Nitric oxide (NO) is a highly active gaseous signaling molecule that is synthesized by NO synthases and mediates many physiological processes, from vasodilation to signal transmission in neurons. In addition, NO has a bactericidal effect, the ability to activate cellular and humoral immunity, induces the proliferation and synthetic activity of fibroblasts, activates the proliferation of keratinocytes and the antioxidant system. The variety of these effects provides NO comprehensive effect in various stages of wound healing and accelerates regeneration. Currently, there are three distinct ways for increasing the concentration of NO in wound tissues: the application of inductors of NO synthesis, NO-containing gas flows, and donor molecules. Using NO donors is one of the most promising and actively developing areas because of the large variety of donor chemical compounds … read more
Category: Articles
Letter to Noridian: Wound and Ulcer Care LCD/LCA
The Alliance submitted a letter requesting that Noridian revise it Wound and Ulcer Care LCD (L38904) and LCA (A58567) to ensure that that CPT and HCPCS code descriptors are correct and to update incorrect/outdated terminology within the policy. The Alliance submitted a detailed list of suggested revisions … read more (available to Alliance members only)
Old and New Pearls for Wound Healing
This old pearl is as pertinent as ever, Kirsner said. While there are many available products on the market for wound healing, dermatologists need to use evidence-based therapies, especially when considering which of the more than 80 cell- and tissue-based products would benefit the individual patient most. Examples of those products with evidence include bi-layered cellular products … read more
Pressure Injuries (Pressure Ulcers) and Wound Care
Although the terms decubitus ulcer, pressure sore, and pressure ulcer have often been used interchangeably, the National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel (NPIAP; formerly the National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel [NPUAP]) currently considers pressure injury the best term to use, given that open ulceration does not always occur. [1] According to the NPIAP, a pressure injury is localized damage to the skin and underlying soft tissue, usually over a bony prominence or related to a medical or other device. It can present as intact skin or an open ulcer and may be painful. It occurs as a result of intense or prolonged pressure or pressure in combination with shear … read more
Effects of physical activity as an adjunct treatment on healing outcomes and
recurrence of venous leg ulcers: A scoping review
Healing time is protracted and ulcer recurrence is common in patients with venous leg ulcers. Although compression is the mainstay treatment, many patients do not heal timely. Physical activity may be a clinically effective adjunct treatment to compression to improve healing outcomes. This scoping review provides a broad overview of the effect of physical activity as an adjunct treatment to compression on wound healing and recurrence. We followed the six-step framework developed by Arksey and O’Malley. We searched electronic databases and trial registration websites for relevant studies and ongoing trials. Two authors independently screened and selected articles. Findings were presented in a descriptive statistical narrative summary. We consulted and presented our findings to the wound consumer group to ensure the relevance of our study. Physical activity interventions in 12 out of the 16 eligible studies consisted of only one component, eight studies were resistance exercises … read more
Using Augmented Reality to Improve Patient Outcomes With Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Digital technology is already immensely integrated within health care, but new innovations in this space could result in unconventional opportunities to improve patient outcomes. Augmented reality (AR), which is the enhancement of reality by virtual content, is one such innovation.1 Augmented reality has many uses in health care, such as education, remote viewing, and hands-free imaging and/or data retrieval.2 The AR device uses a heads-up display, which allows for information to be relayed and displayed in real time to the wearer via an Internet-connected device. The integrated cameras in the device enable the wearer to virtually livestream their point of view. The use of AR to virtually assess wounds has been found to have promising reliability … read more
Antimicrobial Stewardship In Wound Care
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is now one of the leading causes of death around the world. The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared that AMR is one of the top 10 global public health threats facing humanity. The inappropriate use of antimicrobial drugs contributes to AMR and adverse events, and improving antimicrobial prescribing practices is a patient safety priority.[5] In 2013, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimated that at least 2 million illnesses and 23,000 deaths per year were caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the United States. A more recent study estimated that in 2019, 44,800 deaths were directly caused by AMR and 186,000 deaths were associated with AMR in North America … By default, chronic wounds are contaminated by several types of bacteria. When the host (patient) does not adequately respond to bacterial contamination, this contamination can turn into colonization, which can further turn into infection. Wound infections are often caused by bacteria that are becoming increasingly resistant to common antibiotics due to antibiotics misuse and/or overuse.[2][3] It is thus imperative that antibiotic prescribing practices evolve such that antibiotics are prescribed only when they are essential … read more
Practice Management Education Opportunities February 23, Austin, TX
Take the first few steps to coding and billing by joining us for a comprehensive workshop covering the fundamentals of coding and billing for foot and ankle surgeons. Learn the foundation of the coding and billing process from expert colleagues before taking the ACFAS Coding and Billing for the Foot and Ankle Surgeon course. This course is for residents, fellows, new practitioners, office staff of foot and ankle surgeons or anyone who wants to learn more of the basic coding and billing terminology and process. Plus, if you’re a resident and attending Residents Day in the morning the day of the event, this course is a great next step to learning more about coding and billing for your future practice and can be bundled in your pricing … read more
What Do Medical Records Reveal About the Effectiveness of Care for Diabetic Foot Health?
Medical records are frequently the source of clinical data used in research of the diabetic foot. However, due to variations in the records, problems can result in collecting and using the data for such research … Worldwide, there are vast differences in the type of medical record, the quality of the medical record and how providers and or health systems manage the data it contains. Medical records can range from simple, handwritten notes that often include some short cuts or abbreviations, to sophisticated electronic health records. The issues of who collects the data and how it is documented will ultimately influence how it can be harvested, manipulated, and used in research … read more
The use of medical grade honey to achieve healing in an older patient with chronic wounds and
complex co-morbidities: a case report
Aging is associated with an increased likelihood of co-morbidity and other factors that are known to delay wound healing (Gosain and DiPetro, 2004; Bonifant and Holloway, 2019). Additionally, aging itself is a risk factor for chronicity as a consequence of changes in the epidermis and dermis. The dermo-epidermal junction becomes flattened, and elasticity of the skin reduces due to morphological changes in collagen and elastin, which predispose the tissue to shear and friction forces (Gosain and DiPetro, 2004; Bonifant and Holloway, 2019). Moreover, the microcirculation and lymphatic drainage of the dermis is decreased with age, and this affects its ability to adapt to injury and clear the wound of pathogens thus inhibiting wound contraction (Gosain and DiPetro, 2004). Older patients, frequently described in the literature as aged 65 years or above, often have multiple comorbidities, such as poor circulation, poor nutritional and hydration status, and the presence of diseases such as diabetes that affect general health (Leung et al, 2018; Wilkinson and Hardman, 2020). These comorbidities can negatively influence the wound healing trajectory, making vigilance during wound management … read more
Changing wound care through data
By reporting MIPS through the US Wound & Podiatry Registries, you provide data that builds predictive wound healing models that improve patient outcomes … read more
UrgoClean Ag in Real Life
In 2019, the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) reported that over 77 million individuals have diabetes in India, which will increase to over 100 million by 2030 (IDF, 2019). Of these people with diabetes, 25% will develop a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU), equating to 5 million by 2030. Overall, half of ulcers become infected during the healing process, necessitating hospitalisation, while 20% of these patients require amputation. DFUs contribute to approximately 80% of all non-traumatic amputations performed annually in India (Ghosh and Valia, 2017). It is indicated that social epidemiology regarding DFU in India differs from the West due to many factors including socio-economic and cultural factors. This can lead to significant delay in specialist referral, with patients still relying on treatment based on local ethnic methods and not based on scientific data. This results in patients presenting with highly infected ulcers (Rastogi and Bhansali, 2016) … read more
‘No difference’ between endovascular, open vascular surgeries for diabetic foot ulcers
Adults with diabetic foot ulcers and peripheral artery disease who receive revascularization surgery are at no greater risk for amputation or death following endovascular surgery compared with open vascular surgery, according to findings published in the Journal of Diabetes and its Complications … “The present large cohort study showed in a propensity score-adjusted analysis that there was no difference in amputation-free survival in patients with diabetic foot ulcers and peripheral arterial disease regardless of whether endovascular or open vascular surgery was chosen as first-line vascular intervention,” Talha Butt, MD, of the department of cardiothoracic and vascular surgery at Skåne University Hospital in Sweden … read more
Diabetic foot ulcers associated with mortality, hospitalization for chronic conditions
Diabetic foot ulcer episodes were associated with all-cause mortality and all-cause inpatient hospital admissions, according to new results published in Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice … “The impact of diabetic foot ulcers has been historically difficult to quantify, but our study shows that these foot wounds are associated with higher rates of all-cause hospitalization and all-cause mortality,” Brian J. Peterson, co-founder and chief scientist at Podimetrics, told Healio. “In our research, we found that during episodes-of-care for diabetic foot ulcers, individuals are 50% more likely to die and nearly three times more likely to be hospitalized.” … read more
Guard Medical Announces FDA 510k Clearance for Additional Sizes of Its Novel NPseal
the First All-in-One NPWT Surgical Dressing
Privately-held company Guard Medical Inc. today announces FDA 510k clearance for additional sizes (10 and 15cm) of its next generation Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) dressing NPsealTM for the treatment of closed surgical incisions. NPsealTM is an easy-to-use and cost-effective NPWT surgical dressing with an integrated pump that establishes and maintains negative pressure with just a few pinches … “We’re excited to expand our NPsealTM portfolio, now with the 5, 10 and 15 cm sizes. NPsealTM can now be used on a large percentage of closed surgical incisions across multiple specialties. Receiving FDA clearance for the larger sizes is another significant milestone towards becoming the NPWT dressing of choice for the treatment of surgical incisions,” stated Machiel van der Leest, CEO of Guard Medical. “NPsealTM ease-of-use and cost effectiveness makes, for the first time, prophylactic use of NPWT for all eligible closed surgical incisions possible.” …
… read more

Can seaweed heal wounds without scarring? | The Royal Society
Join Dr. Nowsheen Goonoo to discover how seaweed can be turned into affordable dressings for fast and scarless wound healing, especially for diabetic foot ulcers
Guidelines Highlight Role of Nutrition in Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
New guidelines recommend healthcare providers develop and implement an individualized nutrition care plan for individuals with diabetes with or at risk of a DFU
New guidelines endorsed by the American Limb Preservation Society highlighted the importance of nutrition in wound healing for adults with diabetes, who also experience diabetic foot ulcers (DFU).
The guidelines stated that nutritional interventions were “recommended for all patients who could benefit now or in the future from nutritional care.” As such, healthcare providers should develop and implement an individualized nutrition care plan for individuals with or at risk of a DFU, who are additionally malnourished or at risk of malnutrition … read more
Amnio Technology Launches Two New Dual-Layer Allografts
FDA Recognizes Products as Minimally Manipulated, Homologous Use HCT/Ps
Amnio Technology, a global leader in the development of and distribution of amniotic tissue allografts is announcing the launch of two new PalinGen® membrane products, PalinGen® Dual-Layer Membrane and Dual Layer PalinGen® X-Membrane. The new allografts, like the entire family of PalinGen® membrane products, are minimally manipulated, homologous use and chorion-free. The dual-layered nature of the allografts allow for unidirectional application with two outward facing epithelial sides. The proprietary Advantek® process used to manufacture PalinGen® membranes preserves the extracellular matrix components and regulatory proteins present in amniotic tissues. Preserving the characteristics of the natural tissue aids in wound management.
