Individuals with diabetes have around a 34% chance of developing a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU). This debilitating condition may lead to severe complications, including hospitalization, infection, and amputation. A recent study reported grim data on DFU, finding a five-year survival rate of just 29%. Any delay in treatment has been associated with worsened clinical outcomes. The researchers of this study were interested in identifying risk factors for DFU in patients with T2D. Early detection might one day reduce the number of diabetic foot ulcers … read more
Month: December 2021
Foot ulceration associated with increased risk for amputation or death
Using the Scottish Care Information – Diabetes database, Graham Leese (Ninewells Hospital, Dundee, UK) and co-authors observed that out of 23,395 individuals with type 1 diabetes and 210,064 with type 2 diabetes included in the study, a total of 13,093 had a previous foot ulceration and among these, 34.3% developed a further foot ulcer during the follow‑up period (2012–2017). In addition, a total of 9023 people developed a first ulcer during follow-up… read more
Biomechanical and musculoskeletal changes after flexor tenotomy to reduce the risk of diabetic
neuropathic toe ulcer recurrence
OBJECTIVE: To assess the effect of flexor tenotomy in patients with diabetes on barefoot plantar pressure, toe joint angles and ulcer recurrence during patient follow-up.
METHODS: Patients with a history of ulceration on the toe apex were included. They underwent minimally-invasive needle flexor tenotomy by an experienced musculoskeletal surgeon. Dynamic barefoot plantar pressure measurements and static weight-bearing radiographs were taken before and 2-4 weeks after the procedure … read more
History of Foot Ulcer & Risk for Limb Amputation or Death
Since care for diabetic foot ulcers is delivered by a wide range of healthcare professionals, from nurses working in primary care to specialized diabetes foot clinics, collecting population-based data on diabetic foot ulceration is notoriously difficult. Furthermore, epidemiological data on populations with diabetic foot ulceration collected from selected subpopulations is open to bias, hence the importance of unselected population-based data … To address this issue, my colleagues and I conducted a national, population-based, cohort study of people with diabetes, with the aim of describing the incidence of foot ulceration and amputation-free survival associated with foot ulceration status … read more
In Vitro and In Vivo Studies on the Antibacterial Activity and Safety
of a New Antimicrobial Peptide Dermaseptin-AC
Antimicrobial resistance has been an increasing public health threat in recent years. Antimicrobial peptides are considered as potential drugs against drug-resistant bacteria because they are mainly broad-spectrum and are unlikely to cause resistance. In this study, a novel peptide was obtained from the skin secretion of Agalychnis callidryas using the “shotgun” cloning method. The amino acid sequence, molecular weight, and secondary structure of Dermaseptin-AC were determined … The skin safety of Dermaseptin-AC was evaluated on wounds on the back skin of a rat … it was applied to skin wounds. Chronic wounds are often accompanied by high bacterial burdens and, at the same time, antimicrobial resistance is more likely to occur during repeated infections and treatments. Therefore, developing Dermaseptin-AC to treat chronic wound infection may be an … read more
Technology And Innovation Power Wound Care’s Ongoing Evolution – Marketplace Experts
Like all nurses who specialize in wound care, I have seen many changes in our profession over the years. Perhaps most significant are the influences that breakthrough technologies and products have had on our profession … In order to fully appreciate its scope, we must recall recent history. Not so long ago, a non-healing diabetic foot ulcer often resulted in complications and possible amputation. In addition, to follow the healing process of a wound, the measurements had to be taken manually with rulers, a subjective measurement process that is prone to variation between institutions and even individuals … read more
A year of international growth and product advancement
KEELE, England, Dec. 15, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Biocomposites, an international medical devices company that engineers, manufactures and markets world leading products for use in infection management in bone and soft tissue, is pleased to provide the following business update … Enhanced approval for STIMULAN in Canada and Saudi Arabia … In 2021, STIMULAN® products gained a new approval in Canada for mixing with antibiotics: vancomycin, gentamicin and tobramycin, for use in treating bacterial infection in soft tissue surrounding bone. This was followed by a new approval in Saudi Arabia for STIMULAN® to be mixed with antibiotics for use in bone and soft tissue … STIMULAN® is the only calcium matrix antibiotic carrier with an EU approval for use in bone and soft tissue and offers surgeons the flexibility to apply broad spectrum ‘off-the-shelf’ antibiotics at concentrations that will support their patient-specific treatment plans – dramatically improving patient outcomes and redefining standard of care … read more
BioPhotonics Preview – March/April 2022
The measurement of oxygen levels in the blood commonly referred to as blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) is a critical medical diagnostic. The condition of below normal levels (<95%) is termed hypoxemia and is associated with patients who have asthma, heart disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease … SpO2 levels are also of interest for brain and other surgical procedures (i.e. flap surgery), peripheral vascular disease (PVD), tumor development, the healing of wounds from conditions such as diabetic foot ulcer, systemic rheumatic disease, neuropathy and sepsis2–5. Pulse oximeters, a simple optical device that measures the ratios of two critical band-passes of light through an appendage … read more
Novel therapeutic targets for diabetes-related wounds: An update on pre-clinical and clinical research
Diabetes-related wounds, particularly diabetes-related foot ulceration, is mainly caused by lack of foot sensation and high plantar tissue stress secondary to peripheral neuropathy, ischemia secondary to peripheral artery disease and dysfunctional wound healing. Current management of diabetes-related wounds involves the offloading high foot pressures and the treatment of ischemia through revascularisation. Despite these treatments, the global burden of diabetes-related wounds is growing, and thus novel therapies are needed. The normal wound healing process is a coordinated remodelling process orchestrated by fibroblasts, endothelial cells, phagocytes and platelets, controlled by an array of growth factors. In diabetes-related wounds this coordinated process is dysfunctional. Past animal model and human research suggests that prolonged wound inflammation, failure to adequately correct ischemia and impaired wound maturation are key therapeutic targets to improve diabetes-related wound healing … read more
Extracellular Vesicles from HIF-1α-Overexpressing Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
Restore Diabetic Wounds Through Accelerated Fibroblast Proliferation and Migration
Inhibition of cellular adaptation to hypoxia can cause persistent inflammation, thereby increasing tissue damage and complicating wound healing in diabetes patients. Regulating cellular adaptation to hypoxic environments can help in effective wound repair. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α is a key regulator of cell hypoxia. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) regulate wound repair. This study investigated the mechanism of HIF-1α overexpression in adipose-derived stem cell extracellular vesicles (ADSCs-hEVs) in the repair of diabetic wounds … read more
