As 2021 comes to a close, it marks 2 full years that the US, Canada, and other parts of the world have endured the effects of COVID-19 on our personal and professional lives. The pandemic continues to force our hands in so many ways that were unimaginable just a short time ago and has had innumerable unforeseen consequences for patients and providers. In this issue, articles on provider- and patient-centered concerns speak to the social, psychological, and physical components that determine quality-of-life scores and impact activities of daily living … read more
Category: Articles
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces thermal wound complications and length of stay in hospitals, study finds
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can reduce thermal wound complications, length of stay in hospitals due to thermal burns, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) mRNA gene expression, and ICAM-1 serum level, a case-control study published in Annals of Medicine and Surgery concludes.
“The damaging effects of thermal burns need to be managed holistically in order to create a suitable environment for wound healing,” study author Mendy Hatibie Oley (University Sam Ratulangi; R D Kandou Hospital; Hyperbaric Centre Siloam Hospital; all Manado, Indonesia) et al write … read more
Workflow Strategy Snapshots: Fresh Focus for the New Year
Kicking off any new year allows us to pause and reflect on the previous year’s actions and results. When you work within wound care, perhaps your first action this year was to review your schedule of patients to ensure they were provided the proper time to be seen, or review your staffing matrix to ensure you are you are meeting the needs of the scheduled patients, or dig into your supply cabinets to ensure inventory is abundant. Each action is vital to maintain your business and is interconnected to your unique process … read more
Where Are We With Point-Of-Care Testing For PAD In Patients With Diabetes?
How reliable are our screening tools for peripheral arterial disease (PAD)? A recently published meta-analysis suggests that while our current diagnostic testing measures are promising, one should be wary of relying upon any one tool in isolation in patients with diabetes.
In their 2020 study in the Journal of Vascular Surgery, Normahani and coworkers reviewed and analyzed studies to evaluate the accuracy of bedside testing for PAD in patients with diabetes.1 In examining the diagnostic accuracy of the ankle-brachial pressure index (ABPI), the toe brachial pressure index (TBPI) and the tibial waveform assessment, these authors reviewed 11 studies (including a total of 1,543 limbs) … read more
The Human Microbiomes And How They Affect Wound Healing podcast
In this podcast, Laura Swoboda, DNP, APNP, FNP-C, CWOCN-AP, shares expert knowledge on the human microbiome and its influences on the immune response, inflammation, and metabolism, which can impact wound healing … listen
Delayed Care During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Effects on Chronic Wound Therapy
Chronic wound care is challenging for the entire healthcare ecosystem, from clinicians to patients, and COVID-19 has only exacerbated those challenges. Patients are delaying primary care provider and wound clinician visits for ongoing guidance and therapy to reduce possible exposure to the virus. This is understandable, as many chronic wound patients are in the high-risk category if they become ill with COVID-19.1 They are also putting off elective surgeries, annual physicals, and basic preventive care, which can negatively affect long-term outcomes. A survey of wound care clinicians in March 2021 reported a decrease in patient visits from pre-pandemic numbers, and 57% of respondents stated that “wound severity has either increased or significantly increased since the start of the pandemic.”2 At the same time, the pandemic has accelerated patient-driven care and increased usage of interactive devices for care administered at home, rapidly increasing the use of telemedicine across demographics … read more
Safe and effective wound healing preparation reaches Clinical Phase II
APO-2 (Aposec) is a secretome-based trial preparation derived from stressed peripheral blood mononuclear cells. APO-2 was shown to be safe and effective in a multinational Phase I study in patients with diabetic foot ulcers (non-healing foot ulcers). The Data Safety Monitoring Board has therefore recommended continuation into a Phase II clinical trial. This represents a major success for the wound healing preparation developed at MedUni Vienna … read more
Cleveland Clinic surgeon helps draft Amputation Reduction and Compassion Act
But there is legislation moving through Congress that seeks funding to improve public awareness and early detection.
Vascular surgen Dr. Lee Kirksey of the Cleveland Clinic said there is no disease that ravages the body quite like diabetes. The complications can be serious: heart attacks, strokes, kidney failure and the most worrisome and drastic of all, limb loss.
“When I talk to diabetics, their greatest fear and they know that they can have a heart attack or stroke, their greatest fear is having to have an amputation,” said Dr. Kirksey.
According to Dr. Kirksey, as many as 25% of patients with diabetes at some point will develop a foot ulcer and if left untreated, that ulcer can lead to infection and amputation … read more
Chronic Venous Leg Ulcer in Klinefelter Syndrome Treated with Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Case Report
Venous leg ulcers (VLUs) are the most common causes of leg ulcers due to venous insufficiency. Most cases persist for more than 6 weeks, referred to as chronic VLUs. These chronic ulcers have been described as a manifestation of Klinefelter syndrome (KS). Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) is a second-generation platelet concentrate, which contains growth factors required for chronic wound healing. The use of PRF in the management of VLUs in KS has not been reported, to the best of our knowledge. We report a case of chronic VLU associated with KS in a 41-year-old man treated with PRF. Dermatological examination showed a tender, shallow, irregular ulcer partly covered with hard, yellow necrotic tissue on the anterior side of the lower-left leg and hyperpigmented indurated skin on both lower legs. The diagnosis of venous ulcer was established based on clinical manifestation and supported by the result of Doppler ultrasound showed chronic venous insufficiency. Histopathological examination, which showed epidermal acanthosis … read more
Malaysian Diabetics Develop Complications After Delayed Screening, Treatment
A medical doctor says the proportion of diabetes cases that developed complications may have risen by roughly 15 to 20 per cent.
KUALA LUMPUR, Nov 25 — Late detection and interruptions to clinic visits for diabetic treatments during the Covid-19 pandemic have led to complications in some patients … Many had their appointments deferred as the government imposed a nationwide lockdown in March last year … “Because of the first movement control order (MCO 1.0), there is a higher chance for us to see patients who are coming in, not only with diabetic foot ulcers, but some may have rot their toes and limbs,” the doctor said … read more
Lower Extremity Wounds: Differential Assessment and Management
Determining Wound Etiology:
Predominant pain pattern, ulcer location, ulcer appearance, type and amount of wound exudate, and vascular and sensorimotor assessment are some key factors used to determine the primary etiology of lower extremity ulcers.1
Etiology Guides Treatment:
Certain patients will have a clear presentation of wound etiology, whereas others may present with a mixed wound appearance. The certified wound specialist will complete a thorough history and physical assessment when determining wound etiology. From there, an individualized plan of care will be created, implemented, and continuously evaluated. For example … read more
Overcoming Health Inequities In Wound Care
Q: What resources do you use and/or recommend for physicians to educate themselves on health inequities, especially in the field of wound care?
A:
Babajide Ogunlana, DPM, FACFAS, encourages physician to learn first-hand by engaging in community outreach-type programs that seek to improve access to care.
“The field of wound care has a lot of cost implications that tend to tilt the services offered and/or available to the patient in the direction of who can afford it or whose insurance company … read more
DDI holds course on managing diabetic foot complications
KUWAIT: Dasman Diabetes Institute (DDI), a leading diabetes research Institute established by the Kuwait Foundation for the Advancement of Sciences, held recently its specialized three-day course on the ‘Prevention and Management of Diabetic Foot Complications’.
This program was held at the Institute and attended by healthcare professionals. Trainees learned to assess and treat the feet in people with diabetes using evidence-based assessment and treatment methods, aimed at reduction of diabetic foot ulceration and amputation. This program was organized and delivered by Kay Scarsbrook Khan, Chief Podiatrist and Dr Abdullah Al-Ajmi … read more
Factors Affecting the Quality of Life of Hospitalized Persons with Chronic Foot and Lower Leg Wounds
This descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted in a university hospital wound care unit in western Turkey with 134 patients. The data were collected via personal information form, Barthel Index for activities of daily living, visual analog scale, and Short Form-12 questionnaire. Descriptive statistics and Spearman correlation were used for data analysis … read more
Analysis of Factors Influencing Anxiety and Depression among Hospitalized Patients with Chronic Wounds
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the prevalence of anxiety and depression among hospitalized patients with a chronic wound and explore the influence of demographic factors, disease characteristics, social support, and coping styles on their mental status … read more
Wound Care and Healing for Neonates
A study published in the Advances in Skin & Wound Care Journal examined wound care information to help educate about care for the specific physiology of newborns.
A group of researchers aimed to help physicians differentiate the use of hydrocolloids, hydrogels, foam dressings, and barrier creams in the neonatal population and identify issues related to the use of solvents, alginates, collagen dressings, and negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) in neonates, according to an article in the Advances in Skin & Wound Care journal.1
PubMed, Google Scholar, and other journals/textbooks were used to help collect data on wound healing in newborn patients. With this data, the authors of the study aimed to discuss what is already known about wound milieu in premature and full-term neonates, including the unique challenges pediatric clinicians face, the therapies that have proven effective, and the therapies … read more
The Burden of Wound Care
A study investigated the clinical and economic burdens of wound care in the Tropics during a 5-year institutional review.
In an article published in the International Wound Journal, researchers evaluated the clinical and economic burden of wound care in the Tropics during a 5-year institutional population health review that occurred from 2013 to 2017.1
The 55,583 wounds included in the study were classified into different subtypes: neuro-ischaemic ulcers (NIUs), venous leg ulcers (VLUs), pressure injuries (PIs), and surgical site infections (SSIs). There were 41,461 patients admitted during that time with a 95.1% increase in wound episodes per 1000 inpatient admissions during this period (142 and 277 wound episodes per 1000 inpatient admissions in 2013 and 2017, respectively).
In 2017, the average amount of time a patient had to stay in the hospital for wound care were 17.7 … read more
Promoting Pressure Injury Prevention Technology
Do you remember that cartoon from the 1960s (and later reproduced in the 1980s), The Jetsons? It was about a futuristic family that had all kinds of amazing robot helpers and automatic appliances. Rosie the Robot was the wonderbot that would whisk about the house, frantically preforming housekeeping duties, monitoring the security of the home, and generally making sure that everything was online and functioning. Do you ever feel like this as a clinician? Rushing about, multitasking, being pulled in what seems like a hundred different directions, all while expected to perform with “Rosie-like” perfect, machine-like efficiency. Wouldn’t it be wonderful to have Rosie’s artificial intelligence technology … read more
Related: Pressure Injuries and Disparities in Health Care: Important Terms to Know
Pressure Injury Monitoring: Using Technology in a Time of Hospital Overcrowding
In the last 2 years, hospitals and skilled nursing facilities have seen unprecedented surges in admissions attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic sweeping across the world. Just in the United States, we saw a high of 116,243 weekly hospital admissions in mid-January of 2021. This dropped to a low of 13, 424 in mid-June of 2021 and then bumped up again to 86,871 in August of 2021.1 With this fluctuation of numbers, along with staffing shortages and burnout, wound care professionals have seen significant overcrowding in many hospitals and facilities. Caregivers and clinicians are stretched thin. They are taking on more patients, who tend to be sicker and with more acute needs on a global scale. These patients tend to be at higher risk of developing a pressure injury … read more
Cellphones Help MDs Monitor Surgical Patients for Infections
The crystalline clarity with which smartphones can now capture images has been put to another innovative use: monitoring patients who’ve undergone emergency abdominal surgery for surgical-site infections (SSIs) and allowing physicians to diagnose them earlier in the postoperative period before they morph into a much bigger problem.
“Since the COVID-19 pandemic started, there have been big changes in how care after surgery is delivered,” Kenneth McLean, MBChB, University of Edinburgh, Scotland, observed in a statement.
“Patients and staff have become used to having remote consultations and we’ve shown we can effectively and safely monitor wounds … read more
Pressure Injury Prevention: Recognizing the Early Signs of Injury
Here’s a question for you: How long does it take for a pressure injury (PI) to form? Do you think it happens in 30 minutes? 2 hours? 8 hours? The answer is actually all of the above. The time it takes for a PI to develop depends on a number of different factors, which we will discuss here. This blog will describe how a PI forms, some signs that a PI is forming, and how to assess a patient’s skin for a PI. It will then look at some types of intervention and assessment that help in the prevention and treatment of a PI, as well as track its healing or declination … read more
Gel-Based Sensor Continuously Monitors Wounds for Infection
When bacteria make their way into wounds, they literally threaten life and limb—unless they are detected as quickly as possible. A new sensor can nestle in bandages and alert a nearby smartphone when the bacterial population tips over into dangerous territory.
Healthy human skin is covered with bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, which are quick to colonize an open wound. To prevent the bacteria from spreading through the body, which can permanently injure or kill a person, the infected wound may need to be cleaned and treated with antibiotics or—in the most extreme situations—the affected limb may require amputation … read more
Building a Pressure Injury Prevention Plan in a Low-Resource Facility
A nurse recently shared some of her experiences as a charge nurse in a skilled facility during the COVID-19 pandemic. She worked evenings (3-11:30 pm) at a local facility and was overwhelmed by the high number of patients she was responsible for. She typically worked on a 26-bed floor with just one nurse assistant for the shift. She later transferred to the night shift, where she was the only person on a 16-bed unit for the 8 hours. When asked how she was able to reposition patients as frequently as was recommended, the nurse said that she did “the best I could.” She is, unfortunately, not alone … read more
Imcivree Considered for Expanded Label; Semglee Hits Shelves; Buphenyl for T2D?
The FDA accepted a priority review of a supplemental new drug application for setmelanotide (Imcivree), a melanocortin-4 receptor agonist, for the treatment of Bardet-Biedl syndrome and Alström syndrome, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals announced. The FDA assigned a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) goal date of March 16, 2022 … After getting the green light from the FDA, Paracrine announced plans to initiate its pivotal ASCEND trial testing its Celution System for diabetic foot ulcers … read more
ProgenaCare Global announces effective applications of novel keratin matrix technology, ProgenaMatrix
ProgenaCare Global, formerly Cell Constructs, has developed innovative products for wound healing that provide excellent outcomes for patients, while advancing the use of renewable materials. The company’s wound care technology, ProgenaMatrix™, incorporates human keratin as a major component of the highly effective and affordable wound therapy.
The all-natural robust human keratin protein option that constitutes this specialized biomaterial offers a completely unique solution to wound care clinicians. The human keratin technology in ProgenaMatrix is hydrated, non-cellular (not tissue-based), non-resorbing and supports the body’s own healing process. The bio-inspired design makes ProgenaMatrix the next generation of advanced wound therapy in the CMS skin substitute category … read more
Help support Wound Care Weekly
Help support non-profit medical journalism. If you find WoundCareWeekly.com of value please consider a monthly donation to help cover expenses and keep this website going.
ProgenaCare Global Announces Effective Applications Of Novel Keratin Matrix Technology, ProgenaMatrix
ATLANTA, November 17, 2021 / PRNewswire / – ProgenaCare Global, formerly Cell Constructs, has developed innovative wound healing products that deliver great patient outcomes while advancing the use of renewable materials. The company’s wound care technology, ProgenaMatrix™, contains human keratin as the main component of highly effective and inexpensive wound therapy.
The all-natural, rugged human keratin protein option that makes up this specialized biomaterial offers surgeons a completely unique solution. The human keratin technology in ProgenaMatrix is hydrated, non-cellular (non-tissue-based), non-resorbing and supports the body’s own healing process. The bio-inspired design makes ProgenaMatrix the next generation of advanced wound therapy in the CMS skin replacement category.
Keratin technology has been in the published literature for over a century with applications in wound healing, drug delivery, tissue engineering, trauma and medical devices … read more
In South L.A., a legacy of limbs lost to diabetes tells a larger story
Her small toe was turning purple, and the pain was excruciating. Glory Paschal knew how fast this could spiral. She just had to look around her neighborhood in Watts to see how many residents were missing feet and legs.
She fought for a referral to a podiatrist, but by the time she saw one, it was too late.
On Feb. 10, 2011, doctors at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center had no option but to amputate her left leg below the knee.
This summer, the now 53-year-old Black grandmother was back in the hospital, this time with two infections particularly lethal for a diabetic: severe COVID-19 had her gasping for breath and gangrene was eating away at her remaining foot … read more
Paracrine Receives Full FDA Approval of Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) to Launch a
U.S. Pivotal Trial in Patients With Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Paracrine, Inc. announced today that the FDA has granted full approval of its Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) to conduct a new pivotal trial titled Adipose Derived Regenerative Cells (ADRCs) in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFUs): A Prospective, Double-blind, Multi-center, Randomized, Parallel-group Study – The “ASCEND Trial.”
The ASCEND Trial is a Pivotal Trial designed to provide a robust data set on the safety and efficacy of ADRCs in the treatment of patients with DFUs. The trial will include up to 291 patients at 25 clinical sites in the U.S. Trial results will be submitted in a Premarket Approval (PMA) application to the FDA to support regulatory approval.
Dr. Robert G. Frykberg, Co-Principal Investigator for The ASCEND Trial and past Foot Care Council Chair of the American Diabetes Association, stated: “Despite recent advancements in wound care and pharmacotherapy techniques, up to one quarter of patients with diabetes will develop diabetic foot ulcers – a leading cause of disability worldwide. The goal of this pivotal study is to compare the use of ADRCs against the current standard of care and determine if ADRCs can improve clinical outcomes in this challenging patient population.” … read more
Compassionate Debridement at your Fingertips®
 Soft K-Cot® brush-curette is designed to be both minimally invasive and clinically effective for wound hygiene, debridement, and optional tissue sampling. The nitrile finger cot tip is coated with Kylon®, a patented medical fabric which dislodges and collects wound debris efficiently and effectively.
Soft K-Cot® brush-curette is designed to be both minimally invasive and clinically effective for wound hygiene, debridement, and optional tissue sampling. The nitrile finger cot tip is coated with Kylon®, a patented medical fabric which dislodges and collects wound debris efficiently and effectively.
Histologics LLC’s primary objective is to advance a compassionate approach to debridement and wound sampling with devices using Kylon®, a medical fabric enabling frictional tissue cleaning, and debridement with optional specimen capture.
Benefits:
- Fabric disk on finger cot tip is designed for flat or curved wounds that are visible on the body surface
- Versatile use, Ergonomic, and minimally invasive design facilitates user tactile control for targeting and guiding the brushing, sweeping and rotational movements – modulating tactile pressure and method allows for light brushing away of debris versus pressure twisting motion curettage of the wound surface.
- Kylon® medical fabric hooks gently, yet substantially excavates the wound surface, dislodging debris and necrotic tissue, which can be easily wiped off the wound surface with gauze
- Designed for compassionate patient experience and compliance
- Promotes the efficiency of a debriding procedure
- Abundant tissue samples can be collected, stored and transported for laboratory analysis
Indications:
The Soft K-Cot® is indicated for patients with small to moderate sized (no larger than 6cmx6cm), non-fibrotic surfaces of wounds requiring cleansing or debridement in order to remove non-viable tissue and debris. Debridement may stimulate blood flow to encourage tissue regrowth. It is also indicated for scraping or debriding and then transporting tissue requiring histological analyses for further laboratory evaluation regarding infection or other pathology.
Contraindications:
Soft K-Cot® is contraindicated for use with patients with known bleeding disorders or those on anticoagulant therapy, patients with an acute wound infection or condition that is not amenable to debridement, patients with a known allergy to nylon or acrylic plastic, or patients who are pregnant or suspected to be pregnant when a wound biopsy would not be indicated.
Warnings and Precautions:
Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician or other licensed practitioner.
Storage Requirements:
Consult manufacturer on special storage requirements outside of normal room temperatures.
How Supplied/Sizing:
Box of 25 minimum order
Recommended Use:
- Burns
- Chronic Wounds
- Diabetic Foot
- Graft Bed Preparation
- Non/Minimally Exudating Wounds
- Palliative Wounds
- Pressure Ulcers
- Sloughy Wounds
- Surgical Wounds
- Venous Ulcers
Mode of Use/Application:
See manufacturer’s website for detailed instructions for use (IFU):
Instructions for use
Clinically Tested:
Latex-friendly
Product features:
- Single Use
- Disposable
- Instrument
- Sterile
- Variety of sizes
Other features:
- Educational Material Available
- Free Samples/Trials Available
- Published Clinical Study Available
Free Sample Kit Available on Request to:
support@histologicswc.com
Histologics LLC, 4095 E. LaPalma Ave, St N, Anaheim, CA 92807, (888) 235-2275
www.histologicswc.com
support@histologicswc.com
A Review of the Skin Failure Concept
My colleagues, Barbara Delmore PhD, RN, CWCN, MAPWCA and Jill Cox PhD, RN, APN-c, CWOCN, and I have written a paper,1 available electronically ahead of print, that reviews the skin failure concept, defines related controversies, and proposes a model for its pathogenesis. Like all other organs, skin can fail; however, experts continue to grapple with definitions, causative factors, and manifestations. By defining contributing factors that apply to other organ systems, providers establish skin failure as an entity and thus are able to recognize and address it in practice. This also enables providers to assist regulators by incorporating these pathophysiologic factors into modification of quality measurement criteria. Unifying the concept across the health care continuum … read more
Kent Imaging named #15 on the list of “The 20 Most Promising Businesses to Watch in 2021”
Global Business Leaders magazine features Kent Imaging: Setting A New Global Standard in Advanced Tissue Assessment.
CALGARY, ALBERTA, CANADA, November 16, 2021 /EINPresswire.com/ — Kent Imaging Inc., a leading innovator in oxygenation imaging is pleased to report that the company has been named #15 on the list of “The 20 Most Promising Businesses to Watch in 2021” by Global Business Leaders magazine.
Kent Imaging’s flagship product is SnapshotNIR, a handheld and lightweight point-of-care device that can capture tissue oxygenation in superficial tissue with a single click of its camera-like structure. Using multiple wavelengths of near-infrared (NIR) light, SnapshotNIR non-invasively measures relative amounts of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin in the microcirculation of tissue where oxygen exchange is happening.
With the innovative SnapshotNIR device, Kent is focused on delivering improved usability to enhance workflow integration … read more
Wound dressing releases silver nanoparticles when infections occur
Although silver is highly effective at killing bacteria, it can also be toxic to humans in large amounts. That’s where a new wound dressing is intended to come in, as it only releases its silver payload when infections are present.
Currently being developed at the University of South Australia, the dressing is intended mainly for use on children with burn injuries, as they are particularly at risk of serious infections and sepsis. It’s made up of a topically applied hydrogel that contains silver nanoparticles along with proprietary ingredients which are sensitive to changes in pH and temperature … read more
American CryoStem to Study New Standardized Treatment Protocols for Wound Healing
EATONTOWN, NJ / ACCESSWIRE / November 16, 2021 / American CryoStem Corporation (OTC PINK:CRYO), a clinical stage biotechnology company, global licensor and a pioneer in autologous cellular processing and therapies announced today that it has completed the development of a new standardized wound healing protocol utilizing its tissue based technologies with Advanced Regenerative Associates (Tinton Falls, NJ). The Company’s wound healing technologies rely on exemptions from FDA clinical study and approval for the use of human tissue and cell products (PHS 361 and 21CFR1271.10) and is incorporated into the current standards of care protocols currently in use. The new protocol is focusing on realigning the microenvironment of the treatment area to achieve greater healing support during the treatment period utilizing current standard of care protocols. The initial rollout is fashioned as a study to collect additional information about the wound environment and healing progress. The Company intends to obtain informed consent from each participant for the collection, analysis and potential publication of the assessment data as required under current regulations … read more
CūtisCare Increasing Awareness This National Diabetes Month To Save Limbs and Lives
BOCA RATON, Fla., Nov. 14, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — CūtisCare, a leading provider of wound care management services to hospitals and physicians, is continuing our fight this month to raise awareness regarding diabetes and the available treatment options to help save limbs and lives. According to the CDC, diabetes currently adversely impacts the lives of approximately 34 million Americans, and that number is continuing to increase each year. About 25% of people with diabetes will develop foot ulcers, and 1% end up with an amputation in their lifetime. However, as many as 85% of potential amputations can be avoided when advanced modalities, such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy, or HBOT, are added to a treatment plan.
There is good news on the horizon though. Many of these amputations are preventable. HBOT is one therapy that is showing great promise. Louis Pilati MD, CutisCare’s Medical Advisory Board Member, expounds on the manifold benefits of HBOT for patients with Wagner Grade 3 or higher … read more
New tech wound healing
Safe and effective – wound healing preparation reaches clinical phase II: APO-2 (Aposec) is a secretome-based trial preparation derived from stressed peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
APO-2 was shown to be safe and effective in a multinational Phase I study in patients with diabetic foot ulcers (non-healing foot ulcers). The Data Safety Monitoring Board has therefore recommended continuation into a Phase II clinical trial. This represents a major success for the wound healing preparation developed at MedUni Vienna. APO-2 contains the secretome … read more
Diabetes & Speaking In “Tongues”
I have on several occasions had the unpleasant duty of telling family, friends and clients about a medical condition that they may be challenged with; heart disease, stroke, HIV, COVID-19, cancer etc. but none of them seem to have the same impact as DIABETES. Many people who have never seen the inside of a church building will break out into uncontrollable “tongues” that will amaze even the Apostles at Pentecost. That is how much diabetes is feared and it can cause havoc if not managed properly.
Diabetes on its own will not kill even if it wipes your bank account dry BUT the organ complications that come with poor management or no management is the killer … read more
Power to control bleeding Power to heal | LifeScience PLUS
LifeScience PLUS is a leader in advanced wound care technology. We are committed to developing and marketing innovative total wound care solutions: hemostasis (bleeding control), sealant, moist dressing, contamination prevention, and fast tissue growth generation. Our patented, best-in-class flagship product—BloodSTOP® iX Advanced Hemostat with WoundHEAL®—utilizes our revolutionary technology for both acute and chronic wound care.
BloodSTOP iX can be applied in many different specialty care areas with successful and positive outcomes. Our primary focus is to provide medical professionals an innovative product for EMS prehospital point-of-care treatment of traumatic wounds; for surgical procedures, including burn and trauma surgeries; and for treatment of diabetic ulcer and decubitus wounds … learn more
2021 Desert Foot Virtual Conference
Desert Foot Virtual Multi-Disciplinary Limb Salvage and Wound Care Conference is accredited for 35.5 CE/CME/CECH for all podiatric surgeons, surgical residents, MDs, DOs, WOCNs along with the VA, DOD, IHS and AAWC Healthcare Professionals (www.desertfoot.org). Conference Co-Chairmen are Drs Charles Andersen, Matthew Garoufalis and Thomas Serena (Past-President AAWC). The Desert Foot Virtual Conference provides a great opportunity for you to meet and share your scientific leadership with a large part of the federal service wound care and surgical community, as well as hundreds of healthcare professionals in acute care, home care and the private sector. The conference brings together six groups involved with limb salvage preservation of the lower extremity, from healthcare clinicians in the private sector, the Veterans Administration, VA Podiatric Residency Directors, Association for the Advancement of Wound Care (AAWC), Arizona Podiatric Medical Association, and the Department of Defense from across the country to a virtual conference to best meet their educational needs. This important conference will be live streamed, and the education will be taught by our nation’s top key opinion leaders focused on evidence-based and best practices to improve limb salvage techniques, advanced wound care skills, and treat surgical and medical disorders of the lower limb … read more
Hymed: Facilitating Effective Wound Care
Delayed wound healing and the resulting impact to the cost of care impacts both patients and facilities across the healthcare continuum. When it comes to wound care, no one is comfortable choosing a service provider with only a basic understanding of the subject. Thus, a product specialist with a historical legacy of providing effective products will invariably gain market traction due to its reliability. Founded in 1995, Hymed has been a renowned name in the healthcare industry for over two decades, offering safe and efficacious, natural wound care products. The company is the developer of innovative wound care products that utilize collagen (the chief structural protein of the body), hyaluronic acid (HA) and glycosaminogly can chemistry for human and animal use. In addition to wound care, these products find varied applications in joint/tissue support, surgery, eye care, dental, and dermatology, and the cosmetic industry … read more
Africa diabetes cases to soar: WHO
Africa is set to see diabetes cases more than double to 55 million by 2045, the biggest increase across the globe, the World Health Organization (WHO) warned Thursday.
“The COVID-19 pandemic will eventually subside, but Africa is projected in the coming years to experience the highest increase in diabetes globally,” said Dr. Matshidiso Moeti, WHO Regional Director for Africa.
Twenty-four million people are living with diabetes today in Africa, which is also the region with the “highest number of people who do not know their diagnosis,” the WHO statement said … read more
‘Foot Selfies’ May Improve Remote Diabetic Foot Monitoring
“Foot selfies” may be a simple solution to keeping tabs on patients at high risk for diabetic foot complications.
Patients with or at risk of foot ulcers are told to check their feet regularly at home, but doing so can be difficult for those who aren’t flexible or who have vision problems. Those who live alone may not be able to ask someone else to check their feet for them. Some use hand mirrors, but those can be difficult to manipulate and don’t offer feedback … read more
Diabetic foot ulcer treatment could kill COVID-19 virus, researchers say
A new foot ulcer formulation developed by scientists at the University of South Australia could be used to kill the COVID-19 virus, according to new research.