PalinGen® Dual-Layer Membrane and Dual Layer PalinGen® X-Membrane are indicated for patients suffering from non-healing acute and chronic wounds as well as complex and/or open surgical wounds and burns.
Senior Director of New Product Development, Robert Diller, PhD, shared his insight into the motivation for developing a multilayered amniotic product, “The PalinGen® Dual layer membranes have increased durability and slower resorption, which makes them ideal for use in robotic and other surgical applications” … read more
South Korea approves Cuban medicine
In a rare breakthrough into a developed market, the South Korean pharmaceutical regulatory agency approved a Cuban medicine, Cuba’s Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (CIGB) announced in a tweet.
No further context was immediately available.
According to the CIGB tweet, South Korea’s Ministry of Food and Drug Safety approved Heberprot-P, a biotech product that treats diabetic foot ulcers, for use with Korean patients.
Recombinant human epidermal growth factor-based Heberprot, which was first approved in Cuba in 2006, has been registered in Vietnam, Malaysia, Turkey, Argentina, Colombia, Kuwait, Ukraine, and Russia, among others. An agreement with a U.S. company in 2016 to bring Heberprot-P to clinical testing in the United States seems to have faded … read more
Diabetic Neuropathy, Avoiding Amputation, and Foodie – Blog
Dr. Tea Nguyen podiatrist specializes in diabetic wound care, why educates against the webMD diagnosis, her honest and forward speech to patients, fat relocation advances for surgical outcomes, and shares her martial and daily staff tips and foodie.
Dr. Tea Nguyen is Fellowship trained in wound care particularly with diabetics.
Big reason why diabetics have the wounds that can require amputation is because of peripheral neuropathy and losing the pain sensitivity. One of the problem is a patient doesn’t know a cut may have happened and can’t see it because of back pain or poor vision and therefore they get systemic symptoms or a bad smell before they know something is wrong … listen more
A tool to promote patient and informal carer involvement for shared wound care
Shared wound care encompasses approaches and interventions that enable patients to participate in care planning and delivery, rather than just being a passive recipient of services provided. A key step in facilitating greater shared care is identifying the individuals (patients and informal carers) who would be good candidates to be involved in shared wound care. An international survey was conducted to help identify the characteristics that may indicate an individual’s suitability to participate in shared wound care. The results of which informed the development of a guide that clinicians can use to direct discussion to better understand patient and informal carer suitability for shared wound care and identify the approaches and interventions that may be suited to the patient and informal carer’s needs … read more
5 Wound Care Myths Still in Practice Today
Since WCA was founded 20 years ago, our industry has made great strides and advancements in both technology and method. Unfortunately these changes aren’t always well-known, allowing for less effective and sometimes even harmful practices to continue.
In this blog we’ll cover 5 common myths we still see in wound care treatment and how you can avoid them … read more
Factors associated with adherence to using removable cast walker treatment among patients with …
diabetes-related foot ulcers
Adherence to using knee-high offloading treatment is critical for healing diabetes-related foot ulcers (DFUs). However, few studies have investigated patients’ adherence to using knee-high offloading treatment. We aimed to investigate the levels and factors associated with adherence to using knee-high removable cast walker (RCW) treatment among patients with DFUs … read more
Comparing the standard surgical dressing with dehydrated amnion and platelet-derived …
growth factor dressings in the healing rate of diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized clinical trial
In patients having diabetic foot ulcers, a better-improved healing results from dehydrated amnion dressing than platelet-derived growth factor dressing and surgical debridement … This is a multi-arm parallel-group randomized trial including 243 patients with a minimum 4-week medical history of diabetic foot ulcers with Wagner’s grades 1 and 2, no infection, and adequate tissue blood flow … They were randomized to one of three 81-person groups: surgical debridement (the standard method), dehydrated amnion dressing, or platelet-derived growth factor dressing; and were followed up for 12 weeks … Regarding the type of ulcer, the area of ulcer, Wagner’s grade, the period, and the ulcer’s size, all three study groups were comparable … read more
LA Times Today: In South L.A., a legacy of limbs lost to diabetes tells a larger story
It’s devastating for any hospital patient to hear these words from a doctor: “Sorry, we’ll have to amputate.”
But in one Los Angeles neighborhood it’s a diagnosis that’s become overwhelmingly too common.
L.A. Times projects reporter, Joe Mozingo joined us with more.
And one important note — this story contains photos of amputated limbs.
… watch interview of reporter Joe Mozingo
Animal experimental models of ischemic wounds – A review of literature
Critical limb ischemia is a serious form of peripheral arterial disease (PAD). The consequences of lower limb ischemia are pain, claudication and chronic non-healing wounds. Patients with diabetes are especially at a high risk for developing non-healing ulcers. The most serious complication is major amputation. For this reason, there is a significant medical requirement to develop new therapies in order to prevent the progression of PAD. For research purposes, it is crucial to find an appropriate model of chronic ischemia to explore the processes of wound healing. According to recently acquired information, rodents are currently the most commonly used animals in these types of studies. The main advantage of using small animals is the low financial cost due … read more
TissueTech Announces Rebranding, Adopts BioTissue Name Across Entire Business
TissueTech, Inc.—a pioneer in the clinical application of cryopreserved human birth tissue products to treat ocular surface disease and disorders, chronic wounds, and musculoskeletal conditions—has unveiled a corporate rebranding, including a name change and a new logo. BioTissue, Inc. and Amniox Medical, Inc. will now both be known under a single commercial, customer facing entity, BioTissue, Inc. … With three decades of continual advancements in regenerative medicine, BioTissue has been a clear leader in the ocular space. By adopting the BioTissue name across the entire organization, the company will also reflect that innovative heritage and promise in its surgical business, which was previously known as Amniox Medical … “For years, health care professionals have known our products—regardless of their specific applications—for providing mother nature’s most natural gift of healing so their patients can get back to the lives they love,” said Ted Davis, president and CEO, BioTissue. “Our new, unified brand supports our entire pipeline of human birth tissue products to aid the treatment of wounds, musculoskeletal conditions, trauma-induced injuries, ocular surface disease, and burns.” … read more
Complex multilevel and multivessel endovascular revascularization through an occluded
femoral-popliteal bypass in a patient with chronic limb threatening ischemia
Chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI) represents the end stage of peripheral artery disease, a problem of growing prevalence and increased health care costs around the globe. CLTI is a highly morbid disease, incurring significant mortality, limb loss, pain, and diminished health-related quality of life. The major cause of non-traumatic lower extremity amputation are related to diabetes and CLTI. Between 2% to 3% of patients with peripheral artery disease present with a severe case of CLTI, a condition that is correlated with multilevel and multivessel arterial disease, calcification, and chronic total occlusions. Multiple technical strategies to successfully cross long occlusions in arterial segments have been described. Recanalization can be performed using endoluminal, subintimal, and retrograde techniques … read more
First Patients Enrolled in Prospective Randomized Multi-Center Comparative Clinical Study Evaluating Restrata®
for the Treatment of Venous Leg Ulcers
Acera Surgical, Inc. (Acera), a leading bioscience company developing and commercializing a portfolio of fully synthetic materials for regenerative medical applications, today announced its first patient enrollment in a multicenter, head-to-head clinical study evaluating Restrata® for the treatment of non-healing venous leg ulcers (VLUs). William Marston, M.D., the George Johnson Jr. Distinguished Professor of Vascular Surgery at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine is the study’s lead investigator. The study will be the first level 1 clinical comparison between Restrata and a biologic skin substitute.
Venous leg ulcers (VLUs) are a chronic ulcer type which affect 3% of the world population, including over 2 million people annually in the US.1,2 VLUs are a major cause of morbidity and poor quality of life resulting from venous insufficiency in the lower limbs. This type of wound presents clinical challenges as VLUs may require many months of treatment before healing is achieved.3 The US economic burden of VLU treatment was close to $15 billion in 2014 … read more
New Diabetic Foot Ulcer Guidelines Highlight Importance Of Nutrition
New guidelines endorsed by the American Limb Preservation Society highlighted the importance of nutrition in wound healing for adults with diabetes, who also experience diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) … The guidelines stated that nutritional interventions were “recommended for all patients who could benefit now or in the future from nutritional care.” As such, healthcare providers should develop and implement an individualized nutrition care plan for individuals with or at risk of a DFU, who are additionally malnourished or at risk of malnutrition … read more
New guidance highlights the importance of nutrition to support people living with diabetes and foot ulcers
A multidisciplinary team of medical professionals developed guidance for healthcare professionals outlining the importance of nutrition therapy to support wound healing for foot ulcers … The guidance provides expert consensus regarding how nutrition from arginine, glutamine, hydroxymethylbutyrate (HMB), and micronutrients can help improve wound-care therapy for people living with diabetes who are more likely to develop foot ulcers … read more
Implementing a Virtual Assistant in Podiatric Practice | podcast
Incision care and dressing selection in surgical incisions wounds
Findings from an international meeting of surgeons from Northern Europe
Post-surgical incision care must be optimised, particularly in terms of reducing the risk of infection and associated complications (Sandy-Hodgetts et al, 2017; 2018; Morgan-Jones et al, 2019). An international consensus meeting was conducted in 2019 to examine post-surgical care and dressing selection for surgical incisions closed with primary intention (Morgan-Jones et al, 2019). A group of surgeons from Germany, Denmark, Finland and Norway convened online to discuss the findings raised in the 2019 international report and how they fit with local practice with the following aims … read more
Latest APMA Health Policy and Advocacy Wins
APMA works tirelessly to advocate for the podiatric medical profession. Over the past year, APMA has been successful in ensuring podiatrists receive equitable reimbursement, and patients have full access to care provided by podiatrists. Recent successes include:
HealthNet Federal Services (HNFS), the TRICARE administrator for the West Region, agreed to APMA’s previous request, and now permits podiatrists to order non-invasive vascular or arterial studies for TRICARE beneficiaries … read more
Evidence-Based Care in Diabetic Foot Ulcers | Video
My name is Alton Johnson. I’m a DPM, (and a) certified wound specialist as well. Currently, a clinical assistant, professor, podiatrist, pediatric surgeon, wound care specialist at the University of Michigan Hospital System – Michigan Medicine, currently working as a podiatrist and wound care specialist.
