclerosis … read more
Topical Cream Effective Against Diabetic Foot Ulcers
A topical cream that helps regulate macrophage activity was effective in treating diabetic foot ulcers, a clinical trial reported.
In 236 patients with foot ulcers treated for 16 weeks, the proportion who had complete healing of the ulcer was significantly higher in the group randomized to receive the topical cream (60.7%) versus a comparator group treated with absorbent dressing (35.1%; OR 2.84, 95% CI 1.66-4.84, P<0.001), said Shun-Cheng Chang, MD, of the Taipei Medical University in Taiwan, and colleagues … read more
FDA Clears Drug-Device Combination Matrix for Chronic Wound Care
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared the Omeza Collagen Matrix, a drug-device combination matrix for chronic wound care … The approval was granted through the FDA 510(k) premarket notification process. It is the first combination drug/device designed for chronic wound care … The wound care matrix is composed of hydrolyzed fish collagen infused with cod liver oil and other plant-derived oil and wax. After it is applied to a wound, the matrix is incorporated into the wound over time … read more
Take A Load Off: Offloading Tips And Pearls In Wound Care
Diabetic foot ulcerations (DFUs) affect approximately 26 million people worldwide, with a staggering 2.5 times increased risk of death at five years.1-3 While many etiologies and conditions contribute to a wound, offloading is crucial to solving the wound healing puzzle.
In some literature, offloading is the most important aspect of DFU treatment in patients with neuropathy.4-6 The thought behind offloading is relief of mechanical and abnormal stresses that the foot experiences from a loss of protective sensation. This combination results in tissue damage, thought to lead to many DFUs.1,4,7 Specifically, mechanical stress is due to increased plantar pressure and shearing forces during the gait cycle, causing repetitive microtrauma … read more
Reducing Health Disparities in Pressure Ulcer/Injury (PU/PI) Detection & Management October 7-9, 2021 in Atlanta, Georgia
Join the Association for the Advancement of Wound Care (AAWC) for our Pressure Ulcer Summit (PrU), themed Reducing Health Disparities in Pressure Ulcer/Injury (PU/PI) Detection & Management, on October 7-9, 2021 in Atlanta, Georgia.
– Upon completion of this conference, participants will be able to:
– Describe existing disparities related to pressure ulcer/injury (PU/PI) prevention and care.
– Discuss challenges in providing equitable pressure injury prevention and care.
– Describe characteristics of pressure injury and other damage of persons with dark skin tones.
– Identify at least one method of leveling the playing field for pressure injury detection.
Researchers develop new drug-free treatment to accelerate healing of chronic diabetic wounds
About one-fourth of people with diabetes develop painful foot ulcers, which are slow to heal due to low oxygen in the wound from impaired blood vessels and increased inflammation. These wounds can become chronic, leading to poor quality of life and potential amputation … Jianjun Guan, a professor of mechanical engineering & materials science in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, has developed a hydrogel that delivers oxygen to a wound, which decreases inflammation, helps remodel tissue and accelerates healing. Results of the work, which were in a mouse model, are published Aug. 28 in Science Advances. Ya Guan, a doctoral student, and Hong Niu, a postdoctoral research associate, both in Guan’s lab, are co-first authors … read more
Healogics® Raises Awareness of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) to Help Reduce Amputations
Healogics, the nation’s leading provider of world-class wound care services, is raising awareness of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) throughout September. Through this campaign, Healogics is supporting the American Heart Association’s goal to reduce amputations by 20% by 2030 through increased PAD Awareness, diagnosis and treatment … People with PAD often have non-healing wounds in their extremities due to the restriction of blood flow limiting the natural healing process, potentially leading to complications, such as amputation. PAD affects nearly 10 million Americans and is a contributing factor in up to 30% of non-healing wounds on the lower leg. Common symptoms associated with PAD include cramping, numbness, weakness or heaviness in the leg muscles, however up to 40% of people experience no symptoms. One in four people living with late-stage PAD may require amputation within one year … read more
Multifunctional Irrigation-Assisted Vacuum Drainage versus Traditional Drainage in the Treatment of Odontogenic Deep Fascial Infection
Odontogenic deep fascial space infection in the head and neck is a common potentially fatal clinical problem. Traditional drainage method is considered laborious and gravity-dependent. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the clinical effect of a modified multifunctional irrigation-assisted vacuum drainage (MIVD) by comparing it with the traditional drainage method in the treatment of odontogenic deep fascial infection … read more
Wipeout Wounds National Conference Tour
Your Guide to New and Essential Pressure Injury and Ostomy Treatment Protocols
Take control of wound healing by learning about new strategies and tools that will keep you compliant, PLUS spend one-on-one time with industry experts. Learn today and use your knowledge in your clinical practice as soon as tomorrow!
learn more
RITA: The Wound Pros Leverages Artificial Intelligence With Its Wound Measurement App
The Wound Pros (https://thewoundpros.com/) today introduced its automatic wound measurement app, RITA designed to aid healthcare providers in the management and treatment of chronic, non-healing wounds. The Wound Pros is a physician owned and managed wound care company and a leading supplier of wound care dressings with a presence in 16 states across the United States … RITA represents The Wound Pros’ “high-tech” approach that leverages the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning to measure chronic non-healing wounds with pinpoint accuracy. According to Dr. Bill Releford, RITA creator and CEO of the Wound Pros, capturing highly accurate measurements is essential for delivering timely and comprehensive treatments to prevent wounds from worsening and improving healing outcomes.” Clinicians just need to take a picture of a patient’s wound with a smartphone or tablet and RITA will measure its size and generate professional documentation to support treatment and billing alignment. The application integrates seamlessly into The Wound Pros digital wound management platform and allows care teams to remotely monitor patients’ wound progression. RITA offers online and offline capabilities to ensure efficiency and reliability regardless of network connection status … read more
Remote Monitoring Saves Costs in Outpatient Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
In the outpatient setting, combining remote therapy monitoring (RTM) with negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) can support improved adherence to prescribed therapy. A recent study reported that patients receiving NPWT with RTM required fewer therapy days than patients receiving NPWT alone, possibly reducing costs of care. Our objective was to determine whether RTM reduced 90-day costs in patients undergoing NPWT … read more
Oxygen-delivering hydrogel accelerates diabetic wound healing
About one-fourth of people with diabetes develop painful foot ulcers, which are slow to heal due to low oxygen in the wound from impaired blood vessels and increased inflammation. These wounds can become chronic, leading to poor quality of life and potential amputation … ianjun Guan, professor of mechanical engineering and materials science at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, has developed a hydrogel that delivers oxygen to a wound, which decreases inflammation, helps remodel tissue and accelerates healing. Results of the work, which were in a mouse model, are published Aug. 28 in Science Advances. Ya Guan, a doctoral student, and Hong Niu, a postdoctoral research associate, both in Guan’s lab, are co-first authors … read more