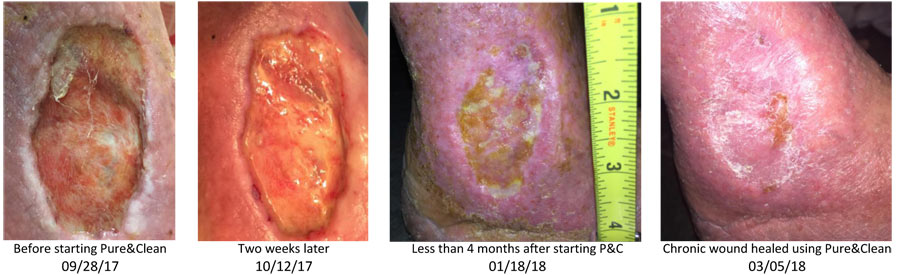
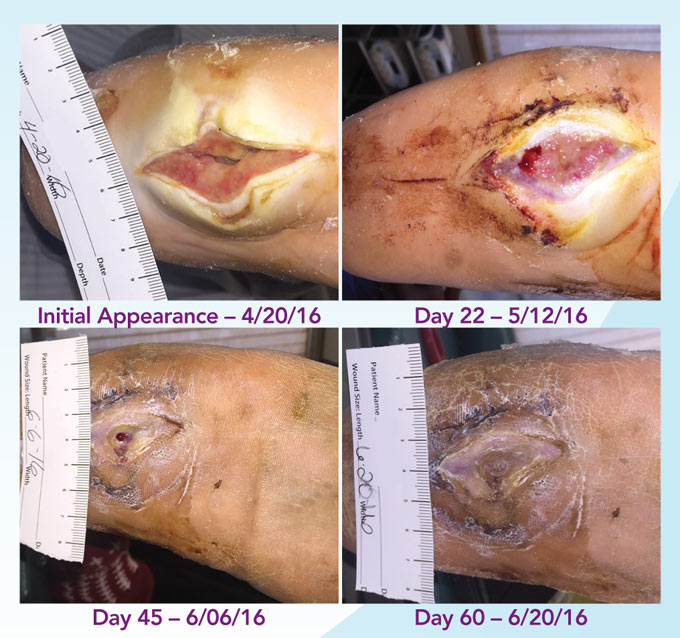
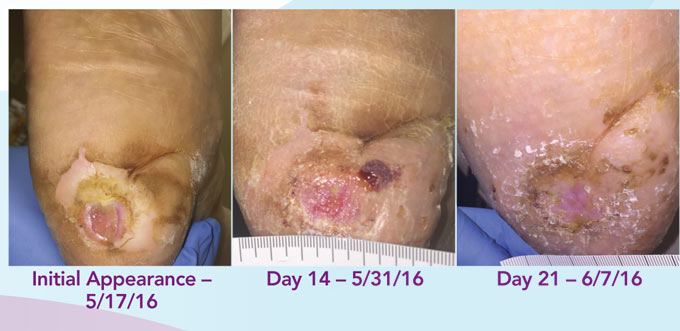
chronic wounds proven by gold-standard trial
Comparative clinical trial shows significant improvement in wound closure and infection control based on treatment with the plasmajet kINPen® MED from neoplas med compared to best practice wound care – cost-effectiveness analysis proves high cost-savings by innovative technology
GREIFSWALD, Germany and FELDKIRCH, Austria, March 22, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — The results of a randomized controlled trial (RTC) may offer new opportunities for the approximately two million patients with chronic wounds solely in Germany: The innovative cold atmospheric plasmajet (CAP-jet) technology showed significantly more healing progress in chronic wounds in comparison to best practice (BP) modern wound care at two study centers. Within six weeks, 59 percent of all wounds healed completely under cold plasma treatment compared to only 5.1 percent in patients under BP therapy. Time to complete healing was also considerably shorter under CAP-jet treatment, and wound infections were overcome statistically significant more rapid. With a very good tolerability profile, an economic analysis of the study data also showed a cost saving of 65 percent for the dressing material alone compared to the BP group. The study data were recently published in the journal Nature Scientific Reports.