By the statement, “Not all DFUs are created equally,” (this) simply means that no one wound is ever the same when it comes to diabetic foot ulcerations. That could be applicable to all ulcerations but in general, you don’t know … watch
Practice Alert New ICD-10 Codes for MASD
In response to an initiative spearheaded by the Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nurses Society (WOCN), new diagnosis codes moisture-associated skin damage (MASD) were added to the current version of the International Classification of Disease, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM). These codes arc used globally to identify diseases and health conditions of patients in the United States. They are also linked to third-party payment for health care and related supplies … read more
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on patients with hidradenitis suppurativa
Compared to prior to the pandemic, fewer patients consulted their primary physician for changing wound dressings and more changed the dressings themselves or were assisted by their family members. 13% of patients avoided doctor visits due to fear of COVID-19 and 26.1% minimised doctor visits … The Dermatology Life Quality Index showed a moderate to very severe impact on patients’ Quality of Life (mean score = 10.06). Only one patient used telemedicine. Due to limited access to primary care and fear of COVID-19, the pandemic had a detectable impact on the hospital management of patients with HS in our facility. Telemedicine still plays a negligible role in primary wound care … read more
Watch this mama chimp treat her son’s open wound by applying insect “poultice”
In November 2019, Alessandra Mascaro was observing a community of chimpanzees in the Loango National Park in Gabon as part of her volunteer service with the Ozouga Chimpanzee Project when she noticed some unusual behavior. A chimp named Suzee was inspecting a wound on the foot of her son, Sia. Suzee suddenly caught an insect from a nearby leaf, put it into her mouth for a moment, and then pressed it to Sia’s wound.
Mascaro caught the unusual interaction on video and forwarded it to two scientists on the project: Tobias Deschner, a primatologist with the Ozouga Chimpanzee Project, and Simone Pika, a cognitive biologist at Osnabrück University. The researchers thought the interaction could be suggestive of prosocial behavior among chimpanzees and the capacity for empathy—a question of heated debate in the field—and they spent the next 15 months looking for other examples of this type of wound-treating behavior … read more
Custom-made footwear designed for indoor use increases short-term and long-term adherence
in people with diabetes at high ulcer risk
To explore changes in footwear adherence following provision of custom-made indoor footwear in people with diabetes at high risk for plantar foot ulceration and in possession of regular custom-made footwear … Adherence indoors and outdoors was assessed objectively as percentage of steps custom-made footwear was worn, at baseline (in regular custom-made footwear), and at 1 and 12 months after providing custom-made indoor footwear (in both indoor and regular footwear). Primary group: participants with low (<80%) baseline indoor adherence; secondary group: participants with high (≥80%) baseline indoor adherence. Peak plantar pressures of the indoor footwear were compared with … read more
A new look For WOCN’s Continuing Education Center (CEC)
We (WOCN) are excited to introduce our new and improved look and feel to the WOCN® Continuing Education Center (CEC). With this new look also comes some exciting additions to the site and resources for users, including:
- New tutorial videos outlining new features of the site and how to utilize the “My Account” functions once logged into the CEC
- More user-friendly ways to navigate the CEC:
- The ability to easily search for content by topics of interest
- The ability to easily search for content by content “tags”
- A refreshed, clean look to match WOCN branding
Check out the tutorial videos below to learn more about the new CEC!
… read more
Multiple factors predict longer and shorter time-to-ulcer-free in people with diabetes-related foot ulcers
Survival analyses of a large prospective cohort followed-up for 24-months
Researchers aimed at determining the factors that are independently linked with time-to-(being)-ulcer-free, time-varying effects and predict adjusted ulcer-free probabilities, in a large prospective cohort with diabetes-related foot ulcers (DFU) followed-up for 24 months … read more
Wound Care Specialization for the Advanced Practice Clinician
Nursing is a unique and varied field often described as a union between art and science. Nursing appeals to many individuals as a first or second career, and these people see the profession through different lenses. When questioned about why they want to enter the field, many students respond that they “want to help others,” “give back to society,” or “find meaning in my work.”
Many of us can recall our transition from student to entry-level nurse, whether we started on the specialized unit of our dreams or were “strongly” encouraged to start in a general setting. There comes the day when we realize that we have begun to master a clinical knowledge set we once thought impossible. If you are at this crossroads in your career … read more
CALL FOR WOUND, OSTOMY, AND CONTINENCE-RELATED PHOTOS
It is a goal of the Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nurses SocietyTM (WOCN®) to continuously improve the educational content of the Wound Treatment Associate (WTA®) and Ostomy Care Associate (OCA®) Programs as well as the resources available to all WOCN members. Additionally, it is a goal of WOCN to work at continuous improvement in the areas of diversity, equity, and inclusion. As such, we’d like to extend an invitation to our WOC nurse colleagues to submit photographs of wounds and ostomies, specifically representing individuals of diverse skin tone. We would also invite you to submit photos related to continence-related issues, also in diverse skin tones. A wide variety of photograph examples serve to improve the education of our members and other healthcare providers by ensuring competency in wound, ostomy, and continence (WOC) assessment for all individuals. In this way, the care of all individuals with wound, ostomy, and continence care needs can be improved … read more
Frank & Lizzie Show: Episode 011, Wound Week 2022
Frank & Lizzie are excited to see you in Philadelphia for The American Professional Wound Care Association’s (APWCA) annual conference, Wound Week 2022 at the Loews Hotel February 24-27, 2022. Frank and Lizzie shared their excitement for this advanced wound care conference with THE experts from all disciplines.
Growing Evidence That Oral Antibiotics are the New IV
A recent systematic review in the American Journal of Medicine aims to challenge the dogma surrounding antibiotic therapy for certain types of infections, including osteomyelitis.1 This constitutes superb work from Wald-Dickler and coworkers, adding to the growing body of evidence that (to coin a phrase from senior author Brad Spellberg, MD) shorter may be better and oral greater than IV … Researchers set out to evaluate if current data supports long-standing tenets regarding the superiority of IV antibiotics for the full treatment course for osteomyelitis, bacteremia and infective endocarditis. Their review included 7 randomized controlled trials regarding osteomyelitis, specifically. None of the 21 total studies among all examined infections demonstrated superiority of IV-only antibiotic treatment … read more
Early Identification of Deep-Tissue Pressure Injury Using Long-Wave Infrared Thermography
A Blinded Prospective Cohort Study
The current clinical standard for diagnosing deep-tissue pressure injury (DTPI) is visual inspection. This method is subjective and only presents to the observer the external “picture;” deeper tissues are disguised from the observer. In contrast, long-wave infrared thermography (LWIT) can capture an image of the area of concern and detect tissue temperature relative to the level of tissue perfusion … To determine the efficacy of a handheld LWIT device and software solution as an adjunct to the current clinical standard of visual skin assessment to detect nonvisual pathophysiologic changes of DTPI … read more
A Case Study of Chronic Wound Management
Mr. King presented with 3 wounds located on the medial and lateral aspects of both ankles. Each wound was present for more than 3 years. In that time, he had been seen by 14 wound care physicians and another 8 podiatric and surgical specialists, in the outpatient setting. His care also included home health nursing visits for over 2 years, most commonly with daily dressing changes ordered by the many physicians trying to treat him … At 77 years old, he has many comorbidities that can impair wound healing such as; PAD, PVD, IDDM II, HDL, CKD II, HTN, Varicose Veins and uncontrolled chronic pitting edema. As a result of his wounds not healing, he was no stranger to receiving poor prognoses on the outcomes and resolution of his wounds. Because of poor choices in treatments and a lack of holistic care, more often, his wounds would get worse not better and in some cases Mr. King was told, “there’s nothing I can do, your wounds are not going to heal,” or “you’re going to lose your legs.” Most of the physicians he saw wanted to do some type of surgery or skin grafts. But Mr. King had known too many people that went in for a surgery on the leg or foot, trying to heal a wound, and ended up with an amputation … read more
Nutrition Interventions in Adults with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) are chronic wounds in the foot or feet associated with neuropathy and/or peripheral artery disease (PAD) of the lower limb in patients with diabetes mellitus. Reports from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that in the United States there are nearly one in four adults living with diabetes, which indicates that a large number of Americans are at risk of DFU. DFUs will develop in up to 34% of patients with diabetes at some time in in their lives, and of those, approximately 15%–25% will require an amputation. Moderate or severe malnutrition has been identified in over half of patients with DFU, and malnutrition in DFU is correlated with increased lower-extremity amputation. Improvements in wound care therapy, including nutrition interventions, can reduce the financial burden of DFUs and increase life expectancy and quality of life … read more
To Conquer or Be Defeated: The Strategy Behind Winning the Wound Infection Battle | webinar
Wound infection has a significant impact on wound healing potential. When managing a wound, the first step is to determine if you are looking at an acute or chronic wound infection. Acute wound infection can be devastating and is often an underappreciated clinical condition that has been reported to increase the cost of care by up to 70%. Chronic wound infections are microbiologically, immunologically, and clinically distinct from acute wound infections and require a different treatment strategy … register
The significance of surface pH in chronic wounds
Wound healing is a complex, multifaceted process which is influenced by both intrinsic and extrinsic factors. The pH of the wound can affect many factors including oxygen release, angiogenesis, protease activity, and bacterial toxicity. Chronic non-healing wounds have an elevated alkaline environment. Healing occurs more readily in an acid environment. Current wound bed assessment is dependent on subjective evaluation with few diagnostic instruments available or suited to routine practice. Monitoring surface pH may provide a method of ‘measuring’ the condition of the wound bed and ultimately aid in determining the wound’s response to treatment … read more
Automating wound care in hospitals
Chronic wounds are a global medical problem closely linked to diabetes. Every year, two per cent of the US population suffers chronic wounds, many resulting in amputation because they do not heal naturally and are typically infected with antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Consequently, conventional treatment methods such as antibiotics are often not an option. However, start-up VulCur Medtech has now developed an automated laser solution writes the Technical University of Denmark in this press release … While competitors are focusing on surface treatment, VulCur MedTech’s treatment goes deeper, cleaning the wounds from the inside out using an automated laser device that kills bacteria while avoiding human cells … read more
The Wound Care Evidence Summit™
The Summit will provide a critically needed multi-disciplinary meeting for payers, government agency policymakers, prominent researchers, wound care medical specialty societies, patient and clinical associations, wound care clinics and manufacturers to address the shared goals of:
- Addressing the current state of wound care research and clinical trial design
- Exploring solutions to address the limitations in the wound care evidence-base
- Communicating with payer medical directors on the development of coverage policies and the use of clinical practice guidelines in coverage decisionmaking
- Defining “next steps” to actualize solutions
- Participating in a uniquely intimate gathering of leading decisionmakers
… register
Bio Plaster Produced from the 3D Printer Aboard the International Space Station
The long-term goal of the experiment is to cover skin wounds with bio-ink from a 3D printer like a band-aid … The new technology should help to significantly improve wound care on space missions, but also in daily medical use on Earth … Human cells from the 3D printer, with which skin wounds can be covered like an adhesive plaster – that is the long-term goal of the Bioprint FirstAid experiment. As part of the mission “Cosmic Kiss”, the German ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer has now carried out the test series on the International Space Station. The mobile hand-held device is intended to significantly improve wound care … read more
Obesity, Diabetes and Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients With Class 3 Obesity
In individuals with class 3 obesity, obesity itself may be as strong as prediabetes or type 2 diabetes (T2D) in driving the risk of peripheral neuropathy (PN), a study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism suggests.