Evolving Survivor: Wound Care From the Patient’s Perspective | Podcast
Having survived flesh eating bacteria, septic episodes, and pulmonary embolisms, one patient discusses his experience as an “evolving survivor,” explaining how hyperbaric oxygen therapy and integrative care helped him … listen
What Is All This Swelling About? An Update on Lymphedema for Healthcare Providers and Patients
Swelling or edema is common. It can result from certain diseases, infections, conditions, trauma, or injury, and even medication.1 Typically, the swelling goes away on its own. Sometimes, however, the swelling continues and can worsen over time … This article serves as a guide to help patients and caregivers understand what swelling is and when medical help is necessary. We will educate patients and their caregivers about lymphedema including common risks and contributing factors. This article will also provide general treatment recommendations for lymphedema and provide general and disease-specific resources for individuals affected by lymphedema … read more
Get Up to Speed With Recent Wound Care Policy Updates
The Fall is a busy time in the policy world, as government agencies such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) finalize policies for the fiscal year ahead such as the CY 2022 Physician Fee Schedule and more. Get up to speed on the latest payment and coverage policies that can impact wound care with this update from the Alliance of Wound Care Stakeholders … Real world evidence: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is opening up the door to more real-world evidence (RWE) in 2022 and beyond with two new draft guidance documents issued: Real-World Data: Assessing Electronic Health Records and Medical Claims Data To Support … read more
Frank & Lizzie Show: Episode 010, Dr. Mark Melin, Wound Week 2022
Frank & Lizzie host Dr. Mark Melin on this episode as they discuss Dr. Melin’s sessions during Wound Week 2022. This includes their courses Diagnosing & Treating Chronic Venous Insufficiency (Friday, February 25 2:45 PM – 3:45 PM EST) and Management of Lower Extremity Edema (Saturday, February 26 2:30 PM – 3:30 PM EST). To find out more information about Wound Week 2022 in Philadelphia February 24-27, go to WoundWeek.com! We hope to see you there.
From baker to wound care innovator – my HS story
Suzanne Moloney, the founder of HidraWear, first experienced the painful symptoms of Hidradenitis suppurativa as a young teen … At the time was a Suzanne a typical teenager who loved sports and running. She kept quiet about what was happening – she was embarrassed, as any 13-year-old would be. By her mid-teens, the lumps were bigger and harder to manage. Suzanne finally mustered up the courage to speak to a GP when they became infected … Suzanne was prescribed antibiotics every time new lumps flared up, which helped but didn’t stop the painful growths coming back. This cycle continued for years as more lumps appeared under her arms and at the tops of her legs … read more
sanaFactur – An Innovative Player in Wound Care Launches a ….
Novel Food Supplement to Support Tissue Regeneration
GRÄFELFING, Germany–(BUSINESS WIRE)– suppliDerm, a new brand by sanaFactur, represents a science based range of food supplements supporting tissue regeneration the immune system, and energy metabolism. All of these are critical for wound patients. ‘Our team of pharmacists, biochemists and nutritional specialists have combined carefully selected micro- and macro nutrients to support the body’s regenerative processes. Many older people and wound patients are suffering from nutritional deficiencies, also impacting their wound healing.’ says Dr. Alexander Maassen, CEO Scientific. A patent has been filed.
sanaFactur is an established brand in Wound Care, currently focusing on antimicrobial products. ‘suppliDerm will perfectly complement our existing portfolio, enabling patients to actively support wound therapy by supporting their regenerative metabolism. We do look forward to launch our food supplement with several flavors internationally, like the US and UK as leading markets for wound care.’ says Olaf Ohm CEO Commercial … read more
A 57-Year-Old Man with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and a Chronic Foot Ulcer Successfully Managed
with a Remote Patient-Facing Wound Care Smartphone Application
BACKGROUND Wounds affect millions of people world-wide, with care being costly and difficult to deliver remotely. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic highlights the urgent need for telehealth solutions to play a larger role as part of remote care strategies for patient monitoring and care. We describe our findings on the use of a patient-facing wound care app (Swift Patient Connect App, Swift Medical, Canada) as an innovative solution in remote wound assessment and management of a diabetic patient’s wound. CASE REPORT In February 2020, a 57-year-old man with type I diabetes and peripheral arterial disease presented with osteomyelitis in the left foot at the fifth metatarsal, arising from a chronic ulcer … read more
Skin Bioprinter for Wound Care on Latest NASA SpaceX Resupply Mission
a German Aerospace Center study centers on bioprinting—using viable cells and biological molecules to print tissue structures. The German Aerospace Center study Bioprint FirstAid demonstrates a portable, handheld bioprinter that uses a patient’s own skin cells to create a tissue-forming patch to cover a wound and accelerate the healing process. On future missions to the Moon and Mars, bioprinting such customized patches could help address changes in wound healing that can occur in space and complicate treatment. Personalized healing patches also have potential benefits on Earth, providing safer and more flexible treatment anywhere needed … read more
Related:
The 3D bioprinting process in the Bioprint FirstAid Handheld Bioprinter
MediWound offers hope for chronic wound treatment – study
In a phase II study, EscharEx demonstrated safe and effective debridement of diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers.
A phase II pharmacology study has found positive initial data of EscharEx, a bioactive therapy for rapid debridement in chronic and hard-to-heal wounds, Israeli biopharmaceutical company MediWound announced on Monday … The US-based study, which is ongoing, examined the treatment of seven patients with either diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) or venous leg ulcers (VLUs) … read more
Biogenic Nanoparticles Synthesized from African Medicinal Plants for Wound Healing
Wounds are described as damage to living tissue that disrupts its normal anatomical structure and function. They develop as a result of tissue damage caused by physical, chemical, thermal, microbiological, or immunological factors … The damage can compromise the skin’s epithelial surface and spread into the surrounding tissues, disturbing other systems such as ligaments, muscles, and nerves … Chronic wounds develop when wounds fail to heal properly and claim the lives of countless people around the world … read more
Ankle-Brachial Index Is Independently Associated With Cardiovascular Outcomes
and Foot Ulcers in Asian Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
BACKGROUND AND AIMS: The ankle-brachial index (ABI) is an efficient tool for objectively documenting the presence of lower-extremity peripheral arterial disease (PAD). The predictive factors of cardiovascular events and diabetic foot ulcer were not clear from the ABI examination in Taiwanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM).