Acceleration of wound healing and wound closure proven
In the study conducted by Prim. Univ.-Professor Robert Strohal, head of the Department of Dermatology and Venereology at the Federal Academic Teaching Hospital Feldkirch, the cold plasma procedure of the Greifswald-based company neoplas med GmbH was scientifically examined in wound care. For this purpose, he compared treatment with the CAP-jet kINPen® MED at the Austrian Federal Academic Teaching Hospitals Feldkirch and Bregenz with current best practice treatment in 78 patients with infected and non-infected wounds. ‘This study was the first to investigate the exclusive effect of tissue accessible cold plasma on wound healing and infection control without the use of an additional standard therapy,’ said Prim. Univ.-Prof. Strohal.
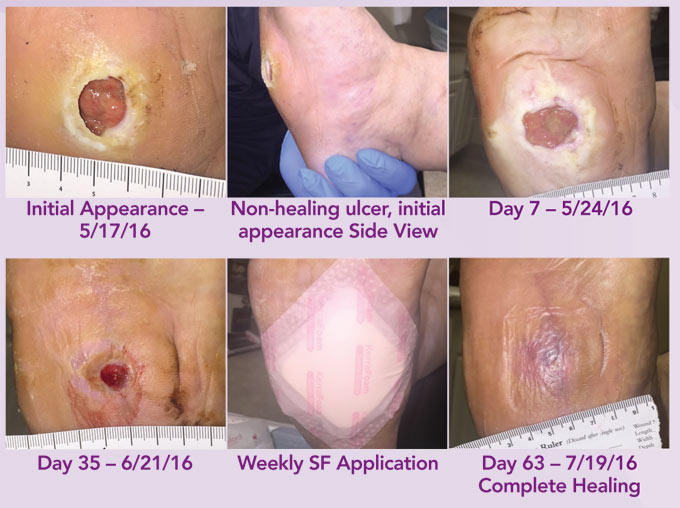
After treatment with the CAP-jet, the proportion of healthy tissue increased significantly faster than under the BP treatment and the wounds under CAP-jet therapy also healed significantly faster. At the end of the study, the wound area in the CAP group had reduced by 94.7 percent compared to the baseline value, in the comparison group it was only 56.3 percent. CAP also proved superior in terms of infection control. In contrast to BP therapy, all wounds infected at the start of the study showed complete resolution of infection signs. In addition, the signs of infection disappeared significantly faster under cold plasmajet therapy.
Patients’ quality of life can improve
Ulrike Sailer, CEO of the company neoplas med GmbH in Greifswald/Germany, explained: ‘The Joint Federal Committee (Gemeinsamer Bundesausschuss, G-BA) as the central decision-making body of the German health care system already recognized last year the potential of cold plasma for the innovative treatment of chronic wounds at our request. Therefore, the G-BA decided to carry out an observational trial for testing with the aim of obtaining health insurance approval. The results of the clinical trial that now have been published clearly demonstrate the superiority of the CAP-jet kINPen® MED compared to BP wound care. These results provide further evidence for the high clinical relevance of the CAP-jet precision technology. At the same time, it represents important news for millions of people who suffer from chronic wounds for years.’
Chronic wounds are often associated with high morbidity and considerable impairments in everyday life as well as the patients’ psyche. Faster wound healing and thus a shorter therapy duration by using the plasmajet kINPen® MED can therefore significantly improve the patients’ quality of life. Furthermore, a lower burden by pain during treatment can be observed, and a reduced number of dressing changes can be assumed. Patients confirmed the very good tolerability and even described the treatment as pleasant in the majority of cases.