The study analyzed plasma global metabolomics and targeted lipidomics in participants with obesity who either had PN (n=44) or didn’t have PN (n=44). These participants were matched for glycemic status and compared with a lean, non-neuropathic control participants … read more
U.S. diabetes deaths top 100,000 for second straight year
Jan 31 (Reuters) – More than 100,000 Americans died from diabetes in 2021, marking the second consecutive year for that grim milestone and spurring a call for a federal mobilization similar to the fight against HIV/AIDS.
The new figures come as an expert panel urges Congress to overhaul diabetes care and prevention, including recommendations to move beyond a reliance on medical interventions alone. A report released earlier this month calls for far broader policy changes to stem the diabetes epidemic, such as promoting consumption of healthier foods, ensuring paid maternal leave from the workplace, levying taxes on sugary drinks and expanding access to affordable housing, among other areas … read more
Steps Towards Preventing and Reducing Hypertrophic Scars: One Surgeon’s Experience
Hypertrophic scarring secondary to wound dehiscence remains an ongoing challenge for foot and ankle surgeons, despite advancements in surgical techniques and products development. Unattractive or thick scars on any patient exasperate me, but they are especially tough to endure when the patient is a child. A significant portion of my practice focuses on pediatric patients. A thick, wide, noticeable scar on this patient cohort can discourage the parents, the patient, and the doctor alike … read more
Building knowledge of wound care through competency-based education programs
Throughout Covid-19, the pandemic media has highlighted the burden it puts on healthcare systems and professionals. Providing timely and professional care to people suffering from acute and chronic wounds has been particularly difficult. There are two challenges: access to care and access to professional care. Although medical professionals are aware of the need for advanced education, it can be difficult to obtain advanced wound care education due to the increased workload and limited access to education.
A nurse specializing in wounds, ostomy, and continence in Canada (NSWOCC) works with Canadian clinicians to address the lack of access to professional wound care. NSWOCC owns and operates the WOC (Wound, Ostomy, and Continence) laboratory. The WOC-Institute is a practice and competence base of various standards to help healthcare professionals improve their wound, ostomy, and excretion skills and understanding by taking advantage of both online and direct learning opportunities. We offer the program of. The WOC-Institute’s competency-based education program is a team of knowledgeable and dedicated nurse leaders from the Canadian Association of Nurses (CNA) certified nurses specializing in wounds, osteoporosis, and excretion … read more
Glycemic Control Reduces Risk of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in Type 1 Diabetes
Early intensive glycemic control decreases the long-term risk of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), according to a study in Diabetes Care … Researchers evaluated the effects of intensive treatment (INT) vs conventional treatment (CON) in patients with T1D from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) on the subsequent risk of DFU and lower-extremity amputations (LEA) in the follow-up Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study … read more
Using Negative Pressure Wound Therapy With Instillation and Dwell Time to Create a Path …
to Closure for Older Patients With Chronic Wounds: A Retrospective Case Series
BACKGROUND: Chronic podiatric wounds are common causes of morbidity and mortality in older patients. Negative pressure wound therapy with instillation and dwell time (NPWTi-d) has been recommended in wounds with high levels of exudate, contaminated wounds, and wounds in which healing progression has stalled. PURPOSE: This retrospective case series describes the use of NPWTi-d to prepare 4 chronic wounds for closure in older patients with multiple comorbidities. METHODS: Patients (N = 4) ranged in age from 65 to 95 years and had wounds present for at least 90 days. Previous treatments included conventional NPWT and debridement. NPWTi-d consisted of instillation of 10 to 20 mL normal saline, dwell time for 1 minute, followed by 3-hour cycles of -125 mm Hg. Antibiotics were administered as needed. Wounds included a 210-day Wagner grade 3 diabetic foot ulcer (3.2 × 1.8 × 0.3 cm3), a 90-day dehisced wound (9.5 × 2.6 × 0.4 cm3), a 300-day neuropathic ulcer … read more
Diabetes: Know it! Fight it! Webinar
Every wound-care clinician treats diabetic patients regardless of your care point. In this course, Nancy will help you evaluate the wound, identify the best plan of treatment and steer you away from the potential setbacks for better healing rates and overall patient outcomes … register
What is the practice and understanding of podiatrists towards patient-centred consultations regarding diabetic foot care?
Background: Patient education is an integral part of diabetes management, yet research shows that increased knowledge alone does not translate into behaviour change. Behaviour change techniques (BCTs) have the potential to increase foot self-care and reduce the incidence of diabetic foot disease. Aims: The aim of this study was to explore the practice and understanding of podiatrists towards patient-centred support versus prescriptive instruction in consultations regarding diabetic foot care. Methods: The study was a cross-sectional design with a web-based questionnaire distributed to members of the College of Podiatry in the UK. Descriptive statistics, conceptual content analysis and the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient were used to analyse the data. Results: Most respondents reported using BCTs in their consultations “often” or “very often” and that they “strongly agree” or “agree” that their consultations were patient-led, yet most were categorised as having a partial or poor understanding of these terms. Three themes emerged regarding barriers and facilitators, including ‘Skills and confidence’, ‘Patients do not want to take control … read more
What’s So Good About WOCN Certification?
In this video, Dr Janice Beitz shares her thoughts of the value of WOCN certification and its positive impact … watch
Advertise on WoundCareWeekly.com
We will soon be relaunching the Wound Care Weekly newsletter to our list of 7,000 wound care and podiatry professionals. We are looking for sponsors to keep the lights on for WCW. In addition to the newsletter, sponsor exposure would include prominent website visibility (website gets close to 30,000 page views per month), Facebook header and sticky posts (FB page has 1,600 likes and followers) and LinkedIn posts (about 1,200 connections). I expect dramatic growth for web traffic from the newsletter based on activity from when it was previously active. Our latest media kit is below, let me know if you have any questions.
WCW-media_kit_2022.pdf
-Andy Durban
The white coat: Symbol of respect, or a liability?
A doctor’s white coat is not only a staple of healthcare attire, but it’s also a symbol of professionalism, authority, kindness, and trust. While medical students know that trust is earned through practice, donning the white coat marks an important milestone in their journey to doctorhood … But the glory of this esteemed garment may dwindle when one considers the harm it could cause. Not only do white coats serve as vehicles for pathogens, but they also shine a light on patients’ perceptions of gender and professionalism, revealing gender bias in some cases … read more
Comments at HCPCS Public Meeting
The Alliance spoke at the Dec. 1-2, 2021 HCPCS Public Meeting in support of the CMS HCPCS Workgroup’s preliminary coding decision to establish three new Level II HCPCS codes for non-pneumatic compression devices. “Including disparate devices into the same HCPCS code would severely limit the ability of CMS and other interested parties to collect data and assess the utilization, cost, efficacy and clinical outcomes of these new devices. Therefore, we are in agreement with the creation of three new K codes since it will allow CMS to establish appropriate product segmentation thereby avoiding issues related to data collection and analysis,” the Alliance told the Workgroup … read more
Antimicrobial peptide derived from insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 improves diabetic wound healing
Impaired keratinocyte functions are major factors that are responsible for delayed diabetic wound healing. In addition to its antimicrobial activity, the antimicrobial peptide derived from insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (AMP-IBP5) activates mast cells and promotes keratinocyte and fibroblast proliferation and migration. However, its effects on diabetic wound healing remain unclear. Human keratinocytes were cultured in normal or high glucose milieus. The production of angiogenic growth factor and cell proliferation and migration were evaluated. Wounds in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice were monitored and histologically examined. We found that AMP-IBP5 rescued the high glucose-induced attenuation of proliferation and migration as well as the production of angiogenin and vascular endothelial growth factor in keratinocytes. AMP-IBP5-induced activity was mediated by the epidermal growth factor receptor … read more
Case Study – Diabetic Foot Abscess and Sepsis: Amputation or Limb Salvage?
A 48-year-old Type II insulin dependent diabetic male presented in the acute care setting with sepsis due to an abscess of the right foot involving bone and deep soft tissue structures of the midfoot. The wound and associated sepsis made limb loss and/or mortality a pressing concern. Options were primary limb amputation versus an attempt at limb salvage … read more
Classifying diabetic foot ulcers
Dermatologists must be able to distinguish between infected and noninfected diabetic foot ulcers because whether or not a DFU is infected can help determine treatment protocol, says Warrent S. Joseph, D.P.M, FIDSA.
While dermatologists are unlikely to treat patients with severe foot infections that require hospitalization, they must be able to diagnose and manage mild-to-moderate infections in diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), and follow current Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) guidelines regarding antibiotic use, according to Warren S. Joseph, D.P.M., FIDSA, who presented at DERMfoot 2018. He is a consultant, lower extremity infectious diseases, Roxborough Memorial Hospital, Philadelphia, and a co-author of the IDSA guidelines, which appeared in Clinical Infectious Diseases in June 2012 … read more
What Is the Difference Between RPM and RTM?
Ever since the CPT® 2022 codebook was released by the American Medical Association, this author has received many calls and e-mails from wound/ulcer management professionals and providers inquiring about the similarities and differences between the 5 new remote therapeutic monitoring (RTM) services codes and the 5 remote physiologic monitoring (RPM) services codes that were created in 2019. Therapists were particularly eager to learn about the new RTM codes and rules. Therefore, this author created the following table, which displays the frequently asked questions and the side-by-side comparison of the answers as they pertain to RPM and RTM … read more
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Managing Minimally Invasive Aesthetic Procedure Complications
A Report of Three Cases
Minimally invasive aesthetic procedures such as filler injections and thread lifts have gained popularity recently. Complications from these aesthetic procedures are difficult to avoid. This increasing public health concern requires a combination of effective therapeutic modalities. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has generated favorable results in treating a diversity of wounds, inflammation, and infection … The cellular inflammatory cascade and wound healing process is triggered by tissue hypoxia. Maintaining an oxygen pressure of at least 30 mmHg in tissues is essential to provide an environment suitable for wound healing … The wound was clinically evaluated every 3 days. As the days progressed, the inflammation began to reside as the area of infection continued to shrink, leaving a once-blurred, now clear margin around the wound (Figure 1C). The wound fully healed within one year … read more
E-Learning and Blended-Learning Program in Wound Care for Undergraduate Nursing Students
To respond to the nursing shortage in the canton of Geneva, the School of Health Sciences increased the yearly number of Bachelor of Nursing students from 426 in 2016 to 497 in 2019 (HES-SO, 2020; 2021). In 2020, 190 students started, representing an increase of 18% since 2016. This increase had a major effect on the current face-to-face teaching methods, not only for the availability of lecturers, but also for the logistical resources. To face this problem, different virtual learning tools such as blended and e-learning were implemented. Blended learning is a combination of online learning and the traditional face-to-face learning (Siemens et al., 2015; Singh, 2003) using different technological approaches such as podcasts, lecture captures, or virtual web-based classrooms (Leidl et al., 2020), whereas e-learning is an online education method … read more
Healogics 2022 Healing Can’t Wait Program Raises Awareness about the Impact of Heart Health on Wound Healing
Healogics, the nation’s leading provider of advanced wound care services, as part of their 2022 Healing Can’t Wait program, is promoting awareness of heart health and its impact to wound healing through their seventh annual Heart Health Awareness campaign. Throughout Heart Health Awareness Month, Healogics will work to spread awareness about how cardiovascular diseases can affect the wound healing process.