METHODS: We enrolled 482 patients with type 2 DM who regularly visited the outpatient department of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and received ABI as well as brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity … read more
Nano-Silver Medical Antibacterial Dressing Combined with High-Flow Oxygen
Therapy Facilitates Ulcer Wound Healing of Superficial Malignant Tumors
Malignant tumors (cancer cells) are metastatic and invasive, and cancer cells can spread throughout the body through hematogenous, lymphatic and implantation metastases. Clinically, the most common tumor metastasis sites are lung, liver, brain, bone, etc. Some patients will have metastasis on the body surface, while in some cases, the tumor directly spreads or invades the body surface.1 The appearance of superficial malignant tumor usually indicates that the tumor is in the middle and late stage. However, many patients seek medical treatment only after the superficial tumor has grown, ruptured, and become infected. The ulceration of superficial malignant tumors can lead to wound bleeding, exudation, pain, infection, and scar hyperplasia, which makes the wound unhealed for a long time, greatly reducing the quality of life of patients.2 At present, surgical resection, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are the mainstays of treatment for superficial malignant tumors.3 Clinically, such patients are required to maintain local dryness of the wound, but frequent dressing changes and large surgical wound make it difficult to keep the wound dry; Moreover, chemotherapy is easy to cause a large amount of exudate in the wound to be in a moist state, coupled with the skin damage aggravation resulted from radiotherapy, leading to the susceptible to wound bleeding and infection and consequently delayed wound healing … read more
Is Your Wound Bioburdened? Case 1
CASE
• 22-year-old male with paraplegia following a fall from a balcony presented with large presacral and buttock pressure injuries that continued to increase in size since last visit >3 months prior. Click here for photo.
• Although the ulcers were large with areas of increased depth, there were minimal clinical signs of bioburden.
• A fluorescence scan revealed red fluorescence indicative of significant bioburden that could not be removed with cleansing or debridement.
• A point-of-care fluorescence scan (MolecuLight i:X) revealed a pattern of scattered red fluorescence (white arrows) indicating elevated bacterial burden (>104 CFU/g) extending beyond … read more
EWMA Podcasts Season 1
- EP07: Personal protective equipment
This podcast episode will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the prevention and management of skin injuries related to the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).This is a follow-up to the EWMA webinar we ran on the 30th April devoted to this topic. Due to a high volume of questions and level of interest that we have received during the webinar we have decided to follow-up with this podcast. In this episode we will be answering some of the questions raised from the webinar. - EP06: Wound Care Essentials during COVID-19
In this short special edition of the EWMA podcasts, Julie Jordan O’Brien talks about how to help wound care patients during COVID-19 and how a healthcare professional (HCP) can change a dressing in a home care setting. - EP05: AMS in Wound Management
In this episode, Samantha Holloway, Chair of the EWMA Education Committee and Teacher Network, speaks to Karen Ousey, Professor of Skin Integrity and Director for the Institute of Skin Integrity and Infection Prevention at the University of Huddersfield, about antimicroabial stewardship in wound management. - EP04: Atypical Wounds
In this episode, Samantha Holloway and Kirsi Isoherranen briefly discuss the best clinical practices and challenges related to the management of atypical wounds. By listening to this podcast you can learn more about how to suspect an atypical wound and will get more information about the diagnostic criteria and available tools - EP03: Person-centred Wound Care
Georgina Gethin discusses with the podcast’s host, Julie Jordan O’Brien, what person-centred care is and why it is so important in wound management. By listening to this episode, you can learn more about the benefits of shared decision-making between the patient and clinicians in wound management and get some practical support in implementing it - EP02: Standardisation Wound Education in EU
Samantha Holloway, Chair of the EWMA Education Committee and Teacher Network, speaks to Sebastian Probst and Ida Verheyen-Cronau about the standardisation of the wound education in Europe. Both podcast guests shares their experience in implementation of the EWMA level 5 and 6 post-registration curricula for nurses in Switzerland and Germany - EP01: Understanding Diabetic Foot
In this episode of the EWMA podcasts, Julie Jordan O’Brien and David G. Armstrong discuss current challenges and opportunities in the management and prevention of diabetic foot ulcers. Jordan O’Brien is a former EWMA Council member who works as anadvanced nurse practitioner in plastic surgery at Beaumont Hospital, in Ireland. Armstrong is Professor of Surgery and Director of the Southwestern Academic Limb Salvage Alliance (SALSA) at the Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California
Evidence for Person-centred Care in Chronic Wound Care
Chronic wounds affect an estimated 2.21 per 1000 population. They are a significant source of morbidity and affect individuals physically, psychologically, socially and financially. Person-centered care is one approach to improve patient outcomes in wound care as it values patients’ perspectives, beliefs and autonomy and considers the person as a whole within the cultural context in which care is provided … read more
Best Practice Statement – Addressing complexities in the management of venous leg ulcers
This document builds on the Best Practice Statement: Holistic Management of Venous Leg Ulcers to address complexities in the management of venous leg ulcers.
The aim of this document is to help ensure consistent clinical practices in relation to the assessment and management of people with VLUs who are outside the scope of the leg ulcer treatment pathway developed by Atkin and Tickle (2016). It will provide guidance based on relevant evidence and the experiences and opinions of clinicians, with a focus on practical, holistic and patient-centred strategies … read more
Researchers develop novel 3D printing technique to engineer biofilms
Anne S. Meyer, an associate professor of biology at the University of Rochester, and her collaborators at Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands recently developed a 3D printing technique to engineer and study biofilms—three-dimensional communities of microorganisms, such as bacteria, that adhere to surfaces. The research provides important information for creating synthetic materials and in developing drugs to fight the negative effects of biofilms … read more
Anti-biofilm Wound Dressing Market: High Prevalence of Diabetes to Drive Growth of the Market in Near Future
The rise in the occurrence of chronic illnesses such as diabetes and cancer throughout the world is driving expansion of the global anti-biofilm wound dressing market. Non-communicable illnesses are becoming more prevalent due to various factors such as smoking, alcohol usage, antibiotic resistance, and unhealthy and sedentary lifestyles.
