and Cavity Ulcers: A Preliminary Report
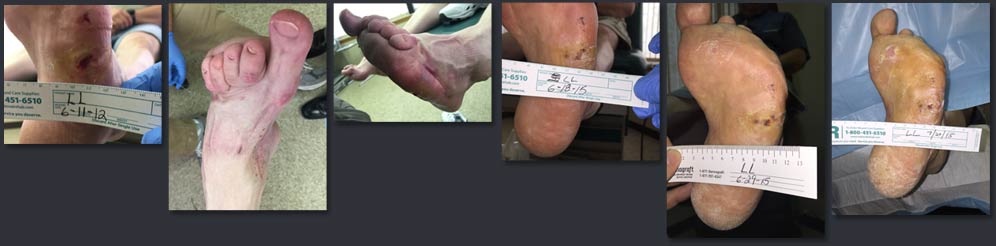
Abstract: Introduction. In chronic wounds the healing is stagnant, and regenerative surgery is often needed. Many engineered tissues with a conventional bidimensional sheet are ineffective for tunneling wounds, because adherence to the wound bed is not complete. An advanced wound matrix for treating wounds with irregular geometries has been developed (Integra Flowable Wound Matrix, Integra LifeScience Corp, Plainsboro, NJ).
Methods and Materials. Between March 2013 and December 2013 the authors treated 18 patients (11 female) with tunneled or cavity ulcers with the advanced wound matrix at the Unit of General and Geriatric Surgery of the Second University of Naples, Naples, Italy. Two patients (11.1%) had postsurgical wounds, two (11.1%) had post-traumatic wounds, and 14 (77.8%) had neuropathic ulcers. After debridement and antibiotic therapy, the lesions were filled with the wound matrix product. Surgical wound edges were either approximated with stitches or left to heal by secondary intention and covered with wet gauze. During the first week, follow-up visits were carried out every 3 days, then once a week until complete healing was achieved. All patients underwent preoperative and postoperative ultrasonography scans and plain radiograph controls. Results. Twenty-one applications were performed. Engraftment was complete in all but 1 patient who had diabetes and graft failure. Three patients needed repeated applications to complete the filling of the lesions. Median (range) pain Visual Analog Scores—on a scale of 0 to 10, where 0 = no pain, and 10 = intolerable pain—were 6.3 (range 3-8) preoperatively and 0.5 (range 0-2) at first follow-up (P ≤ 0.001). All but 2 patients showed a progressive remodeling of the tissue gap at scheduled radiographic controls. Conclusions. To the author’s knowledge, the advanced wound matrix used in this study is the only available biomaterial for the treatment of tunneled lesions. It stimulates tissue regeneration by filling surfaces which cannot be repaired spontaneously or by using conventional biomaterials in the form of sheets. Its application is atraumatic, painless, and safe … read more