An alarming 48 percent of Americans currently suffer from cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular disease can take many forms:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Peripheral Artery Disease(PAD)
- Vascular Insufficiency Diseases
Health Equity podcast #6: Preventing diabetic foot ulcers
In this episode, we are joined by Dr. Ernest Moy, Executive Director of the Office of Health Equity and Dr. Jeffrey Robbins, director of VA Central Office Podiatry Service. Also participating is Suzanne Shirley, director of Partnerships and Community Engagement with the VA Innovation Ecosystem.
Do you know why it is so crucial to address diabetic foot ulcers?
Moy discusses differences in Veterans affected by diabetic foot ulcers and why this program to manage and reduce foot ulcers can improve the health of our Veterans.
… listen
Wound Care in Home Health Under the Value-Based Purchasing Expansion: What is on the Horizon?
The webinar will examine Medicare’s proposed value-based purchasing expansion in the Home Health Market for 2021. More specifically, we will look at how that impacts wound care and how leveraging the right wound products can help navigate these changes … register
Local Tranexamic Acid Reduces Surgical Blood Loss
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is a synthetic lysine analog that reduces perioperative blood loss by blocking lysine-binding sites on plasminogen molecules. It has been reported to be effective in limiting blood loss and transfusion needs in various orthopedic surgeries and for pediatric patients at high risk of blood loss.1,2 Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) supporting the capacity of TXA to reduce blood loss and improve outcomes associated with various surgical procedures have increased fourfold in the 10 years since Evidence Corner addressed this topic, which highlighted the capacity of locally delivered TXA to reduce blood loss during … read more
The US Wound & Podiatry Registries
As part of a QCDR, the US Wound & Podiatry Registries serve many purposes:
Follow the natural history of a disease, estimate the magnitude of a problem, document the type of patients served, estimate complication rates, understand variations in outcomes, determine clinical effectiveness of treatments in the real world, understand cost-effectiveness, monitor safety, measure and improve clinical quality … read more
Prevention or Delay of Type 2 Diabetes and Associated Comorbidities: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) “Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes” includes the ADA’s current clinical practice recommendations and is intended to provide the components of diabetes care, general treatment goals and guidelines, and tools to evaluate quality of care. Members of the ADA Professional Practice Committee, a multidisciplinary expert committee (https://doi.org/10.2337/dc22-SPPC), are responsible for updating the Standards of Care annually, or more frequently as warranted. For a detailed description of ADA standards, statements, and reports, as well as the evidence-grading system for ADA’s clinical practice recommendations, please refer to the Standards of Care Introduction … read more
The power of compression therapy in leg ulcer management
This video explains why and how health care professionals involved in wound management should help ensure patient’s access to compression therapy:
Physician Residents Shadowing a Certified WOC Nurse to Develop Interprofessional Competencies
A Quality Improvement Project
The aim of this quality improvement (QI) project was to assess a shadowing experience with a certified WOC nurse (CWOCN) on 4 interprofessional collaborative practice domains: interprofessional communication, role awareness and responsibilities, teams and teamwork, and values and ethics for interprofessional practice … read more
Stop Chasing Your Tail With High-pH Product Selection | webinar
Are you unknowingly promoting a hostile wound healing environment with your choice of wound cleanser, allowing for the colonization of bacteria in the wound bed? Recent studies have shown that pH is a critical factor in the balance of wound healing, and the use of high-pH products such as sodium hypochlorite can be detrimental to healthy tissue. Furthermore, more data have recently been published to show that high-pH environments trigger metabolic responses in fungi that lead to further degradation of skin conditions or environment. High pH in the wound bed also seems to select positively for pathogens … register
The Wound Man
For years I was the only medical doctor doing inpatient wound consults in my hospital. I was continually amazed at the variety of wounds that reflected a wide gamut of human disease. Each wound was unique, and beyond the many pressure injuries and venous stasis lesions there were wounds from cancer, substance abuse, vasculitis, trauma, surgical dehiscence, and hematologic disorders … read more
The Amputation Prevention Symposium | August 17-20, 2022
Driven by a team of multidisciplinary course directors and led by Jihad A. Mustapha, MD, a pioneer in the field of interventional cardiology, AMP provides an unrivaled experience for endovascular and vascular specialists to gain knowledge on the latest advances in revascularization and explore groundbreaking techniques that will improve the future for CLI patients … The unequaled CLI education paired with the paramount interaction among faculty and attendees makes AMP an impactful, inspiring experience that you cannot miss … register
The Issue of Noncompliance in Wound Care Patients
Dealing with patients who either can’t or won’t participate in their care can be a challenge for health care providers across all settings. In wound care, this lack of participation can result in greater financial costs, diminished quality of life, and suboptimal clinical outcomes. This is part one of a two-part series on noncompliance in wound care patients. Part one addresses possible reasons for noncompliance. In part two, strategies to address these issues and increase patient participation are discussed … read more
Improving Quality of Life in the Treatment of Chronic Venous Leg Ulcers
Third-Degree Burn on the Neuropathic Lower Extremity in a Patient With Diabetes While …
Wearing a Copper–Containing Compression Sock: A Case Report
Many patients who have diabetes and peripheral neuropathy wear compression socks, which are widely available and may be purchased with a copper component. There is also a well-documented history of patients with neuropathy developing thermal burns from heat sources. Patients with diabetes are at an increased risk of complications when they sustain burns. PURPOSE: To describe a patient with diabetes and neuropathy who developed third-degree burns while wearing a copper-containing compression sock. CASE REPORT: A 68-year-old man with type 2 diabetes and peripheral neuropathy wore a copper-containing compression sock while sitting in the sun for several hours. Afterward, he noted severe blistering and was ultimately diagnosed with several areas of second- and third-degree burns. Wound treatment included sharp debridement … read more
CMS Approves 9 Wound Care & Hyperbaric Medicine Quality Measures for 2022
CMS (the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services) has approved 9 wound-care and hyperbaric medicine relevant quality measures for the 2022 reporting year. The quality measures were developed jointly by the US Wound Registry (USWR) and the Alliance of Wound Care Stakeholders. You can view the details here … read more
Hospital-Acquired Pressure Injuries: Management and Risk Adjustment
Hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs) continue to occur despite our many improvement strategies. In this webinar, we will discuss the challenges we encounter in HAPI prevention and the sustaining of HAPI improvement strategies, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Three methods to address these challenges will be presented … register
COVID-19 Accelerates Virtual Wound Care
One of the journal’s initial goals was to keep our readers abreast of the latest developments and research in our specialty field.1 The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in the greatest generational threat to “in-person” wound care and patient visits. We have been challenged with the need for social distancing, quarantines, lockdowns, and limited visitation to healthcare facilities. Healthcare professionals, patients, and providers have been forced to find viable alternative methods of care delivery … read more
Micro Medical Solutions receives FDA breakthrough device designation for MicroStent vascular stent
Micro Medical Solutions (MMS) recently announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted breakthrough device designation for its MicroStent vascular stent. This novel technology is designed to achieve and maintain vessel patency, enhance wound treatment, and improve quality of life and blood flow in order to reduce amputation and mortality for patients with chronic limb-threatening ischaemia (CLTI) resulting from peripheral arterial disease (PAD) … read more
Venous Disease: Ulcers and So Much More
As wound care practitioners, we commonly encounter patients who are referred for evaluation and management of venous ulcers due to venous hypertension. These ulcers are the most common lesions of the lower extremities, affecting 1%-3% of the US population.1 Patient may have coexisting medical comorbidities such as cardiac failure and advanced arterial disease, which may impact the usage of compression therapy. The longstanding venous disease may be associated with additional morbidities such as pain, disability, and malignant transformation. Effective clinical outcomes require patient adherence with recommendations that involve a lifelong commitment to management. This article will serve as a generalized overview of this burdensome disease … read more
Calcipotriol Speeds Wound Healing, Lessens Itching in Small DEB Trial
Treatment with ointment containing a low dose of calcipotriol — an analog (similar compound) of vitamin D3 — helped to speed wound closure and reduce itching in people with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) in a clinical trial.
“While corroboration of our results by large-scaled studies is pending, our preliminary data suggest that topical low-dose calcipotriol ointment significantly reduces itch, accelerates wound healing, and can be safely implemented into the daily wound care of DEB patients,” the researchers wrote … read more
Likelihood of Hospital Admission Up During Foot Ulcer Episodes
Diabetic foot ulcer episodes are associated with an increased likelihood of all-cause inpatient admissions and death compared with periods after ulcer healing, according to a study published online Jan. 18 in Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.
Brian J. Petersen, from Podimetrics in Somerville, Massachusetts, and colleagues examined data from the Medicare Limited Data Set from 2013 to 2019 to develop and validate an episode-of-care model for diabetic foot ulceration. Episodes of care were defined by clustering diabetic foot ulcer-related claims such that the longest time interval between consecutive claims in any cluster did not exceed a duration … read more
An electrically charged thin film patch used to promote wound healing
A team of researchers working at the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China has developed an electrically charged thin film patch for promoting faster wound healing. In their paper published in the journal Science Advances, the group describes their patch, how it works, and how well it performed when tested on rats … Humans have been looking for ways to promote faster healing of wounds for thousands of years in order to reduce both the length of time a patient experiences pain and the chances of infection. In this new effort, the researchers created an electrically charged thin film patch … read more
Building a better bandage
With a $2 million grant from NIH, MSU is working to better understand and treat chronic wounds
The National Institutes of Health has awarded Michigan State University’s Morteza Mahmoudi more than $2 million to further his team’s efforts in finding effective treatments for chronic wounds … Chronic wounds are complex injuries affecting millions worldwide that don’t heal on their own and can lead to amputation or even death. Mahmoudi said available bandaging techniques can be costly and are currently unable to overcome all of the challenges that prevent wounds from healing … read more
Non-invasive, tiny indicator changes color if the wound shows early signs of infection
The non-invasive indicator, which is around the same size as one of our fingertips, is the first of its kind. It does not make any contact with the wound but detects the beginnings of infection by sniffing the air above it.