Healthcare facilities, such as hospitals, have been overburdened as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic … read more
Payers Continue to Release Pertinent Coverage Policies
At the 2021 SAWC Fall, this reimbursement consultant/educator/author was honored to provide a main session reimbursement presentation, as well as a 3-hour interactive reimbursement post-conference workshop. The attendees at both venues were very attentive and asked many excellent questions. On the plane ride home, this author reflected on the questions that were asked at both sessions and came to the conclusion that many wound/ulcer management professionals either 1) have not implemented a process for monitoring and reviewing pertinent payers’ coverage policies or 2) have not incorporated these important “playbook guidelines” into their wound/ulcer management assessments, care plans, coding selections (diagnosis, evaluation & management, procedure, and product), and documentation … read more
Wound Care Technology: Advanced Tissue Therapeutics
Human knowledge is growing exponentially. This explosion is clearly evident in the field of Medicine. We hear almost daily about advances in cardiovascular and oncologic treatments. Medicine appears to be on the verge of extending human life well beyond 100 years. Fortunately, Wound Care physicians and their patients are also reaping the benefits of this rapid knowledge advancement. In the last decade, key elements in the body’s cellular healing processes have been elucidated. A major thrust has been in the development of human tissue therapies … read more
Expecting The Unexpected: When A Small Wound Has Big Implications
Acral lentiginous melanoma only accounts for only two to 10 percent of all reported melanoma types.1 Although the term “lentiginous” often refers to the typical dark coloration of the pathology, the dark coloration is not always a clinical finding, as multiple studies report amelanotic lesions, as well.2,3,4 Therefore, it is pertinent for every practitioner to give due diligence to any suspicious lesion and to know the key findings that may help differentiate a serious lesion from one that is more benign … read more
Compassionate and Versatile Brush-Biopsy for Histologic Wound Sampling
Soft K-Biopsy® – SFT-1000
SoftBiopsy® is a sterile single-use brush-curette is designed to be both minimally invasive and clinically effective for tissue sampling. The plastic applicator tip is coated with Kylon®, a patented medical fabric which dislodges and collects wound base tissue post-debridement, efficiently and effectively.
The SoftBiopsy® is designed with a trumpet shaped brush tip to easily press into the wound base surface and remove and trap a biopsy sample for anatomic pathology as curettings (tangential biopsy sample). When used post-debridement, it is optimal for molecular (PCR) or microbiological culture.
Organism ID Sampling Method
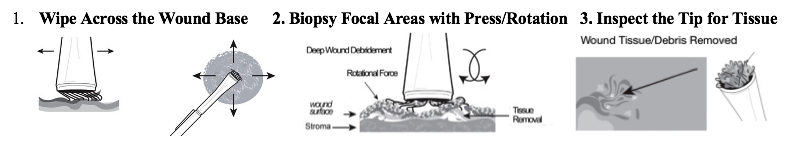
Once the biopsy is obtained, tissue samples for analysis are easily collected in the KYLON® hook tapered tip head and snapped off and placed into the vial to preserve tissue for organism (culture, PCR) or anatomic pathology lab analysis.
Request that your pathology lab that performs wound related tests contact us to become a Kylon® device “Center of Excellence”.
Benefits:
- Fabric pad on tapered applicator tip is designed for visible surface wounds that are visible on the body surface
- Versatile use, Ergonomic, and minimally invasive design facilitates user tactile control for targeting and guiding the brushing, sweeping and rotational movements – modulating tactile pressure and method allows for tissue. removal and trapping using a pressure-twisting motion of the wound surface
- Kylon® medical fabric hooks gently, yet substantially obtain abundant tissue samples that are trapped in the hook array, snapped free from the handle, and transported for laboratory analysis
- Designed for compassionate patient experience and compliance
Clinical Scenarios: (Refer to Instructions for Use)
The SoftBiopsy® is indicated for tangential biopsy of wounds on visual surfaces in order to obtain a sterile biopsy sample. Once the tissue filled tip is detached and placed in a vial, it is transported for histological analyses and further laboratory evaluation regarding infection or other pathology
Contraindications:
SoftBiopsy® is contraindicated for use with patients with known bleeding disorders or those on anticoagulant therapy, patients with an acute wound infection or condition that is not amenable to biopsy, patients with a known allergy to nylon or acrylic plastic, or patients who are pregnant or suspected to be pregnant when a wound biopsy would not be indicated
Warnings and Precautions:
Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician or other licensed practitioner.
Storage Requirements:
Consult manufacturer on special storage requirements outside of normal room temperatures.
How Supplied/Sizing:
Box of 25 minimum order
Recommended Use:
- Burns
- Chronic Wounds
- Diabetic Foot
- Graft Bed Preparation
- Non/Minimally Exudating Wounds
- Palliative Wounds
- Pressure Ulcers
- Non-Eschar/Solid/Fibrotic Wounds
- Sloughy Wounds
- Surgical Wounds
- Venous Ulcers
Mode of Use/Application:
See manufacturer’s website for detailed instructions for use (IFU)
Clinically Tested:
Latex-friendly
Product features:
- Single Use
- Disposable
- Instrument
- Sterile
Other features:
- Educational Material Available
- Free Samples/Trials Available
- Published Clinical Study Available
Manufacturer: Histologics LLC – www.histologicswc.com
Histologics LLC’s primary objective is to advance a compassionate approach to debridement and wound biopsy sampling with devices using Kylon®, a medical fabric enabling biopsy with tissue capture, or frictional tissue cleaning, and debridement.