In a study published in the journal Applied Physics Letters, the team looked at the treatment of antimicrobial-resistant bacterial infections, experimenting to find an effective non-antibiotic antimicrobial strategy to combat the infections in diabetic foot ulcers.
The authors found that enhancing cold plasma ionized gas with peracetic acid was “highly effective” at eradicating common wound pathogenic bacteria and at inactivating SARS-Cov-2 … read more
Sherlock Holmes and the case of the missing evidence
Portfolio of hydrophilic PU foams and hydroactive nonwovens with sustainability credentials
Freudenberg Performance Materials will showcase its multi-layer material compositions of hydrophilic PU foams and hydroactive nonwovens for sustainable woundcare at Compamed in Düsseldorf from November 15-18 2021.
The Eco-Check label endorses particularly sustainable solutions for the design of wound plasters which use bio-based raw materials, allowing biodegradation in an industrial composting setting after the product has been used.
M 1701 for traditional woundcare plasters comprises 100% polylactid acid derived from natural resources and offers good woundcare characteristics, while M 1714 has superior absorption for more challenging wounds and consists of a mix of bio-based fibres. With a smooth wound contact layer, M 1714 has already been evaluated for industrial compostability and conforms with the ISO 13432 standard … read more
DIAGNOSTIC ACCURACY OF POINT-OF-CARE FLUORESCENCE IMAGING FOR THE DETECTION OF
BACTERIAL BURDEN IN WOUNDS
High bacterial load contributes to chronicity of wounds and is diagnosed based on assessment of clinical signs and symptoms (CSS) of infection, but these characteristics are poor predictors of bacterial burden. Point-of-care fluorescence imaging (FL) can improve identification of wounds with high bacterial burden (>104 CFU/g). FL detects bacteria, whether planktonic or in biofilm, but does not distinguish between the two. In this study, diagnostic accuracy of FL was compared to CSS during routine wound assessment … read more
Mechanosensor Plays Critical Key Role in Skin Wound Healing
PIEZO1, an ion channel mechanosensor found within cells, has been revealed to play a key role in regulating the speed of skin wound healing by researchers at the University of California, Irvine (UCI).
Published today in eLife, the study (“Spatiotemporal dynamics of PIEZO1 localization controls keratinocyte migration during wound healing”) found that in mice lacking the ion channel protein PIEZO1 in keratinocytes, skin wounds heal faster than in mice with increased PIEZO1 function in keratinocytes … read more
DCMH selected for Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment Study for veterans
The Wound Care unit at Decatur County Memorial Hospital has been selected to participate in a new study on the uses of hyperbaric oxygen treatment in partnership with the Indiana Department of Health and the Department of Veterans Affairs.
The HBOT Pilot Program will study the effect that hyperbaric chamber treatments can have on PTSD and traumatic brain injuries in veterans.
The VA seeks to improve the lives and health of veterans, and they have seen significant anecdotal evidence of the symptoms of PTSD decreasing and traumatic brain injuries improving during hyperbaric therapy … read more
Ion channel mechanosensor plays a key role in regulating the speed of skin wound healing
an ion channel mechanosensor found within cells, has been revealed to play a key role in regulating the speed of skin wound healing by researchers at the University of California, Irvine (UCI).
Published today in eLife, the study, titled, “Spatiotemporal dynamics of PIEZO1 localization controls keratinocyte migration during wound healing,” found that in mice lacking the ion channel protein PIEZO1 in keratinocytes, skin wounds heal faster than in mice with increased PIEZO1 function in keratinocytes … read more
Sonoma Pharmaceuticals (SNOA) Announces Expanded Long-Term Partnership
with Dyamed Biotech for New Territories and Products in Southeast Asia
Sonoma Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Nasdaq: SNOA), a global healthcare leader developing and producing stabilized hypochlorous acid (HOCl) products for a wide range of applications, including wound care, eye care, nasal care, oral care, dermatological conditions and disinfectant use, and its long-time partner, Dyamed Biotech Pte Ltd., announce a renewed and expanded long-term partnership for Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia and Thailand for multiple indications using Sonoma’s patented Microcyn® Technology.
Dyamed Biotech Pte Ltd., one of Sonoma’s first international partners, successfully commercializes Dermacyn® Wound Care, Dermacyn® Scarless for Scar Reduction, and Dermacyn® Ezyma Spray for itch relief associated with atopic dermatitis. Dyamed expects to launch Ocucyn® Eye Care and Oracyn® Oral Care in 2022. The Dermacyn® line of products are widely used at many hospitals throughout Singapore and Malaysia … read more
An Observational Clinical Trial Examining the Effect of Topical Oxygen Therapy (Natrox™) on the Rates of
Healing of Chronic Diabetic Foot Ulcers (OTONAL Trial)
Natrox™ topical oxygen therapy (TOT) (Inotec AMD Ltd, Hertfordshire, UK) employs a small battery-powered “oxygen generator” to concentrate atmospheric oxygen and feeds pure, moist, oxygen through a fine, soft tube to a dressing-like “oxygen distribution system”, which is placed over the wound and is held in place by a conventional dressing. The aim was to determine the effectiveness of Natrox™ for non-healing diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) over a 3-month period.Longitudinal, single-arm, open prospective registry study using 12 weeks of TOT using a 4 week run-in period. 20 patients recruited to OTONAL had chronic DFU greater than 3 months duration or minor amputation sites with less than 50% healing in 4 weeks.There were 13 (65%) males and the mean age was 65.7 (±11.6) years. The mean glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) was 6.9 (±1.3) mmol mol-1 and mean wound duration before TOT was 114 (±79.1) days. 18/20 (90.0%) patients had concomitant lower limb revascularization angioplasty for chronic limb threatening ischaemia. The mean size … read more
Diabetic foot ulcers on the rise
November is Diabetes Awareness Month, a time to bring attention to this fast-growing, life-threatening epidemic. Currently more than 34 million Americans have diabetes and this number is expected to increase to 54.9 million by 2030. Increases have been attributed to a rise in obesity rates and an aging population, but new research shows that younger people are being diagnosed with the disease. From 2001 to 2017, the number of people under age 20 living with diabetes increased by 45 percent, and the number living with type 2 diabetes grew by 95 percent. This troubling development is expected to further challenge the healthcare system in the coming decades … read more
Healing skin ischemia-reperfusion injuries with interleukin-36 receptor antagonists
Skin wounds from ischemia-reperfusion injuries — tissue damage caused by blood returning to tissues after a period of oxygen deprivation — may not heal appropriately in some patients, owing to elusive underlying immunological mechanisms. Scientists from Japan have now succeeded in proposing a means to solve this medical conundrum by understanding the role of interleukin-36 receptor antagonists as they act to inhibit the effects of interleukin-36 cytokines, which could help identify new therapeutic targets for wound healing … read more
We Are Failing Our Patients With Diabetes
My career in medicine has spanned approximately 26 years. Nineteen-ninety-six was my first year of residency training as well as my first real exposure to the emerging specialty of wound care.
To put things into perspective, during my first year of training, there were approximately 300–500 wound care products on the market. That may seem like a lot, especially considering there are now thousands of products that wound providers and others may choose from. Consider, however, that when I began clinical practice, the resources available were considerably different when compared to what is available today … read more
Lipid-lowering and anti-thrombotic therapy in patients with peripheral arterial disease
Patients with peripheral arterial disease (PAD) are at very high risk of cardiovascular events, but risk factor management is usually suboptimal. This Joint Task Force from the European Atherosclerosis Society and the European Society of Vascular Medicine has updated evidence on the management on dyslipidaemia and thrombotic factors in patients with PAD. Guidelines recommend a low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC) goal of more than 50% reduction from baseline and <1.4 mmol/L (<55 mg/dL) in PAD patients. As demonstrated by randomized controlled trials, lowering LDL-C not only reduces cardiovascular events but also major adverse limb events (MALE), including amputations, of the order of 25%. Addition of ezetimibe or a PCSK9 inhibitor further decreases the risk of cardiovascular events, and PCSK9 inhibition has also been associated with reduction in the risk of MALE by up to 40%. Furthermore, statin- based treatment improved walking … read more
Talk on Malta’s first biomedicine experiment at the International Space Station
Joseph Borg, a lecturer and researcher in Applied Biomedical Science at the University of Malta’s Faculty of Health Sciences, will deliver a talk and presentation on Wednesday, November 10 at 7pm at Spazju Kreattiv, Valletta, regarding an experiment on diabetes he is conducting at the International Space Station (ISS) as part of Project Maleth.
Prof. Borg’s experiment is the first Maltese presence at the ISS, launching the nation into a new era of involvement in space … read more
Magnitude of Surgical Site Infections, Bacterial Etiologies, Associated Factors and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns of
Isolates Among Post-Operative Patients in Harari Region Public Hospitals, Harar, Eastern Ethiopia
Surgical site infections (SSIs) are infections that occur one month after a surgical operation or one year after implant surgery and a surgical procedure, either at the injury site or near the injury site. Surgical site infections are still a major global problem, especially in developing countries, where they cause increased morbidity and mortality. There is a dearth of information regarding SSIs in the eastern Ethiopia, particularly in this study area … read more
Simple Color Change Test Identifies Wound Infections
Researchers at the University of Bath in the UK, along with outside collaborators, have developed a simple color change test that rapidly indicates whether a wound is infected with harmful bacteria. The test works by detecting virulence factors released by the bacteria, which prompt a simple color change in a solution. The test could help clinicians to determine whether to prescribe antibiotics, and may help to avoid unnecessary prescribing. As the test can be administered at the point of care, and does not require expensive and time-consuming laboratory analysis, it may be very useful in low-resource or remote regions … read more
The epidemic of diabetic limb amputation in poor communities and parts of Cleveland
Differences in outcomes across race, ethnicity and income exist for virtually every chronic health condition that Americans experience. Without exception, minority and poor white Americans die younger and suffer more preventable diseases.
November is diabetes awareness month. Few diseases impact every system of the body in the way that diabetes increases the risk for stroke, heart attack and kidney failure.
Of these devastating conditions, loss of limb, or amputation, is one of the most-dreaded complications of diabetes … read more
Advanced Tissue Technologies Provide Flexibility in Regenerative Medicine
Products derived from human and animal tissues, often referred to as tissue technologies, have offered outstanding results in medical care for decadesin the specific areas of soft tissue, nerve, and tendon repairs. These products are notable for aiding individual patients suffering from severe tissue damage, while also supporting large-scale reconstruction efforts for those who were injured in disasters, including 9/11, earthquakes and wars. Medical experts such as Ian Valerio, MD, MS, MBA, of Massachusetts General Hospital, have underscored the benefits and potential opportunities of regenerative therapies in managing complex wounds. One breakthrough product –Integra® Dermal Regeneration Template (Integra Template) — has paved the way for the continuing development of other regenerative medicine products … read more
Prestigious NSF grant awarded to FIU engineering professor for ‘smart’ bandages
In the future, a “smart” bandage being developed at FIU’s College of Engineering and Computing could remotely send real-time information directly to physicians to advise them how well a patient’s chronic wound is healing.
That’s the hope of the project’s mastermind, Satheesh Bojja Venkatakrishnan, a research assistant professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
Venkatakrishnan’s work in the development of a wireless, adhesive bandage to monitor wounds has led to a prestigious National Science Foundation (NSF) Research Initiation Initiative (CRII) grant, also known as a “mini CAREER” award. The highly competitive, $175,000 grant is awarded annually to support the promising research of a small number of principal investigators who are early career academicians … read more
Streaming Mon 6th – Fri 10th December 2021 | 6pm – 7pm (GMT)
With 10 hours of incredibly current topics, Wounds Week 3 will give a chance for the wound care community to come together in these difficult times, engaging in key education free of charge.
Each session has a live Q&A so participants can benefit from one-on-one interactions with the experts and engage in the event, no matter their COVID-19 situation. All our sessions are CPD-certified, and you will receive a certificate for watching on-demand too!
… read more
It’s Time to #BreakTheSilence on Diabetic Foot Ulcers
RedDress is launching a nationwide public awareness campaign, “Break the Silence,” educating Americans about the prevalence and prevention methods of diabetic foot ulcers.
Diabetic foot ulcers are sometimes omitted from the national discussion about diabetes and its complications. “Break the Silence” aims to reduce the stigmas associated with diabetic foot ulcers, while promoting and educating Americans about the prevalence and risk factors associated with this complication of diabetes. “Break the Silence” will run through November and coincide with National Diabetes Awareness Month.
Approximately 25 percent of diabetics will suffer a diabetic foot ulcer in their lifetime, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 1,2
“These ulcers are as serious as some cancers. We need to have a national conversation. Right now, we’re looking at diabetes in very broad strokes. I think we have to have a greater dialogue and more information about diabetic foot ulcers, in general,” expressed Dr. Robert Snyder, Dean of Barry University School of Podiatric Medicine in Miami, one of our partner physicians participating in the “Break the Silence ” campaign … read more
AI guides care of slow-healing wounds
Industry researchers have used machine learning to predict healing times for wounds based in part on patient data stored in electronic health records.
The team suggests its model can help clinicians make optimal decisions for treating slow-to-heal abrasions, lacerations and so on by knowing which new and preexisting patient traits are most likely to influence outcomes.
The study was conducted by staff members of Net Health, a supplier of software and analytics services, and is current in Advances in Wound Care.
The team trained AI prediction models on data from more than 1.2 million wounds … read more
Predicting Chronic Wound Healing Time Using Machine Learning
Chronic wounds have risen to epidemic proportions in the United States and can have an emotional, physical, and financial toll on patients. By leveraging data within the electronic health record (EHR), machine learning models offer the opportunity to facilitate earlier identification of wounds at risk of not healing or healing after an abnormally long time, which may improve treatment decisions and patient outcomes. Machine learning models in this study were built to predict chronic wound healing time … read more
Quinn Receives $1.6 Million NIH Grant for Research on Chronic Skin Wounds
Biomedical engineering professor Kyle Quinn has received a four-year, $1.6 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to develop non-invasive, real-time “optical biopsies” of chronic skin wounds.
The goal of Quinn and researchers in his lab is to provide digital histopathology images — the microscopic examination of tissue to study the manifestation and progression of disease — and other quantitative information without the need for an invasive biopsy, tissue processing and staining with histology dyes … read more
SKIN BACTERIA CAN HELP WOUNDS TO HEAL
Skin wounds heal by coordinated induction of inflammation and tissue repair, but the initiating events are poorly defined. Here we uncover a fundamental role of commensal skin microbiota in this process and show that it is mediated by the recruitment and the activation of type I interferon (IFN)-producing plasmacytoid DC (pDC). Commensal bacteria colonizing skin wounds trigger activation of neutrophils to express the chemokine CXCL10, which recruits pDC and acts as an antimicrobial protein to kill exposed microbiota, leading to the formation of CXCL10–bacterial DNA complexes … read more
Cuba inaugurates a biotechnological industrial complex
Cuba inaugurated this Monday the CIGB-Mariel Biotechnological Industrial Complex, the first high-tech industry located in the Mariel Special Development Zone (ZEDM), the island’s flagship megaproject for commerce and attracting foreign investment …Among the Cuban drugs that he will produce, he cited the anti-covid vaccine Abdala and the Jusvinza drugs -for the treatment of severe and critical patients with covid-19-, Heberprot P -employed to cure diabetic foot ulcers- and Heberferon, applied to patients with skin cancer, dengue and conjunctivitis … read more
University of Huddersfield and Regional Hospital Wiener Neustadt collaborate for wound management projects
The Institute of Skin Integrity and Infection Prevention (ISIaIP) at Huddersfield has signed a memorandum of understanding with the Regional Hospital Wiener Neustadt that will create a satellite office of the ISIaIP south of the Austrian capital Vienna. The alignment will enable joint research projects, international teaching and more publications.
The two institutions have collaborated for several years, with Professor Ojan Assadian having served as a Professor with the ISIaIP for more than four years before returning to Vienna, where he is Medical Director of the Regional Hospital Wiener Neustadt as well as … read more
Childhood Obesity Is Soaring to New Levels
Kids’ weight has spiked during the pandemic, but it’s part of a long-term trend
As a pediatric endocrinologist in a busy New York City hospital, I am acutely aware of the impact COVID-19 has had on my patients. The physical, emotional, social, and academic costs of the pandemic are evident every time I examine a child diagnosed with the virus. However, I am also deeply aware of another health risk that is threatening the well-being of my patients — the significant increase in obesity that we have seen in children and teenagers over the past 18 months.
Before COVID-19, obesity affected around 20% of American children 2 to 19 years of age. Now, the numbers are expected to rise much further, with modeling studies predicting at least a 3% to 4% weight gain in children during the pandemic … read more
The impact of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia and wound care
In the wake of the coronavirus pandemic, the critical limb ischemia (CLI) Global Society aims to develop improved clinical guidance that will inform better care standards to reduce tissue loss and amputations during and following the new SARS-CoV-2 era. This will include developing standards of practice, improve gaps in care, and design improved research protocols to study new chronic limb-threatening ischemia treatment and diagnostic options. Following a round table discussion that identified hypotheses and suppositions the wound care community had during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the CLI Global Society undertook a critical review of literature using PubMed to confirm or rebut these hypotheses, identify knowledge gaps, and analyse the findings in terms of what in wound care has changed due to the pandemic and what wound care providers need to do differently as a result of these changes. Evidence was graded using the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine scheme. The majority of hypotheses and related suppositions were confirmed, but there is noticeable heterogeneity, so the experiences reported herein are not universal for wound care providers and centres … read more
Innovative Israeli ‘copper’ dressing helps cure diabetic wounds
Herzliya-based MedCu’s product have already been approved by the US FDA.
An innovative Israeli-made wound dressing has been found to drastically stimulate the healing of diabetic wounds, a new study by physicians at the Rambam Health Care Campus in Haifa has found.
Copper Oxide Impregnated Wound Dressings, developed by Herzliya-based MedCu Technologies, have already received clearance by the major international regulatory bodies – including the United States’ FDA – for use in acute and chronic wounds.
“What is special about our dressing is that it contains particles of copper oxide,” said Dr. Gadi Borkow … read more
Vivex Biologics, Inc. to Attend the Symposium of Advanced Wound Care
Leading regenerative medicine company to participate in initiatives to further educate and improve patient care.
Vivex Biologics, Inc., a leading regenerative medicine company specializing in the development of naturally sourced treatment options, will be attending the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC) in Las Vegas on October 29-31, 2021.
SAWC brings together wound care teams, including physicians, nurses, physical therapists, researchers, scientists, podiatrists and dietitians, to improve the overall outcome of patients through furthering wound care education. The event will be comprised of various presentations, case studies, clinical research and practice innovations on topics including wound healing and wound care issues.
VIVEX professionals will host booth #440 during the forum, showcasing VIVEX’s portfolio of wound care products and solutions. The inherent properties of VIVEX’s amniotic allograft products provide mechanical protection and act as a barrier for external wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, pressure ulcers and burns while VIVEX’s Integrity Processing™ retains the nutrient-rich growth factors essential for signaling … read more
Organogenesis Showcases Latest Advanced Wound Care Innovations and Research at SAWC Fall 2021 Conference
Organogenesis Holdings Inc. (Nasdaq: ORGO), a leading regenerative medicine company focused on the development, manufacture, and commercialization of product solutions for the Advanced Wound Care and Surgical & Sports Medicine markets, today announced that the latest advanced wound care research on its PuraPly® AM, Affinity®, Apligraf®, and NuShield® product lines will be showcased at the 2021 Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC) Fall Conference held October 29-31 in Las Vegas, Nev.
Attendees of this year’s event are encouraged to visit the Organogenesis-supported lunch symposium, “New Scientific Data Supporting the Use of an Antimicrobial Native Collagen ECM and Real-World Case Studies Highlighting a Treatment Algorithm Approach” held Friday, Oct. 29, from 11:40 a.m. – 1:10 p.m. PST in the Innovation Theatre … read more
Independence Blue Cross Taps Podimetrics to Prevent Diabetic Amputations Via RPM
Independence Blue Cross (Independence) and Podimetrics, a virtual care management company dedicated to preventing diabetic amputations, today announced an agreement for Podimetrics to remotely monitor Independence fully insured commercial members who have diabetes and a history of a diabetic foot ulcer with the use of the cellular-connected SmartMat … read more
Healogics 8th Annual Diabetes Awareness Campaign, Chronic Wound Healing through Specialized Care
Healogics, the nation’s leading provider of world-class wound care services, is proud to announce the eighth annual Diabetes Awareness Campaign throughout the month of November, which is National Diabetes Awareness Month. The Healogics wound care specialists, at the more than 600 Healogics Wound Care Centers® nationwide, will be raising awareness of the importance of early intervention and specialized care for diabetes-related chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers … Diabetic foot ulcers are a leading cause of lower-limb amputations and according to the American Diabetes Association, an average of 10 Americans will undergo an amputation due to diabetes every hour. Of the 34.2 million Americans currently living with diabetes, up to 25% may develop a diabetic foot ulcer. These hard-to-heal wounds often go undetected due to the lack of feeling in the lower extremities due to nerve damage caused by diabetes … read more
Scientists report new hydrogel to protect wounds from germs
RUDN University and Shahid Beheshti University (SBU) chemist together with colleagues from Iran created a hydrogel film for wound dressing. It protects the wound from germs and is harmless to healthy tissues. Moreover, its porous structure can hold antibiotic, which kills dangerous microorganisms and provide additional protection. The results are published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.
The main aim in treating wounds is to prevent infection. With an open wound, microbes gain direct access inside the body. This significantly complicates wound healing and can cause more serious consequences, so it is important to develop antibacterial coatings for wounds. One of the modern approaches to this is hydrogel films. Unlike traditional remedies, hydrogels mimic healthy tissue and cover the wound, protecting it from germs. They also help to cool the wound and not over-dry it. In addition, hydrogels can contain … read more
NUS scientists develop a smart bandage to monitor chronic wounds
A research team led by Professor Lim Chwee Teck from the National University of Singapore’s (NUS) Department of Biomedical Engineering and Institute for Health Innovation & Technology (iHealthtech), in collaboration with clinical partners from Singapore General Hospital, has developed a smart wearable sensor that can conduct real-time, point-of-care assessment of chronic wounds wirelessly via an app. A world’s first, the novel sensor technology can detect temperature, pH, bacteria type and inflammatory factors specific to chronic wounds within 15 minutes, hence enabling fast and accurate wound assessment … read more
Utilizing Nanofibers for Treatment of Skin Infections
With the advancement in nanotechnology, its medical applications have provided a significant difference to the level of diagnosis and therapeutics. The use of nanotechnology for regenerative medicine, including wound healing, is an example of how this industry has advanced and developed novel treatments to provide better care to patients … read more
Assessing Oxygenation Status in the Management of Lower Extremity Wounds – webinar
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD), the narrowing or blockage of the vessels carrying blood from the heart to the legs, can have detrimental effects on lower limb health, and can lead to critical limb ischemia, limb loss, and even death. Patients with poor arterial health can develop hard-to-heal ulcers as the blood pools in the lower extremity, causing localized swelling and ulceration.
Transcutaneous monitors that measure tissue oxygen can assist with determining the health of the limb and the ability for a lower extremity wound to heal, and can detect the presence of vascular disease. Understanding these values is vital as it will help the provider to guide clinical decisions in in the plan of care, whether it involve curative measures such as compression therapy or advanced wound care interventions such as negative pressure wound therapy or skin grafts, or palliative or amputation, depending on the patient’s goals. Transcutaneous oxygen measurement can be used to determine amputation level in non-healable wounds … register
A Dual Celebration: Milestones in Diabetes Mellitus and Pressure Injury Research
This month we celebrate World Diabetes Day on November 14,1 which is the birthday of Dr Frederick G. Banting, one of four key collaborators in the discovery of insulin. He pursued the idea that an important element in the pancreas could help save the lives of persons with type 1 diabetes: insulin. It took the other members his team—collaborators at of the University of Toronto— to isolate insulin from the pancreas and formulate it into a lifesaving clinical reality. All of this happened 100 years ago this November, when the researchers demonstrated that insulin extract reduced blood sugar in laboratory animals.1 Because they felt so strongly that this medical breakthrough had to be available to all, they sold the patent for 100 cents ($1) so insulin could be affordable for everyone who needed … read more
How Might Protein Alteration From NPWT Affect Wound Healing?
Excellent continued efforts in elucidating the role that perturbation of the wound matrix (via negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT)) has on angiogenesis, healing and regeneration. A recent study in Molecular Medicine Reports used label‑free quantitative mass spectrometry to analyze differences in granulation tissue protein expression profiles before and after NPWT for patients with diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs).1 They aimed to take a closer look at how NPWT promotes DFU healing. As such, the study identified multiple novel proteins altered by NPWT, paving the way for future studies in this area … read more
Practice Management Education Opportunities Coding Fundamentals
Take the first few steps to coding and billing by joining us for a comprehensive workshop covering the fundamentals of coding and billing for foot and ankle surgeons. Learn the foundation of the coding and billing process from expert colleagues before taking the ACFAS Coding and Billing for the Foot and Ankle Surgeon course. This course is for residents, fellows, new practitioners, office staff of foot and ankle surgeons or anyone who wants to learn more of the basic coding and billing terminology and process. Plus, if you’re a resident and attending Residents Day in the morning the day of the event, this course is a great next step to learning more about coding and billing for your future practice and can be bundled in your pricing … read more

Lower Extremity Wounds: Is It Venous, Arterial, Neuropathic, or a Combination?
Lower extremity wounds manifest in a multitude of ways, with numerous causative or trigger factors. These types of wounds are often costly to treat, are frequently refractory, and have a high risk for recurrence. A comprehensive assessment and an evidence-based treatment plan, along with ongoing patient education and routine follow-up, are essential components of an effective plan of care … read more
Healing of a Chronic Pressure Injury in a Patient Treated With Medical Cannabis for Pain and Sleep Improvement
A Case Report
A small body of evidence suggests medical cannabis may facilitate wound healing, but the exact mechanism of this effect is unclear. PURPOSE: This case report describes a patient with a pressure injury (PI) who received cannabis oil treatment for pain management and sleep improvement. METHODS: A 37-year-old woman with multiminicore disease, scoliosis, short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, and epilepsy presented to the Neurology Centre of Toronto with chronic pain and sleep disturbance, including difficulty initiating and maintaining sleep. She also had a 5-year history of a PI between her right iliac crest and right rib cage that had progressively worsened. The patient received a medical cannabis oil protocol that used a combination of cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol … read more
The Courage to Do the Right Thing by Caroline Fife
Nearly 200 years ago, the brilliant French historian Alexis de Tocqueville traveled the fledgling United States and observed that in lieu of hereditary wealth and aristocracy, we were building a society on individualism, market capitalism, and honoring the hard-working common man. However, in his 1835 book, he cautioned that laws could never be a substitute for public morality and that such a society was less endangered by “the great profligacy of a few”, but by the “laxity of morals amongst all.” Those words were prophetic. Individualism and market capitalism have enabled us to create the most technologically advanced healthcare system in the world, but Medicare will be bankrupt in less than 10 years. Although there are a lot of reasons for this dire situation, they include “a laxity of morals amongst all and the great profligacy of a few.” … read more
Treating Wounds in the Very Young
Through the years, I have been asked to see and treat neonates, infants, and children with wounds of various etiologies. These have included genetic problems, pressure injuries occurring in the hospital, operative wounds, and, as they aged, the full spectrum of trauma and burns. I have always been honored to do so, but it must be remembered that treating the young can present its own challenges. Many who treat infants and children look at them as just small adults and proceed to treat them the same way. I learned very early on that neonates, infants, and children should not be treated as just small adults, because they have issues related to their development, age, and genetics that may make adult treatments ineffective at best and harmful at worst. The selection of dressings and bandages must be carefully based on the … read more
The Alliance of Wound Care Stakeholders outlines how wound care may be affected by …
CMS CY 2021 hospital outpatient and physician fee schedule proposed rules
The Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services have released for comment its proposed CY 2021 updates to the Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System and Physician Fee Schedule. Below, verbatim, are several provisions the Alliance of Wound Care Stakeholders has identified as particularly impacting wound care clinicians, which the Alliance will be tracking and preparing comment on … read more
Pressure Ulcer/Injury Case Study: Using Advanced Wound Healing Modalities in Post Acute Care Settings
In this case presentation, Martha Kelso, RN, LNC, HBOT, reports on the case of an 87-year-old male patient who presented with a stage 4 pressure ulcer/injury of 7 years’ duration … video
Extensive Type V Aplasia Cutis Congenita Without Fetus Papyraceus or Placental Infarction
Aplasia cutis congenita (ACC) is a congenital disorder characterized by the absence of epidermis, dermis, and sometimes subcutaneous tissue and bone. There are nine types of ACC based on the number and location of the lesions as well as the presence or absence of associated deformities, with type I ACC being the most common. Type V affects the trunk with a characteristic pattern resembling the “H” letter of the alphabet, generally accompanied by fetus papyraceus (death of one of the twin fetuses) or placental infarction. Type V ACC without fetus papyraceus and placental infarction is a rare case. We reported a case of type V ACC in a 3-day-old baby girl, with clinical manifestation of extensive ulcers on the scalp, back, buttocks, and both lower extremities, in an “H”-shaped pattern, with history of placenta accreta, but no fetus papyraceus or placental infarction was found. The patient received dialkyl carbamoyl chloride hydrophobic swab with hydrogel (Sorbact® gel dressing-BSN Medical) and hydrocolloid wound dressing with good response, as indicated by the wounds becoming dried up … read more
Latest Clinical Evidence Presented at SAWC 2021 Illustrates the Significant Clinical Utility of the MolecuLight Point-of-Care …
Imaging Platform
7 Clinical Posters and Presentations Highlight the Breadth of Clinical Benefits
of the MolecuLight Device for Wound Care Applications
TORONTO and LAS VEGAS, Oct. 28, 2021 /PRNewswire/ – MolecuLight Inc., the leader in point-of-care fluorescence imaging for real-time detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial loads, announces the presentation of 7 clinical posters and presentations at the Symposium of Wound Care (SAWC) Fall 2021, held from October 29 – 31, 2021 in Las Vegas, Nevada. SAWC is one of the largest multidisciplinary meetings of wound care professionals.