It can be added to already existing bandages and allows infections to be detected without taking off the dressing – something which can inhibit the healing process and increase the likelihood of wound infection … read more
RevitaDerm Wound Care Gel Recalled Over Bacterial Contamination, FDA Warns
Double-check your medicine cabinet: One lot of RevitaDerm, a wound care gel, is being recalled due to bacterial contamination, per a notice posted by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Blaine Labs triggered the voluntary recall after testing revealed that one bottle of RevitaDerm contained Bacillus cereus, a bacteria that could lead to “life-threatening, invasive infections,” per the FDA. No adverse events related to this recall have been reported yet … read more
New Guidelines For Addressing Nutrition Deficits In People With DFUs
Current estimates show that 37.3 million people, or 11.3 percent of the United States population, have diabetes.1 More than one-third of these patients will develop a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) and recently published guidelines suggest that more than half of these patients have moderate or severe malnutrition.2
Recognizing the dearth of randomized controlled trials that specifically look at nutrition in people with DFUs as well as the challenges with nutrition adherence in this patient population, the authors of the new guidelines have emphasized practical screening and assessment tools, including key tips for physical exams, patient history and lab testing workups. The guidelines also provide an overview of dietary factors and nutrients, ranging from hydration and calorie intake … read more
Medical device-related pressure ulcers and the COVID-19 pandemic: from aetiology to prevention
This article describes the aetiology of medical device-related pressure ulcers (MDRPU) and the vicious cycle that leads to these (typically, hospital-acquired) injuries. In this cycle, the primary, deformation-inflicted cell damage leads to a secondary inflammatory oedema-related damage and then to tertiary ischaemic cell and tissue damage. These three damage factors act cumulatively, and, once the first deformation-inflicted massive cell death initiates in the distorted tissues, each of these factors escalates the cell death and tissue damage further, under and near the applied medical device. The primary pathophysiological factors of the COVID-19 pandemic — including the cytokine storm, hypoxia and hyper-coagulation, which are typical to seriously ill patients who require life-support (skin-contacting) medical devices — can fuel the damage spiral of pressure injury. A continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) mask is a classic example of a commonly used medical device … read more
Integrating adjunctive therapy into practice: recognising ‘hard-to-heal’ wounds
The problem of delayed wound healing has been highlighted in several publications which has stimulated debate on variance and the need for updated care pathways. This paper demonstrates how adjunctive therapy can be added to the ‘standard care’ model, described in the National Wound Care Strategy Programme’s recommendations for lower limb wounds, to enhance outcomes for patients with ‘hard-to-heal’ lower limb wounds (NWCSP, 2020). A decision-making pathway based on published literature is described which uses wound assessment and observed response to treatment to allow the effective and targeted introduction of adjunctive therapies for ‘hard-to-heal’ wounds. This approach will allow the cost-effective introduction of new and evolving therapies, such as WoundExpress™ (Huntleigh Healthcare), which addresses the underlying problems associated with resistant lower limb oedema and … read more
Acetic Acid and Dakin’s Solution: Is Ancient Medicine Appropriate in Modern Times?
A study showed that in wound care there is an overuse of practices that lack evidence and science to support them and an underuse of approaches with evidence. The use of Dakin’s solution and acetic acid are two examples of what that study was referring to. Wound care clinicians, and especially certified wound care clinicians, have a responsibility to provide patients with wound care treatments based on science or clinical evidence. I myself am guilty of promoting practices that didn’t meet those criteria back in the early days of my career because I largely trusted the clinicians teaching me were doing the right thing. As I gained more knowledge and experience and heard some of my practices challenged by other “experts” in the industry, I began to question things … read more
Tiny dot that shows early signs of infection, invented by NI scientists
A small dot that changes colour if a patient’s wound shows early signs of infection has been invented by scientists at Queen’s University Belfast … The non-invasive indicator does not make any contact with the wound but detects the beginnings of infection by sniffing the air above it – it is the same size as a fingertip … It is the first of its kind and is predicted to bring major benefits to healthcare, especially because it can be added to already existing bandages … read more
Self-Bonded Hydrogel Forms Basis of Flexible Wound Patch
With wounds being a part of everyday life, it is important to evaluate the level of healing of individuals. This can vary due to conditions that slow down healing, such as diabetes and can be categorized into acute and chronic wounds … Acute wounds can take up to a number of months to heal; however, chronic wounds may extend to several years, with continued inflammation being a large issue … Approximately 300,000 people are hospitalized per year in the United States for acute wounds … read more
Ted Davis to Succeed Amy Tseng as President and CEO of TissueTech
TissueTech, Inc., a pioneer in the clinical application of cryopreserved human birth tissue products to treat ocular surface disease and disorders, chronic wounds, and musculoskeletal conditions, has named Ted Davis as the company’s new president and CEO. Davis—a seasoned biologics and orthopedics executive—takes the helm of an emerging company experiencing exponential growth, succeeding TissueTech founder and former CEO Amy Tseng, who retired January 3. Tseng remains a member of the company’s board of directors … TissueTech, Inc. is an emerging biotechnology company and leader in regenerative medicine using human birth tissue. TissueTech’s pioneering amniotic membrane products are processed using its proprietary CRYOTEK® cryopreservation technology, designed to retain the tissue’s structural and functional integrity. Today, TissueTech is breaking new ground with multiple Investigational New Drug clinical trials underway as the company pursues 351 biologics’ approval for products to treat patients’ unmet clinical needs. TissueTech is committed to empowering healthcare professionals with solutions to deliver optimal patient outcomes by fostering innovation through evidence-based science. Since its inception, clinicians have performed over 600,000 human implants with its products and published over 380 peer-reviewed studies supporting TissueTech’s platform technology. Learn more at https://tissuetech.com
… read more
Perceptive Solutions Integrates with Epic, Joins Epic App Orchard Marketplace
WoundZoom Digital Wound Management solution now available on Epic’s App Orchard Marketplace
STEVENS POINT, WI – JANUARY 27, 2022 – Perceptive Solutions, Inc., developer of WoundZoom
Digital Wound Management, today announced its integration partnership with Epic and the availability of
WoundZoom in the Epic App Orchard marketplace. The purpose of this partnership is to provide a
seamless exchange of wound care data between WoundZoom and a facility’s Epic EHR system.
Perceptive Solutions joins the Epic App Orchard as a trusted integration partner so our customers can
leverage the benefits of WoundZoom while eliminating additional steps in their workflow. Data captured
using WoundZoom at the bedside, such as precise wound measurements, images, and clinical
assessments automatically sync to patients’ charts, creating a more efficient workflow and a complete
patient record in the EHR.
“Our innovative digital wound management solution enables clinicians to spend more time with patients
through automated charting, wound imaging and elimination of the manual measurement process. We are
excited to provide accessibility of WoundZoom to hundreds of healthcare organizations using EPIC,” said
Mark Lacerte, President of Perceptive Solutions. “The technology integration through Epic’s certification
process enables seamless and efficient data flow from our solution into Epic’s clinical charts. This enables
healthcare facilities to more efficiently share valuable wound care data between both clinical and
administrative team members within their EHR.”
About Perceptive Solutions
Perceptive Solutions modernizes the practice of wound care with technology-enabled systems designed to
increase clinical efficiency, improve care quality, and mitigate risk. Integrating smoothly with your EHR,
WoundZoom utilizes the latest AI and imaging technology to capture accurate wound images and
measurements from your smart device, automatically prompt and document appropriate actions, and
create a continuous, standardized clinical record across shifts, floors, and facilities. For more information,
visit https://perceptivesol.com/
Media Contact
Karen Guzdzial
Director of Marketing
(727) 225 7944
karen.guzdzial@woundzoom.com
Wound Care / Ulcer Debridement March 17, 2022
On March 17, 2022, APMA will host the fourth installment of its Coding Basics Webinar Series, “Wound Care / Ulcer Debridement.” Sarah Abshier, DPM; Mitchel Hilsen, DPM; and Lawrence Santi, DPM, will present.
This content is available to APMA members only. If you are a member, please log in to see the full content.
New Year’s Resolutions In Wound Care: Reflections And Looking Forward
Most of the panelists cite the COVID-19 pandemic as a common thread impacting their wound care practices last year. Kazu Suzuki, DPM, CWS shares that patients deferring care and mental stress on both patients and health care workers were dominant themes. He adds that his hospital system is over capacity and has been for months. Christine Miller, DPM, PhD, FACCWS, CWSP says that although her team routinely faces challenges due to socioeconomic issues, the pandemic led to the extra burden of staffing shortages … read more
Relationships of Changes in Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior With Changes in Physical Fitness
and Cardiometabolic Risk Profile in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: The Italian Diabetes and Exercise Study 2 (IDES_2)
OBJECTIVE
In the Italian Diabetes and Exercise Study_2 (IDES_2), behavioral counseling promoted a sustained increase in physical activity (PA) volume (+3.3 MET h ⋅ week−1), moderate- to vigorous-intensity PA (MVPA) (+6.4 min ⋅ day−1), and light-intensity PA (LPA) (+0.8 h ⋅ day−1) and decrease in sedentary time (SED-time) (−0.8 h ⋅ day−1). Here, we investigated the relationships of changes in PA/SED-time with changes in physical fitness and cardiometabolic risk profile in individuals with type 2 diabetes … read more
Promoting digital, data driven wound care
By: Una Adderley
Una Adderley discusses the importance of data collection and analysis in changing practice and outcomes.
If I were a stick of rock, you would find the word ‘NURSE’ right through me (or maybe ‘community tissue viability nurse’ if there was enough room for all those letters!) So, in 2018, when I came into post as director of the National Wound Care Strategy programme (NWCSP), I saw the issue primarily through a clinical lens. I was not so cloistered that I thought wound care was just a nursing issue, but I did think that it was primarily a clinical challenge. If we could just get the clinical pathways sorted and get everyone who saw people with wounds (GPs, paramedics, podiatrists, surgeons and so on) to work in a more collaborative and coordinated way, we would solve the problem … read more
Promising Natural Products in New Drug Design, Development, and Therapy for Skin Disorders
An Overview of Scientific Evidence and Understanding Their Mechanism of Action
The skin is the largest organ in the human body, composed of the epidermis and the dermis. It provides protection and acts as a barrier against external menaces like allergens, chemicals, systemic toxicity, and infectious organisms. Skin disorders like cancer, dermatitis, psoriasis, wounds, skin aging, acne, and skin infection occur frequently and can impact human life. According to a growing body of evidence, several studies have reported that natural products have the potential for treating skin disorders. Building on this information, this review provides brief information about the action of the most important in vitro and in vivo research on the use of ten selected natural products in inflammatory, neoplastic, and infectious skin disorders and their mechanisms that have been reported to date. The related studies and articles were searched from several databases, including PubMed, Google, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect. Ten natural products that have been reported widely on skin disorders were reviewed in this study, with most showing anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-microbial, and anti-cancer effects as the main therapeutic actions. Overall, most of the natural products reported in this review can reduce and suppress inflammatory markers, like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS), induce cancer cell death through apoptosis, and prevent bacteria, fungal, and virus infections indicating their potentials. This review also highlighted the challenges and opportunities of natural products in transdermal/topical delivery systems and their safety considerations for skin disorders. Our findings indicated that natural products might be a low-cost, well-tolerated, and safe treatment for skin diseases … read more
Robert S. Kirsner, MD, PhD,’s Wound Healing Pearls
Robert S. Kirsner, MD, PhD, discusses new and tried-and-true wound healing methods in his presentation at the Maui Derm for Dermatologists meeting.