Website:
Email:
Phone:
(888) 235-2275
Toll-free:
(888) 235-2275
Fax:
(888) 738-9757
A Challenging Case Of Limb Preservation For A Patient With Neuropathic Pedal Dislocation
In the summer of 2020, an 82-year-old male presented to the emergency department to evaluate right foot pain and swelling over the past week. He saw his primary care physician earlier in the morning, who referred him for more emergent evaluation. He states he fell at home one week ago, injuring his right foot. This initially resulted in minimal pain, but over one week, the pain and swelling continued to worsen. He notes that he had no open wounds or active bleeding at the time of the initial injury. However, over that week, in addition to the escalating pain and swelling, he developed a bleeding ulcer on the dorsal aspect of the right foot. He could stand and ambulate … read more
Impact of repeated remote ischemic conditioning on diabetic foot ulcers: A proof-of-concept study
The WHS Communications Committee is pleased to launch the WRR Fireside Chat video series to feature groundbreaking research in Wound Repair and Regeneration (WRR).
Each video Drs. Mitch Sanders, PhD and Kyle Quinn, PhD will feature a recent article in WRR.
Impact of repeated remote ischemic conditioning on diabetic foot ulcers: A proof-of-concept study
Author: Matthew Regulski, DPM
Technology in Wound Care
In all fields of medicine, technology is changing and improving how we treat our patients. Wound care is no exception. From improved charting with electronic medical records to new treatment options to expanding access with the use of telemedicine, in wound care offices, technology plays an increasing role in our day to day interactions with patients.
The majority of physicians use an electronic medical record (EMR) for documentation, and in wound care, the way we use EMR’s to document is changing. New imaging technologies improve the accuracy of documentation and facilitate the process. For example, many wound centers still measure wounds with a ruler to document the length x width x depth and describe the type of tissue present in the wound. This opens up the possibility of user error, which may ultimately affect the way the wound is treated and the healing outcome overall. With newer imaging systems like the one from Tissue Analytics, the provider can picture, measure, and analyze the wound in one step, allowing for faster and more accurate documentation … read more
Is There An Optimal Metatarsal Length To Prevent Reulceration After Ray Amputations?
The podiatric surgeon frequently utilizes partial ray amputations aiming to remove infection while preserving bipedal ambulatory status and preventing further morbidity or mortality. An estimated 50 to 70 percent of lower extremity amputations take place due to diabetic complications, most commonly diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) formed in the setting of peripheral neuropathy. Patients with diabetes often face additional comorbidities, including peripheral vascular disease and a diminished immune response, both of which increase the risk for ulcer development and complicate healing potential. Although amputation is an effective method of eradicating osseous infection, removing pedal anatomy will alter normal biomechanics and increase pressure distribution to surrounding structures. Furthermore, amputation of pedal structures involved in the gait cycle will require increased metabolic expenditure during ambulation. One hypothesis … read more
Roles of Oxidative Stress and Raftlin in Wound Healing Under Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy
Negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is an effective way to promote wound healing. However, its mechanisms have not been investigated thoroughly. Growing evidence suggests that oxidative stress and Raftlin levels play important roles in wound healing. However, whether NPWT promotes wound healing through this mechanism remains unclear.
Purpose: Our study focuses on the different levels of oxidative stress and antioxidant response between wounds treated by NPWT and routine dressing change. The objective of this study was to measure the differences in Raftlin levels between the two groups, which is a new biomarker related to wound healing … read more
Preventing complications at wound dressing changes
This module aims to make clinicians aware of:
- The importance of skin health and what makes it vulnerable to damage.
- The damage that can occur when using medical adhesives and improper removal techniques.
- The impact that MARSIs (medical adhesive-related skin injuries) can have on patients.
- Ways to reduce the risk of MARSIs by providing appropriate treatment for at-risk patients groups.
Executive Summary: Debridement
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Nurses Developed by Nurses Specialized in Wound, Ostomy and Continence Canada (NSWOCC)
Debridement is described in the literature as having a high level of clinical risk and may result in patient harm when performed by untrained nurses. As a result, specialized knowledge, skills, and competencies are required to initiate, direct, and perform safe and effective debridement. This executive summary provides an overview of Debridement: Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Nurses from the Nurses Specialized in Wound, Ostomy and Continence Canada (NSWOCC). The primary objective of these recommendations is to positively influence patient outcomes and enhance safety. The 12 recommendations place the safety of the patient and nurse at the forefront and highlight the educational, competency, certification, preceptor/mentorship, and legal requirements for nurses to initiate, direct, and perform all methods of debridement. We designed these recommendations to be circulated and implemented widely by … read more
Determining Amputation Level To Optimize Functional Outcomes
Diabetes is the leading cause of non-traumatic amputations in the lower extremity.1 Around 15 percent of all patients with diabetes will develop a lower extremity ulceration, with these patients being 17 to 40 times more likely to require an amputation.1 Unfortunately for most, the decision to amputate is not always clear cut and the determination of where to make a definitive amputation is not always as it seems on plain films or advanced imaging, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT). There are several factors to consider when performing limb salvage procedures for these patients with diabetes … read more
APMA’s 2021 Diabetes Campaign, “Es Hora,” Focuses on Hispanic Males
November is Diabetes Awareness Month, and APMA’s Communications Committee is launching a new public education campaign designed to reach one of our most at-risk patient populations: Hispanic males. The campaign, “Es Hora,” offers a wealth of educational materials for you to use in your practice.