“We are thrilled to have so many customers presenting their impressive clinical findings at this year’s SAWC Fall conference”, says Anil Amlani, MolecuLight’s CEO. “The clinical topics being presented span the wound care continuum, from improved wound assessment and treatment planning, to monitoring of wound cleaning and debridement efficacy, and the resulting improvement in wound healing rates. Presenters will also describe detection and treatment of wound-related cellulitis, and findings from the recently published Delphi consensus-based guidelines for the use of the MolecuLight platform. The outcomes presented in these studies illustrate the significant clinical improvements to wound care provided to clinicians by the MolecuLight i:X“.
A submission on MolecuLight by Dr. Charles A. Andersen was one of the top scoring abstracts out of more than 200 submissions. This is the fifth consecutive SAWC meeting at which an abstract on improved patient care achieved through use of the MolecuLight i:X has received this honour.
The 5 clinical posters and 2 presentations featuring the MolecuLight i:X from SAWC Fall 2021 are as follows:
Poster #CR-005
12-Week RCT Evaluating Impact of Routine Fluorescence Imaging of Bacteria on DFU Healing Rates
Alisha Oropallo, MD¹, Scott Gawlik DPM¹, Dean Vayser, MD²
¹Northwell Comprehensive Wound Health Center and Hyperbarics, Lake Success NY,
²ILD Research Centre, San Diego, CA
Download poster
Poster #CR-006
Cleansing Techniques for Wound Hygiene: Which Are Most Effective?
Alisha Oropallo, MD1, Amit Rao MD1, Jai Joshi1
1Northwell Comprehensive Wound Health Center and Hyperbarics, Lake Success NY
Download poster
Poster #LR-025
Detection of bacterial fluorescence from in vivo wound biofilms using a point-of-care
fluorescence imaging device
Andrea J. Lopez1, Laura M. Jones2, Landrye Reynolds1, Rachel C. Diaz1, Isaiah K. George1, William Little1, Derek Fleming3,4, Anna D’souza2, Kendra Rumbaugh3, Allie Clinton Smith1, Monique Y. Rennie2
1Department of Honors Studies, Texas Tech University, Lubbock TX, USA; 2MolecuLight Inc. Toronto, ON Canada; 3Department of Surgery, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center; 4Division of Clinical Microbiology, Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
Download poster
Poster #CR-020
Are Semi-quantitative Clinical Cultures Inadequate? Comparison to Quantitative Analysis of 1053 Bacterial Isolates from 350 Wounds
Thomas E. Serena1, Phil Bowler2, Gregory Schultz3, Anna D’souza4, Monique Rennie4
1SerenaGroup Research Foundation, Cambridge MA USA; 2Phil Bowler Consulting, Warrington UK; 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Florida, FL, USA; 4MolecuLight Inc. Toronto
Download poster
Poster #PI-003
Guidelines for point-of-care fluorescence imaging for detection of wound bacterial burden based on Delphi consensus
Charles A. Andersen¹, Alisha R. Oropallo², Raymond Abdo³, Jenny Hurlow⁴, Martha R Kelso⁵, M. Mark Melin⁶ and Thomas E. Serena⁷
1Madigan Army Medical Center, Renton WA; 2. Zucker School of Medicine Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, NY; 3St. Louis Foot & Ankle LLC, St. Louis MO; 4Consultant Wound Care Practitioner, Memphis TN; 5Wound Care Plus LLC, Blue Springs MO; 6M Health Fairview, Edina MN; 7SerenaGroup Research Foundation, Cambridge MA
Download poster
Oral Presentation & Poster #PI-002
Diagnosis and Treatment of the Invasive Extension of Bacteria (Cellulitis) from Chronic Wounds Utilizing Point-of-Care Fluorescence Imaging
Charles Andersen¹, Katherine McLeod¹, Rowena Steffan¹
¹Vascular/Endovascular/Limb Preservation Surgery Service, Madigan Army Medical Center, Joint base Lewis-McChord, WA USA
Download poster
Podium Presentation
Innovation Spotlight: Shining a Light on Bold Ideas in Wound Care
Charles Andersen¹
¹Vascular/Endovascular/Limb Preservation Surgery Service, Madigan Army Medical Center, Joint base Lewis-McChord, WA USA
In additional to the clinical posters and presentations at SAWC (Symposium on Advanced Wound Care) Fall 2021, the recently launched MolecuLightDX will be available for demonstration in the MolecuLight booth #439 in the Exhibit Hall at Caesars Palace in Las Vegas, Nevada.
About MolecuLight Inc.
MolecuLight Inc., a privately-owned medical imaging company that has developed and is commercializing its proprietary fluorescent imaging platform technology in multiple clinical markets. MolecuLight’s suite of commercially released devices, including the MolecuLight i:X® and DX™ fluorescence imaging systems and their accessories, provide point-of-care handheld imaging devices for the global wound care market for the real-time detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial burden (when used with clinical signs and symptoms) and for digital wound measurement. The company is also commercializing its unique fluorescence imaging platform technology for other markets with globally relevant, unmet needs including food safety, consumer cosmetics and other key industrial markets.
Download for Image:
SOURCE MolecuLight
Related Links
Probiotics accelerate wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcer
Patients with diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) who were given probiotic supplements for 12 weeks had faster wound healing and improved glycemic control compared with similar patients on placebo, according to researchers who recently published their results in Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.
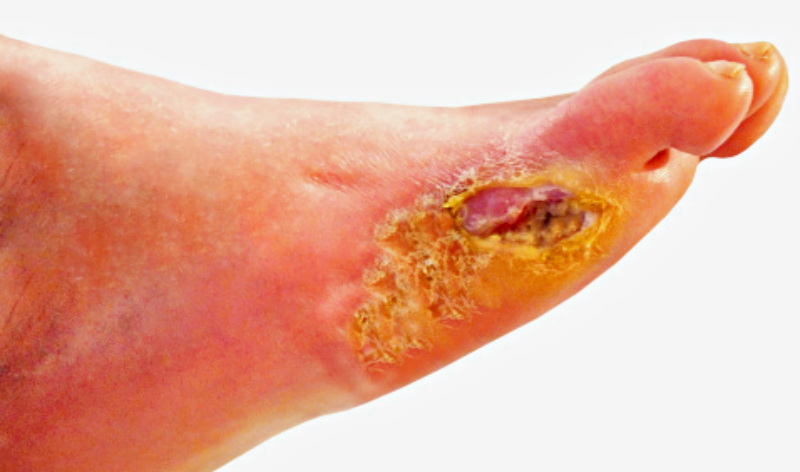
Diabetic foot ulcers healed faster in patients given probiotics.
“Due to the increasing global antimicrobial drug resistance issues, the idea of probiotic consumption is interesting and pertinent because probiotics have the ability to strengthen the immune system, have anti-inflammatory effects, and therefore, could increase the wound healing process,” wrote lead co-author Zatollah Asemi, PhD … read more
Does the Documented History Tell the Patient’s Wound Story Accurately?
Information regarding coding, coverage, and payment is provided as a service to our readers. Every effort has been made to ensure information accuracy. However, HMP Communications and the authors do not represent, guarantee, or warranty that coding, coverage, and payment information is error-free and/or that payment will be received. The ultimate responsibility for verifying information accuracy lies with the reader.
Welcome to the second article dedicated to documentation issues in wound care (click here for the first part). The intent of this article is to point out inconsistencies found in the documentation of a patient’s wound care history and provide possible suggestions on how to avoid creating those inconsistencies. Reviewing numerous wound care records has provided me with interesting findings that I would like to share with you … read more
Efficacy and Safety of a Hyaluronic Acid–Containing Cream in the Treatment of Chronic, Venous, or Mixed-Origin Leg Ulcers
A Prospective, Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
Topical applications of hyaluronic acid (HA)–containing formulations, based on the complex and vital role of HA in all stages of the wound-healing process, are routinely used with standard therapy to promote faster healing of chronic wounds. However, evidence to guide clinical decisions on the use of topical HA in the healing of vascular leg ulcers is limited. Objective. This study compared the efficacy and safety of topical application of a hyaluronic acid cream vs a neutral comparator (identical cream without HA) in treating subjects with chronic leg ulcers of vascular origin. Materials and Methods. This was a prospective, multicenter double-blind randomized controlled trial. One hundred sixty-eight subjects with chronic leg ulcers of venous or mixed (venous and arterial) origin were randomized to receive either topical applications of 0.2% HA cream or neutral comparator cream for a maximum of 20 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint was complete ulcer healing (100% reepithelialization of the wound area centrally assessed at 20 weeks or before and confirmed 3 weeks later). In both groups, topical treatment was associated with standard therapy (ulcer cleansing and optimized compression) … read more
Valsartan nano-filaments alter mitochondrial energetics and promote faster healing in diabetic rat wounds
Chronic wounds are a common and debilitating condition associated with aging populations that impact more than 6.5 million patients in the United States. We have previously demonstrated the efficacy of daily topical 1% valsartan in treating wounds in diabetic mouse and pig models. Despite these promising results, there remains a need to develop an extended-release formulation that would reduce patient burden by decreasing the frequency of daily applications. Here, we used nanotechnology to self-assemble valsartan amphiphiles into a filamentous structure (val-filaments) that would serve as a scaffold in wound beds and allow for steady, localised and tunable release of valsartan amphiphiles over 24 days. Two topical treatments of this peptide-based hydrogel on full-thickness wounds in Zucker Diabetic Fatty rats resulted in faster rates of wound closure. By day 23, all val-filament treated wounds were completely closed, as compared to one wound closed in the placebo group. Mechanistically, we observed enrichment of proteins involved in cell adhesion and energetics pathways … read more
2nd Annual Virtual PRESENT Superbones Superwounds West Conference a Crowd Pleaser
The 2nd Annual Virtual PRESENT Superbones Superwounds West Conference took place October 9-10, 2021. For the past 13 years, since 2008, PRESENT has been running the Superbones Superwounds West each year as a live-in person event in Las Vegas. The pandemic situation has required us to deliver education virtually these past 2 years and this is the 9th full live virtual conference put on by the PRESENT e-Learning Team since March of 2020. The post-event survey for this event revealed that 100% of attendees are likely to return to this conference in its virtual format … read more

Incidence, hospitalization and mortality and their changes over time in people with a first ever diabetic foot ulcer
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are a severe complication associated with diabetes, a precursor for amputation, and a major cause of patient suffering and high health-care costs.1,2 While the continuous efforts of multidisci-plinary foot clinics and preventive activities in primary care have reduced the incidence of major lower limb amputations in most countries, the prevention of DFUs remains a major challenge.3- 5 Over the years several risk factors associated with the development of a DFU have been discovered, but despite this, little is known about the factors leading directly to the first ever ulceration.6 Therefore, the predictive power of even seasoned cli-nicians in our experience remains low, and combined with the poorly reported, but relatively low, incidence of first ever DFUs, the possibilities for primary prevention is extremely limited.7 These challenges have led to re-current DFUs being studied far more than the first ever DFUs, but despite continuous improvements in healing … read more
Hillrom | WatchCare™ Incontinence Management System | Customer Video
Explore how the WatchCare™ Incontinence Management System provides caregivers with real-time incontinence detection and is designed to protect patient’s skin, optimize caregiver efficiency and improve patient experience. The information contained in these videos is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. You assume full responsibility for how you choose to use this information. Please speak with your healthcare provider about any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Hill-Rom retains all right, title, and interest in and to the video, and retains the right to demand that you immediately cease use of the video and unembed the video. Hill-Rom may discontinue or disable videos you have embedded at any time for any reason. You will not misrepresent the content contained in the video or use it in conjunction with price comparisons, in derogatory comparisons or in negative comparisons, with Hill-Rom’s competitor’s products, or in derogatory or negative commentaries about Hill-Rom’s products – doing so may subject you to liability. Any and all claims made by you regarding the use, operation, quality, etc. of Hill-Rom’s products are your own, and you shall be responsible for ensuring that all such claims comply fully with all applicable federal, state and local laws.
Joerns Healthcare Introduces Point-of-Care Imaging to Wound Care Portfolio Through MolecuLight Partnership
CHARLOTTE, N.C. and PITTSBURGH, Oct. 19, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Joerns Healthcare, a healthcare technology and equipment services company, announces the addition of the MolecuLight i:X® and DX™ wound imaging platforms to its wound management portfolio through an exclusive agreement with MolecuLight Corp. to provide MolecuLight’s fluorescence imaging technology for point-of-care detection of the bacterial burden in wounds. The MolecuLight i:X and DX devices are the first-of-their-kind handheld imaging devices that help clinicians quickly and easily visualize the bioburden of wounds as part of the standard clinical examination. The device can be used on all wounds, in all care settings and provides invaluable information in real-time to inform and support clinician decision-making. The automated wound measurement and assessment platform simplifies wound management to maximize healing and patient satisfaction.
“The revolutionary MolecuLight i:X and DX devices are the first point-of-care devices that simplify wound management and put immediate decision-making data at the clinician’s fingertips. The addition of this bedside imaging tool to our Connexio™ platform creates the first holistic system designed to enable immediate, evidence-based decisions for wound management. The device also eliminates the manual, administrative burden clinicians traditionally face by automating the data flows to their EMR platform of choice. The result is improved healing rates, reduced wound management costs, improved patient satisfaction and increased clinician efficiencies,” says Doug Ferguson, Chief Strategy Officer of Joerns Healthcare … read more
Where Do You Get Your Information?
One of the rewarding and fun projects I have been involved with for the past 2 years has been the development of a YouTube video program called “Inside the Doctors” Lounge.”
“The Lounge” is part of a bigger project called MD Coaches and is a talk show–like forum that takes place in an imaginary doctors’ lounge within the YouTube universe. Anyone who has spent time in a doctors’ lounge understands it is a place of respite and where discussions with colleagues can cover a wide range of topics, but most importantly, there is no associated fear of violating HIPAA or other repercussion. Everyone in the Lounge has an opinion, and discussions can become spirited, whether in agreement or not.
My colleagues (Rhonda Crowe, Randy Cook, Rick Zollinger and Dael Waxman) and I recently … read more
Helixmith Announces Phase 3 Study Results of Novel Gene Therapy Treatment for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
at 2021 Annual Meeting of Diabetic Foot Ulcer Conference (DFCon)
Data indicate that gene therapy appears to be effective, particularly in neuroischemic ulcers
SAN DIEGO, Oct. 22, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Helixmith, a gene therapy company based in Seoul, Korea and San Diego, CA, announced today the results of a Phase 3 study for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers with their novel gene therapy VM202 (Engensis) at the 2021 annual meeting of the Diabetic Foot Conference (DFCon) held in San Francisco and virtually. The study, “Gene Therapy for Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Analysis of a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Study of Engensis (VM202), a Plasmid DNA Expressing Two Isoforms of Human Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF),” demonstrated a positive trend toward wound closure, potential healing effects and an acceptable safety profile. This is the first study using gene therapy for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. DFCon is the premier international, interdisciplinary diabetic foot conference in North America.
The purpose of the un-prespecified interim analysis was to evaluate the status of a 7-month Phase 3 study conducted to test the effect of intramuscular injection of Engensis into the calf muscles of participants having chronic nonhealing diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) with concomitant peripheral artery disease. In the interim ITT population (n=44), there was a positive trend toward wound closure in the VM202 group from month 3 to month 7. Ulcer closure effects were prominent, particularly in neuroischemic ulcer. In 23 patients having this type of foot ulcers, the percentage of subjects reaching complete ulcer closure was significantly higher in the VM202 group at months 3, 4 and 5 (p = 0.0391, 0.0391, and 0.0361, respectively). Engensis seems to also improve hemodynamic features; a potentially clinically meaningful 0.15 increase in ABI was observed in the VM202 group at day 210 in ITT population (p=0.0776). The company believes that intramuscular injections of VM202 plasmid DNA to calf muscle may have promise in treatment of chronic neuroischemic DFUs … read more
A Comprehensive Review of the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Management of Diabetic Foot Infections
GENERAL PURPOSE: To review an approach to diabetic foot infections (DFIs), including acute osteomyelitis, while also discussing current practices and the challenges in diagnosis and management.
TARGET AUDIENCE: This continuing education activity is intended for physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and nurses with an interest in skin and wound care.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES/OUTCOMES: After participating in this educational activity, the participant will1. Identify the risk factors for developing DFIs.2. Outline diagnostic techniques for assessing DFIs.3. Select the assessment techniques that support a diagnosis of osteomyelitis.4. Choose the appropriate pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic treatment options for patients who have DFIs … read more
MicroVascular Tissues Announces Peer-Reviewed Publication of Positive HIFLO Clinical Trial Results Using mVASC® Graft
Data on Nonhealing Wagner 1 & 2 Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Ulcers Published in IWJ. Additional Data to be Presented at Upcoming 2021 SAWC and DFCon Meetings.
SAN DIEGO, CA, UNITED STATES, October 20, 2021 /EINPresswire.com/ — MicroVascular Tissues, Inc., (MVT), a regenerative tissue company, today announced that the results of its HIFLO Trial assessing patient outcomes after treatment with mVASC® Microvascular Tissue Graft product have been published in an article entitled, “Improved Healing of Chronic Diabetic Foot Wounds in a Prospective Randomized Controlled Multicenter Clinical Trial with a Microvascular Tissue Allograft” in the International Wound Journal (IWJ), one of the preeminent journals aimed at improving patient care in the wound care industry.
The HIFLO trial was a Level 1, prospective, single-blind, randomized clinical trial conducted at six U.S. sites that assessed outcomes in 100 subjects with nonhealing Wagner grade 1 and 2 neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). The primary endpoint was the percentage of ulcers healed within 12 weeks. Secondary and research endpoints included wound area percent reduction, time to healing, improvement in blood flow (perfusion) and peripheral neuropathy … read more
AiCuris Announces Expansion of its Collaboration with Lysando with a Focus on Diabetic Foot Infections
AiCuris Anti-infective Cures AG, a leading company in the discovery and development of drugs against infectious diseases, and the biotechnology company Lysando AG with its Regensburg-based subsidiary Lysando GmbH, today announced the expansion of their existing long-term collaboration for the development and optimization of Artilysin(R)-based drug candidates for the topical treatment of infected, chronic wounds such as diabetic foot infections.
AiCuris and Lysando joined forces in 2019 to drive the fight against antimicrobial resistance, with innovative approaches based on Lysando’s Artilysin(R) technology platform, a new class of phage-lysine derived artificial designer molecules with a novel mode of action and the potential to replace conventional antibiotics. Under the terms of the agreement … read more
Visceral Fat Associated With Increased Arterial Stiffness in Youth With Obesity
Data show In youth with obesity, but not healthy weight, visceral fat was positively associated with PWV and was predictive of PWV beyond BMI and waist circumference.
New research dove into associations between visceral fat and arterial stiffness in youth with healthy weight, obesity, and type 2 diabetes (T2D), in order to discover whether the relationships were independent of body fatness estimates as a predictor of cardiovascular events … read more
WoundZipper Application to Distal Forearm Laceration
Application of WoundZipper to a patient with a laceration of distal forearm.
The procedure includes sterilizing affected area with betadine and alcohol prior to application of the WoundZipper. No local anesthetic is required as the procedure is painless. The total procedure time is less than 1 minute. The patient is more comfortable during the procedure and is able to go home in minutes.
The patient returned to clinic after five days for a wound check. The patient was left with a faint, linear scar after 5 days. No suture or staple marks are visible.
Please visit WoundZipper.com for more information about the product.
Case Presentation: Dr. Maher Arafa, MD
Narrator: Kyle Dickinson, PA-C
Video Production: Val Valgardson, MFA
Singapore researchers develop bandage that can wirelessly assess wounds
Researchers in Singapore say they have developed a bandage that can detect and wirelessly send medical information related to chronic wounds, such as temperature and bacteria type. With the ability to capture and transmit such data in under 15 minutes, the wearable sensor is touted to speed up assessment of such wounds and provide more timely treatment.
Called VeCare, the platform encompasses a “wound sensing bandage”, an electronic chip, and a mobile app through which data is transmitted, said the research team from the Department of Biomedical Engineering and Institute for Health Innovation & Technology (iHealthtech) at National University of Singapore (NUS). The researchers also worked with clinical partners from Singapore General Hospital (SGH) … read more
Journal of Wound Care – July issue available online
Research and best practice – all in one resource
Wound Central is a specialist publication from Journal of Wound Care, for healthcare professionals across North America involved in skin integrity and wound management. It shares the latest clinical best practice, peer-reviewed research and medical education, brought to you with the support of the following associations:
- American Vein and Lymphatic Society (AVLS)
- Association for the Advancement of Wound Care (AAWC)
- Academy of Physicians in Wound Healing (APWH)
- Wound Care Education Institute (WCEI)
July issue is available now. Register here to read the latest issue and more.
Vomaris Announces First Patient Enrollment in Study on Effects of Bioelectric Wound Care in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
TEMPE, Ariz., Oct. 18, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Vomaris Innovations, Inc. announces the first patient enrollment in a study using its bioelectric antimicrobial wound care technology following surgical treatment for Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS).
About HS
HS is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects 1-4% of the global population. It occurs more often in women than men and is characterized by recurring pus-filled skin abscesses that drain and can develop tunnels under the skin. This results in pain, scarring and suffering that is both physical and emotional. Because HS most commonly occurs in areas where skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks and breasts, it presents unique treatment challenges.
Current treatments are aimed at managing lesions and their symptoms, trying to reduce recurrence and scarring, and coping with the associated psychological impact. Unfortunately, no one treatment is universally effective and there is no cure for HS. When tunnels develop under the skin, a surgical procedure called deroofing is commonly done. While this removes painful lesions and preserves the surrounding tissue, it leaves large open wounds … read more
COVID in the ICU: Can Patients Be Too Obese for ECMO?
Published guidelines recommend against extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for morbidly obese COVID-19 patients in severe distress, but a Florida researcher said his center’s experience indicates that such advice needs another look.
At Orlando Regional Medical Center, mortality in COVID patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and body mass index (BMI) values above 40, while not good, was no worse than previously reported for all critically ill COVID patients in a large database, said Sergio Ramirez, MD, a critical care fellow at the institution … read more
related:
2,000th ECMO patient
Decline in Diabetic Foot Ulcers Observed in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (UK)
Although diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) are considered both a major cause of patient suffering and high healthcare costs in the treatment of diabetes, low predictive power of DFUs makes primary prevention practices extremely limited for clinicians and patients.
Stemming from this challenge, a recent study examined incidence rates (IR) and changes over time for the first DFU in patients with diabetes seen in primary care in the United Kingdom … read more
From Chronic to Curable? RHEACELL is Developing a Novel Cell-Therapy Agent for the Treatment of Chronic Venous Ulcers
Heidelberg-based biopharmaceutical company is conducting a follow-up study with highly purified stem cells (AMESANAR (R) ) for the treatment of previously incurable chronic ulcers.
Heidelberg, 19. October 2021 – More than 80,000 people in Germany suffer from chronic venous ulcers (CVU). Triggered by venous insufficiency, wounds and weeping ulcers can develop that may not heal for years. Severely affected patients experience intense pain every day. Until now, there has been no effective treatment – but this could change soon … read more
How a medieval ‘leechbook’ could be the latest cutting-edge treatment to beat superbugs
Could novel vaccines or even a medieval recipe for eye balm provide new ways to defeat the teeming armies of antibiotic-resistant superbugs?
There is no doubt we desperately need new solutions to tackle infectious bacteria: the World Health Organisation (WHO) lists antimicrobial resistance as a top ten global health threat, saying that by 2050 it will kill more people than cancer if resistance keeps rising at current rates … In April, the WHO warned that none of the 43 antibiotics now being developed can beat the world’s 13 most lethal bacteria, such as Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, both of which cause blood infections and pneumonia … read more
Relief Therapeutics Reports Two Publications of Positive Data on Nexodyn(R) AOS for Hard-to-Heal Ulcers
GENEVA, SWITZERLAND / ACCESSWIRE / October 20, 2021 / RELIEF THERAPEUTICS Holding SA (SIX:RLF)(OTCQB: RLFTF) (” Relief “), a biopharmaceutical company seeking to provide patients therapeutic relief from serious diseases with high unmet need, today announced that its wholly owned subsidiary, APR Applied Pharma Research SA (” APR “), reported two papers published in the peer reviewed Journal of Wound Care , concluding that the company’s Nexodyn(R) acid-oxidizing solution (AOS), developed with APR’s proprietary Tehclo(R) technology, may represent a valuable therapeutic addition to standard of care (SOC) for the management of hard-to-heal ulcers requiring long periods of treatment. The data also confirmed the safety of Nexodyn(R) AOS.
Conducted by Elia Ricci, M.D., Director of the Difficult Wound Healing Unit, St. Luca Clinic, Department of Surgery A, Pecetto Torinese (TO), Piedmont, Italy, the prospective case series evaluated the clinical impact of Nexodyn(R) AOS in addition to SOC. Between February 2015 and February 2017, a total of 60 patients with hard-to-heal ulcers of various etiologies took part in the study. Patients were treated for 70 days with Nexodyn(R) AOS and the usual SOC wound dressings. The follow-up study, also conducted by Dr. Ricci, included a subset of 31 patients (51.7%) whose wounds had not fully healed by day 70, who opted to continue with treatment for another 22 weeks (for a total treatment time of 32 weeks) … read more
Wound Care Today 2021 conference 19-20 October, Marshall Arena, Milton Keynes
Wound Care Today 2021 offers delegates a unique learning platform, FREE of charge, to enhance their delivery of care through clinical updates, personal development, practical learning zones and networking in a friendly, open and above all else safe environment … Due the huge popularity over the last three years, we’ll have the same mix of clinical and professional development themed sessions – with a host of expert speakers presenting at the conference … read more
Bionix® Introduces AlphaCleanse™ to Wound Care Line
New AlphaCleanse™ Antimicrobial Wound Care System Offers a More Efficient and Convenient Approach to Wound Care Treatment
TOLEDO, Ohio, Oct. 18, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Bionix® is pleased to announce their new, single-use product—AlphaCleanse™ Antimicrobial Wound Care System with NovaGran™ Hypochlorous Acid.
The all-in-one kit is designed to provide healthcare professionals with the tools for efficient, effective treatment of chronic wounds … Contained in the AlphaCleanse™ Antimicrobial kit are the Bionix® Igloo® Shield and Probe Applicator, NovaGran™ Hypochlorous Acid, and a highly absorbent LiquidLock™ pad. Having all of the components in one kit saves time and protects against the cross contamination that is possible if the user has to search through various boxes for the tools to treat the wound … read more
Study of 236 patients reveals utility of MolecuLight i:X® in detection and management of wound-related cellulitis
Published results describe use of point-of-care imaging for the early detection and proactive management of wound-related cellulitis
TORONTO, Oct. 12, 2021 /PRNewswire/ – MolecuLight Inc., the leader in point-of-care fluorescence imaging for real-time detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial loads, announced the publication in International Wound Journal1 of an independent prospective observational study examining the impact of incorporating fluorescence imaging into standard care for the diagnosis and management of wound-related cellulitis. Dr. Charles Andersen, a surgeon at the Madigan Army Medical Center, led this study on wound-related cellulitis, defined as an invasion of bacteria from chronic wounds into the adjacent dermis.
The publication, “Diagnosis and Treatment of the Invasive Extension of Bacteria (Cellulitis) from Chronic Wounds Utilizing Point-of-Care Fluorescence Imaging“, included 236 patients visiting Madigan’s outpatient wound care center over a 16-month period between January 2020 and April 2021. In the study, wound-related cellulitis was diagnosed in 6.4% (15/236) of patients. Consistent among all patients diagnosed with wound-related cellulitis was an irregular pattern of red (bacterial) fluorescence visualized on the MolecuLight i:X point-of-care imaging system that extended beyond the wound bed and periwound. This unique pattern of red fluorescence could not be removed through cleansing or debridement.