Robert S. Kirsner, MD, PhD, chairman and Harvey Blank professor in the Dr. Phillip Frost Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Surgery at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine in Miami, Florida, shares his pearls for greater efficacy in his presentation at the current Maui Derm for Dermatologists meeting held in Maui, Hawaii. His pearls included: letting evidence guide decisions, debriding the wound edge along with the wound, using microbes to improve healing, and more … read more
Guidelines and standards for comprehensive clinical diagnosis and interventional treatment for diabetic foot in China
Diabetic foot (DF) is one of the most common complications of diabetes and is associated with high morbidity, disability, lethality and low cure-rate. The clinical diagnosis and treatment of DF need to be standardized. The Chinese Diabetic Foot Cell and Interventional Therapy Technology Alliance has released six editions of guidelines and standards for clinical diagnosis and interventional treatment of DF, which filled the gap in the domestic DF treatment standard and played an important role in improving the level of diagnosis and treatment in China. In line with the latest developments in diagnosis and treatment, the Alliance, along with other 89 institutions, developed and issued the new edition based on the sixth edition to help standardize the clinical diagnosis and treatment of DF in China … read more
Covid-19 lockdown appears to have had a positive effect on diabetic foot ulcers
We conducted a prospective, observational, single-center study without modification of care. All patients followed for a DFU in the study center between 15th April 2020 and 11th May 2020 were included. The baseline assessment occurred 4 weeks after the beginning of lockdown and the follow-up visit 4 to 6 weeks after easing of lockdown. The primary analysis was based on the SINBAD classification … read more
Wound care research sponsored by the Department of Defense
Due to the need for more information about Department of Defense sponsored wound healing research, the Wound Healing Foundation initiated the writing of this article. It briefly describes the Vision, Mission and Goals of the Department of Defense Strategic Medical Research Plan. It also describes the current objectives of Department of Defense research funding and where to access this information in detail. The grant cycle, the timing of request for proposals and some of the specifics of their requirements are also mentioned. A brief discussion of budgeting and overhead is also included … read more
Role of Ultrathin Skin Graft in Early Healing of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
A Randomized Controlled Trial in Comparison With Conventional Methods
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are a global burden on health care systems. Despite the availability of various treatment modalities, many DFUs do not heal. Nonhealing wounds can lead to various complications, which add to significant morbidity in terms of the degree of moisture retained in the dressing, pain, foul order, and restriction of daily activities. A different treatment modality that can promote the wound healing process earlier (and is cost-effective, easy to use, and readily available) may be necessary to consider. Objective. The purpose of the current study was to demonstrate the efficacy of ultrathin skin grafting (UTSG) in the early healing of DFUs in terms of cost-effectiveness, reduced total number of hospital visits, and final wound outcome (ie, limb salvage rate). Materials and Methods. A randomized controlled trial was conducted in which 52 patients were treated with either UTSG … read more
The International Alliance Of Wound Care Scholarship Foundation® Announces inaugural scholarship recipients
Three rising wound care clinicians receive up to $1,500 each
KOKOMO, Ind., Jan. 25, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — The International Alliance of Wound Care Scholarship Foundation® has awarded inaugural scholarships to three recipients to commence their scholarship award program! … These scholarships are awarded to health care professionals for advanced wound care education and certification. This aids IAWCSF® in its purpose to help reduce the U.S. and global burden of wounds and associated costs by creating a larger number of providers who are educated specifically in treating wound care issues. After a thorough evaluation and assessment by the IAWCSF® Scholarship Review Board, three scholarship recipients were selected as follows … read more
The International Alliance of Wound Care Scholarship Foundation®
RECELL® System Data to be Presented at 44th Annual John A. Boswick Burn & Wound Care Symposium
AVITA Medical, Inc. (NASDAQ: RCEL, ASX: AVH), a regenerative medicine company that is developing and commercializing a technology platform that enables point-of-care autologous skin restoration for multiple unmet needs, announced today that six abstracts highlighting the clinical benefits of the RECELL® Autologous Cell Harvesting Device (RECELL® System) have been accepted at the 44th Annual John A. Boswick Burn & Wound Care Symposium. The international conference will be held in Maui, Hawaii, January 22-27, and covers the latest advancements in burn care, wound healing, and infection control … read more
DME for Partial Foot Amputations
The last issue of the year for Podiatry Management is typically dedicated to diabetes. Consistent with that, this article will expand on this issue’s article on PFA (partial foot amputation) written by Jeanette Smith … Devices typically used for patients with PFA range from stuffing a block of materials (toilet tissue, paper towels, rags, etc.) into the toe box of the shoe to a sophisticated hybrid lower extremity prosthetic prescribed by a physician. This article will provide some basic information on why it is important to provide the proper device … read more
Medtronic Recalls HawkOne Directional Atherectomy System
Medtronic has recalled 95,110 HawkOne Directional Atherectomy Systems because of the risk of the guidewire within the catheter moving downward or prolapsing during use, which may damage the tip of the catheter … The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has identified this as a Class I recall, the most serious type, because of the potential for serious injury or death … The HawkOne Directional Atherectomy system … read more
Utilizing a Comprehensive Wound Care Team to Lower Hospital-Acquired Pressure Injuries in an Academic Public Hospital
Hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs) have significant impacts on patient morbidity and mortality, with approximately 2.5 million patients treated for pressure-related injuries annually. This study aimed to describe the influence of a comprehensive wound care team on HAPIs over an 8-year period … read more
StrataGRT–A Breakthrough in Treatment on Chronic and Hard-to-Treat Wounds | video
Transcript: Hello, my name is Dr Matthew Regulski. I’m the medical director for the wound Institute of ocean County, New Jersey, and senior partner at Ocean County Foot & Ankle Surgical Associates … I want to bring to your attention today about a new fast filming, forming silicone that I think has made significant progress in the treatment of both chronic and acute wounds. I’ve been in practice for 17 years and I treat chronic wounds of all types. This has made a substantial impact on the treatment of very hard-to-heal chronic wounds … watch
Wound Management in Post-Acute Care: The Patient Journey
Friday, February 18, 2022 | 9:00AM – 4:20PM EST
Our seminar is both virtual and immersive. With a focus on applying tomorrow what you learn today, this unique experience enables you to participate in your own learning through exploration of case scenarios and interactive exercises … Effective wound prevention and management in the post-acute care setting is essential to reducing unnecessary hospital readmissions and improving patient outcomes … register
The Courage to Do the Right Thing
I was introduced to this problem early in my career. More than two decades ago, I was an Associate Professor at the University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston … Wound Center was the first of its kind (at least, that I know of) to perform “point of care” electronic documentation (in the room with the patient), using a system that internally calculated the physician’s billed level of service and collected discrete data about patients and their wounds … CMS proposed a facility billing system based on wound SIZE. That proposed system was never adopted because during a meeting with CMS, Intellicure President and CEO, David Walker, used Intellicure data from thousands of patient visits to demonstrate that, if implemented, 99% of wound center visits would be billed at the lowest level of … read more
.
Ouch! Assessing and Managing Acute and Chronic Wound Pain
Pain has been a prevalent health care challenge in the United States for some time, with data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showing that approximately 16% of men and 20% of women experience pain on most days or even every day.1 As health care providers, we understand that unrelieved pain and suffering have direct results on the healing cascade and impair both physical and mental health. The topic of pain is almost always addressed in the health care setting, with pain even at one time being recognized as the “fifth vital sign.” … read more
Chronic Wound Telemedicine Models Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Scoping Review
To present the results of a scoping review exploring chronic wound care telemedicine before and during the pandemic, including the characteristics of the models implemented … This continuing education activity is intended for physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and nurses with an interest in skin and wound care… read more
Development of a prediction model for foot ulcer recurrence in people with diabetes using …
easy-to-obtain clinical variables
We used data from a prospective analysis of 304 people with foot ulcer history who had 18-month follow-up for ulcer outcome. Demographic, disease-related and organization-of-care variables were included as potential predictors. Two logistic regression prediction models were created: model 1 for all recurrent foot ulcers (n=126 events) and model 2 for recurrent plantar foot ulcers (n=70 events). We used 10-fold cross-validation, each including five multiple imputation sets for internal validation. Performance was assessed in terms of discrimination using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) (0–1, 1=perfect discrimination), and calibration with the Brier Score (0–1, 0=complete concordance predicted vs observed values) and calibration graphs … read more
Aedicell Expands Availability of Advanced Wound Therapies to US Patients
ROCHESTER, N.Y., Jan. 24, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — To provide a growing number of patients with advanced regenerative wound therapies, Aedicell secured a Group Purchasing Agreement with Premier, Inc. making its skin substitute product Dermavest® available nationally to Premier alliance members. To accommodate the expected demand, Aedicell announces plans for a new production facility located in Cape May County, NJ, in addition to its American Association of Tissue Banks certified facility in Rochester, NY.
Premier, Inc. is a leading healthcare improvement company, uniting an alliance of more than 4,400 U.S. hospitals and health systems and approximately 225,000 other providers and organizations to transform healthcare.
“We’re here to transform the lives of people needing skin substitutes by transforming human tissue into therapies,” said Aedicell CEO Ted Burke. “This Premier Agreement will make our clinically proven therapies with enhanced patient outcomes available to more people at a lower cost, and our new facility in New Jersey will enable us to meet the expected demand for our products.” … read more
COVID-19 Proning Teams Benefit From Wound Care Specialist Nurse
The inclusion of a certified wound and skin care nurse on a multiprofessional prone-positioning team significantly reduces the odds of pressure injuries developing in patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19, according to a study published in the January issue of the American Journal of Critical Care … Connie Johnson, R.N., from Penn Medicine Princeton Health in Plainsboro, New Jersey, and colleagues evaluated the association between including a certified wound and skin care nurse on a multiprofessional pronation team and the prevention of pressure injuries … read more
Targeted nanoparticle delivery provides boost for diabetes transplant
Delivering immunosuppressant treatment via targeted nanoparticles could open the door to a long-lasting cure for type 1 diabetes. Transplanting insulin-producing cells is a promising approach to treat the disease; however, it is plagued by issues of immune rejection. In a new study, published January 17 in Nature Nanotechnology, mice treated with a reengineered therapy could tolerate a transplant for much longer with fewer side effects … For the 1.6 million people in the U.S. living with type 1 diabetes, keeping the body’s blood sugar levels within the right window at all times can be an ongoing challenge … read more
Have a slow healing wound? You need to be eating more protein.