This content is available to APMA members only. If you are a member, please log in to see the full content … read more
Coding and Billing for the Foot and Ankle Surgeon
Take the first few steps to coding and billing by joining us for a comprehensive workshop covering the fundamentals of coding and billing for foot and ankle surgeons. Learn the foundation of the coding and billing process from expert colleagues before taking the ACFAS Coding and Billing for the Foot and Ankle Surgeon course. This course is for residents, fellows, new practitioners, office staff of foot and ankle surgeons or anyone who wants to learn more of the basic coding and billing terminology and process. Plus, if you’re a resident and attending Residents Day in the morning the day of the event, this course is a great next step to learning more about coding and billing for your future practice and can be bundled in your pricing … read more
Getting Back to Basic Wound Care
Author: Bill Richlen PT, WCC, DWC
My 25 years in the wound care field has been an incredible journey. Over the years I have been witness to better understanding of wound healing, better research and improved products and technology that has changed the way wounds are managed. At the same time, I regularly hear my students and colleagues share some of the practices being implemented today, along with many myths still being perpetuated, and it makes me wonder “what happened to the basics?”. I once learned from a colleague and now include it my teaching that there are 2 fundamentals to heal all wounds: 1) healthy patient; and 2) healthy wound. As long as those fundamentals are achieved, a wound is likely going to heal despite what you do it … read more
Evidence in wound care
There is an ever-growing variety of products and devices available to practitioners to improve healing rates and patient outcomes, but practitioners should be able to critically appraise evidence to make appropriate evidence-based changes to practice. This position document reviews the available evidence in wound care, looking especially at the critical appraisal of level 1 evidence, before considering the steps required to translate evidence to practice … read more
Printing technique creates effective skin equivalent, heals wounds
Chronic wounds are deep and difficult to repair. Often, the top of the injury heals before the bottom, so the wound collapses in on itself. Over time, this can result in scar tissue and reduced skin function … The technique is the first of its kind to simulate three layers of skin: the hypodermis, or fatty layer, the dermis, and the epidermis … “You effectively have three different cell types. They all grow at different speeds,” said author Alan Smith. “If you try to produce tri-layered structures … read more
MolecuLight Announces Availability of its MolecuLight i:X® Platform on Epic’s App Orchard
Save MolecuLight i:X fluorescence wound images and measurements in Epic
Toronto, CANADA – (August 12, 2020) MolecuLight Inc., the leader in point-of-care fluorescence imaging for real-time detection of bacteria in wounds, announces the availability of its MolecuLight i:X® platform on the Epic App Orchard Marketplace and the integration of its platform with Epic’s leading EMR (electronic medical record) platform.
Users who use Epic for the treatment of wounds can upload standard and fluorescence images, and measurements captured with the MolecuLight i:X device at the point-of-care to the patient’s record. The integrated platforms allow clinicians to optimize their workflow and document their patients’ wounds digitally. The MolecuLight i:X application – iX Imaging – is available on the App Orchard.
“We are proud to announce the inclusion of our MolecuLight i:X platform in the Epic App Orchard Marketplace to allow customers to generate and access documentation of patients’ wounds”, says Anil Amlani, MolecuLight’s CEO. “The MolecuLight i:X is the only point-of-care device enabling clinicians to capture wound images showing clinically significant bacteria, information that improves clinical decision making to ensure the fastest path to healing. The integration of this additional information into existing documentation protocols will provide clinicians with a more complete wound dataset.” … read more
NHS Resolution reviews medical negligence claims by patients with diabetes and lower limb complications
The NHS’s defence organisation, NHS Resolution, are reviewing past medical negligence claims against the NHS by patients with diabetes who suffered lower limb complications. Most of these cases relate to patients with non-healing foot ulcers, who then needed major lower limb amputations. The aim of the review is to identify and report on the themes which are common in these cases to help the NHS learn from its mistakes. NHS Resolution hope that by raising awareness of the risks and need for consistent, correct treatment of diabetes-related lower limb problems, both the number of amputations and the cost to the NHS can be reduced. The key message of the review will be that lower limb amputations are often preventable, but this requires NHS organisations to work together to improve care for these patients. The review will be published within the next few months … read more
Wound photography for evaluation of surgical site infection and wound healing after lower limb trauma
AIMS: Deep surgical site infection (SSI) is common after lower limb fracture. We compared the diagnosis of deep SSI using alternative methods of data collection and examined the agreement of clinical photography and in-person clinical assessment by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) criteria after lower limb fracture surgery … read more
Wound Healing Gets a Boost from 3D Printed Platelet-Rich Plasma
Researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences report replicating a crucial component of our blood may aid wound healing … The findings are published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials in a paper titled, “3D Printed Scaffolds Incorporated with Platelet-Rich Plasma Show Enhanced Angiogenic Potential while not Inducing Fibrosis,” and led by researchers at the Tissue Engineering Research Group (TERG) and SFI AMBER Centre based at RCSI’s department of anatomy and regenerative medicine … read more
3 Steps For Turning Wound Care Into Staff Inspiration
Staffing was a challenge in skilled nursing care prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, and like all segments of health care, the problem has only worsened for SNFs since March 2020. But new figures from the Bureau of Labor Statistics are nevertheless a shock to the system … Since the start of the pandemic, the industry lost a startling 221,000 jobs — or 14% of its workforce — from March 2020 to October 2021. This is a significantly greater loss than any other health care segment, well ahead of the 8.2% drop in assisted living staff … read more
ZZ Biotech Announces First Patients Dosed in Phase 2 Clinical Trial of 3K3A-APC for
Treatment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