Cellulitis is a serious clinical condition, accounting for 10% of all infectious disease-related US hospitalizations2 and up to $3.7 billion in costs annually 3. Cellulitis can lead to serious complications including bacteremia, necrotizing fasciitis, endocarditis, or shock4,3. Severe cellulitis in patients with other comorbid conditions may result in death. Timely and accurate diagnosis of cellulitis is notoriously challenging due to a lack of gold standard diagnostic techniques and a similar clinical presentation as other inflammatory conditions (e.g., stasis dermatitis). In those patients misdiagnosed, 85% experience avoidable hospital admission and 92% receive unnecessary antibiotics5.
“The results of this study show how MolecuLight point-of-care imaging presents an intriguing solution to revealing extension of bacteria into tissue, reducing misdiagnosis of wound-associated cellulitis, and enabling more proactive early treatment, particularly in patients lacking obvious symptoms”, says Dr. Charles A. Andersen, Chief, Vascular/ Endovascular and Limb Preservation Surgery Service (Emeritus), Chief Wound Care Service and Medical Director Wound Care Clinic at Madigan Army Medical Center, Tacoma, WA. “Given that at least 30% of cellulitis cases are misdiagnosed,6,5 the addition of consistent and objective information provided by fluorescence scans can significantly reduce the uncertainty associated with diagnosis of wound-related cellulitis. In addition, the use of fluorescence imaging to support earlier detection and proactive management of wound-related cellulitis can limit progression of infection and avoid the need for intravenous antibiotics and the high costs associated with inpatient admission”.
An example case of wound-related cellulitis from the study is shown (above) where the wound does not appear to have cellulitis or elevated bacterial burden upon assessment with standard-of-care clinical signs and symptoms (left). In contrast, when imaged with the MolecuLight i:X (right), an irregular pattern of red (bacterial) fluorescence extending beyond the wound bed and periwound is visible, and could not be removed with vigorous cleansing, indicating that the bacteria are located subsurface. This pattern of red fluorescence, demonstrating invasive extension of bacteria into surrounding tissues, was consistent in all wounds in the study where wound-related cellulitis was diagnosed.
Dr. Andersen will present the findings of this publication in a talk titled, “Diagnosis and Treatment of the Invasive Extension of Bacteria (Cellulitis) from Chronic Wounds Utilizing Point-of-Care Fluorescence Imaging“ at the upcoming clinical conference, SAWC (Symposium on Advanced Wound Care) Fall 2021 on Sunday, October 31, 2021 at 9:00 am at Caesars Palace in Las Vegas, Nevada.
|
References |
|
|
1 |
Andersen, C.A. et al, “Diagnosis and Treatment of the Invasive Extension of Bacteria (Cellulitis) from Chronic Wounds Utilizing Point-of-Care Fluorescence Imaging“, International Wound Journal 2021: 1-13 |
|
2 |
Lazzarini L et al, J Infect. 2005;51(5):383-389. |
|
3 |
Raff AB et al, JAMA. 2016;316(3): 325-337. |
|
4 |
Pasternack MS. Mandell, Douglas, & Bennett’s Principles & Practice of Infectious Diseases. Vol 1; Phil., PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2010:1289-1312. |
|
5 |
Weng QY et al, JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153(2):141-146. |
|
6 |
Levell NJ et al, Br J Dermatol. 2011;164(6):1326-1328. |
About MolecuLight Inc.
MolecuLight Inc., a privately-owned medical imaging company that has developed and is commercializing its proprietary fluorescent imaging platform technology in multiple clinical markets. MolecuLight’s first commercially released device, the MolecuLight i:X fluorescence imaging system and its accessories provide a point-of-care handheld imaging device for the global wound care market for the detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial burden (when used with clinical signs and symptoms) and for digital wound measurement. The company is also commercializing its unique fluorescence imaging platform technology for other markets with globally relevant, unmet needs including food safety, consumer cosmetics and other key industrial markets.
Image:
Download at: https://moleculight.box.com/s/oab22c1vi8ud1j8oymylbfogp2lg12bk
SOURCE MolecuLight
Related Links
The Polymath: Lee Rogers, DPM, RCPS, FFPM
Dr. Lee Rogers is a fellowship-trained podiatrist in diabetic limb salvage. Dr. Rogers is the Chief of Podiatry and Associate Professor of Orthopedics at University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. He has authored over 150 published papers, books, and book chapters on limb salvage and policy and practice and he has delivered more than 500 lectures around the world:
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome for Dermatology Application: A Review
Secretome, also known as conditioned medium, is a secreted molecule from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) that has a variety of biological activities that can be used in various therapies, especially on the skin applications. A lack of conventional therapies makes secretome as a promising alternative therapy. The presence of growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular vesicles including microvesicles and exosomes in secretome has been widely reported, which serves in improving the proliferation and migration of cells to help in skin regeneration. Therefore, we were able to optimize the use of this secretome in a well-needed special review related to its work in addressing various skin problems. So, in this article, we discussed the benefits and biological activity of secretome on the skin application. This review was compiled based on the approval of several sites, such as Scopus, PubMed, Science Direct, and Google Scholar with the terms “MSC secretome for skin,“ “secretome for skin,“ “secretome dermatology,“ “secretome conditioned medium for skin,” ”secretome conditioned medium for skin wound … read more
Fireside Chat with Dr. Breanne Everett
Dr. Breanne Everett is the CEO, President and Co-Founder of Orpyx Medical Technologies Inc., a company which creates medical-grade wearable technologies with unique pressure sensors to help prevent diabetic foot ulcers often caused by peripheral neuropathy, and to aid athletic performance. Dr. Everett was recognized as Graduate of the Last Decade from the University of Calgary, has been named one of the top 100 most powerful women in Canada, and has received the Governor General’s Innovation Award. Dr. Everett is a Loran Scholar, and sits on the CMA’s Joule Innovation Council, the Governor General’s Innovation Award Assessment Committee, and the Rideau Hall Innovation Advisory Council.
Orpyx high-tech insoles a step toward a better future for diabetics
During her studies at the University of Calgary, medical doctor Breanne Everett became interested in plastic and reconstructive surgery, concerned about the burden that diabetic foot complications posed to patients and our health-care system … Orpyx sensory insoles are helping people with diabetes to maintain mobility by helping prevent diabetic foot ulcers and possible limb loss, using advanced pressure, temperature and movement sensor technology and analytics … read more
Join the AAWC Sunday, October 24 online for a live replay encore presentation of the OUTSTANDING PrU EDUCATION, at no cost!
AAWC is delighted to be able to offer a live online replay of a select number of presentations from our Pressure Ulcer Summit.
The PrU Summit, themed Reducing Health Disparities in Pressure Ulcer/Injury (PU/PI) Detection & Management, took place on October 7-9, 2021. As part of the AAWC’s commitment to educating health care professionals on this important topic and as a thank you to the generous support from our sponsors and exhibitors, a live online replay conference will be aired globally, at no cost. More information.
The Role of Nutritional Inventions in Wound Care
A study in the Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery journal investigated the role of nutritional intervention in wound care.
The nutritional intervention and its role in wound care has been a controversial topic, according to authors of a review recently published in the Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery journal.1 This is the first literature review of mineral and vitamin wound intervention using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines by wound type, according to the review’s authors.
The authors of this review sought to outline the nutrients and delivery methods used in identified relevant studies, analyze treatment outcomes, and summarize the nutrient effectiveness. They also proposed evidence-based conclusions to improve outcomes of wound healing and increase the consistency of nutritional intervention in wound care … read more
Diverting or Swirling, New Blood-Flow Tech Shows Promise for CLTI
From deep-vein arterialization to a 3D stent, data presented at VIVA 2021 encourage novel thinking about peripheral vascular management.
New technologies that divert or improve blood flow offer promising options for patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI), according to two presentations this week at VIVA 2021 … We know there are a group of these patients who are nonrevascularizable with standard means, either percutaneous angioplasty or surgical bypass, and it’s in this group of patients where we’d like to divert the blood flow into the venous system to try and deliver that oxygenated blood to the foot and allow their wounds to heal,” noted Daniel Clair, MD (Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN) … read more
Epidemiology and Risk of Amputation in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus and Peripheral Artery Disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) stems from atherosclerosis of lower extremity arteries with resultant arterial narrowing or occlusion. The most severe form of PAD is termed chronic limb-threatening ischemia and carries a significant risk of limb loss and cardiovascular mortality. Diabetes mellitus is known to increase the incidence of PAD, accelerate disease progression, and increase disease severity. Patients with concomitant diabetes mellitus and PAD are at high risk for major complications, such as amputation. Despite a decrease in the overall number of amputations performed annually in the United States, amputation rates among those with both diabetes mellitus and PAD have remained stable or even increased in high-risk subgroups. Within this cohort, there is significant regional, racial/ethnic, and socioeconomic variation in amputation risk. Specifically, residents of rural areas, African-American and Native American patients, and those of low socioeconomic status carry the highest risk of amputation … read more
Unsalvageable: Preventable Amputations Rise During COVID
Leafer Miller didn’t hear much after the doctor told him they had to “sacrifice the leg.”
Lying on the emergency room gurney, the self-proclaimed video game nerd and former athlete struggled to comprehend life without the leg that had propelled him on the track and to the turf for tackles on the soccer field.
“It was always in the back of my mind as a worst-case scenario,” the 35-year-old Fresno, CA, native says. “But I wasn’t expecting that to be the case.”
The amputation was the result of a recurring American narrative: A diabetes diagnosis in his early 20s; a sequence of layoffs and hirings that left his insurance status in flux; missed primary care visits when providers went out of network; and skipped insulin doses due to unaffordable price tags.
“Sometimes, it would come down to insulin or rent,” Miller says, “I felt like my hands were tied.” … read more
Prioritizing Foot Ulcers During Lockdown Paid Off in Belgium
Belgium’s efforts to prioritize care at its diabetic foot ulcer clinics during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown minimized both delays in care and adverse outcomes, new data suggest … The country has had a national diabetic foot care program in place since 2005, with 34 multidisciplinary clinics recognized by the Belgium Ministry of Health for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) … The system has resulted in a decline in lower-limb amputations in the country … And while all nonurgent medical care in Belgium was postponed during the national COVID-19 lockdown period March 14-May 3, 2020, the clinics followed advice from professional associations to consider all active DFUs as urgent … read more
Maggots used to clean wounds in NHS as antibiotics fail some patients
Live maggots are being increasingly used to clean wounds by the NHS amid the threat of antibiotic resistance threatening patients’ well-being … According to a report in The Daily Telegraph, the treatment – which involves applying sterilised fly larvae to wounds to eat dead tissue – was common practice in the first half of the 20th century, but faded with the use of antibiotics in the 1940s … However, thanks to antibiotic resistance, maggots are again being used in the NHS and overseas. The paper reports that superbugs kill around 700,000 people a year, a figure predicted to reach 10 million by 2050 … read more
New wound gel to treat foot ulcers
An international research team, led by the University of Canterbury‘s Professor Rudi Marquez, has developed a new wound gel that promises horses and humans. This new wound gel will be used to treat foot ulcers and kick-starts tissue regeneration.
As scientists noted, it could have a significant impact on healing horses and humans alike.
To create this gel, scientists used a protein that helps the skin inside the human mouth to heal quickly … read more
A single center’s 15-year experience with palliative limb care for chronic limb threatening ischemia in frail patients
Our institution’s multidisciplinary Prevention of Amputation in Veterans Everywhere (PAVE) program allocates veterans with critical limb threatening ischemia (CLTI) to immediate revascularization, conservative, primary amputation or palliative limb care based on previously published criteria. These four groups align with the approaches outlined by the Global Guidelines for management of CLTI. The current study delineates the natural history of the palliative limb care group of patients and quantifies procedural risks and outcomes … read more
Launch of New MolecuLightDX™ Device to Enable Point-of-Care Imaging of Wounds in New Expanding Market Segments
MolecuLight Platform is Becoming the Standard-of-Care for Real-Time Imaging of Elevated Bacterial Burden in Wounds Across All Wound Care Settings
TORONTO, CANADA – (October 14, 2021) MolecuLight Inc., the leader in point-of-care fluorescence imaging for real-time detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial loads, announced the launch of the MolecuLightDX™, a new point-of-care device model targeted at the unique needs of new expanding wound care market segments in the USA. The DX is an expansion of MolecuLight’s product line and compliments the MolecuLight i:X®, the “workhorse” wound imaging device that has quickly become a standard in wound care practices worldwide, with over 2,000 units sold.
“The i:X and DX are the only commercially-available point-of-care devices to enable real-time detection of elevated bacterial burden in wounds. With the introduction of the MolecuLightDX, we are thrilled to expand our product line and provide added functionality for these wound care market segments,” says Anil Amlani, MolecuLight’s CEO.
Specifically, the MolecuLightDX has the following new features frequently required in these segments:
- Comprehensive EMR (electronic medical record) integration options for multiple EMR environments,
- Patient-centric user interface and workflow to allow for easy patient and wound tracking,
- An Administrator workflow and system configuration capability, and
- Docking system for easier charging of the devive.
As with the i:X, the DX has the same accurate, rapid digital wound measurement for documentation of procedures and of wound progression. Newly available on the DX is a stickerless measurement capability which automatically measures wound area without the need for wound stickers.
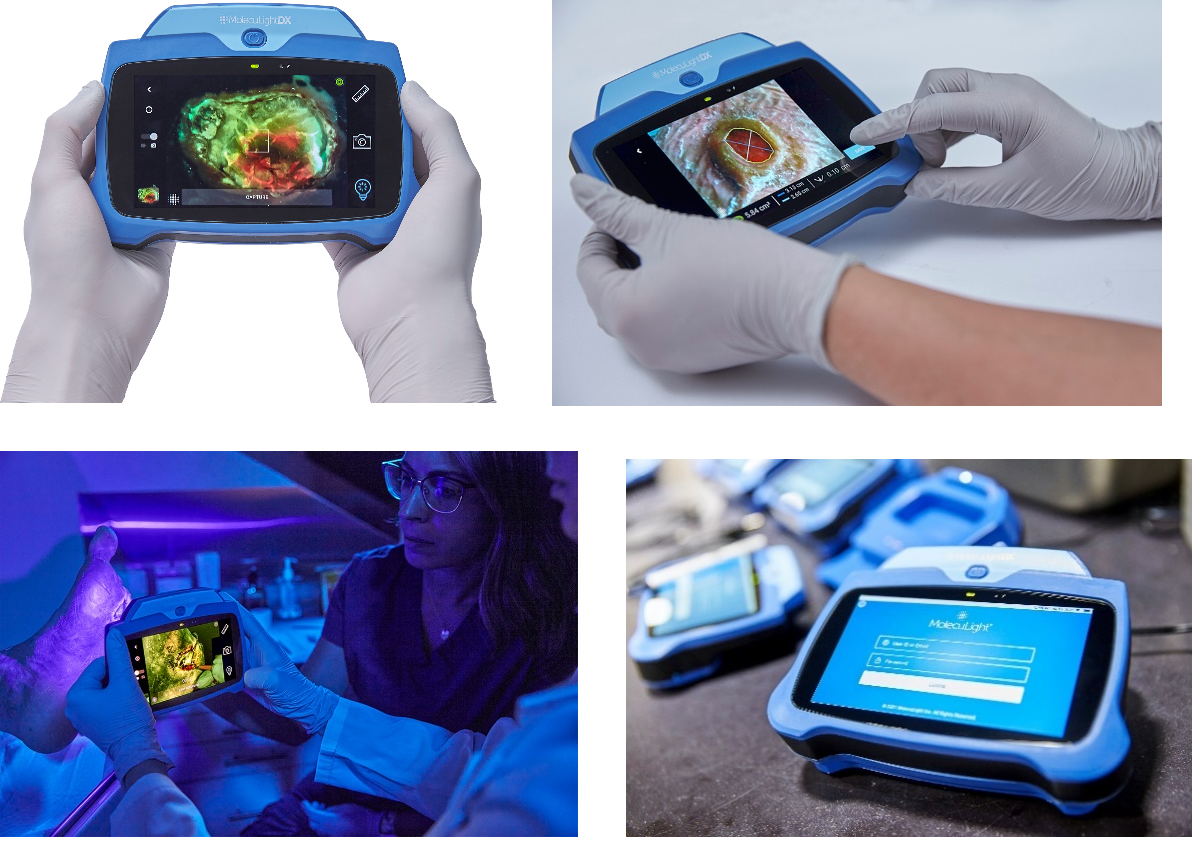
“With the expansion of our product line, we can now offer clinicians in any care setting the unmatched capabilities of the MolecuLight platform, with a feature set and price point that matches their specific needs”, says Amlani. “MolecuLight customers will continue to receive our comprehensive activation and training support on both platforms, including on-site training with patients, e-Learning courses and certification and ongoing in-person and remote support by our Clinical Applications team.”
In addition, all MolecuLight procedures will be able to benefit from the reimbursement pathway available in the United States for the MolecuLight procedure, which is applicable to both the MolecuLight i:X andDX devices. The reimbursement pathway includes two CPT® codes for physician work to perform “fluorescence wound imaging for bacterial presence, location, and load” and facility payment for Hospital Outpatient Department (HOPD) and Ambulatory Surgical Center (ASC) settings through an Ambulatory Payment Classification (APC) assignment.
The MolecuLightDX has received FDA clearance for sale in the USA, as well as the CE Mark and Health Canada approval for commercial availability in Europe and Canada.
The MolecuLightDX will be displayed in the MolecuLight exhibit booth at the upcoming clinical conference, SAWC (Symposium on Advanced Wound Care) Fall 2021, on Sunday, October 31, 2021 at 9:00 am at Caesars Palace in Las Vegas, Nevada. To request an on-site clinical demonstration of the MolecuLightDX, please go to www.moleculight.com, or email info@moleculight.com.
About MolecuLight Inc.
MolecuLight Inc., a privately-owned medical imaging company that has developed and is commercializing its proprietary fluorescent imaging platform technology in multiple clinical markets. MolecuLight’s suite of commercially released devices, including the MolecuLight i:X® and DX™ fluorescence imaging systems and their accessories, provide point-of-care handheld imaging devices for the global wound care market for the real-time detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial burden (when used with clinical signs and symptoms) and for digital wound measurement. The company is also commercializing its unique fluorescence imaging platform technology for other markets with globally relevant, unmet needs including food safety, consumer cosmetics and other key industrial markets.
Rob Sandler
Chief Marketing Officer
MolecuLight Inc.
M. +1.647.362.4684
rsandler@moleculight.com
www.moleculight.com
Wound Care Advantage Launches National Awards Program Honoring The Unsung Hero Of Wound Healing: The Patient
Wound Care Advantage (WCA), the leading provider of consulting and digital services for wound care programs, is pleased to announce a new awards program honoring inspirational patients who demonstrate exceptional strength and fortitude during treatment. Sponsored by WCA, the Wound Care Hero Awards are designed to give special recognition to patients treated by wound care programs in the WCA Network, which comprises programs across 20 states.
The award was inspired by LaVonna Tipton, a cancer survivor who was treated for non-healing wounds at Clark Regional Medical Center, a WCA Luvo Network partner in Winchester, Kentucky. Despite the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, she attended every session of her hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which involved daily sessions, five days a week for one month. Her wounds, caused by previous cancer treatments, were fully healed, thanks to her diligence and the work of the Clark Regional team … read more
DIABETIC FOOT: FACTS AND FIGURES
A series of great informational graphics from Dr. Armstrong …. read more
Treatment of Non-Healing Diabetic Foot Wounds with Vaporous Hyperoxia Therapy in Conjunction with Standard Wound Care
Vaporous Hyperoxia Therapy (VHTTM), a patented FDA-510 (k) cleared technology, is an adjunct therapy used in conjunction with standard wound care (SWC). VHT is said to improve the health of wounded tissue by administering a low-frequency, non-contact, non-thermal ionic anti-microbial hydrating mist alternating with concentrated topical oxygen therapy (TOT). VHT was used to treat 36 subjects with chronic diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) that were previously treated unsuccessfully with SWC. The average age of DFU in the study was 11 months old and the average size was over 3 cm2. Wounds were either Wagner Grade 2 or 3 and most commonly on the plantar surface around the midfoot … read more
WoundsWeek Streaming Mon 6th – Fri 10th December 2021 | 6pm – 7pm (GMT)
With 10 hours of incredibly current topics, Wounds Week 3 will give a chance for the wound care community to come together in these difficult times, engaging in key education free of charge.
Each session has a live Q&A so participants can benefit from one-on-one interactions with the experts and engage in the event, no matter their COVID-19 situation. All our sessions are CPD-certified, and you will receive a certificate for watching on-demand too!
BioLab Sciences Named Bioscience Company of the Year
The emerging regenerative biotechnology company was recognized for its innovative regenerative therapies and advancements in wound healing
BioLab Sciences, an emerging regenerative biotechnology company, today announced it has been named Bioscience Company of the Year by the Arizona Bioindustry Association (AZBio), the foremost organization exclusively focused on Arizona’s bioscience industry. The biotechnology company was recognized for its innovations in regenerative therapies and advancements in wound healing. BioLab Sciences, which launched in 2018, has grown from a small team of four to 70 employees, with more than 47 full-time new hires joining the company in 2021 alone. The company has come to be known for its best-of-breed advanced wound care and regenerative products: Fluid GFTM, Membrane WrapTM, Amino RestoreTM, and its flagship product, MyOwn SkinTM, a revolutionary regenerative therapy that is transforming the wound care industry … read more
Vascular Care Falls Short Before Amputation for CLI: Medicare Analysis
Too few patients underwent angiography or interventions, and suboptimal care was linked with more deaths and readmissions.
Alook back at the care patients with critical limb ischemia (CLI) received in the year prior to amputation suggests that most received minimal vascular care, with 69% not undergoing a revascularization attempt that might have saved the limb or improved overall survival.
Earlier this year, the American Heart Association noted in a policy statement that after a period of decline in the 1990s and early 2000s, major and minor amputations have been on the rise. National surveys, too, reflect a dramatic undertreatment problem in the outpatient setting among patients with PAD … read more
The Current Situation for Non-healing Wounds
Accessibility of Wound Data in Canada
While even healing wounds require significant health-care resources, ultimately the majority of the resources used are for wounds that are non-healing.1,2 Non-healing wounds, which originate from different etiologies such as arterial and venous insufficiency, pressure and diabetic foot complications, are a serious public health problem that have devastating consequences for patients and result in high costs to health-care systems … read more (PDF)
Current Challenges in Wound Care
Chronic wound care is a wound that persists after 4-6 weeks, and a complex wound is one that a health care professional is the one who needs to take care of it. The lack of progression and the complex nature of the wounds are due to multiple reasons and can be explained by the following factors1:
- patient-related factors (lack of assessment of comorbidities or factors contributing to the wound, and difficulties related to the patient’s behavior and cooperation);
- factors related to the wound (surface, volume, damage to the noble tissues, misdiagnosis of the etiology of the wound, and lack of diagnosis of infectious or ischemic complications of the wound);
- factors related to the skills and knowledge of health professionals (absence of standardized or appropriate care protocols);
- factors related to environmental or social difficulties in terms of resources available for the treatment of the wound.
Effects of Simultaneous versus Staged VAC Placement in the Treatment of Deep Neck Multiple-Space Infections at a …
Tertiary Hospital Over a Four-Year Period in China
Deep neck infections (DNIs) are a group of serious bacterial infections occurring in the potential spaces and fascia of the neck. The incidence of DNIs is not clear. Although many studies have shown that the incidence of DNIs has decreased due to the use of antibiotics and improvements in sanitary conditions, reports also indicate an increased incidence of DNIs in the last 10 years. Deep neck multiple-space infections (DNMIs) are the most serious among all types of DNIs and often spread further to cause mediastinal infections, invade the carotid sheath, and possibly compromise the airway, resulting in life-threatening conditions.
Treatments for DNMIs include life-supporting measures, surgical drainage, and appropriate use of antibiotics. Among these treatments, surgical drainage is key. Although traditional extensive surgical drainage is effective for treating DNMIs, some limitations remain for this approach, ie, drainage depends on gravity, the locations for the drainage tube and incision are limited, dressing changes and wound irrigation more than once a day may increase patient suffering, and secondary wound infection may occur. In recent years, vacuum-assisted closure (VAC)
Malta’s first space research touches back down on earth
Project seeking to innovate diabetic ulcer treatment
Led by associate professor of biomedical science at the University of Malta Joseph Borg, the Project Maleth team sent samples of micro-organisms that cause diabetic ulcers to the International Space Station (ISS), in a bid to analyse how the tissue will react under extreme conditions.
They hope that the information they glean from the results will be able to help patients by developing new ways to treat diabetes and its symptoms … Launched from Cape Canaveral in Florida on August 28, Project Maleth spent just over a month aboard the International Space Station … read more
America’s Amputation Crisis May Soon Get Much Worse
Proposed Medicare cuts create greater barriers to screening and revascularization services
Few medical procedures are as life-altering as an amputation. But statistics show hundreds of thousands of Americans have their limbs surgically removed each year because they don’t have access to adequate vascular screening and care.
In the rural communities of North Carolina that we serve, the nearest “in-hospital” alternative to our office-based treatment locations is at least 2 to 3 hours away, which can result in delays in care that lead to poor clinical outcomes. The patients we serve are living with vascular diseases such as peripheral artery disease (PAD) and critical limb ischemia (CLI) … read more
1M diabetic people in Egypt at risk of amputation given hope by Sound Foot initiative
CAIRO – 4 October 2021: A total of L.E. 15 million have been allocated to support “Sound Foot” initiative to reduce the risks of diabetes, according to a Monday statement by the Ministry of Solidarity.
Some L.E.5 million of that budget will go to raising awareness on the diabetic foot and early detection. L.E. 10-15 million will go to treatment.
On Monday, Maker of Good Development, a charity organization that was established five years ago, held a conference to launch the initiative as part of the presidential initiative of Haya Karima. Minister of Solidarity Nivine el-Kabbag said in the conference that the Sound Foot initiative is a … read more
Footing the bill for diabetes
The world’s first Diabetic Foot Clinic was opened in 1981 at King’s College Hospital by Professor Michael Edmonds.
Since I jointly set up the Diabetic Foot Clinic at King’s College Hospital in 1981, I have seen how multidisciplinary care can have a huge impact on patient outcomes. Specialists working together under one roof can intervene and stop the progression of a disease which, if untreated, can swiftly lead on to tissue necrosis and gangrene. But, if I had to pick the one crucial thing that has really revolutionized our practice – helping to achieve a 50 percent reduction in major amputations … read more
Are Restaurants Exacerbating the Obesity Epidemic?
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began, almost all discussion of restaurant-related health has centered on one topic: how to protect diners and staff from the virus. But another health issue has been largely overlooked: how restaurants compromise Americans’ health by selling fare that is high in caloric density, fat, added sugars, and sodium, but low in essential fiber. And during a pandemic where obesity and other pre-existing health conditions have been risk factors for severe disease, this discussion couldn’t be more relevant.
It’s common knowledge that fast food sold by chains such as McDonald’s, Burger King, Wendy’s, and the like has a poor nutritional profile. But the appetizers, entrees, and desserts sold at full-service restaurants aren’t much better … read more
4 leading surgeons discuss surgical wound infections (video)
Medtech company Next Science has released video of a popular panel discussion it sponsored at the recent AAOS Annual Meeting. The 28-minute video can be viewed below or on youtube
The presentation, “Biofilm and Surgical Site Infections,” features insights from four leading orthopedic surgeons:
– Dr. Robert M. Harris, Hughston Clinic (Columbus, GA)
– Dr. Jon E. Minter, Northside Hospital (Atlanta, GA)
– Dr. Randall Otto, SSM Health (St. Louis, MO)
– Dr. Ravi K. Bashyal, NorthShore University Hospital (Chicago, IL)
Each year, there are about 1.5 million surgical site infections (SSIs) in the U.S., and patients with SSIs are five times more likely to be readmitted and twice as likely to die. SSIs also contribute an additional $3.5 billion annually to the cost of healthcare.