Significant advantage in treatment costs
A cost-effectiveness analysis based on the available study data showed that 21.4 percent fewer physician visits and 34.3 percent fewer dressing changes were necessary in the CAP-jet group compared to BP. The savings alone in dressing material resulted in a cost advantage for CAP-jet therapy of 64.7 percent compared to BP. Previously, average costs of 10,000 € per patient and year were assumed. Ulrike Sailer: ‘Thus, the cold plasmajet kINPen® MED offers not only a more efficient and tolerable technology, but also opens up the opportunity for significantly higher cost-effectiveness in the treatment of chronic wounds.’
Further information material can be found under the following link: https://1drv.ms/u/s!Aph6cOwNbPEJgQCIbClSETCZ_lal?e=BvkuGi
Background Information:
The study included 78 patients with wounds up to 10 x 20 cm in size and existing for at least 6 weeks. The patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio into two groups and treated for the study duration of 6 weeks either with the CAP-jet kINPen® MED (30 seconds per cm2 wound area) or suitable wound dressings according to BP wound care. Only one wound per patient was evaluated.
With regard to the treatment regime, CAP-jet therapy was administered 3 times in the 1st week in the CAP group, 2 times in the 2nd week and once a week in the following observation period; furthermore, the wounds were covered with gauze and a secondary dressing. In contrast, the BP group was treated with a wound phase-adapted dressing; infected wounds were additionally cleaned with an antiseptic. In both groups, patients with venous ulcers received compression therapy. The primary endpoint of the study was the amount of granulation tissue at the end of the study. In addition, cold plasma effects on wound infection, wound area, healing time, wound pH and exudate volume (wound fluid) as well as local tolerability were investigated.
Improvement in wound infection: All 13 wounds infected at baseline in the CAP-jet group showed complete resolution of infection signs without the need for additional antiseptics. In contrast, 4 of the 18 wounds infected at baseline in the BP group showed no improvement despite the use of antiseptics. Furthermore, the signs of infection decreased significantly faster under CAP-jet therapy compared to BP therapy. These data confirm the previously published evidence on the good antimicrobial efficacy of CAP.
Cold plasma is a gas containing ionized atoms, ions and electrons that has been shown to disinfect wounds and activate the wound healing process. With its fine jet, the plasmajet kINPen® MED enables highly precise treatment in anatomically and pathologically challenging areas under visual control and without touching, which is not possible with other wound therapies.
About neoplas med GmbH
neoplas med GmbH was founded in 2009 as a spin-off of the Leibniz Institute for Plasma Science and Technology e. V. (INP) in Greifswald, Germany. Ulrike Sailer took over the position of managing director at the end of 2019. Based on the INP research into plasma medicine, the emerging company develops innovative products for medical applications. The first product developed on this basis is the CE-marked kINPen® MED atmospheric pressure plasmajet, the first internationally approved and marketed plasmajet for the treatment of chronic wounds and pathogen-induced skin disorders. It is the result of a long-lasting cooperation with the INP institute, the university hospital of Greifswald, Germany, the Charité hospital of Berlin, Germany, and various industrial partners. In July 2021, the Federal Joint Committee, as the central decision-making body in the self-governing health care system, decided on a trial study with the cold plasmajet procedure and thus took an important step towards reimbursement by the health insurance companies.
About kINPen® MED
The plasmajet kINPen® MED is the first atmospheric pressure plasmajet to receive CE approval for the treatment of chronic wounds and pathogen-induced skin disorders. The plasmajet applies a physical cold plasma with a temperature of < 40 degrees Celsius with pinpoint precision and without wound contact. Areas with an uneven profile, recesses or cavities can be reached easily and treated evenly. The noble gas argon used for the generation of the plasma provides a controlled atmosphere around the generated plasma beam, thus ensuring a consistent high treatment quality.
Press contact
Claudia Kerber
Phone: +49 3834 515 201
Mobile: +49 (0)162 23 770 70
claudia.kerber@neoplas-med.eu
neoplas med GmbH
Walther-Rathenau-Straße 49a, 17489 Greifswald, Germany