HOUSTON–(BUSINESS WIRE)–ZZ Biotech, a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company developing the experimental drug 3K3A-APC for some of the biggest unmet needs in stroke, neurodegenerative disease and chronic wound healing, today announced that the first patients have been dosed in a Phase 2 clinical trial evaluating 3K3A-APC for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease. The study is being conducted at Macquarie University, in Sydney, Australia, and seeks to investigate whether 3K3A-APC is safe and potentially effective in patients with ALS. The Firies Climb for Motor Neurone Disease provided an AU$1 million donation to support this clinical trial … The Phase 2 open label trial (NCT05039268) will enroll a total of 16 patients with ALS into two dose cohorts. The primary study outcomes are to ensure the safety and tolerability of 3K3A-APC in ALS patients and to determine whether 3K3A-APC is able to reduce the pathological changes that are thought to cause ALS. The study will evaluate biomarkers of microglial and monocyte activation and should provide evidence as to whether microglial activation is a major pathogenic contributor to ALS … read more
Singapore tests out ‘smart bandage’ for remote recovery
SINGAPORE – Researchers in Singapore have developed a smart bandage to enable patients to have chronic wounds monitored remotely via an app on a mobile device, potentially saving them visits to the doctor … A research team at the National University of Singapore has created a wearable sensor attached to a transparent bandage to track progress in healing, using information like temperature, bacteria type, and levels of pH and inflammation … “Traditionally when someone has a wound or ulcer, if it’s infected, the only way to examine it is through looking at the wound itself, through visual inspection … read more
Stem cell memories may drive wound repair, and also chronic disease
A trifling paper cut is a site of frenzied activity. Within it, a squad of epidermal stem cells briskly regenerate to patch up the wound. A closer inspection of this war-torn swath of epidermis will reveal that while some of the stem cells are native to the area, others are newcomers—former hair-producing stem cells, that—upon sensing nearby injury—migrated from the hair follicle to the wound bed, where they transformed to resemble indigenous epidermal stem cells … read more
Novel Plasma Gas-Based Strategy Kills Resistant Bacteria, COVID-19 Virus
A novel, antibiotic-free strategy for fighting antimicrobial-resistant bacteria using cold plasma ionized gas to activate key molecules has shown early efficacy in eradicating bacteria commonly found in chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers. The gas also killed the SARS-CoV-2 virus on surfaces … read more
A Comparative Study of Efficacy of Povidone Iodine Versus Super Oxidized Solution in Lower Limb Ulcers
BACKGROUND Wounds and their management are important in the practice of surgery. Super oxidised solution is a recent concept in wound management. It is an aqueous solution which is electrochemically processed which is non-toxic, non-irrigating and is having a neutral pH. Povidone iodine is the most common topical wound care product used in surgical practice. Both are affordable solutions for the patients. There are very few studies comparing the efficacy. In this study, we wanted to compare the efficacy of super oxidised solution and povidone iodine in the management of lower limb ulcers. METHODS A prospective study was conducted on 100 patients who were randomized into two groups. Group A was treated with super oxidized solution and Group B were treated with povidone iodine. Assessments of wounds were done on various days (1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21). Various outcomes of data were analysed using statistical analysis. RESULTS The average percentage reduction in wound size on day 21 was 47 % in Group A compared to 24 % in Group B. Early appearance of granulation tissue, disinfection, decrease in wound size, and less duration of hospital stay was achieved in Group A. CONCLUSIONS The results were more favourable towards super oxidised solution than povidone iodine. In this comparative study, super oxidized solution had faster efficacy and wound healing … read more
Sherlock Holmes and the Case of the Missing Evidence
Diversity and Pressure Injury Prevention: Important Terms to Know
Erythema: A result of injury or irritation that causes dilation of blood capillaries and manifests as patchy reddening of the skin. Occurs after a patient/resident is exposed to unrelieved pressure for 2 hours. It can be identified as a deep, localized redness; can also be blue or purple.
Hyperemia: The condition of having excess blood in vessels that supply an organ or area of the body. Occurs after patient/resident is exposed to 30 minutes of unrelieved pressure. It can be identified as a localized, non-blanchable redness.
Perfusion: The passage of blood through arteries and capillaries into tissues or organs. When insufficient, there is an increased chance that the patient may have complications.
… more
Wound Care Search Engine
Beyond being a great source for news, Wound Care Weekly is also an effective search engine for wound care related content. Google searching will reflect results targeted toward the general public where our search results will be derived from thousands of articles written almost exclusively for medical professionals.
Use italics for more focused search results “foot ulcer”
Smart wound dressing provides suture-free closure of surgical incisions
It is a staple of science fiction to mock sutures as outdated. The technique has, after all, been in use for at least 5,000 years. Surely medicine should have advanced since ancient Egypt. Professor Hossam Haick from the Wolfson Department of Chemical Engineering at the Technion has finally turned science fiction into reality. His lab succeeded in creating a smart sutureless dressing that binds the wound together, wards off infection … read more
Research holds promise of new information about skin injuries
Biomedical engineering professor Kyle Quinn has received a four-year, $1.6 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to develop non-invasive, real-time “optical biopsies” of chronic skin wounds.
The goal of Quinn and researchers in his lab is to provide digital histopathology images — the microscopic examination of tissue to study the manifestation and progression of disease — and other quantitative information without the need for an invasive biopsy, tissue processing and staining with histology dyes … read more
‘Death is a greater risk’ than amputation after diabetic foot ulcer
People with diabetes and a history of foot ulcer are more likely to die than undergo amputation during 6 years of follow-up, a potential measure of effectiveness of diabetes care, registry data from Scotland show.
In an analysis of real-world data comparing people with diabetes with and without foot ulcer, researchers also found amputation or death occurred for approximately one in two of those with a prior foot ulcer … read more
Frank & Lizzie Show: Episode 009, Dr. Jeffrey Lehrman and Moira Sykstus, Wound Week 2022
On this episode, Frank & Lizzie’s guests Dr. Jeffrey Lehrman and Moira Sykstus share insight on their upcoming “Coding, Compliance, and Documentation in Wound Care” course held during the American Professional Wound Care Association’ s (APWCA) Wound Week 2022 conference in Philadelphia. This course will be held on Thursday, February 24, 2022 at the Loews Hotel. The conference will be held Feb 24-27, 2022. For more information about Early Bird Discounts, New Member deals, and more, visit woundweek.com.