Perianal Infections in Patients With Hematologic Malignancy
The Risk of Fournier’s Gangrene Leading to Mortality and Irreversible Organ Damage
The efficacy of surgical intervention for perianal infection in patients with hematologic malignancy is not well-established. Objective. This article presents a case series of perianal infection progressing to Fournier’s gangrene (FG) in patients with hematologic malignancy to guide physicians, because to the author’s knowledge, there were no randomized or prospective studies presenting the management strategies reported herein. It was hypothesized that surgery might reduce mortality and morbidity in patients with inflammation spreading beyond the perianal region, in patients with abscess formation, and in those who show no improvement with medical therapy. Materials and Methods. The data of 4 adults with hematologic malignancy who developed perianal infection progressing to FG between January 2010 and December 2018 were reviewed retrospectively … read more
NPWT Won’t Work If Your Patients Won’t Use It webinar | October 07, 2021
Nurses are tasked with managing an array of complex wounds. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is often viewed as a highly specialized skill, but it does not have to be complex. Join this webinar to learn how NPWT’s mechanism of action can address acute wounds, chronic wounds, and closed incisions. This session will provide education on the types of wounds appropriate for the various types of NPWT and equip nurses to confidently manage a patient with NPWT … read more
6th Annual ACFAP Pediatric Foot & Ankle Seminar October 7th-9th
This CME event will feature leading authorities on pediatric foot & ankle conditions. It will cover topics ranging from pediatric H&P, flatfoot, equinus, sports medicine, surgery, and rotational conditions. The meeting will be preceded on Thursday October 7th by a one day national park excursion. Featured at this meeting will be spectacular Death Valley National Park … read more
The Compassionate Amputation: Think Outside The Limb
Faced with the challenges of non-healing diabetic ulcerations, a patient’s realization of progressively declining health, the burden of expansive health costs and the unrelenting frequency of doctor appointments, can cumulatively lead to a heavy emotional toll and state of despair. In dealing with high-risk patients, how we navigate the nuances of these aforementioned complexities may define our role in the lives we impact. While mental health consequences of chronic disease are well-documented, I feel there is no louder or stronger a case than the fragile cohort of those plagued with diabetes at the critical point where discussion about amputation becomes essential … read more
What COVID-19 taught us: New opportunities and pathways from telemedicine and novel antiseptics in wound healing
The COVID-19 pandemic deeply impacted the capacity of the health systems to maintain preventive and curative services, especially for the most vulnerable populations. During the pandemic, the wound healing centres in Italy assisted a significant reduction of the frequency of their hospital admission, since only urgencies, such as severe infections or wound haemorrhagic complications, were allowed to the hospital. The aim of this multidisciplinary work is to highlight the importance of a new pathway of wound care with patient-based therapeutic approach, tailored treatments based on the characteristics of the wound and fast tracks focused on the outpatient management, reserving hospital assessment only for patients with complicated or complex wounds. This analysis highlights the point that patients with chronic wounds need to be critically evaluated in order to find the best and most appropriate care pathway, which should vary according to the patient … read more
National Wound Care Strategy Programme: clinical work stream: lower limb update
The National Wound Care Strategy Programme (NWCSP) continues to make great progress. I appreciate many of you may have signed up to the stakeholder group and have been questioning our silence, but I can promise you that we have been working very hard behind the scenes to be able to provide you with tangible outcomes following your feedback. We have just finalised the ‘clinical navigation tool’ for all lower limb wounds, which is currently out for consultation with the registered stakeholder group. It is hoped that implementation of the tool will provide a consistent approach for all patients, irrespective of where they live in the UK and who their service provider is. The tool addresses all lower limb wounds, including diabetic foot ulceration, leg ulceration and pressure ulceration on the heel as it has been recognised that one of the fundamental issues is the correct ‘labelling’ of patients … View PDF
Footnotes: Nutritional Considerations For Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Hi, there. My name is Nicole Curreri, and I’m currently a fourth‑year podiatry student at Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine. My co‑authors, Ms. Diana Johnson, who’s a nutritionist and dietician, along with Dr. Khurram Kahn, a DPM at Temple (University School of Podiatric Medicine), have worked together on an article that emphasizes the role of nutrition in healing and treating diabetic foot ulceration.
Podiatrists treat lower extremity wounds secondary to pressure, diabetes, neuropathy, trauma, etc. Most commonly, we treat diabetic foot ulcerations. About 10 to 15 percent of patients with diabetes will go on to develop a diabetic foot ulceration … read more
Foot Revascularization Avoids Major Amputation in Persons with Diabetes and Ischaemic Foot Ulcers
The study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of foot revascularization in persons with diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) and below-the-ankle (BTA) arterial disease. Consecutive patients referred for a new active ischaemic DFU requiring lower limb revascularization were considered. Among those, only patients with a BTA arterial disease were included. Revascularization procedures were retrospectively analysed: in the case of successful foot revascularization (recanalization of pedal artery, or plantar arteries or both) or not, patients were respectively divided in two groups, successful foot perfusion (SFP) and failed foot perfusion (FFP). Healing, minor and major amputation at 12 months of follow-up were evaluated and compared. Eighty patients (80) were included. The mean age was 70.5 ± 10.9 years, 55 (68.7%) were male, 72 (90%) were affected by type 2 diabetes with a mean duration of 22.7 ± 11.3 years. Overall 45 (56.2%) patients healed, 47 (58.7%) had minor amputation and 13 (16.2%) major amputation. Outcomes for SFP and FFP were respectively: healing … read more
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF DIABETIC FOOT ULCERS DURING THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC IN CHINA
Flow chart from David G. Armstrong link
iWound® USA and iWound® Canada Collaborates with Archangel™ Mercy, LLC. to Transform How and Where Wounds are Healed
TORONTO, Oct. 1, 2021 /PRNewswire/ – iWound USA and iWound Canada announced today that they have collaborated with Pittsburgh based, Archangel, to complete the expansive list of wound care services that they currently provide. Archangel is a dynamic, mobile and web-based wound care platform designed to guide clinicians to assess, document, treat, heal and achieve better wound care outcomes. iWound will act as a reseller of Archangel while providing first in class care via wound consultation, telemedicine, and education.
The iWound-Archangel collaboration will provide evidence-based treatment plans, customized formularies and workflows and the ability to order products for their patients regardless of the patient’s insurance.
“iWound’s key to success hinges on our experienced wound care professionals delivering expert advice powered by the predictable, successful patient outcomes analytics that Archangel provides to complete our comprehensive, wound care solution,” said Ray Garneau, President of iWound … read more
Wound Management Docs Might Want to Read this Interview with Wound Clinic Nurses
Editor’s note, this is from Aug 18, 2020 but I thought it might be of interest :
The theme of the August issue of Today’s Wound Clinic is “Multidisciplinary Care.” I decided to interview my amazing staff (pictured holding the hospital award for the clinic coming back the strongest since the pandemic, from left to right: Tara Stone, Debi Thompson, Donna Dulaney and Michelle Hebert). I think every physician who practices wound management ought to read this interview. They were brutally honest and probably said some things that other nurses would like to say but haven’t had a “safe space.” I welcome the constructive comments of other nurses, technicians, and therapists about how we can collaborate better in the care of our very complex patients. Here’s a safe space for those comments … read more
GROWING YOUR BUSINESS WITH WOUND CARE
You know me, you’ve heard me say it before—wound care is important for all DMEPOS providers because every patient has skin, and skin health affects each of us. The skin is our largest organ. Not only does it protect us against the ever-changing environment, it also maintains our integrity. Without proper treatment to lacerations, surgical incisions, burns and injuries, the “wound” could lead to life threatening consequences. All providers see patients who are prone to skin issues because of co-morbidities, surgeries or advanced age.
If you can’t tell, I’m trying to make the case that everyone should be in wound care. If you haven’t considered expanding or elevating your business with wound care, you should. It’s human nature to shy away from wounds, and you may not know what to ask or how to get started (VGM Wound Care can help with that). But your patients have health issues which put them at an increased risk for skin breakdown. Respiratory issues, cardiovascular problems, diabetics, and para- and quadriplegics are just a few of the conditions that … read more
New publication fosters improved wound care for ulcers, limb salvage, burns, trauma, and more
New Rochelle, NY, January 10, 2012–The rapidly advancing field of tissue injury and repair has an important new forum. Advances in Wound Care will report the latest research findings, innovative wound care strategies, industry product pipeline, and developments in biomaterials and skin and tissue regeneration to optimize patient outcomes. The bimonthly online publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc is an Official Publication of the Wound Healing Society, offering rapid dissemination of the latest scientific discoveries, translational research, and clinical developments in acute and chronic wound care. The inaugural issue is available free online at www.liebertpub.com/wound
The Challenges and Advantages of Office-Based Wound Care
Change in health care is in the winds these days. The current pandemic has allowed us to explore different ways of delivering health care, both in how we see patients and where we see patients.1 Although telemedicine might not be ideal for wound care patients, it opened the door to an option of remote supervision of wound care, which was previously inconceivable. Likewise, the shuttering of hospital outpatient departments deemed “non-essential” as the pandemic raged made office-based wound care look more promising. After all, podiatrists have been doing it for years.2
This article will explore some of the advantages and challenges for those in the practice of office-based wound care. Physician office-based wound care is the new frontier—well, new to the folks who are accustomed to providing these services in a hospital outpatient department … read more
Effectiveness of a synthetic human recombinant epidermal growth factor in diabetic patients wound healing
Pilot, double-blind, randomized clinical controlled trial
To investigate whether the addition of human recombinant epidermal growth factor (h-EGF) to 2% carboxymethyl cellulose gel is more effective in diabetic wound healing than standard treatment, a pilot, double-blind, randomized and controlled clinical trial with therapeutic intervention was performed at a university hospital. The sample consisted of 25 patients (14 in the intervention group that used rh-EGF and 11 in the control group that used 2% carboxymethyl cellulose gel). Data were tabulated in SPSS and analysed by intention to treat, without loss or exclusion of participants. Twenty-five subjects participated with a mean age of 60.6 years, a predominance of males in both groups and 100% prevalence of type-2 diabetes. Within 12 weeks, complete wound healing occurred in three ulcers in the intervention group versus one ulcer in the control group. The percent reduction in the wound area was significantly higher in the intervention group than in the control group (p = 0.049). Concerning the types of tissue, an increase in … read more
APMA Sponsored Webinar: Turn an Exam Room into a Multi-million Dollar Revenue Stream
In this webinar sponsored by Molecular Lab Partners, Joe Case, the CEO of Molecular Lab Partners, will discuss how they can help you bring Molecular Testing in-house with relative ease. Their turnkey process not only guides clinicians through the Physician Office Lab implementation process but also makes molecular testing fast and easy with Ready To Run, Custom Plated Assays In Convenient Break-Away Plates. Operating your own Physician Office Lab not only improves patient care with one-hour results on wound, nail fungus, and antibiotic resistance, but also provides you with a new revenue stream on testing you are already performing daily.
“I have to admit, I am always skeptical with consulting services related to in-office ancillary services. However, Molecular Lab Partners has definitely changed my mind! The entire POL implementation process, from the lab design and equipment procurement, to the hiring process of our Laboratory Director, Supervisor and Techs, has been seamless. I highly recommend the entire team at MLP.” ~ James Baldwin III, DPM … read more
HMP Global Announces Details of New “SAWC Change” Campaign
HMP Global announced details of the new “SAWC Change” campaign part of the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC Fall), taking place as an in-person gathering, October 29-31, 2021 in Las Vegas.
The meeting has forged partnerships with the Wound Healing Foundation (WHF) and debra of America to support their efforts to advance innovative wound care research and outcomes for patients who suffer with chronic wounds.
For every registration to SAWC Fall, a donation will be made to each association … read more
Targeted Nutrition Therapy: Key Ingredients to Support Wound Healing
Time may not be able to heal wounds, as the saying goes, but the body can—with proper medical and nutritional support, according to recent data for targeted nutrition therapy.During the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care Spring 2021 virtual meeting, Maritza Molina, RDN, and David G. Armstrong, PhD, DPM, of the Keck School of Medicine of USC, in Los Angeles, discussed how incorporating nutrition as part of the overall treatment plan can promote healing, decrease treatment duration and improve patients’ overall quality of life … read more
Micreos secures €32 million for its endolysin-based platform as sustainable alternative to antibiotics
THE HAGUE, The Netherlands, Sept. 30, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Dutch biotechnology company Micreos announced it has secured another €32 million in funding to further develop its endolysin platform technology, based on targeted killing of only unwanted bacteria. This funding round will help Micreos accelerate its clinical development programs for atopic dermatitis, diabetic (MRSA) wounds and bloodstream infections, based on its pharmaceutical lead compounds, XZ.700 and SP.800.
Endolysins as precision anti-bacterials
In its search for solutions, Micreos’ researchers, in close collaboration with the Swiss Federal Technology Institute ETH Zurich, turned to nature’s own precision anti-bacterials, named endolysins. Unlike antibiotics, these highly specific enzymes have the ability to target only unwanted bacteria, while preserving the microbiome, comprising billions of ‘good’ bacteria, essential for our health. Endolysins are safe and environmentally friendly. Because of their working mechanism, development of resistance is not expected.
Addressing unmet medical needs
XZ.700 targets Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), including the antibiotic-resistant MRSA, while preserving Staphylococcus epidermidis, considered to be beneficial on the skin and conducive to wound healing. SP.800 targets all staphylococcal species … read more
But Who Were Marie and Tooth?
Recently, during an academic discussion, the topic of Charcot Marie Tooth disease came up. It’s a very important disease to a podiatrist, so it makes sense that we were discussing its effect on a patient. During this discussion, my mind started wandering a bit (yes, I’ll admit it), and I thought, “I know who Charcot was, but who were Marie and Tooth?” After growing up in the medical world, I knew the prevalence of eponyms (in fact, it’s one of my favorite topics to read about), so I knew that Marie and Tooth were people. But who were they? It’s easy to forget that there were actual people behind these eponyms, people with lives, loves, adventures, passions and failures. So, let’s take a digression away from things clinical and look into a window on the past … read more
Patient Engagement, Diabetes and Diabetic Foot Ulcers | EWMA Podcast
In this episode, you can listen to a conversation between the EWMA Podcast Host Samantha Holloway and Dr Athanasios Hassoulas, director of the MSc in Psychiatry programme and Senior Lecturer in Psychological Medicine at Cardiff University. They will talk about the meaning and impact of patient engagement and empowerment in relation to diabetes and diabetic foot ulcer management. The podcast provides reflections on the topic as well as recommendations on how to implement these person-centred tools in your meetings with diabetic foot ulcer patients in you daily clinical practice … listen
Turkish scientist’s work shows spinach can speed up wound healing
Spinach does not give you instant muscles as it did to Popeye, though its healthy properties are highly valued. Now, a Turkish researcher has added a new one to them. According to assistant professor Serkan Dikici, baby spinach, in its decellularized form, can accelerate the healing of wounds.
Dikici, who works at the bioengineering department of Izmir Institute of Technology, won a doctoral researcher award in the United Kingdom for his study.
The young scientist attended Sheffield University as a Ph.D. student in tissue engineering and for his Ph.D. study, he chose the development of biomaterials for healing of chronic wounds, to replace or reduce the use of guinea pigs in this field … read more
Organizations Join Forces to Boost Wound Healing Care and Research
HMP Global’s Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC) Fall has established partnerships with the Wound Healing Foundation and debra of America to boost their research and improve care of patients with chronic wounds, such as those with epidermolysis bullosa (EB).
The SAWC Fall is scheduled to take place as an in-person meeting Oct. 29–31 in Las Vegas. For every registration, a donation will be made to each organization, according to HMP Global’s press release. To register, go here.
Established in 1999, the Wound Healing Foundation is a nonprofit dedicated to boosting scientific research and care of wound healing patients by funding research and promoting education and outreach.
debra of America works to improve the quality life of people with EB. Launched in 1980 to fill the gaps in knowledge about EB, the organization offers free services to U.S.-based EB patients and their families, and funds innovative research ultimately aimed at finding a cure for the disease … read more
As an Active Cleanser, Nexodyn(R) AOS Shows Superior Wound Healing Performance Compared to Standard of Care
Relief’s Subsidiary, APR Applied Pharma Research, Reports Data Published in Journal of Wound Care, Indicating Nexodyn(R) AOS Highly Effective Treatment to Support Healing of Hard-to-Heal Leg Ulcers … RELIEF THERAPEUTICS Holding SA (SIX:RLF)(OTCQB:RLFTF) (“Relief”), a biopharmaceutical company seeking to provide patients therapeutic relief from serious diseases with high unmet need, today announced that its wholly owned subsidiary, APR Applied Pharma Research SA (“APR”), reported data published in the peer reviewed Journal of Wound Care, indicating that the company’s Nexodyn(R) acid-oxidizing solution (AOS), developed with APR’s proprietary Tehclo(R) technology, was found to be a highly effective treatment to support wound healing in infected or non-infected hard-to-heal leg ulcers. The data also confirmed the safety and tolerability of Nexodyn(R) … Conducted by Robert Strohal, M.D., Professor and Department Head, Department of Dermatology, Federal Academic Teaching Hospital of Feldkirch, Austria, and colleagues, the open-label, randomized controlled MACAN study was conducted at two centers is Austria. A total of 50 patients were enrolled, with either infected or non-infected hard-to-heal leg ulcers of different etiology. Patients were treated for six weeks either with Nexodyn(R) AOS or standard of care (SOC) wound dressings … In the patient group treated with Nexodyn(R) AOS, wounds exhibited a faster and more pronounced wound size reduction compared with wounds in the SOC group. Additionally, compared to SOC, the treatment group showed a markedly greater percentage of complete healing of hard-to-heal ulcers by the end of the study period (32% versus 8%, respectively). Furthermore, Nexodyn(R) demonstrated its ability to significantly reduce the wound pH (p<0.0001) and thus promote a faster healing process. In all patients with infected leg ulcers, local infection was overcome more rapidly with Nexodyn(R) AOS treatment. Overall, the efficacy of Nexodyn(R) AOS was found to be not only non-inferior but superior to SOC wound dressings … read more
RETHINK Talks: An Interview with ReNew Wound Care
This interview is brought to you by ReNew Wound Care. This interview took place during a live Q&A session with ReNew Wound Care CMO Dr. Rekha Bhandari at the SNN RETHINK event in Chicago held on September 1, 2021. The interview has been edited for clarity … read more
Study shows how management of serious diabetic foot ulcers was possible during the COVID-19 lockdown
New research being presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), held online this year (27 Sept-1 Oct), reveals how Belgium’s efforts to maintain a diabetic foot care programme during the COVID-19 pandemic can offer valuable lessons to the rest of the world.
“Thanks to the great efforts of diabetic foot clinics, continued availability of diabetic foot ulcer services during lockdown, although in a limited capacity, were really helpful, and may be the reason why we didn’t see late presentation and the impact on the severity of ulcers was limited to slightly larger wounds”, says lead author Dr An-Sofie Vanherwegen from Sciensano, Brussels, Belgium. “Our findings will hopefully guide diabetic foot clinics in serving their patients using innovative strategies … read more
Expanding horizons to upskill wound practice and research
With our horizons limited by Covid-related travel restrictions, it is more important than ever to experience and learn about our multicultural world through reading about wound-related research and practice in other jurisdictions and countries. Two such articles provide this important international insight and are included in this issue of the journal. The first by Obilor and colleagues describes the assessment of nurses’ knowledge, attitude and competence in wound assessment in a tertiary healthcare facility in southwest Nigeria. Here they found that many of the nurses surveyed were lacking in wound assessment competence … read more
The HealSource™ Clinical Practice Guidelines
The HealSource™ Clinical Practice Guidelines provide a standardized method for the delivery of care, treatment and services to patients with wounds or ulcers.
These clinical practice guidelines are a useful guide when caring for patients, providing general guidelines for the treatment of chronic wounds and the application of hyperbaric oxygen treatment. The data relies heavily on three significant and highly respected contributions to the fields of wound care and hyperbaric medicine:
The Wound Healing Society guidelines for the best care of chronic wounds
The Wound Ostomy Continence Nurses Society clinical practice guidelines
The Oxygen Therapy Committee Report of the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medicine Society
The Fairy Tale is Over in the Wound Center
Once upon a time there was a happy land where at least half the patients seen in a hospital-based outpatient wound center (HOPD) were Medicare Fee for Service (FFS) beneficiaries. Their treatments were covered and we got paid for providing them. The most the patient had to worry about was the 20% “patient responsible portion.” In that kingdom, only private payers required prior authorization for services like hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), or “skin substitutes,” but at least they actually authorized those treatments upon request … read more
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for paediatric patients: an unintended consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a useful adjunctive treatment for selected complicated wounds, including severe diabetic lower extremity ulcerations and compromised skin grafts or flaps. The Sars-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic has disrupted healthcare delivery, with its effects extending to delivery of HBOT. During the pandemic, paediatric patients in our geographic region who were referred for HBOT faced challenges as centres temporarily closed or were unprepared to treat younger patients. Our monoplace HBOT centre modified existing practices to allow for treatment of these patients. This study aims to outline the steps necessary to adapting a pre-existing HBOT centre for the safe treatment of paediatric patients … read more
Strategies and Techniques for Transitioning NPWT Patients to the Post-Acute Care Setting
Join Dr. Klein as he shares his experience transitioning NPWT patients to the post-acute care setting.
– Examine the prevalence of hospital readmissions, the economic impact, and the importance of preventing readmissions to improve wound healing.
– Discuss common challenges associated with discharging a NPWT patient to the post-acute care setting and the steps to develop a comprehensive discharge plan.
– Review strategies for educating patients and empowering them to be an active participant in their treatment plan as they transition from the acute to post-acute care setting.
– View case studies utilizing negative pressure wound therapy to optimize wound healing.
Read more and register
Improving Vascular Access Dressing Integrity in the Acute Care Setting
Hospitals have a major focus on improving healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) with intense scrutiny on central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs) and other hospital-onset bacteremias. Efforts at prevention have long targeted the skin of the patient and healthcare worker processes such as hand hygiene, maximum sterile barrier precautions, antiseptic skin preparation, use of chlorhexidine-impregnated dressings, and other interventions.1–3 Maintaining the health and integrity of the patient’s skin receives considerable attention; however, less common are efforts to establish partnerships between wound/ostomy and infection prevention and/or vascular access teams to improve and promote HAI prevention processes … read more
Partial calcanectomy with antibiotic biocomposite injection for diabetes patients with heel ulcers and calcaneal osteomyelitis
a single stage treatment
Heel ulcers with calcaneal infection are difficult to treat, with frequent relapses. The authors report a series of four patients who presented with a heel ulcer and calcaneal osteomyelitis. The results show that using a single stage partial resection of calcaneum with primary closure of wound and an antibiotic biocomposite injection (Cerament®, Bonesupport) injection is a viable and useful technique in managing calcaneal osteomyelitis … read more
ACFAS 2022 – Austin Convention Center Feb. 24-27
Whether you come for the captivating sessions, hands-on workshops, or reconnecting with colleagues, ACFAS offers four days of learning as unique and as vibrant as the city of Austin itself! The ACFAS Annual Scientific Conference offers a wide range of topics so there is something for everyone, highly respected faculty, and the opportunity to enhance your knowledge and skills. Don’t miss out on this once-a-year learning experience … REGISTRATION IS NOW OPEN! REGISTER BY 2/9 BEFORE ONSITE FEES APPLY … read more
Podiatry Management’s annual Buyers’ Desk Reference
Podiatry Management’s annual Buyers’ Desk Reference is a user-friendly guide to products and services currently being offered to the podiatric community … read more
Study provides new tool to assess amputation risk following popliteal vascular injury
A large, multicentre cohort study provides a simple, practical method to effectively stratify patients preoperatively into low- and high-risk major amputation categories.
According to lead author Leigh Ann O’Banion (University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, USA), “traumatic popliteal artery injuries present a serious clinical challenge because they are associated with the greatest risk of limb loss of all peripheral vascular injuries, with major amputation rates of 14–25%.” … read more
Principles of Wound Healing
A wound is a break in the continuity of a bodily tissue, such as the skin or mucous membrane. Wounds can be caused by events that are external to the organism – such as trauma, burns, or surgical incisions; and wounds can also be of endogenous origin – such as a distal ischemic event involving the toes due to embolism or arterial stenosis … Wound attributes, such as its causative mechanism, size, depth and location are useful for characterizing its type. When a wound is being assessed, it is also important to determine the stage of wound healing, extent of tissue repair, presence of any obvious elements preventing complete wound closure, and the patient’s psychological status. Complete restoration of tissue integrity requires multidisciplinary care and patient adherence to the recommended treatment …The patient’s baseline clinical condition greatly influences the wound healing process. Healthy individuals tend to recover quickly, with restoration of skin integrity and scars that have a better appearance as well as fewer complications. Patients with chronic diseases (e.g. diabetes mellitus and hypertension, malnutrition or obesity) tend to present delayed wound healing and have greater risk of complications such as infection, and functional and psychological sequelae … read more
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease (LEAD) Awareness and Discussion
By Holly Hovan, MSN, GERO-BC, APRN, CWOCN-AP
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is also known as lower extremity arterial disease (LEAD), peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD), or arteriosclerosis obliterans.1 LEAD is a disease that impacts the circulatory system, specifically the arteries (narrowing, which can result in a decreased supply of blood flow to the limb), and can eventually lead to limb loss or amputations. It is important to bring awareness to LEAD and its diagnosis, treatment, and prevention to improve access to care and screenings and ultimately to prevent limb loss … read more
Negative pressure wound therapy for surgical wounds healing by primary closure
Indications for the use of negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) are broad and include prophylaxis for surgical site infections (SSIs). Existing evidence for the effectiveness of NPWT on postoperative wounds healing by primary closure remains uncertain … To assess the effects of NPWT for preventing SSI in wounds healing through primary closure, and to assess the cost‐effectiveness of NPWT in wounds healing through primary closure … read more
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Prevention Strategies
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) may affect up to 25% of people with diabetes at some point in their lifetime. Once a person has developed a DFU, there is a 50% chance the ulcer will become infected.1 DFUs are also among the leading causes of amputation.2
Wound care specialists encounter DFUs regularly in the clinic, and these wounds can be very difficult to treat because of the underlying metabolic insufficiency. This blog provides a guide to current best practices with regard to DFUs and prevention … read more
Effect of Flap Selection on the Postoperative Success of Sacral Pressure Injuries: A Retrospective Analysis
Pressure injuries (PIs) continue to be a substantial problem and burden for the present-day health care system and are the leading cause of chronic wounds worldwide. There is no current consensus on the long-term results of the use of flaps in sacral PI reconstruction and optimal flap choice. Objective. This study aimed to evaluate whether flap selection influences postoperative results in sacral PI reconstruction. Materials and Methods. Patients who underwent surgery for PIs in the authors’ clinic between 2002 and 2016 were retrospectively analyzed. A total of 63 patients with stage 3/stage 4 sacral PIs and who underwent reconstruction with fasciocutaneous (FC) flaps (group 1), musculocutaneous (MC) flaps (group 2), or perforator (P) flaps (group 3) were included in the study. The mean duration of the follow-up period was 14.4 months, and patients were evaluated in terms of their demographic data … read more
Evidence Summaries for Improved Wound Care Practice
This month’s issue includes three important review articles related to alternative/local wound care, support surface evaluation testing, and skin failure. The “alternative” medicine review was originally submitted by three colleagues from Nanavati College of Pharmacy in India. The editorial team connected the investigators with Dr Laura Bolton, a collaboration that resulted in an excellent scoping review summarizing 50 years of literature.
Natural and synthetic agents have been used to optimize local wound care for centuries. The authors reviewed 281 abstracts outlining 274 studies with 28,315 participants … read more
The Use of an Antimicrobial Moisture Management Dressing Paired With a Gellable Fiber Technology under a Two-layer Compression System
in the Treatment of Heavily Exudating VLUs Improves Clinical Outcomes and Cost Savings
Introduction: Chronic venous insufficiency is the 7th most common chronic disease and is the underlying cause of 95% of leg ulcers1. Venous leg ulcers (VLUs) are difficult to treat and even with proper care can take a minimum of 12 weeks to heal2. VLUs are a clinical challenge because they are notoriously heavily draining wounds. This drainage contributes to the formation of excessive bioburden, devitalized tissue, and microorganisms, all which prolong wound healing. In order to effectively manage VLU exudate it is not uncommon to change dressings 3 or more times weekly. More frequent dressing changes increase the overall cost of care and may further contribute to delayed wound healing … read more
MolecuLight i:X® Receives FDA 510(k) Clearance for the Device’s Ability to Detect Wounds Likely to Contain Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA)
New FDA Clearance Illustrates the Utility of the i:X to Reliably Predict Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a Bacterial Pathogen that Precludes Wound Healing and Often Evades Conventional Treatment Methods
TORONTO, CANADA – (September 23 2021) MolecuLight Inc., the leader in point-of-care fluorescence imaging for real-time detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial loads, announces that it has received FDA 510(k) clearance for the detection of wounds containing clinically significant levels (>104 CFU/g) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) for the previously cleared MolecuLight i:X imaging device. The i:X device visualizes fluorescence, enabling the point-of-care detection of wounds containing elevated levels of bacteria. This new FDA clearance supports the ability of the i:X device to increase the clinician’s ability to detect the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in wounds using the cyan fluorescence signal. This augmented labeling is based on a detailed retrospective statistical analysis of over 350 patients.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) is a common bacterial pathogen that precludes wound healing. PA is notorious for its intrinsic resistance to many antibiotics and its tendency to form biofilm matrices that evade antibiotics and other conventional treatment methods1. The presence of PA in wounds is associated with rapid deterioration and more severe wound outcomes 2,3. The MolecuLight i:X is the only imaging device that provides real-time information on whether a wound is likely to contain elevated levels of PA (>104 CFU/g). The i:X is becoming an essential tool for assisting in clinician decision-making regarding the assessment and treatment of wounds.