The role of non-medicated dressings for the management of wound infection
There is growing concern regarding the treatment of infection, caused by the rise of antimicrobial resistance. This position document looks at current treatment approaches to identifying and treating biofilm in wounds, focusing on the mechanism of action and role of non-medicated wound dressings (NMWDs) within antimicrobial stewardship practices and evidence that supports their effectiveness … read more
Strategies to reduce practice variation in wound assessment and management
The T.I.M.E. Clinical Decision Support Tool
This document seeks to help clinicians support those who do not have specialist wound training to accurately assess patients and their wounds and arrive at a broad-based, systematic rationale that will ultimately help reduce variations in clinical decision-making. The T.I.M.E. Clinical Decision Support Tool provides a structured approach to wound bed preparation … read more
Development and Implementation of an Individualized Turning Program for Pressure Injury Prevention
Using Sensor Technology in Nursing Homes: A Quality Improvement ProgramA Quality Improvement Program
Turning nursing home residents every 2 hours has been a long-held standard for pressure injury (PrI) prevention in individuals with mobility impairments although evidence to substantiate this practice is limited. New guidelines recommend personalizing turning schedules to support person-centered care but lack specific recommendations about which turning frequencies are appropriate for various risk levels. PURPOSE: This quality improvement program aimed to determine the feasibility and outcomes of using individualized turn schedules for newly admitted nursing home residents. METHODS: An expert panel of wound clinicians developed, tested, and implemented a turn frequency tool that allowed staff in 2 nursing homes to select a turning schedule of 1, 2, 3, or 4 hours based on resident risk factors. Turning schedules were operationalized using a wearable sensor-based visual cueing technology that alerted staff to resident repositioning needs. Nonparticipating resident data were collected for comparison of PrI incidence. Descriptive statistics were calculated for all covariates. Significance of differences tests were performed as … read more
A Review: Matrix Metallopeptidase-9 Nanoparticles Targeted for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetes foot ulcers are a leading cause of death in diabetic individuals. There are very few medicines and treatments that have received regulatory clearance for this indication, and numerous compounds from various pharmacological classes are now in various stages of clinical studies for diabetic foot ulcers treatment. Multiple risk factors contribute to diabetic foot ulcers, including neuropathy, peripheral artery disease, infection, gender, cigarette smoking, and age. The present difficulties in diabetic foot ulcers treatment are related to bacterial resistance to currently utilized antibiotics. Inhibition of the quorum sensing (QS) system and targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9 (MMP-9) are promising. This study focuses on the difficulties of existing treatment, current treatment technique, and novel pharmacological targets for diabetic foot ulcer. The electronic data base search diabetic for literature on foot ulcers treatment was carried out using Science Direct, PubMed, Google-Scholar, Springer Link, Scopus, and Wiley up to 2021. Becaplermin, a medication that targets MMP-9, glyceryl trinitrate, which inhibits the bacterial quorum sensing system, probiotic therapy, and nano technological solutions are just a few of the novel pharmaceuticals being developed for diabetic foot ulcers … read more
Study shows how management of serious diabetic foot ulcers was possible during the COVID-19 lockdown
New research being presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), held online this year (27 Sept-1 Oct), reveals how Belgium’s efforts to maintain a diabetic foot care program during the COVID-19 pandemic can offer valuable lessons to the rest of the world … “Thanks to the great efforts of diabetic foot clinics, continued availability of diabetic foot ulcer services during lockdown, although in a limited capacity, were really helpful, and may be the reason why we didn’t see late presentation and the impact on the severity of ulcers was limited to slightly larger wounds”, says lead author Dr. An-Sofie Vanherwegen from Sciensano … read more
WoundSource Upcoming Webinars

Presenter: Robert J. Klein, DPM, FACFAS, CWS; Catherine T. Milne, MSN, APRN, CWOCN-AP and Dot Weir, RN, CWON, CWS

Presenter: Naz Wahab, MD, FAAFP, FAWPCA

Presenter: Neesha Oozageer Gunowa MSc, PGCert, BSc, SPT, DN, RN, QN
Efficacy of Hydromechanical Therapy in Nonhealing, Chronic Wounds
as a Cost- and Clinically Effective Wound Care Modality
Chronic wounds pose a widespread challenge to health care, with many new, costly wound care modalities introduced in recent years with varying degrees of success. Bacterial biofilms have been postulated as one of the main culprits of the stagnation of chronic wound healing. For years, surgical fields have used pressurized irrigation for cleansing surgical wounds, but its utility in managing nonhealing chronic wounds has often been overlooked. Objective. In this case series, the authors aimed to demonstrate that hydromechanical therapy with pressurized irrigation can be a cost-effective and clinically effective wound care modality … read more
Trends in Wound Care Audits & Denials, with Dr. Caroline Fife and Dr. Helen Gelly
Last week I (Dr. Caroline Fife) enjoyed a relaxed, unscripted conversation with Dr. Helen Gelly about trends in wound care audits and charge denials, with a live audience Q&A. You can watch the recording of the conversation and Q&A below.
You can also find the audio of this event on Google Podcasts by searching for the Intellicure Wound Care Podcast.
Cold plasma ionised gas as new treatment for diabetic foot ulcers could also kill COVID-19 virus indoors
A new formulation developed by University of South Australia scientists to treat antimicrobial-resistant bacterial infections in diabetic foot ulcers could also be used to kill the COVID-19 virus circulating in air conditioning systems … Enhancing cold plasma ionized gas with peracetic acid eradicates bacteria in wounds and substantially reduces SARS-CoV-2 viral loads, Australian and UK scientists claim in a paper published in Applied Physics Letters … read more
The FDA’s Take on Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatments
This is fairly complex issue. There are many factors in responding to your question. Really, it’s multi-factor issue. Part of the challenge is that the regulatory agency, FDA, has a very clear, and at the same time, very narrow definition of wound healing. That is 100% wound closure with no drainage or no need for any dressing … read more
Embedding Predictive Analytics Into Your Wound Care Workflow Webinar
This webinar, presented by Matt Berezo, Joshua Budman, Abbey Cooper, and Cathy Thomas Hess will discuss how wound care-specific analytics can impact a practice’s workflow. Specifically, the presenters will discuss several clinical analytics models, how they are validated, and how clinicians can use them to improve their clinical and operational outcomes … register
Resolving Patient and Provider Concerns: Overcoming Another Year of Disruption
As 2021 comes to a close, it marks 2 full years that the US, Canada, and other parts of the world have endured the effects of COVID-19 on our personal and professional lives. The pandemic continues to force our hands in so many ways that were unimaginable just a short time ago and has had innumerable unforeseen consequences for patients and providers. In this issue, articles on provider- and patient-centered concerns speak to the social, psychological, and physical components that determine quality-of-life scores and impact activities of daily living … read more
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces thermal wound complications and length of stay in hospitals, study finds
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can reduce thermal wound complications, length of stay in hospitals due to thermal burns, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) mRNA gene expression, and ICAM-1 serum level, a case-control study published in Annals of Medicine and Surgery concludes.
“The damaging effects of thermal burns need to be managed holistically in order to create a suitable environment for wound healing,” study author Mendy Hatibie Oley (University Sam Ratulangi; R D Kandou Hospital; Hyperbaric Centre Siloam Hospital; all Manado, Indonesia) et al write … read more