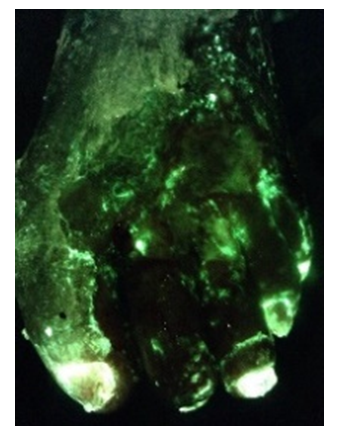
Image and video courtesy of Dot Weir
“Bacterial removal is a critical component of wound care and wound healing. The ability of the MolecuLight i:X to detect and visualize wounds containing elevated bacterial burden while we are with the patient enables a proactive and objective approach to wound management”, says Dot Weir, RN, CWON, CWS, Clinician at Saratoga Hospital Center for Wound Healing and Hyperbaric Medicine, Saratoga Springs, New York and Co-Chair of SAWC, the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care. “Wounds harboring Pseudomonas often require unique treatments. This new FDA clearance recognizes the added benefit of the i:X in visualizing and differentiating Pseudomonas aeruginosa in wounds through the cyan fluorescence signal it produces on the images. This is especially important because detecting the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at the point-of-care allows wound care professionals to act immediately to tailor our cleaning, debridement, antimicrobial strategy and treatments accordingly.”
This video showing the cleansing of a diabetic foot ulcer is an example of the MolecuLight i:X’s cyan fluorescence signal indicating the likely presence of PA. The cyan is clearly visible on the patient’s foot (see image) as well as on the gauze after cleansing, indicating that the wound contains clinically significant (>104 CFU/g) levels of PA:
Video link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5YiT4zTUL8
References
1 Raizman et al., “Rapid Diagnosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Wounds with Point-of-Care Fluorescence Imaging“, Diagnostics 2021, 11(2), 280
2Turner et al., “Requirements for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acute Burn and Chronic Surgical Wound Infection”, PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004518
3McManus et al., “Twenty-five-year review of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia in a burn center”, Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 4, 219–223
About MolecuLight Inc.
MolecuLight Inc., a privately-owned medical imaging company that has developed and is commercializing its proprietary fluorescent imaging platform technology in multiple clinical markets. MolecuLight’s first commercially released device, the MolecuLight i:X fluorescence imaging system and its accessories provide a point-of-care handheld imaging device for the global wound care market for the detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial burden (when used with clinical signs and symptoms) and for digital wound measurement. The company is also commercializing its unique fluorescence imaging platform technology for other markets with globally relevant, unmet needs including food safety, consumer cosmetics and other key industrial markets.
For more information, contact:
Rob Sandler
Chief Marketing Officer
MolecuLight Inc.
T. +1.647.362.4684
Image: Download at: https://moleculight.box.com/s/b4d44tv25dq5wr834ilx7ldiqzl1orxi
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5YiT4zTUL8
Advances in Wound Care Technology: What We See Is What We Get … and More
The science of wound care dressings has progressed a long way over the years, especially during the not-too-distant past. As recently as the early 1990s, the main dressings available to patients included transparent films, hydrocolloids, foam, and calcium alginate. Although not incredibly common, moist wound care was also utilized more than many clinicians would care to admit some 30 years later. Standard dressings at the time were wet-to-dry and betadine.
Today, dressing technology has transitioned from a passive to an active role. Yet, the sophistication of dressings that our patients enjoy today would not be possible without understanding the clinical progression that has occurred, even among those treatments that have since been abandoned … read more
Periwound Skin Management
Periwound skin management is just as important as wound bed preparation in wound healing. The goal of periwound management is to maintain an optimal moist wound healing environment while preventing skin breakdown and infection. Skin is more vulnerable in patients with certain comorbidities and conditions. Periwound skin breakdown is just one of the culprits that delay wound healing and increase pain … read more
Use of a Novel Silicone-Acrylic Drape With Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Four Patients With Periwound Skin Breakdown
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is applied using a foam dressing and an adhesive acrylic drape to create a seal. Removal of this drape can be painful and may play a role in periwound skin breakdown during dressing changes. A novel silicone-acrylic hybrid drape (HA-drape) has been developed for use with NPWT to allow for repositioning after initial placement and easier removal. Objective. This retrospective case series reports on the use of HA-drape in 4 patients who experienced periwound skin breakdown. The goal was to minimize skin breakdown while maintaining a seal on the dressing. Materials and Methods. Four patients with mild to moderate periwound skin breakdown were selected to receive NPWT with HA-drape … read more
The wound healing effect of local leukocyte platelet-rich plasma after total hip arthroplasty
A randomized controlled trial:
Rapid wound closure is important after arthroplasty procedures to prevent postoperative complications. Platelets are rich in growth factors and leukocytes contribute to innate immunity. We hypothesized that topical leukocyte platelet-rich plasma (L-PRP) derived from the blood of patients would be beneficial to wound healing. In this randomized controlled trial, patients subjected to elective total hip arthroplasty (THA) were assigned by concealed allocation either L-PRP application onto the sutured fascia or no application (control) after the THA intervention. In addition, all patients received 1.5 g protein/kg, 5 g L-arginine, 500 mg vitamin C and 44 mg zinc daily over the 4-week postoperative period to obtain optimal nutrition. The primary endpoint was complete healing of the skin incision. The secondary endpoints were blood transfusions, length of hospital stay, pain and wound infections. Sixteen patients in the L-PRP group and 17 patients in the control group completed the trial. L-PRP treatment accelerated complete wound healing after 3 weeks (seven in the L-PRP group vs. zero in the control group, p = 0.003) and after 4 weeks … read more
From PMC: Current Clinical Recommendations for Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma
The ISWCAP and ASEAN wound conference 2021
The ISWCAP and ASEAN wound conference was held online on the 19–20 June 2021. Over the two-day programme the 434 participants saw 22 lectures and plenary sessions along with sponsored lunch symposia.
The chair of the organising committee Prof. Dr. Harikrishna K.R.Nair gave the opening address for what he described as “An inspiring two days, with a wealth of knowledge shared among the wound care family”. There were updates from Gulnaz Tariq on the World Union of Wound Healing Societies (WUWHS) events and Karen Ousey on behalf of the International Wound Infection Institute (IWII), along with sessions on diabetic foot ulcers, amputation, surgical site infection, oxygen therapy and much more. It was a truly international event with both speakers and delegates from Europe, North America, South America mainly Brazil, South Africa and Asia.
Recordings of that day will be uploaded onto the Malaysian Society Of Wound Care Professionals (MSWCP) website www.mswcp.org
EWMA Journal of Wound Management
July 2021 issue of the Journal of Wound Management. Official journal of the European Wound Management Association
This issue of the Journal of Wound Management includes seven original manuscripts. the full issue can be accessed here: Journal of Wound Management. No 22, vol. 2, July 2021
One Podiatrist’s Experience With A Novel NMES Device For Patients With PAD
In previous articles, I have written about medicine having endless career opportunities. One opportunity in the medical field is that to evaluate and potential provide feedback on an array of products or medical devices, in hopes of participating in the betterment of patient care. To me, advising on new innovations is always an exciting time because I believe becoming aware of the latest and cost-efficient technology to aid my patients with pain relief, healing, or even improved quality of life is imperative.
In recent months, I had the unique opportunity to trial a circulation booster device for the legs and feet … read more
Innosphere re-ups with diabetic ulcer gel developer
Innosphere Ventures Fund bought in again on GelSana Therapeutics Inc. An earlier backing funded product development for the start-up’s therapeutic gels … This second seed-stage buy-in will accelerate research work, prepare a U.S. Food and Drug Administration submission and begin to build a pipeline of products … GelSana’s hydrogels aim to improve healing of diabetic ulcers and other wounds: closing cuts and sores faster, growing stronger skin and enabling controlled delivery of healing therapies … A product prototype was aimed at diabetic foot ulcers but “we believe the unique properties of GelSana’s hydrogels may have much larger applicability in wound healing,” founder and CEO Melissa Krebs said … read more
Wound Care Advantage and Swift Medical Announce Partnership
Wound Care Advantage, the nation’s leading wound care consulting firm and Swift Medical, the global leader in digital wound care, announces a new strategic partnership.
Wound Care Advantage (WCA) , the nation’s leading wound care consulting firm and Swift Medical, the global leader in digital wound care, announces a new strategic partnership that brings Swift Medical’s advanced wound imaging platform to WCA’s Network hospitals to enhance their collective impact on the wound care industry.
Swift Medical’s technology platform will be integrated into the WCA network of tools and resources that empower hospitals to run successful wound care programs. Swift Medical’s technology connects directly with hospital EHR systems to enable seamless clinical workflows, such as advanced wound imaging, documentation and analytics.
“We are very pleased to partner with Swift Medical to bring their wound imaging technology to our wound centers,” says Melissa Bailey, President of Wound Care Advantage. “Our hospital partners are looking for continuum solutions and the introduction of Swift’s wound imaging platform into the WCA Network is an effective tool that compliments the operational expertise we provide.”
Expert EWMA group highlight need for investment in maternity services research
“Investment in maternity services research is essential for our understanding of the extent of wound-related complications for the postpartum mother and improved clinical pathways for wound management,” write Charmaine Childs (Sheffield Hallam University, Sheffield, UK), Kylie Sandy-Hodgetts (University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia), and colleagues in an evidence-based consensus document for healthcare workers published by the European Wound Management Association … read more
Bacterial Biofilm Destruction: A Focused Review On The Recent Use of Phage-Based Strategies With Other Antibiofilm Agents
Biofilms are bacterial communities that live in association with biotic or abiotic surfaces and enclosed in an extracellular polymeric substance. Their formation on both biotic and abiotic surfaces, including human tissue and medical device surfaces, pose a major threat causing chronic infections. In addition, current antibiotics and antiseptic agents have shown limited ability to completely remove biofilms. In this review, the authors provide an overview on the formation of bacterial biofilms and its characteristics, burden and evolution with phages. Moreover, the most recent possible use of phages and phage-derived enzymes to combat bacteria in biofilm structures is elucidated. From the emerging results, it can be concluded that despite successful use of phages and phage-derived products in destroying biofilms, they are mostly not adequate to eradicate all bacterial cells. Nevertheless, a combined therapy with the use of phages and/or phage-derived products with other antimicrobial agents including antibiotics, nanoparticles, and antimicrobial peptides may be effective approaches to remove biofilms from medical device surfaces and to treat their associated infections in humans … read more
Managing the Surge: Delayed Chronic Wound Care During COVID-19
A growing body of research, as well as first-hand accounts from clinicians on the ground, indicate that a significant percentage of patients with chronic wounds have delayed preventative and emergent wound care during the COVID-19 pandemic.1 While it will take time to assess the full impact of these trends, existing evidence suggests delayed wound care can result in more severe infections, increased hospital admissions, and lead to more amputations.2 Therefore, it will be critical for providers, hospitals, outpatient departments, payers and policymakers to understand and plan for a surge in patients with untreated and unmanaged non-healing wounds and related acute-on-chronic complications as a result of delayed care during the COVID-19 pandemic … read more
Examining the Science of Chronic Wounds and the Leading-Edge Approach to Elevating Early Wound Care
Drs. Randall Wolcott and Andrew Rader host a discussion on the persistence of wound chronicity without early combination treatment strategies and review recent compelling data to support the need to change the status quo of early wound care … Register
Medical Device-related Pressure Injuries Associated With Electroencephalogram Leads in a Tertiary Care Children’s Hospital
Medical device-related pressure injuries (MDRPIs) present a substantial safety risk for children who are hospitalized. PURPOSE: This study aimed to describe patient and clinical characteristics of children who develop MDRPIs related to electroencephalogram (EEG) leads, determine risk factors associated with their development, and determine if there are common risk factors that can lead to actionable strategies to reduce MDRPIs related to EEG leads. METHODS: A retrospective review was completed of the electronic health records of all 3136 children who had EEG lead placements between January 1, 2014, and April 16, 2018, at a large tertiary care children’s hospital. Data abstracted included demographic variables, patient and pressure injury characteristics, as well as length of stay. RESULTS: Twenty-four (24) of the 3136 children (0.8%) developed an MDRPI. Most were stage 2 pressure injuries. Patients who developed a pressure injury were significantly younger than patients who did not (median age, 0.9 and 5.2 years … read more
Closure of a Difficult-to-Manage Chronic Pressure Injury with the Use of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma
Pressure injury (PI) corresponds to a skin damage of ischemic aetiology that affects the integrity of the skin and is produced by prolonged pressure or friction between a hard internal and external surface. Treatment can be challenging when there is no resolution with usual care. The use of autologous platelet-rich plasma (APRP) gel arises as a therapeutic possibility in the presence of chronic pressure injuries. The case of a patient with chronic PI who has been treated with APRP is presented, achieving resolution of the lesion … read more
Improving patient outcomes with medical technology
An ideal healthcare system cures every type of medical condition an individual may have. However, healthcare professionals have always had to judge whether they can cure a patient or simply manage their condition to provide a better quality of life.
Many pharmaceutical interventions and treatment options are designed to manage people’s illnesses, not necessarily cure them. This increases the cost of healthcare – particularly as people live longer and the proportion of illnesses that are manageable rather than curable increases – as do the requirements for long-term care.
Some conditions have proven particularly hard to cure, such as diabetes and high blood pressure, leaving no choice but to manage and monitor a condition across an extended period. However, this is costly and poses many challenges to medical and clinical resources … read more
Use of social media in medicine: the future – Webinar
This free-to-attend CPD webinar has been organised by British Journal of Hospital Medicine, supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Cook Biotech, Inc, West Lafayette, IN, USA.
In this webinar, the presenters will share their tips and insights into how healthcare professionals can make the most of social media platforms to share and learn new skills. They will also provide guidenace on the potential risks and how to avoid pitfalls.
*** This webinar is CPD certified and all attendees will receive a personalised CPD certificate sent by email after the session.***
The Frank & Lizzie Show: Episode 007, Dr. Marc “Dutch” Matthews
On this episode, Frank & Lizzie sit down with Dr. Marc “Dutch” Matthews from the Arizona Burn Center to discuss his experience with Vashe, a hypochlorous acid preserved wound cleanser solution. Dutch explains how this pH skin neutral wound solution has helped changed his practice for the better, but more importantly the lives of his patients.
A NOVEL APPROACH TO TREATING HARD-TO-HEAL WOUNDS
OUR INNOVATIVE WOUND THERAPY IS DESIGNED FOR OUTPATIENT SETTINGS
Stiehl Tech is a medical device company focused on creating innovative surgical products for both outpatient and inpatient settings.
Selective Mechanical Debridement
Our Perilav wound irrigation system adapts time-tested surgical debridement methods for the outpatient setting. We make it easier for nursing home staff or home health providers to treat wounds in a more comfortable patient setting. Our unique treatment enclosure bags make a standard treatment safer and simpler by containing fluid and wound debris in an easily disposable bag … read more
UA Surgeon Armstrong Urges New Focus on Diabetic Ulcers
Remission — rather than repair — needs to be the goal of treatment, according to Dr. David Armstrong, whose report on diabetic foot ulcers appears in the New England Journal of Medicine … Foot ulcers are a prevalent complication for millions of people with diabetes. Estimates indicate that as many as one-third of people with the disease will develop at least one foot ulcer over the course of their lifetime. These wounds can lead to further complications such as strokes, heart attacks, infections, loss of limbs and premature death … read more
Lipodystrophy, a Common Risk in Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Patients with lipodystrophy have a high risk of diabetic foot ulcers, especially in the younger population.
Lipodystrophy is a disorder characterized by an abnormal fat distribution in the body. It can refer to an irregular loss or accumulation of fat tissue, and can even cause macrovascular and microvascular complications. Diabetic foot ulcers are a chronic complication of diabetes that can cause loss of lower limbs from amputations. DFU is also a risk factor in diabetes-related mortality. Previous studies have not found a correlation between lipodystrophy and DFU or even a treatment to reduce these complications. Lipodystrophy is a complication caused mainly by familial partial lipodystrophy. This study used an observational retrospective cohort study to understand the correlation between these two disorders, lipodystrophy and diabetic foot ulcers, and which age was the most critical … read more
RedDress Announces Distribution Agreements in 12 European Countries
Ponte Vedra Beach, Sept. 20, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — RedDress, a privately held U.S. and Israel-based wound care company, announced today strategic agreements in 12 European countries to distribute its innovative CE-marked wound care solution for exuding cutaneous wounds, ActiGraft® system, throughout Europe.
“We are proud to announce our expansion into Europe,” said Alon Kushnir, CEO of RedDress. “Our distribution partnerships in these key areas enable us to deliver our innovative solution in one of the world’s leading wound care markets and will accelerate our growth globally. We are looking forward to providing Europeans with an effective alternative treatment modality as a solution for their hard-to-heal chronic wounds.”
These strategic distribution agreements support RedDress’ global mission to improve the health and lives of patients around the world living with chronic wounds by expanding access to ActiGraft in several European countries:
Austria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Germany, Greece, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Switzerland, Turkey, and Ukraine
Measurement properties of quality of life instruments for adults with active venous leg ulcers: a systematic review protocol
Objectives The primary objective is to identify instruments used to measure quality of life (QoL) in studies of people with active venous leg ulcers (VLUs). The secondary objective is to map the qualities of each instrument to make recommendations for clinical practice and future research.
Introduction VLUs have a negative impact on patients’ QoL. Prolonged healing and frequent recurrence leads to pain, prolonged disability and psychosocial morbidity. Accurate measurement of QoL can optimise the evaluation of VLU treatments and guide clinician and patient decision-making … read more
Researchers explore promising treatment for MRSA ‘superbug’
A new Cornell study has found the antimicrobial properties of certain stem cell proteins could offer a potential treatment to reduce infection in skin wounds.
Treating wounds with the secretion of a type of stem cell effectively reduced the viability of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus – better known as MRSA – according to a new study from researchers at the Baker Institute for Animal Health, part of the College of Veterinary Medicine (CVM). Moreover, the secretion stimulated the surrounding skin cells to build up a defense against the bacterial invader, the researchers found … read more
The History and Effectiveness of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy – Part One
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) uses controlled negative pressure to remove fluid from open wounds. This is done through a sealed or foam dressing connected to a vacuum pump and canister1. Closed-system negative pressure is relatively new in modern medicine and will continue to evolve for better patient outcomes.
Although NPWT has increased in utilization over the past decade due to positive results and data showing its effectiveness in healing many acute and chronic wounds, it has potential for even more growth and innovation … read more
Microneedle patch penetrates biofilms to treat chronic wounds
Chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers can be very difficult to treat, partially because of antibiotic-resistant “biofilms” that form over the affected tissue. A new type of microneedle patch, however, has been shown to deliver medication through such films … Bacterial bioflms are made up of colonies of bacteria that stick together by building up a slimy polymer matrix. Unfortunately, topically applied antibiotics and other medications have difficulty penetrating that matrix, so they can’t reach the infected tissue underneath … read more
Next Science: Products that help treat wounds
Founded by scientist Matthew Myntti, the company develops products to reduce biofilm-based infections, which can be fatal.
As a scientist at Medtronic’s Jacksonville office working on chronic infections, Matthew Myntti said he began to understand the life-threatening nature of chronic wounds, and the infections that come with them.
He left the medical technology company in 2012 to start his own research focused on treating chronic wounds and keeping them from becoming infected … read more
“Elephant-trunk” negative pressure wound therapy for fixing artificial dermis with basic fibroblast growth factor for critical limb ischemia
INTRODUCTION: The treatment of intractable toe ulcer with critical limb ischemia (CLI) is a challenge because of its poor blood flow and the wound. Here, a novel fixation technique for artificial dermis with negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) was reported.
METHOD: After the amputation of toe, artificial dermis made of collagen-gelatin sponge (CGS) was grafted onto the wound where human recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) was sprayed. The foot was put on adhesive iodine-impregnated drape, the artificial-dermis area was covered with a sponge dressing of which another end reached to the drape, and the vacuum port was applied on the dressing sponge sandwiched with two drapes … read more
Rates of T1D-Related Amputations Decline in Sweden
Results of a Swedish retrospective cohort study showed reduced rates of type 1 diabetes-related amputations over the past 2 decades.
In recent years, Sweden has seen a sharp decline in incidence of lower-level extremity amputations among individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D), according to results of an observational cohort study. Findings were published in Diabetologia.
Because diabetes-related foot ulcers are common and healing is often delayed, limb loss through amputation “is not an infrequent final outcome,” the authors explained.
In addition, “about half of all nontraumatic amputations in the western world are attributable to diabetes … read more
The Hemostatic and Wound Healing Effect of Chitosan Following Debridement of Chronic Ulcers
Chitosan has been proven to be helpful in wound care as a hemostatic agent. The hemostatic effect is due to the positively charged chitosan interacting with negatively charged red blood cell membranes, initiating the agglutination of red blood cells and platelets. This promotes the activation of thrombin, which activates the clotting pathway, leading to thrombus formation. Objective. Based on the properties of chitosan as a rapidly acting hemostatic agent, the authors sought to determine if a chitosan gelling fiber wound dressing could control bleeding of freshly debrided wounds. The effect of the chitosan dressing on overall healing and patient and provider satisfaction was also evaluated. Materials and Methods. Wounds of any etiology requiring sharp debridement in patients older than 18 years who were capable of consent were eligible. Wounds were sharply debrided by curettage … read more
Swift Medical’s new imaging platform expands the digital wound care company into decentralized trials
Digital wound care company Swift Medical launched Swift Scientific, a digital imaging platform to support decentralized clinical trials.
The platform allows for large-scale image collection and management so researchers can monitor the effects of medical interventions at a multisite trial or from study participants’ homes.
Swift’s product, Swift Skin and Wound, is an AI-enabled platform that lets patients or providers capture high-precision images of skin conditions or injuries with a smartphone. It tracks disease progression and healing, and allows for remote communication and data sharing … read more
Wound Week 2022 | Call for abstracts
All abstracts for the Wound Week 2022 must be submitted electronically via the online platform: www.abstractscorecard.com
Hosted by the American Professional Wound Care Association (APWCA), Wound Week 2022 provides attendees with an innovative, unparalleled educational opportunity that will feature superior content delivered by multidisciplinary faculty with clinical expertise in the field of wound healing/care. Presenting your scholarly work at the APWCA Annual meeting will showcase your knowledge and dedication to discovery in wound care in front of a prestigious audience … read more
Antibacterial nanozymes: Healing chronic wounds with nanochemistry
Chronic infected wounds are often highly problematic for diabetic patients. However, a team of Chinese researchers has now developed a targeted approach to wound healing that makes use of nanomedicine, and their research has been published in the journal Angewandte Chemie. The researchers were able to deactivate wound-infecting bacteria using a solution of nanocapsules that alter the wound environment and unleash reactive oxygen species … read more
Evaluation & Management vs. Hospital Owned Outpatient Provider-Based Department Clinic Visits
If you had an opportunity to listen to the webinar entitled “2021 Mid-Year Reimbursement Reports: A Live Discussion Series,” that Jolayne Devers and this author presented on July 28, 2021, you know that the topic was Wound Care Audits Have Resumed: Are You Prepared? The attendees submitted many excellent questions during the webinar and sent many more emails to this author following the webinar. To accommodate the high volume of questions, this author promised to address the topics and questions in this and future Business Briefs columns.
One of the topics that generated many questions and follow-up emails was “Physician/qualified healthcare professional (QHP) evaluation & management (E/M) services are different than hospital owned outpatient wound/ulcer management provider-based department … read more
Abstracts from the Amputation Prevention Symposium (AMP) August 11-14, 2021
An Endovascular Approach as a Backup for Open Surgery After Corynebacterium striatum Vascular Graft Infection
Gabriel C. Inaraja-Pérez, MD, PhD, FEBVS; Manoela Oliveira Brito, MD; Alejandra Bartolomé Sánchez, MD; Daniela Acuña Paz y Miño, MD; Eva María Martin Herrero, MD, PhD; Jose-Manuel Buisán-Bardají, Prof. MD; Jorge Coghi Granados, MD
A Hybrid Approach to ALI Utilizing Penumbra Aspiration Thrombectomy in Conjunction With Catheter-directed Thrombolysis
Emily M. Rey, DO; Ganesh Arun, DO; Kristian O. Hochberg, MD; Sang Lee, MD
Cost-Effectiveness of Office-Based Labs for Treating Peripheral Arterial Disease
Morish Shah; Ashish Chaturvedi, BS; Paramjit S. Chopra, MD; Manasvi Paudel, BS; Kashish Shah
Hybrid Approach for Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia: A Case Report
Vincent Demesmaker, MD; Arnaud Kerzmann, MD; Evelyne Boesmans, MD; Vlad Alexandrescu; Jean-Olivier Defraigne
Observations Regarding the Effect of COVID-19 on Amputations Performed in a Tertiary Referral Health System
Dayle K. Colpitts, DO; Richard F. Neville, MD, FACS, DFSVS; Arkadii Sipok, PhD; Anthony Comerota, MD, FACS
Salvage of Popliteal-Dorsalis Pedis Bypass: A Case Series
Crystal James, MD; Denise Alabi, BA; Mabel Chan, MD; So Park, MD; John C. Lantis, II, MD
PRELUDE BTK vs. POBA Analysis: Serration Angioplasty and POBA
Marianne Brodmann, MD
Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Pressure Injuries: How Do You Tell the Difference?
In evaluating a patient with a wound on the foot, a question that often comes to mind is whether that wound is caused by pressure, diabetes mellitus (DM), ischemia, trauma, or a combination. For example, a patient with DM who happens to have an ulcer on the foot may have a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) or possibly something else. One of the bigger challenges that many clinicians face is trying to determine the etiology of a foot ulcer. There has been a great deal of debate about DFUs and pressure injuries (PIs) on the feet of patients in terms of how to appropriately assess, classify, and treat them. The confusion and lack of evidence in differentiating between these two types of foot ulcers, particularly on the heel, can lead to misdiagnosis, which can increase both financial and patient-related costs … read more
AOFAS Annual Meeting, September 22-25 Charlotte, North Carolina
AOFAS President, Bruce E. Cohen, MD, invites you to AOFAS Annual Meeting, September 22-25, for the premier meeting for foot and ankle education that gives you the choice between attending in person in Charlotte, North Carolina, or virtually. Learn more: https://aofas.org/annualmeeting
World Union of Wound Healing Societies (WUWHS) announces Congress Postponement
Professor Marco Romanelli and Gulnaz Tariq, President and President Elect of WUWHS have announced the postponement of the forthcoming Congress to 1-5 March 2022. With concerns around the availability of travel and the wish for the organisers not to divert attention of busy HCPs from their own local facilities during the Covid-19 pandemic, they have taken the difficult decision to postpone … read more
Enhancing Pressure Injury Prevention Strategies Based on New Technology: From Learning More to Doing Better
he med-surg health care environment is constantly changing, driving complexity in care. The most recent findings from the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services state that pressure injuries develop in nearly 2.5 million patients annually, representing 8.3% of hospital admissions; the resulting financial burden for care is estimated to be between $3.3 and $11 billion annually.1 Although most occurrences of hospital-acquired conditions sharply decreased between 2010 and 2017, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality reported that pressure injuries increased by 6%.2
Pressure injuries develop when there is localized damage to the skin or underlying tissues due to pressure—and sometimes combined with shear—that impacts the skin’s ability to provide oxygen and nutrients and remove waste byproducts … read more
Koya Medical and Essity Sponsor Forum for Physicians, Lymphedema Therapists and Researchers to Discuss Health Effects of Space Travel
Koya Medical, a transformative healthcare company focused on developing breakthrough treatments for lymphedema and venous diseases, and Essity, a leading global hygiene and health company that has as history of supporting space travel through the manufacturing of compression suits for astronauts, are sponsoring a forum to highlight the importance of venous and lymphatic health for space travel. The event takes place October 8, 2021 at the 35th annual congress for the American Vein & Lymphatic Society (AVLS).
The unique environment of space travel – reduced gravity, radiation exposure, varying atmospheric conditions, and the mental and physical stresses – imposes many challenges to human physiology and adaptability. The current goal is to create “nominal human function,” to extended safe habitation and exploration in space, and to ensure that humans thrive and quickly recover upon returning to Earth’s “1G” environment. For more than 50 years, NASA’s Human Research Programs have studied the intricacies of the human body in the weightlessness of space. Understanding the effects of spaceflight on humans is essential, and NASA and its European, Japanese, Russian and Australian colleagues have been particularly interested in investigating how the body reacts to long-duration spaceflight as the agency plans for extended missions on the Moon and Mars … read more
Predictors of Foot Ulcers Among Diabetic Patients at a Tertiary Care Center, Egypt
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a major public health problem worldwide and is considered one of the main global health emergencies of the 21st century.1 The prevalence of DM is increasing in both developed and developing countries, recent estimates indicate that there were 463 million adults living with diabetes in 2019 which is projected to increase to 642 million in 2040.2,3 In the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region, the number of patients with diabetes is expected to increase from 34.6 million in 2013 to 67.9 million by 2035.2 The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) classified Egypt among the top 10 countries in the world with the highest prevalence of diabetes, where about 9 million adults between 20 and 79 years of age were living with DM in 2019. The number of patients with DM in Egypt has increased rapidly from about 4.5 million in 2007 to 7.5 million in 2013, and is expected to increase to 13.1 million by 2035.4 … read more
Wound Management of Venous Leg Ulcers in the Right Lower Extremity Limb
A 68-year-old male presented for care with lymphedema and multiple, copiously draining ulcerations on the right lower extremity (Figure 1). Symptoms were present for years and failed to respond to compression, foam dressings, or abdominal pads. Previous medical history included hypertension requiring use of anti-hypertensive medication … read more
Challenges faced by doctors and nurses in wound care management during the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey and their views on telehealth
AIM: This study aimed to determine the problems faced by physicians and nurses dealing with chronic wound care during the COVID-19 pandemic and their views on telehealth.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A descriptive and cross-sectional design was used in this study. The sample comprised physicians (n = 74) and nurses (n = 271) interested in chronic wound care. Data were collected through a questionnaire form consisting of open- and closed-ended questions … read more
Wounds UK Annual Conference | 8–10th November
this year’s Wounds UK Annual Conference will take place from 8–10th November with the ultimate goal to embrace the opportunity to connect, collaborate and learn in person. The sessions over the 3 days have been especially developed to have a greater emphasis on interaction and networking.
The programme will be diverse and will include updates from the National Wound Care Strategy Programme, tools for learning, patient engagement and shared care planning, and updates on the current science and terminology of healing. After the conference, you will return to your clinical settings armed with solutions to problems and campaigns for improving delivery of care … read more
The Analgesic Benefits of Ketorolac to Local Anesthetic Wound Infiltration Is Statistically Significant But Clinically Unimportant
A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Objective: Even though ketorolac-infiltration is said to provide superior postoperative analgesic benefits in different surgical procedures, its safety and efficacy remain to be validated because of the lack of high-quality evidence. We aimed to summarize the efficacy and safety of ketorolac-infiltration based on published randomized-controlled trials (RCTs) … read more
Surgical wound dehiscence Improving prevention and outcomes
Surgical wound dehiscence (SWD) is a significant issue that affects large numbers of patients and
is almost certainly under-reported. The impact of SWD can be considerable: increased mortality,
delayed hospital discharge, readmission, further surgery, delayed adjuvant treatment, suboptimal
aesthetic outcome and impaired psychosocial wellbeing … download PDF
Combined Regenerative Approach for a Complex Lower Extremity Wound
More than 400 million patients worldwide are affected by diabetes; over their lifetime, at least 25% will develop foot ulcers that often result in high rates of nonhealing wounds and amputation. The authors present the case of a 43-year-old female patient with multiple comorbidities who presented with a large (8 cm x 4 cm), noninfected, hindfoot plantar ulcer that extended down to the bone and calcaneus. Over 2 weeks, the patient was successfully treated using a combination of an acellular dermal matrix, nanofat grafting, and negative pressure wound therapy, lessening the effects of the ulcer on the patient’s quality of life and achieving limb salvage. Utilizing the regenerative procedures described herein may improve patient care and decrease costs … read more
History and Physical as the Best Diagnostic Tool for the Wound Care Clinician
This chapter is an excerpt from Chapter 8: Wound Assessment by Monica Stout and Jayesh Shah, Wound Care Certification Study Guide 3rd Edition, (Best Publishing Company, 3rd quarter, 2021), and Chapter 8: Wound Assessment by Dr. Jayesh Shah, Wound Care Certification Study Guide 2nd edition, Best Publishing Company, 2016. Reprinted with permission of Best Publishing Company.
Even with the technological innovations of the 21st century, history taking still remains the best diagnostic tool and least expensive tool to make a good diagnosis. Recognizing clues from a patient’s history can give important information about the patient’s wound … read more
COVID-19 Skin Manifestations | A Guide for WOC Nursing Practice
The COVID-19 pandemic has created unique challenges for WOC nursing practice. Clinicians have identified skin manifestations on or near the bony prominence that are atypical of classic pressure injury among persons diagnosed with COVID-19. In some cases it may be difficult for the clinician to initially discern COVID-19 related skin manifestations from other etiologies … read more
Reducing the incidence and severity of pressure injuries in a high level care residential aged facility: a quality improvement project
Aims Reduce pressure injuries (PIs) in residents of a high level care facility by increasing staff knowledge and skills through clinical support and a skin integrity education package.
Method This project was a quality improvement (QI) activity and data were de-identified and reported in aggregate. Pre- and post-implementation data included staff knowledge testing and PI prevalence and severity.
Results Pre-implementation data indicated that staff knowledge was very limited, skin inspections and PI risk assessment were not performed, and use of pressure redistribution devices was low, with point prevalence at 64% of mainly severe PIs. Despite ongoing external clinical … read more
New Insights on Wound Healing Unraveled
Despite advancements in treating wounds, the molecular mechanisms behind wound healing is not fully understood. Now, researchers at the University of California, Irvine (UCI), have identified a new molecular pathway that promotes wound healing in the skin. Their findings could even play a role in nonhealing wounds.
Their findings are published in the journal JCI Insight in a paper titled, “GRHL3 activates FSCN1 to relax cell-cell adhesions between migrating keratinocytes during wound reepithelialization.”
“The migrating keratinocyte wound front is required for skin wound closure. Despite significant advances in wound healing research, we do not fully understand the molecular mechanisms that orchestrate collective keratinocyte migration,” the researchers wrote. “Here, we show that, in the wound front, the epidermal transcription factor Grainyhead like-3 (GRHL3) mediates decreased expression of the adherens junction protein E-cadherin; this results in relaxed adhesions between suprabasal keratinocytes, thus promoting collective cell migration and wound closure.” … read more
EZ Debride is Now Available in Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, and Bruni
SAN ANTONIO, Sept. 2, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — EZ Debride, a registered and patented brand of MDM Wound Ventures Inc. developed and manufactured out of San Antonio and Kerrville, Texas, is announcing the distribution agreement with UCT Medical Co Ltd. Seoul, South Korea.
“At Intega Healthcare, we are excited to partner with MDM Ventures to introduce EZ Debride to our customers. EZ Debride is an innovative product that will offer clinicians an option to safely remove non-viable tissues with precision and minimal discomfort for patients. EZ Debride complements our innovative Wound Care Portfolio that comprises cellular-therapy & regenerative-tissue treatments, advanced wound care, surgical, and wound closure range. The partnership with MDM is allowing us to offer our clinicians a complete set of products and services which expands their patient treatment options.” Rebecca Ng, Business Development and Operations Director at Intega Healthcare … read more
The Clinical Role in Antimicrobial Resistance and Best Practices for Prescribing Antibiotics Podcast
In this podcast, Laura Swoboda, DNP, APNP, FNP-C, CWOCN-AP, discusses how clinicians should be mindful of their role in antimicrobial resistance and commit to responsible prescribing practices … listen
Surgical treatment of pressure injuries in children: A multicentre experience
Pressure injuries (PI) are infrequent in paediatric patients, prevalence estimates ranging from 1.4% to 8.2%, and reaching values as high as 43.1% in critical care areas. They can be associated with congenital neurological or metabolic disorders that cause reduced mobility or require the need for medical devices. In children, most pressure injuries heal spontaneously. However, a small percentage of ulcers that is refractory to conservative management or is too severe at presentation (Stage 3 or 4) will be candidates for surgery. We retrospectively reviewed the clinical history of paediatric patients affected by pressure injuries from four European Plastic Surgery Centres. Information was collected from clinical and radiology records, and laboratory reports. An accurate search of the literature revealed only two articles reporting on the surgical treatment of pressure injuries in children. After debridement, we performed surgical coverage of the pressure injuries. We report here our experience with 18 children aged 1–17 years, affected by pressure injury Stages 3 and 4. They were successfully treated with pedicled (17 patients) or free flaps (1 patient). The injuries involved the sacrum … read more
Physical activity, sleep and wound healing in adults with venous leg ulcers: a prospective observational cohort pilot study protocol
Background Adults with venous leg ulcers (VLUs) are less likely to be physically active and show greater sleep disturbances than the general population. Limited evidence suggests these issues contribute to VLU healing delays.
Objectives The primary objective is to determine if physical activity (PA) and sleep levels are associated with VLU healing. The secondary objectives are to: 1) evaluate the feasibility and acceptability of a wrist-worn accelerometer device, wActiSleep-BT device wear (ActiGraph); 2) evaluate the utility of self-reported PA instruments to measure PA for people with VLU; and 3) determine whether PA and sleep levels are associated with i) delayed healing, ii) self-reported quality of life (QoL) and/or iii) self-reported VLU pain … –
The Biomechanics of Diabetic Foot Amputation
According to the International Diabetes Federation, approximately 463 million adults live with diabetes mellitus (DM), a number projected to increase to 700 million by 2045; a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) will occur in about 15% of that population. Multiple factors contribute to the development of those wounds including diabetic peripheral neuropathy, biomechanical imbalances, trauma, and peripheral vascular disease. In addition, 85% of all lower limb amputations in patients with diabetes are preceded by a DFU resulting in significant biomechanical challenges for these patients, many of who never become ambulatory again. Prior to surgical intervention, patients come with inherited and acquired biomechanical imbalances or weaknesses such as equinus, severe pronation/supination, mid and forefoot deformities, and muscle weakness unrelated to their other diseases. Surgeons may not take these into consideration when making decisions about amputation level … read more
A Few Notes on Caring for the Diabetic Foot
Monique Abner, MD, CWSP, shares a song she wrote to help patients with diabetes care for their feet and prevent complications.
watch video
Low-cost sensors rapidly detect infections in wounds
Low-cost, screen-printed carbon sensors have been used to rapidly detect bacteria commonly found in wounds, which could pave the way for a real time medical device.
A study carried out by the University of Strathclyde and NHS Ayrshire & Arran used sensitive portable electrochemical sensors, which detected infections in clinical samples within half an hour, much quicker than current hospital laboratory testing.
The detection of infection in clinical practice can be expensive and … read more
The Healing Power of Oxygen, by Dr. Joseph P. Cavorsi
Oxygen is an abundant chemical within our atmosphere that is essential for most living things. Everyone associates oxygen with breathing and the lungs, but the process goes far beyond. All cells in the body need oxygen to create energy to live. Inadequate oxygen delivery to the cells can lead to dysfunction of the cells, contributing to many disease states, and in severe cases may lead to cell death … read more
Innovation Medical Group Selects SnapshotNIR to Visualize Wound Healing in Advanced Wound Care
ent Imaging is pleased to announce that Innovation Medical Group (formerly Utah Foot and Ankle), in Salt Lake City, Utah, has selected SnapshotNIR as a standard of care throughout their clinical network.
Innovation Medical Group provides unique, advanced wound therapy for a wide variety of foot and ankle conditions including diabetic foot and wound care. SnapshotNIR provides physicians at their clinics the ability to conduct rapid wound assessments, allowing for more accurate healing trajectory predictions, the potential to mitigate risks early and improve clinical outcomes. SnapshotNIR provides a tracked and documented assessment of tissue viability and wound healing, supporting the responsible use of appropriate advanced wound care modalities and monitoring the therapeutic benefit.
“Understanding the wound is the first step to healing,” states Dr. Doug Toole. “Tissue oxygenation values are not detectable through the unaided eye or with traditional perfusion imaging … read more

Omeza Receives FDA Clearance for Omeza® Collagen Matrix
First Drug Device Combination of Its Kind for Chronic Wound Care Sarasota, FL, September 2, 2021 — Omeza, a skin science company, announced today the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cleared Omeza® Collagen Matrix through the FDA 510(k) premarket notification process. Omeza® Collagen Matrix is Omeza’s first Rx product, and the first drug/device combination…
HMP Global Announces Keynote Speaker for October Symposium on Advanced Wound Care
HMP Global recently announced world-renowned fetal pediatric surgeon Oluyinka Olutoye, MD, PhD will deliver the Keynote Address during the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC Fall), taking place October 29-31, 2021 in Las Vegas, Nevada. In a session focused on Research, Discovery & Innovation on Friday, October 29, 2021 at 9:10 AM PDT, Dr. Olutoye’s address will combine inspiration with critical insight, and detail how his early research evolved to clinical care and brought fetal wound healing to the field … Dr. Olutoye first achieved international recognition in 2016 after successfully completing an unprecedented operation on a baby-in-utero. Under Dr. Olutoye’s leadership, a team of 21 doctors removed a sacrococcygeal teratoma from a baby’s tailbone, establishing Dr. Olutoye as an innovator and difference-maker in the surgical field. His groundbreaking work and specialized clinical expertise in fetal and neonatal surgery has yielded promising research on the role of the inflammatory response in scarless fetal wound healing and in-utero correction of severe congenital malformations.
To learn more and register for SAWC Fall visit sawcfall.com.
Study finds sharp fall in amputations among people with type 1 diabetes
Amputation in type 1 diabetes is becoming relatively less common in Sweden. The rate has fallen by just over 40 percent over an approximately 20-year period, a University of Gothenburg study shows.
The results, published in the journal Diabetologia, are based on registry data on 46,088 people with type 1 diabetes in the years 1998–2019. The study involved linking data from the Swedish National Diabetes Register, the National Patient Register, and a couple of other Swedish national registers … read more
The Benefits of Merging Medical Care and Technology
Technology is always advancing, and it is one industry that never stands still. Another industry that is constantly pushing boundaries too is the medical or healthcare industry. Merging two industries to ensure high rates of success is essential. When you look at the advantages of merging technology with medical care and medical treatment, you realize that the potential is limitless and endless … For example, wound care is an area where little has changed over recent years. However, this may be something that can change with the introduction of the silicone-covered wound dressing, which enables cleaner and faster healing for certain types of wounds. These dressings can be changed even easier and quicker, which is, of course, beneficial to those changing, and cleaning up wounds, in any healthcare setting … read more
A novel macrophage-regulating new drug has shown promise in treating diabetic foot ulcers according to the latest issue of article ….
Accumulating scientific evidence has revealed that targeting macrophage phenotypes might be a potentially effective therapy in DFUs because hyperglycemia increases the ratio of proinflammatory M1 to pro-regenerative M2 macrophages. This study is the first international Phase 3 randomized clinical trial of an investigation drug able to regulate M1/M2 macrophage activities in the patients with diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). The investigational compound has been given a research code: ON101 (trade name: Fespixon) has demonstrated the clinical superiority to the standard care (an absorbent dressing). The primary endpoint, complete healing, was found in 60.7% of the ON101 group and 35.1% of the comparison group during the treatment period (p=0.0001). Time to complete healing, the secondary endpoint, was faster in the ON101 group (p=0.002). The researchers have reported that “Topical application of ON101 with gauze … read more
Painful and Non-painful Diabetic Neuropathy, Diagnostic Challenges and Implications for Future Management
Peripheral neuropathy is one of the most common complications of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Up to half of patients with diabetes develop neuropathy during the course of their disease, which is accompanied by neuropathic pain in 30–40% of cases. Peripheral nerve injury in diabetes can manifest as progressive distal symmetric polyneuropathy, autonomic neuropathy, radiculo-plexopathies, and mononeuropathies.
The most common diabetic neuropathy is distal symmetric polyneuropathy, which we will refer to as DN, with its characteristic glove and stocking like presentation of distal sensory or motor function loss … read more
Wound Care Centers Market Expected To Reach Over USD 32.60 billion By 2028: Data Lab Forecast
The Wound Care Centers Market study comprises a comprehensive market analysis that encompasses key aspects of the industry and defines current market dynamics in detail. It assesses growth patterns, magnitudes, and specific business developments under the current Wound Care Centers market scenario. The study report shows a balanced presentation of statistical and theoretical data with an accurately estimated forecast that includes the growth prospects in the specified period. The study also determines the market share and size of the Wound Care Centers along with the metric forecast associated with its growth and development during the forecast period. The study mainly focuses on the precise growth projections contained in the report … read more
Screening for Depression in Patients with Chronic Wounds
Wounds with a duration longer than 30 days are considered chronic. For example, diabetic foot ulcers comprise a large majority of these wounds and often exceed the expected 12-week healing period because of underlying factors that cannot be fully corrected.1 Patients with chronic wounds face considerable psychological stress because they need continuous medical care and frequent visits to healthcare facilities. The presence of these wounds significantly disrupts the daily life of patients, including changes in sleeping patterns, diet, and mobility. Loss of mobility may lead to feelings of loneliness, powerlessness, and dependency, as patients rely on family or friends to help fulfill their basic needs such as commuting, activities of daily living, and personal hygiene. Further, patients may experience chronic pain, exudate, and odor, which negatively impact social interactions, relationships, sexuality, and self-confidence. All of these psychosocial factors add up and may lead to a slow onset of anxiety and depression in patients with chronic wounds … read more
Reducing Hospital-acquired Pressure Injuries Among Pediatric Patients Receiving ECMO
BACKGROUND: Pediatric patients immobilized for certain procedures, such as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), are at high risk for developing hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs). PURPOSE: To evaluate the rate of HAPI occurrence in ECMO patients before and after implementation of prevention interventions. METHODS: Patients younger than 18 years of age who were placed on ECMO from January 2012 through March 2020 were identified, and patient data … read more
Assessing the Links Between Eschar Removal and Management of Severe Burns
When treating severe burns, surgeons generally consider eschar removal to be the major factor and the top challenge in both initiating and planning for the optimal course of treatment for each patient. Before grafting, all devitalized tissue must be removed, leaving a wound bed of only healthy tissue. Some burn wounds are clearly full-thickness on initial examination, and some are clearly superficial, with relatively straightforward decision making. However, some wounds have an indeterminate depth and are more challenging. Deep partial-thickness, indeterminate-, and … read more
Webinar: Documenting Drainage Quantity
Coverage of surgical dressings by third-party payers depends, in part, on the volume of drainage of the ulcer being treated. Providers who dispense surgical dressings and expect payment from a third-party payer must document the drainage quantity of the ulcer. This webinar will review this requirement, list the options for drainage documentation, and detail exactly how drainage documentation should be documented in the medical record.
At the end of Dr. Lehrman’s presentation stay for a Question & Answer session where he will answer any questions that you might have.
What You Will Learn:
- List the keywords needed in documenting ulcer drainage when dispensing surgical dressings.
- Define different terms used to document ulcer drainage quantity.
- List the drainage volume requirements associated with commonly used surgical dressings.
Register Now!
Singapore researchers develop novel 3D model to study vascular diseases
A Singapore team of scientists and clinicians from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) and Tan Tock Seng Hospital (TTSH), have developed a three-dimensional (3D) model of the human artery blood vessel wall. Called an “arterial wall-on-a-chip”, it will help researchers study atherosclerosis … read more
Topical Cream Effective Against Diabetic Foot Ulcers
A topical cream that helps regulate macrophage activity was effective in treating diabetic foot ulcers, a clinical trial reported.
In 236 patients with foot ulcers treated for 16 weeks, the proportion who had complete healing of the ulcer was significantly higher in the group randomized to receive the topical cream (60.7%) versus a comparator group treated with absorbent dressing (35.1%; OR 2.84, 95% CI 1.66-4.84, P<0.001), said Shun-Cheng Chang, MD, of the Taipei Medical University in Taiwan, and colleagues … read more
FDA Clears Drug-Device Combination Matrix for Chronic Wound Care
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared the Omeza Collagen Matrix, a drug-device combination matrix for chronic wound care … The approval was granted through the FDA 510(k) premarket notification process. It is the first combination drug/device designed for chronic wound care … The wound care matrix is composed of hydrolyzed fish collagen infused with cod liver oil and other plant-derived oil and wax. After it is applied to a wound, the matrix is incorporated into the wound over time … read more
Take A Load Off: Offloading Tips And Pearls In Wound Care
Diabetic foot ulcerations (DFUs) affect approximately 26 million people worldwide, with a staggering 2.5 times increased risk of death at five years.1-3 While many etiologies and conditions contribute to a wound, offloading is crucial to solving the wound healing puzzle.
In some literature, offloading is the most important aspect of DFU treatment in patients with neuropathy.4-6 The thought behind offloading is relief of mechanical and abnormal stresses that the foot experiences from a loss of protective sensation. This combination results in tissue damage, thought to lead to many DFUs.1,4,7 Specifically, mechanical stress is due to increased plantar pressure and shearing forces during the gait cycle, causing repetitive microtrauma … read more
Reducing Health Disparities in Pressure Ulcer/Injury (PU/PI) Detection & Management October 7-9, 2021 in Atlanta, Georgia
Join the Association for the Advancement of Wound Care (AAWC) for our Pressure Ulcer Summit (PrU), themed Reducing Health Disparities in Pressure Ulcer/Injury (PU/PI) Detection & Management, on October 7-9, 2021 in Atlanta, Georgia.
– Upon completion of this conference, participants will be able to:
– Describe existing disparities related to pressure ulcer/injury (PU/PI) prevention and care.
– Discuss challenges in providing equitable pressure injury prevention and care.
– Describe characteristics of pressure injury and other damage of persons with dark skin tones.
– Identify at least one method of leveling the playing field for pressure injury detection.
Researchers develop new drug-free treatment to accelerate healing of chronic diabetic wounds
About one-fourth of people with diabetes develop painful foot ulcers, which are slow to heal due to low oxygen in the wound from impaired blood vessels and increased inflammation. These wounds can become chronic, leading to poor quality of life and potential amputation … Jianjun Guan, a professor of mechanical engineering & materials science in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, has developed a hydrogel that delivers oxygen to a wound, which decreases inflammation, helps remodel tissue and accelerates healing. Results of the work, which were in a mouse model, are published Aug. 28 in Science Advances. Ya Guan, a doctoral student, and Hong Niu, a postdoctoral research associate, both in Guan’s lab, are co-first authors … read more
Healogics® Raises Awareness of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) to Help Reduce Amputations
Healogics, the nation’s leading provider of world-class wound care services, is raising awareness of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) throughout September. Through this campaign, Healogics is supporting the American Heart Association’s goal to reduce amputations by 20% by 2030 through increased PAD Awareness, diagnosis and treatment … People with PAD often have non-healing wounds in their extremities due to the restriction of blood flow limiting the natural healing process, potentially leading to complications, such as amputation. PAD affects nearly 10 million Americans and is a contributing factor in up to 30% of non-healing wounds on the lower leg. Common symptoms associated with PAD include cramping, numbness, weakness or heaviness in the leg muscles, however up to 40% of people experience no symptoms. One in four people living with late-stage PAD may require amputation within one year … read more
Multifunctional Irrigation-Assisted Vacuum Drainage versus Traditional Drainage in the Treatment of Odontogenic Deep Fascial Infection
Odontogenic deep fascial space infection in the head and neck is a common potentially fatal clinical problem. Traditional drainage method is considered laborious and gravity-dependent. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the clinical effect of a modified multifunctional irrigation-assisted vacuum drainage (MIVD) by comparing it with the traditional drainage method in the treatment of odontogenic deep fascial infection … read more
Wipeout Wounds National Conference Tour
Your Guide to New and Essential Pressure Injury and Ostomy Treatment Protocols
Take control of wound healing by learning about new strategies and tools that will keep you compliant, PLUS spend one-on-one time with industry experts. Learn today and use your knowledge in your clinical practice as soon as tomorrow!
learn more
RITA: The Wound Pros Leverages Artificial Intelligence With Its Wound Measurement App
The Wound Pros (https://thewoundpros.com/) today introduced its automatic wound measurement app, RITA designed to aid healthcare providers in the management and treatment of chronic, non-healing wounds. The Wound Pros is a physician owned and managed wound care company and a leading supplier of wound care dressings with a presence in 16 states across the United States … RITA represents The Wound Pros’ “high-tech” approach that leverages the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning to measure chronic non-healing wounds with pinpoint accuracy. According to Dr. Bill Releford, RITA creator and CEO of the Wound Pros, capturing highly accurate measurements is essential for delivering timely and comprehensive treatments to prevent wounds from worsening and improving healing outcomes.” Clinicians just need to take a picture of a patient’s wound with a smartphone or tablet and RITA will measure its size and generate professional documentation to support treatment and billing alignment. The application integrates seamlessly into The Wound Pros digital wound management platform and allows care teams to remotely monitor patients’ wound progression. RITA offers online and offline capabilities to ensure efficiency and reliability regardless of network connection status … read more
Remote Monitoring Saves Costs in Outpatient Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
In the outpatient setting, combining remote therapy monitoring (RTM) with negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) can support improved adherence to prescribed therapy. A recent study reported that patients receiving NPWT with RTM required fewer therapy days than patients receiving NPWT alone, possibly reducing costs of care. Our objective was to determine whether RTM reduced 90-day costs in patients undergoing NPWT … read more
Oxygen-delivering hydrogel accelerates diabetic wound healing
About one-fourth of people with diabetes develop painful foot ulcers, which are slow to heal due to low oxygen in the wound from impaired blood vessels and increased inflammation. These wounds can become chronic, leading to poor quality of life and potential amputation … ianjun Guan, professor of mechanical engineering and materials science at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, has developed a hydrogel that delivers oxygen to a wound, which decreases inflammation, helps remodel tissue and accelerates healing. Results of the work, which were in a mouse model, are published Aug. 28 in Science Advances. Ya Guan, a doctoral student, and Hong Niu, a postdoctoral research associate, both in Guan’s lab, are co-first authors … read more
Tele Wound Care Navigation for Wound Care Providers
The digital age is upon us, like it or not, ready or not. For the past few years, payers have incentivized, encouraged, reimbursed, and adopted various digital, remote monitoring systems and devices as a way to encourage providers to adopt more digital, remote methods. Although complete telehealth services were not reimbursed in all care settings in all Zip Codes by all payers throughout the United States at the beginning of 2020, many of the restrictions and barriers to provide nearly complete digital services were suddenly released in response to the needs of a nation in the throes of a pandemic … read more
Improved wound management at lower cost: a sensible goal for Australia
Chronic wounds cost the Australian health system at least US$2·85 billion per year. Wound care services in Australia involve a complex mix of treatment options, health care sectors and funding mechanisms. It is clear that implementation of evidence‐based wound care coincides with large health improvements and cost savings, yet the majority of Australians with chronic wounds do not receive evidence‐based treatment. High initial treatment costs, inadequate reimbursement, poor financial incentives to invest in optimal care and limitations in clinical skills are major barriers to the adoption of evidence‐based wound care. Enhanced education and appropriate financial incentives in primary care will improve uptake of evidence‐based practice. Secondary‐level wound specialty clinics to fill referral gaps in the community, boosted by appropriate credentialing, will improve access to specialist care. In order to secure funding for better services in a competitive environment, evidence of cost‐effectiveness is required. Future effort to generate evidence on the cost‐effectiveness of wound management interventions should provide evidence that decision makers find easy to interpret. If this happens, and it will require a large effort of health services … read more
Next Science to Exhibit Surgical Product Portfolio at AAOS 2021
JACKSONVILLE, Fla.–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Next Science Limited (ASX:NXS), an innovative medical technology company, announced that it will exhibit at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) annual meeting and conference in San Diego, California, from Aug. 31 – Sept. 3. Next Science, whose mission is to heal patients and save lives by addressing the impact of biofilms on human health, will exhibit at Booth No. 5035.
Next Science will showcase its portfolio of ground-breaking products, including:
- XPERIENCE™ No Rinse Antimicrobial Solution, a non-toxic surgical solution that is designed to help prevent surgical site infections (SSIs) by rinsing away debris and microorganisms; and
- SURGX®, a topical gel that is applied to a closed surgical incision to help prevent superficial SSIs.
Next Science also will host a presentation that addresses the impact of biofilms on SSIs, discusses risk mitigation strategies and shares clinical results from high-risk patients. The session, Biofilm and Surgical Site Infections, takes place on Sept. 1 from 12:40 – 1:25 p.m. in Meeting Room 1 and will be led by four prominent orthopaedic surgeons:
- Dr. Robert Harris, Hughston Clinic
- Dr. Jon E. Minter, Northside Hospital
- Dr. Randall Otto, SSM Health
- Dr. Ravi K. Bashyal, NorthShore University Hospital
What Measurement Of Wound Healing Is Most Valuable?
Great, provocative work recently in the International Wound Journal by our colleagues Professor Keith Harding and coworkers.1 In their study, they note that healing in total can be a challenging metric to measure, as every wound is very different. In the research world, this translates into difficulty in matching study cohorts, especially when there are not very large subject pools available. Also, they note that the lengthy time necessary to heal many wounds requires that the associated study also takes substantial time. This makes high-quality RCTs with statistically significant and applicable data few and far between.
Taking a slightly different viewpoint on evaluating outcomes in wound healing … read more
Sustained oxygenation accelerates diabetic wound healing by promoting epithelialization and angiogenesis and decreasing inflammation
Nonhealing diabetic wounds are common complications for diabetic patients. Because chronic hypoxia prominently delays wound healing, sustained oxygenation to alleviate hypoxia is hypothesized to promote diabetic wound healing. However, sustained oxygenation cannot be achieved by current clinical approaches, including hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Here, we present a sustained oxygenation system consisting of oxygen-release microspheres and a reactive oxygen species (ROS)–scavenging hydrogel. The hydrogel captures the naturally elevated ROS in diabetic wounds, which may be further elevated by the oxygen released from the administered microspheres. The sustained release of oxygen augmented the survival and migration of keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts, promoted angiogenic growth factor expression and angiogenesis in diabetic wounds, and decreased the proinflammatory cytokine expression … read more
Novel Cellulose Fibre-Based Flexible Plasmonic Membrane for Point-of-Care SERS Biomarker Detection in Chronic Wound Healing
Wound management is stretching the limits of health systems globally, challenging clinicians to evaluate the effectiveness of their treatments and deliver appropriate care to their patients. Visual inspection and manual measurement of wound size are subjective, often inaccurate and inconsistent. Growth factors, such as pro-inflammatory cytokines and proteases, play important roles in cutaneous wound healing. However, little is known about the point-of-care monitoring of the changes in such markers during the healing process. Here, we explore the capability of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) as a viable point-of-care platform to monitor the changes of these surrogate indicators of healing status in chronic wounds …. read more
Smart plaster could accelerate the healing of chronic wounds
Circulatory disorders, diabetes or lying in the same position for extended periods can all lead to chronic wounds that do not heal. There are hardly any effective treatment options. A materials science research team from Kiel University (CAU), together with colleagues from the University Medical Center Schleswig-Holstein (UKSH), Harvard Medical School, U.S., and Dankook University in South Korea, has developed a wound patch with enhanced healing functions which can be individually adapted for each patient. The 3D-printed patch has antibacterial properties, supplies the wound with oxygen and moisture, and supports the formation of new tissue … read more
Watch Richelle Roethler Present the Treatment Plan for a Pilonidal Cyst Removal
Richelle Roethler, RN, APN, FNP, CWCN-NP
In this presentation, Richelle Roethler, RN, APN, FNP, CWCN-NP, describes her treatment plan for a 40-year-old man with a surgical wound, which was left to close by secondary intention, located on the coccyx.
PODIATRY MANAGEMENT FEATURES KERECIS FISH SKIN
Durable Healing Outcomes of Topical Wound Oxygen (TWO2) Therapy Highlighted at Leading International Clinical Conferences
OCEANSIDE, Calif., Aug. 26, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Advanced Oxygen Therapy Inc. (AOTI) announced today that its unique multimodality Topical Wound Oxygen (TWO2) therapy was recently highlighted at multiple leading international clinical conferences across the United States and United Kingdom. AOTI participated both as a sponsor and exhibitor at these events that were conducted in a hybrid format, where attendance could be either in person, or virtually, to allow for the greatest clinician engagement, something that has now become standard during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
Clinical Societies
Clinical Societies
The prestigious Malvern Diabetic Foot Conference, the world’s longest standing international multidisciplinary diabetic foot meeting, was held in Malvern, UK, from July 7 – 9, where during the New Treatments for Diabetic Foot Lesions session, the growing portfolio of high quality clinical evidence supporting the effectiveness of cyclical-pressure TWO2 therapy in healing DFU, was expertly summarized by Professor Robert Frykberg, DPM, MPH., who also presented the results from the recently published paper entitled: Topical oxygen therapy for diabetes-related foot ulcers: A systematic review and meta-analysis, by Professor Golledge et al., which further highlighted the strength of the TWO2 RCT.
The Annual Scientific Meeting (The National) of the American Podiatric Medical Association was held in Denver, USA from July 29 – August 1, where a breakthrough abstract by Matthew G. Garoufalis, DPM and Aliza M. Lee, DPM, MS, entitled: The Power of TWO2: Real World Evidence of the Long-Term Healing and Health Benefits of Cyclical Pressurized Topical Wound Oxygen Therapy in Diabetic Foot Ulcerations was presented, further demonstrating significant reductions in Hospitalization and Amputations over 12-months for DFU patients treated with TWO2, compared to those who were not.
The 2021 Vascular Annual Meeting of the Society for Vascular Surgery was held in San Diego, USA from August 18 – 21, where during a Vascular Live Presentation, entitled: TWO2 Therapy for Healing DFU and VLU: Reducing Hospitalizations and Amputations, the eminent vascular surgeon, Anil Hingorani, MD, summarized the cyclical oxygen pressure noncontact compression mechanism of action of TWO2, reviewed real word cases and even provided a video testimonial from a patient who had suffered with nonhealing Venous Leg Ulcers (VLU) for years, until finally healing with the addition of TWO2 therapy.
Dr. Mike Griffiths, CEO and Medical Director of AOTI, commented; “AOTI is proud to continue to support the world’s leading clinical societies and wound care physicians in their quest for more durable healing of Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Venous Leg Ulcers by utilizing our unique multimodality approach. Our evidence-based TWO2 therapy is applied by the patient safely at home, which when combined with our enhanced Telehealth features, helps clinicians maintain critical continuity-of-care during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. It is especially rewarding to hear in a patient’s own words the significant impact that durably healing their refractory wounds has on their daily lives. It’s both quite humbling and motivating for us all to continue in our cause to make TWO2 therapy available to all who could benefit from its life altering outcomes.”
About AOTI
AOTI is a privately-owned company based in Oceanside, California USA and Galway, Ireland that provides innovative solutions to resolve severe and chronic wounds worldwide. Our products reduce healthcare costs and improve the quality of life for patients with these debilitating illnesses. Our patented non-invasive Topical Wound Oxygen (TWO2) therapy is unsurpassed in closing all chronic wound types.
For more information see: www.aotinc.net
Contact:
Dr. Mike Griffiths
CEO and Medical Director
317543@email4pr.com
(760) 672 1920
SOURCE AOTI Inc.
What to Know About Diabetes Prevalence and Management in Asia
The number of people who live with diabetes has been increasing worldwide over the last several decades, but there has been a significant jump in the number of people with diabetes — particularly type 2 diabetes — in Asia and China.
Currently, more than 60 percent of people with type 2 diabetes live in Asia, primarily in China and India.
There are many complicated factors that play a role in why diabetes diagnoses are increasing in this part of the world. Rapid industrialization and urbanization lead to lifestyle changes that factor into the increasing rate of diabetes in Asia … read more
Pandemic Derails Small Success in Lowering Diabetes-Related Amputations
Rates of minor diabetes-related lower extremity amputations (LEAs) in hospitalized patients increased between 2009 and 2017 in all racial and ethnic groups, in both rural and urban areas, and in all geographic regions across the United States, a new retrospective, observational study indicates … read more
A multi‐centre, single‐blinded randomised controlled clinical trial evaluating the effect of resorbable glass fibre matrix in the treatment of DFUs
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) represent one of the many complications of long-standing diabetes.1 Not only are these wounds expensive to treat, with a recent systematic review showing that the mean cost was over $31 000 in 2015,2, 3 but complications, especially infection, can require prolonged antibiotic administration, deep and extensive debridement, and lower extremity amputations when these measures fail. Even relatively shallow (UT1A, Wagner 1) DFUs that do not respond to standard of care (SOC) are at risk for amputation of the affected area.2-5 This risk increases for patients who have had prior DFUs or amputations. Any product, therefore, that can prevent infection or disrupt biofilm while promoting wound healing in a moist environment is worthy of further investigation … read more
Experimental chronic wound dressing made from human protein
If you’re trying to make a wound dressing that will be well-tolerated by the human body, you may be best off using human-derived materials. That’s the approach that German researchers have taken, creating a tropoelastin-based bandage. Tropoelastin protein molecules are produced naturally by the human body, and they’re the main building block of elastin, a biopolymer which gives the skin and organs their elastic properties. In the past, scientists have tried to reduce scarring by injecting tropoelastin directly into wounds, without much success … read more
The “self-treatment of wounds for venous leg ulcers checklist”
Patients who have chronic wounds such as leg ulcers should be active participants in their treatment and care. This participation may include self-treatment of the wound which involves the patient cleaning the wound, applying and removing wound dressings, and/or applying and removing compression therapy. The aim of the study was to develop a Checklist to assist nurses to appraise the conduct of wound treatment when undertaken by the patient. A three-phase mixed methods study was conducted. A systematic and evidence-based approach to developing and using structured observations for the study of health behaviour guided the process of developing, piloting and refining the Checklist … read more
Incidence and characteristics of diabetic foot ulcers in subjects with type 2 diabetes in Catalonian primary care centres
The main objective was to assess the incidence of diabetic foot ulcers in type 2 diabetes individuals from primary care centres in Catalonia, Spain … read more
Barriers to Prevention and Timely Presentation of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Perspectives of Patients from a High-risk Urban Population in the US
Diabetic foot amputation is a preventable complication that is increasing in incidence in the United States, with disparities across geography, race, ethnicity, and income. This qualitative study explored the experiences of people in a low-income urban area in the United States in preventing and obtaining care for foot ulcers. Sixteen adults with foot ulcers were identified through purposive sampling based on records of hospital stays and primary care visits. Semi-structured interviews were transcribed and analyzed for key themes. Participants described inadequate understanding of diabetic foot disease: many sought care only after developing advanced symptoms. They identified social and health system factors as barriers to timely access to care. Some participants described a realization of the seriousness of their condition and an ability to improve self-care after developing an ulcer. Patients’ experiences can inform the design of amputation-reduction initiatives to achieve more desirable results, including enhanced self-management capabilities, timely access, and attention to social determinants … read more
TECHNOLOGY EFFECTIVE AGAINST ANTIBIOTIC-RESISTANT PATHOGEN
RESEARCH SHOWS ANTIBIOTIC-RESISTANT CANDIDA ALBICANS IS KILLED BY EXPOSURE TO VOMARIS BIOELECTRIC V.DOX™ TECHNOLOGY
Vomaris Innovations, Inc. announced today the publication of results demonstrating that the company’s bioelectric V.Dox™ Technology is effective in killing antibiotic-resistant Candida albicans pathogens. The manuscript, “Ketoconazole Resistant Candida albicans is Sensitive to a Wireless Electroceutical Wound Care Dressing,” was published in Bioelectrochemistry https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2021.107921. The research was led by Chandan K. Sen, Ph.D., Director of the Indiana Center for Regenerative Medicine and Engineering at Indiana University and Distinguished Professor and J. Stanley Battersby Professor of Surgery at the IU School of Medicine.
Antibiotic resistance is one of the greatest global public health challenges of our time1. Every year, more than 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occur in the United States2, and 700,000+ people die globally3. Meanwhile, the discovery of novel antimicrobials is not keeping up with the emergence of new superbugs.1,4 “Antibiotic resistance is growing, and we are fast running out of treatment options. If we leave it to market forces alone, the new antibiotics we most urgently need are not going to be developed in time,” predicts Dr. Marie-Paule Kieny, WHO’s Assistant Director-General for Health Systems and Innovation.
In the study, researchers sought to determine whether the wireless electroceutical wound care dressing or “WED”, was effective in managing pathogenic molecular processes employed by ketoconazole-resistant yeast Candida albicans. Candida albicans poses a major threat to skin and wound infection. It’s typically treated topically with the drug ketoconazole. However, ketoconazole-resistant pathogens are an emerging threat in the management of skin infection. The authors believe that the emergence of multidrug resistance in Candida albicans warrants the need for alternative, non-pharmacological methods of wound treatment.
Vomaris’s WED, powered by V.Dox™ Technology, is a proprietary pattern of embedded microcell batteries that wirelessly generates a low level of electricity in the presence of moisture. The research team used an in vitro model to test WED alone, ketoconazole alone, and the combination of WED + ketoconazole, against ketoconazole-resistant Candida albicans. Three controls were used, including no treatment, plain polyester fabric, and a fabric impregnated with silver.
The researchers found that WED functioned in a multi-pronged manner to effectively treat ketoconazole-resistant Candida albicans. Findings included:
- Prevented hyphal growth. The development of hyphae (long, branched filaments) is a critical part of albican’s growth cycle. Stopping hyphal growth prevents C. albicans from causing infection and subsequent tissue damage.
- Impaired efflux pump system. Damaging this system prevents albicans from rejecting helpful antibiotics.
- Damaged cell wall integrity. Weakening the cell wall structure allows antibiotics to reach the pathogen.
- Disrupted biofilm formation. C. albicans develops a biofilm ‘shield’ to protect it from immune system and antibiotic attack. WED interfered with its ability to form biofilm.
- In contrast, silver alone was ineffective in all experiments.
“This work presents clear evidence that the wireless electroceutical dressing kills ketoconazole-resistant Candida albicans,” said Dr. Sen. “Our findings introduce the option of a novel biophysical solution for fighting chronic wound infection in which antibiotic-resistant pathogens are prevalent.”
“These latest findings by Dr. Sen and team add to our growing body of evidence on the significant role electricity can play in combatting antibiotic-resistant pathogens. In this era of antibiotic stewardship, a wound care product that kills pathogens without the use of antibiotics is an important technological breakthrough,” said Vomaris President and CEO Michael Nagel. “Our V.Dox Technology is already FDA cleared and is the only bioelectric product of its kind in the marketplace today.”
IU School of Medicine is the largest medical school in the U.S. and is annually ranked among the top medical schools in the nation by U.S. News & World Report.
About Vomaris
Vomaris Innovations, Inc. (www.vomaris.com) is a privately held medical device company specializing in bioelectric technology that is redefining infection control and wound healing. Vomaris’s patented V.Dox™ Technology is defining the bioelectric wound care market; it’s the only platform in the world that powers a new generation of antimicrobial dressings for the wound and incisional care markets. The company currently has six randomized controlled trials in progress.
Vomaris and V.Dox and respective logos are trademarks of Vomaris Innovations, Inc.
First-of-Its-Kind Virtual Workshop to Offer Hands-on Skills Practice in Its Live Coverage of Wound Hygiene Principles
Malvern, PA – July 30, 2021 – WoundCon, the first and largest global virtual wound care conference, is proud to announce a new and innovative live event that is free to attend and offers 5.25 CME/CE credits. Biofilm-Based Wound Care is a virtual, hands-on skills workshop that will be presented with closed captioning in eight languages, including Chinese, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, French, German, Polish and English.
The workshop will take place on Friday, September 24, 2021 from 7:00AM to 3:50PM EDT and will be available on-demand for two weeks after the event … read more
New Net Health Innovation Can Predict Risk of Amputations and Wound Healing Rates
Net Health recently announced the addition of two pioneering predictive analytic capabilities embedded in the workflow of the company’s widely used electronic health record (EHR) platform.
Offering artificial intelligence-based capabilities, the Net Health Wound Care software platform now includes the Risk of Amputation Indicator, developed to reduce the risk of amputations, and the Wound Healing Velocity Indicator, developed to predict wound healing rates, according to the company. Net Health says both capabilities will provide insights needed to develop optimal patient therapies, implement effective interventions, and plan treatment paths that will improve outcomes … read more
Silver Ion Hydrocolloid Gauze and Self-Adhesive Polyurethane Foam Dressing Combination Therapy Can Better Promote Healing of Skin Graft Donor Area Than Traditional Therapy
The management of skin graft donor area has been a troublesome problem in reconstructive surgery. Currently, no guidelines exist for the management of skin graft donor areas, and the disposal methods vary from clinician to clinician. Objective. With the goal of providing a better basis for improved patient care, the authors conducted a case control study to investigate whether a combination of silver ion hydrocolloid gauze and self-adhesive polyurethane foam dressing (AG+foam group) was effective in healing skin graft donor sites. Materials and Methods. Forty-eight patients requiring intermediate-thickness skin graft between January 2014 and December 2015 were included in the study. Inclusion criteria included a skin graft measuring at least 40 cm2 to be harvested from the ipsilateral thigh and patient age of 14 years to 60 years. All patients were treated differently according to the … read more
Made Easy: Wound bed preparation
Study Shows Increased Risk For Foot Infection-Related Hospitalizations In People With Diabetes
According to a recent publication in Diabetologia, there is an increased risk of infection-related hospitalization in patients with diabetes.1 This includes foot infections, for which the risk of hospitalization was nearly six times greater in patients with diabetes than those without. Remarkably, the risk for hospitalization in patients with diabetes for all infection types, including foot infection, respiratory infection, urinary tract infection, GI infection, sepsis, and post-operative infection was 67 percent higher than the non-diabetic group. In addition, the study authors noted a stronger association between diabetes and hospitalization related to infection in younger participants and Black patients … read more
A report of 12 months’ of data collected from a diabetic foot clinic at a public hospital in Phnom Penh, Cambodia
This report interprets data gathered from a diabetic foot ulcer clinic in an outpatient department of a public hospital in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. The data were gathered between September 2019 and August 2020 and were entered into a Microsoft Excel™ spreadsheet. It gives basic demographic information of Cambodian patients with diabetic foot ulceration and provides data that can be used to measure any future research or audit. The data collection timeframe … read more
Wound Healing Foundation (WHF) Thomas K. Hunt Lecture Video
We (Wound Healing Foundation) honor Dr. T.K. Hunt, a stalwart wound care expert and supporter of the Wound Healing Foundation. Dr. Hunt is the founding President of the Wound Healing Society and the namesake for the Wound Healing Foundation’s scientific and intellectual Endowed Lecture
Evidence for Person-centred Care in Chronic Wound Care
Chronic wounds affect an estimated 2.21 per 1000 population. They are a significant source of morbidity and affect individuals physically, psychologically, socially and financially. Person-centered care is one approach to improve patient outcomes in wound care as it values patients’ perspectives, beliefs and autonomy and considers the person as a whole within the cultural context in which care is provided.
UPCOMING WEBINAR, Thursday, August 26, at 1PM EDT The Effects of Biofilm and Prolonged Inflammation on the Wound Bed
Speaker: Gregory S. Schultz, PhD
Optimizing treatments to rapidly heal individual chronic wounds requires assessing multiple factors and implementing effective treatments to correct the problems that impair healing as described in the TIMERS guidelines, which emphasizes reducing the wound biofilm bioburden.
ECONOMIC VALUE OF PODIATRIC SURGERY WHEN ADDED TO A VASCULAR SURGERY PROGRAM
Over the last decade, multidisciplinary “toe and flow” programs have gained great popularity with proven benefits in limb salvage. Many vascular surgeons have incorporated podiatrists into their practices. The viability of this practice model requires close partnership, hospital support, and financial sustainability. We intend to examine the economic values of podiatrists in a busy safety-net hospital in the Southwest United States … read more
Case Presentation: Diabetic Foot Infection and Failed Oral Antibiotics
In this video, Robert J. Klein, DPM, FACFAS, CWS, discusses a case that involves a 51-year-old male with a diabetic foot infection (dog bite) and failed outpatient therapy with oral antibiotics. The patient was then admitted IVABx and for OR debridement and NPWT. Watch the video to learn more about the patient’s outcome.
watch video
Brian Wise is named Woundtech CEO
HOLLYWOOD, Fla., Aug. 16, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Woundtech, a leading wound management company serving Medicare Advantage health plans and at-risk senior care provider groups, announced that Brian Wise has been named as its Chief Executive Officer. Brian Wise succeeds Founder Jeffrey Galitz, MD who will continue as a member of the Board of Directors and advise the company on strategic and clinical direction.
Brian Wise is an accomplished healthcare leader with over twenty years of experience scaling complex care management services and technology under value-based and capitation arrangements. Brian most recently served as Chairman of Cix Health, a patient mobile app empowering patients and family members to manage complex chronic conditions. He was the founder and CEO of Advance Health which later merged with CenseoHealth to become Signify Health. Signify Health offers solutions to payers and healthcare providers to succeed in managing value-based care. Brian also served in senior leadership roles at Amerigroup and Coventry Health Care … read more
Significant Reductions in Amputations, Emergency Visits, and Hospital Readmissions Associated with Advanced Treatment Using Skin Substitute Products …
MiMedx Group, Inc. (Nasdaq: MDXG) (“MIMEDX” or the “Company”), an industry leader in utilizing amniotic tissue as a platform for regenerative medicine, today announced publication of its peer-reviewed study in the Journal of Wound Care (JWC), addressing the observed impact of Advanced Treatment (AT) using all high-cost skin substitute products in lower extremity diabetic ulcers (LEDUs) based on data from the Medicare Limited Dataset (October 1, 2015 through October 2, 2018). The study assessed outcome in patients receiving AT with all high-cost skin substitute products, as designated by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), for LEDUs versus No Advanced Treatment (NAT), and found that AT use could lead to a 42% reduction in major and minor amputations and all related costs, compared to NAT. Further, the study highlights preferable outcomes when AT follows parameters for use (FPFU), underscoring the importance of early treatment with regular intervals and well-defined treatment guidelines … read more

Hidradenitis suppurativa treatment should be ‘layered,’ address psychosocial impacts
Providers should avoid monotherapy when treating hidradenitis suppurativa, and instead use a “layered and rotated” approach that also addresses the isolating psychosocial aspects of the disease, noted a speaker here … read more
Application of Topical Sucralfate and Topical Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves Wound Healing in Diabetic Ulcer Rats Wound Model
One of the most devastating complications of diabetes mellitus is diabetic ulcers. Not only because these ulcers heal slowly, these ulcers may also cause disability and even results in limb loss.1 A diabetic ulcer is a chronic wound usually found in the soles of the diabetic patient’s feet. The occurrence of diabetic ulcers is mostly associated with neuropathy and vasculopathy in the form of the peripheral arterial disease which happens in the lower limb of the diabetic patient.2 Around 2% to 5% of all population in the world suffers from diabetic ulcers.3 The hyperglycemic state in diabetics causes molecular and physiological changes that cause diabetic ulcers to become difficult to heal, increasing its risk to secondary infection and potentially causing limb amputation if it is not treated properly.4 Diabetic ulcers account for nearly 90% of all lower limb amputation cases, with a reported mortality rate per year of 5.5% due to diabetic ulcers.
The main aim of diabetic ulcer therapy is to prevent extensive damage and secondary infection of diabetic ulcers, thereby minimizing the risk of further damage or even limb amputation. A thorough therapy for diabetic ulcers includes wound debridement, wound dressing, revascularization procedures, infection management, and ulcer off-loading … read more
A Human Fibroblast-Derived Growth Factor Preparation in the Management of a Chronic Surgical Wound in a Diabetic Patient: A Case Report
The treatment of choice in patients with ischaemic heart disease is coronary artery bypass grafting. The procedure entails the harvesting of the great saphenous vein through a significant leg incision, which may result in infections and wounding at the incision site. Patients with diabetes mellitus pose a greater risk of developing non-healing wounds, which may significantly affect the patient’s quality of life. The use of anti-inflammatory factors and other chemokines derived from cultured human fibroblasts may represent a useful therapeutic approach for the management of surgical wounds in patients with the greatest probability of being wound healing compromised. This case study describes the treatment of a non-healing surgical tibial wound in a male diabetic patient treated with a preparation of human anti-inflammatory interleukins cytokines, and growth factors. The treatment resulted in swift recovery, significant pain reduction and complete wound closure with minimal scarring … read more
A molecular approach to maggot debridement therapy with Lucilia sericata and its excretions/secretions in wound healing
Chronic wounds caused by underlying physiological causes such as diabetic wounds, pressure ulcers, venous leg ulcers and infected wounds affect a significant portion of the population. In order to treat chronic wounds, a strong debridement, removal of necrotic tissue, elimination of infection and stimulation of granulation tissue are required. Maggot debridement therapy (MDT), which is an alternative treatment method based on history, has been used quite widely. MDT is an efficient, simple, cost-effective and reliable biosurgery method using mostly larvae of Lucilia sericata fly species. Larvae can both physically remove necrotic tissue from the wound site and stimulate wound healing by activating molecular processes in the wound area through the enzymes they secrete. The larvae can stimulate wound healing by activating molecular processes in the wound area through enzymes in their excretions/secretions (ES). Studies have shown that ES has antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, angiogenic, proliferative, hemostatic and tissue-regenerating effects both in vivo and in vitro. It is suggested that these effects stimulate wound healing and accelerate wound healing … read more
Wound Practice and Research Volume 29 Number 2
Editorial
Connect, Collaborate, Innovate
Prof Allison J Cowin and Dr Peta Tehan
Original research
Dissemination of microbiota between wounds and the beds of patients with pressure injuries: a cross-sectional study
Mao Kunimitsu, Gojiro Nakagami, Aya Kitamura, Takeo Minematsu, Yuko Mugita, Kazuhiro Ogai, Junko Sugama, Miku Aoki, Chika Takada and Hiromi Sanada
Original research
Reducing the incidence and severity of pressure injuries in a high level care residential aged facility: a quality improvement project
Allyson Waird, Susan Monaro
Review
Caring for a child with Epidermolysis Bullosa: a scoping review on the family impacts and support needs
Colin J Ireland, Lemuel J Pelentsov, and Zlatko Kopecki
Clinical Trial Protocol
Physical activity, sleep and wound healing in adults with venous leg ulcers: a prospective observational cohort pilot study protocol
Yunjing Qiu, Victoria Team, Christian R Osadnik, Jane O’Brien, Louise Turnour, Ayoub Bouguettaya, Rosemary A McGinnes and Carolina D Weller
Review protocol
Measurement properties of quality of life instruments for adults with active venous leg ulcers: a systematic review protocol
Shiwen Liu, Victoria Team, Yunjing Qiu and Carolina D. Weller
Abstracts
Abstracts from the Wounds Australia Conference 4 – 6 May 202
Medicinal Plants as Efficacious Agents for Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies
A diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is a chronic, nonhealing wound that occurs in approximately 15% to 25% of patients with diabetes, and amputation is necessary in approximately 5% to 24% of these patients. Medicinal plants have demonstrated promising wound healing activities in animal models of DFUs as well as in clinical studies. These plants, which are described as medicinal in different regions of the world, are not considered to be standard medicinal treatments in Western medicine at this time. Some medicinal products, such as bromelain—an herbal protease currently used for enzymatic debridement of wounds—have been obtained from plants, showing the important role of these natural products as sources of wound healing agents. This paper aims to review clinical studies on the effects of medicinal plants in patients with DFUs based on the improvement of local and systemic parameters related to wound healing. Electronic databases including PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane Library were searched for studies from inception through May 2019 using the keywords “diabetic foot ulcer” … read more
Scenes From the COVID Resurgence in Wound Clinics
Physicians weathered the first wave of COVID-19 over a year ago, coping with challenges such as a lack of personal protective equipment, providing care via telehealth, and a lack of vaccines. With the Delta variant, many hospitals may be swamped with patients with the coronavirus. Several physicians spoke to Today’s Wound Clinic about their challenges.
“We are busier than ever,” says Matthew Regulski, DPM, ABMSP, CMET, FAPWH(c), the medical director of the Wound Care Institute of Ocean County, New Jersey. “We have so many wound patients. Our wound centers are jam-packed.” … read more
DFCON DIABETIC FOOT CONFERENCE October 21 – 23, 2021
DFCon is the premier international, interdisciplinary diabetic foot conference in North America. This year, the DFCon will be hybrid, so it will be possible to attend both virtually and physically. As always, the program will be designed for the wide spectrum of generalists and specialists who diagnose and manage the diabetic foot. Didactic talks, panel discussions, Q&A sessions, specialty symposia and workshops will delve into diagnostic and interventional strategies for diabetic foot ulcers and amputation prevention. DFCon is singular in that it allows close interaction with world-renowned clinician scientists working on both tried and true methods and cutting-edge technology
Frank & Lizzie Show: Episode 006, Dr. Naz Wahab
Join Frank & Lizzie as they discuss the newest wound care technology in the toolbox with Dr. Naz Wahab, MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA. The group will be discussing how this handheld imaging device differs from thermography, how it captures tissue oxygenation in the microvascular system, it’s application in the daily operations of the wound care clinic, and learning curves experienced. For more information and to see the impressive clinical outcomes achieved with Kent Imaging SNAPshot, contact eric@kentimaging.com
Assessment of Microcirculation in the Type 2 Diabetic and Impaired Glucose Tolerance Feet of Elderly Men by CEUS
Objective: To evaluate the foot microcirculation in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and impaired glucose tolerance patients (IGT) with contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS).
Methods: The study included 37 patients with T2DM but without diabetic foot (DM group), 15 patients with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT group) and 10 elderly males with normal fasting blood glucose (FBS) and negative glucose tolerance tests (control group). Color Doppler flow imaging (CDFI) and CEUS were performed on the right foot great toes for detecting the blood perfusion performance. CEUS images were recorded and parameters of CDFI and flow time-intensity curves (TICs) were analyzed by the Student’s t-test
… read more
Skin closure device aids wound care in a variety of knee procedures
The goals of surgical wound closure include enabling the wound to heal rapidly without infection or complication and returning the incisional region to the best level of function and appearance. How effectively health care professionals use their time in the surgical suite and postoperatively can be a determining factor in the selection of a closure modality … read more
Webinar: Innovations in Wound Care
This 30-minute presentation features learning opportunities that will provide in-depth instruction and demonstration in wound care treatments. After this webinar, the learner will be able to:
- Identify the role of proper wound cleansing
- Discuss how to select and use non-toxic wound cleansers
- Describe advantages of collagen for managing a chronic wound
RedDress Secures Capstone Health Alliance Contract to Expand Access to ActiGraft®
RedDress, a privately held U.S. and Israel-based wound care company, announced today that it has secured a contract with Capstone Health Alliance, one of the nation’s largest regional group purchasing organizations representing 300 hospitals in all 50 U.S. states.
Chronic non-healing wounds impose a significant economic burden on the healthcare system, health care providers, and patients. The ActiGraft® system aims to deliver an affordable and efficacious wound solution to Capstone Health Alliance Members to help improve the health and lives of patients … read more