Frustrated with a chronic wound that refuses to close? Or stay closed? It’s time you cashed in on the power of protein … Your body is programmed to heal, over and over again. Even in the face of diabetes and artery/vein diseases … So how can you speed up the body’s natural healing process? By listening to what your body is asking for. And when you have a wound, your body is craving protein … Healing the body with food isn’t about using “natural” foods on an open wound. Raw honey, apple cider vinegar, tea bags, coconut oil, and “miracle” food don’t belong on your wound. They post a huge risk of infection and moisture imbalance, which will slow healing … read more
Higher rates of all-cause mortality and resource utilization during episodes-of-care for diabetic foot ulceration
Researchers aimed at ascertaining if higher all-cause rates of mortality and resource utilization are recorded during periods of diabetic foot ulceration. In addition, an episode-of-care model for diabetic foot ulceration has been developed and validated.
- The Medicare Limited Data Set between 2013 and 2019 was analyzed for retrieval of data for this study.
- Episodes-of-care were defined by clustering diabetic foot ulcer linked claims such that the longest time interval between consecutive claims in any cluster did not extend beyond a duration which was adjusted to match two characteristics of foot ulcer
New organic dressing invented in Oman could help wounds heal faster
A new bandage-type dressing for wounds, which has been made from plants, could be used to help them heal faster, a researcher in Oman has discovered … Saied Vakilian, a researcher at the Laboratory for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine at the Natural and Medical Sciences Research Centre at the University of Nizwa, led a team that used compounds made from two medicinal plants to help wounds heal faster … “This winning project aimed to evaluate a bioactive multilayer wound dressing based on chitosan and alginate,” said Vakilian … “To enhance healing potential, dracaena cinnabari and aloe vera were loaded as separate layers into the scaffold. The bare and bioactive multilayered scaffolds were fabricated by an iterative layering freeze-drying technique.” … read more
Medical Innovation And The Fight Against Amputation
Many specialists unite with one goal: preventing amputation. When podiatrists encounter patients that may lose a leg from peripheral arterial disease (PAD), vascular treatment is an urgent need. But, the question may arise: “Why doesn’t the vascular community seem to agree on how to best intervene?” … A July 2015 research paper compared the primary and secondary outcomes of angioplasty versus open vascular surgery.1 The research found both treatments equally effective in amputation prevention, improving the quality of life and life expectancy of patients with critical limb ischemia (CLI), but that endovascular treatment offered additional benefits of lower cost, lower complication rates, and easier recoveries. The study also showed a lower 30-day mortality rate for angioplasty. The article summary stated, “Based on these results it is suggested that angioplasty should be considered as the first choice for feasible CLI patients.” … read more
Response to: Remote Diabetic Foot Temperature Monitoring for Early Detection of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
We read with pleasure the recent article in your journal on the cost-effectiveness of remote diabetic foot temperature monitoring by Brooks et al.1 Diabetic foot ulcers pose a major healthcare burden, and insight into cost-effectiveness of treatments in this field is scarce, especially in preventing foot ulcers.2 Studies with original data are clearly preferred to inform clinicians, researchers and policy-makers on the potential cost-savings and health gains of preventative interventions. But modelling analyses such as by Brooks et al can provide relevant insights … For modelling analyses to be meaningful, assumptions must be based on both published evidence and clinical reasoning, and must be reasonable and logical. For a cost-effectiveness analysis on remote foot temperature monitoring, two assumptions are key … read more
BHU scientists find cure for chronic wounds. Here’s how they managed it
The team led by Prof Gopal Nath of the department of Microbiology said that wounds that took months and years to heal, could now be cured in days or months
A team of scientists from the Banaras Hindu University (BHU) have found a cure for those suffering from chronic wounds, particularly with diabetic foot ulcers. The team led by Prof Gopal Nath of the department of Microbiology, Institute of Medical Sciences, said that wounds that took months and years to heal, could now be cured in days or months. The findings of study have been published in the National Centre for Biotechnology Information, National Institutes of Health, US … read more
How TWC and Wound Clinics Will Evolve in 2022
Wound care continues to evolve as care expands beyond the wound clinic. As we move to 2022, Today’s Wound Clinic Clinical Editor Caroline E. Fife, MD, FAAFP, CWS, FUHM, and Managing Editor Brian McCurdy discuss meeting the challenges and how TWC will continue evolving in its digital format … watch video
Effectiveness of negative pressure wound therapy with instillation and dwelling after stoma closure
a retrospective and propensity score matching analysis
The use of temporary diverting stoma has become more common in low colorectal anastomosis to reduce anastomotic complications. Surgical site infection (SSI) at the stoma closure site has been one of the most frequent postoperative complications. The aim of this study was to compare the short-term outcomes between conventional primary suture closure and negative pressure wound therapy with instillation and dwelling (NPWTi-d) therapy following purse-string suturing, using propensity score matching analysis. We retrospectively evaluated the medical records of 107 patients who underwent stoma closure between January 2016 and October 2020. The primary outcome was the proportion of SSI. The secondary outcome was the day of postoperative length of stay. Propensity score matching with one-to-one match was performed for reducing treatment selection bias … read more
Survey on Wound Hygiene
An article in the Journal of Wound Care surveyed participants on awareness, implementation, barriers, and outcomes of wound hygiene.
Data from a survey created to better understand wound care awareness, implementation, barriers, and outcomes was recently published in the Journal of Wound Care. The survey, which was created by the Journal of Wound Care projects team with consultation from ConvaTech, was 26 questions long and featured a variety of multiple and open-ended questions. It was sent out by email and online, being open for a little over 12 weeks. Nonprobability sampling was used and authors of the survey reviewed the outputs to help analyze the data with the support of a medical writer … read more
Case Study – Diabetic Foot Abscess and Sepsis: Amputation or Limb Salvage?
A 48-year-old Type II insulin dependent diabetic male presented in the acute care setting with sepsis due to an abscess of the right foot involving bone and deep soft tissue structures of the midfoot. The wound and associated sepsis made limb loss and/or mortality a pressing concern. Options were primary limb amputation versus an attempt at limb salvage … In addition to his diabetes, past medical history included chronic kidney disease stage 3, sleep apnea with continuous positive airway pressure dependence, peripheral neuropathy, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, hypothyroid, morbid obesity, Moya disease, and secondary renal hyperparathyroidism … read more
An Autologous Protein-Based Topical Ointment for Hard-to-Heal Skin Wounds
There is increasing evidence regarding the wound healing potential of platelet-derived autologous by-products. We provide preliminary data regarding the use of a new plasma rich in growth factors–derived autologous topical ointment for the management of hard-to-heal wounds … read more
EXPLAINED: Barrier Products
Barrier products, such as skin barrier films, are designed to protect the skin by minimising its exposure to excessive moisture and irritants. These may be topical preparations (available in a spray, foam applicator or wipe format) that can be applied to the skin without stinging, and dry quickly to create a breathable and transparent film. They provide a protective water-repellent barrier against irritants and harmful bodily substances, such as urine and faeces … Barrier films will not affect dressing application and are simple for both healthcare providers and patients/carers to use. Sterile products are particularly useful as they can be used on both intact and injured skin and are recommended for use in patients with a high risk of infection … read more
Wound Care Evidence Summit 2022
The Summit will provide a critically needed multi-disciplinary meeting for payers, government agency policymakers, prominent researchers, wound care medical specialty societies, patient and clinical associations, wound care clinics and manufacturers to address the shared goals of:
- Addressing the current state of wound care research and clinical trial design
- Exploring solutions to address the limitations in the wound care evidence-base
- Communicating with payer medical directors on the development of coverage policies and the use of clinical practice guidelines in coverage decisionmaking
- Defining “next steps” to actualize solutions
- Participating in a uniquely intimate gathering of leading decisionmakers
How Are Wound Clinics Coping With Omicron?
At wound clinics, physicians and staff have dealt with a lot over the past two years while the pandemic has raged. First, they were in the trenches as COVID-19 arose and hospitals were swamped, with many patients on ventilators. Even after many were vaccinated, the Delta variant caused another surge. Now, the Omicron variant is spreading quickly, with physicians facing an even more contagious version of the disease … “It still feels like the hits just keep on coming and we are not out of it yet,” says Caroline E. Fife, MD, FAAFP, CWS, FUHM. “Omicron is spreading so fast it’s mind blowing.” … The transmissibility of Omicron is a concern, as evidenced by what experts are seeing in data, according to Dr. Fife … read more
A Human Fibroblast-Derived Growth Factor Preparation in the Management of a Chronic Surgical Wound
in a Diabetic Patient: A Case Report
The surgical treatment of choice for ischaemic heart disease is Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG). The Great Saphenous Vein (GSV) is the most frequently used conduit for CABG, and the technique for harvesting the GSV entails a long open skin incision, usually comprising the entire leg. The vast proportion of patients experience leg wounds as opposed to sternal wounds. The rate of great saphenous vein harvest site infections (GSVHSI) is reported to be between 1% and 24%. Risk factors associated with GSVHSI include peripheral vascular disease, diabetes mellitus, smoking, obesity, and chronic renal failure. It is well a recognized fact that one of the most significant challenges to wound healing is infection, leading to a poor prognosis and increased morbidity.4 Hence, although rare, complications arising from the great saphenous vein harvest site may require surgical debridement leading to a delay in recovery and may negatively impact the patient … read more
Innovations in Wound Care: The role of wound cleansing in the management of wounds
This 30-minute presentation features learning opportunities that will provide in-depth instruction and demonstration in wound care treatments. After this webinar, the learner will be able to:
Identify the role of proper wound cleansing
Discuss how to select and use non-toxic wound cleansers
Describe advantages of collagen for managing a chronic wound
… read more
Scientists Find Cure For Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Cure For Diabetic Foot Ulcers: People with diabetes, often struggle with diabetic foot ulcers, but not anymore. A team of scientists from the Banaras Hindu University (BHU) have found a cure. The findings of the study were published in the National Centre for Biotechnology Information, National Institutes of Health, US. The team led by Prof Gopal Nath of the department of Microbiology, Institute of Medical Sciences, said that wounds that took months and years to heal, could now be cured in days or months … read more
Nanoparticles Improve Immunosuppression, Could Boost Diabetes Treatment
Islet transplantation has emerged over the past few decades as a potential cure for type 1 diabetes. However, transplantation efforts have faced setbacks as the immune system continues to eventually reject new islets. Current immunosuppressive drugs offer inadequate protection for transplanted cells and tissues and are plagued by undesirable side effects … read more
Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Biofilm Infection and Recurrence (DFU Biofilm)
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) are one of the most common reasons for hospitalization of diabetic patients and frequently results in amputation of lower limbs. Of the one million people who undergo non-traumatic leg amputations annually worldwide, 75% are performed on people who have type 2 diabetes (T2DM). The risk of death at 10 years for a diabetic with DFU is twice as high as the risk for a patient without a DFU. The rate of amputation in patients with DFU is 38.4%4. Infection is a common (>50%) complication of DFU. Emerging evidence underscores the significant risk that biofilm infection poses to the non-healing DFU. Biofilms are estimated to account for 60% of chronic wound infections. In the biofilm form, bacteria are in a dormant metabolic state. Thus, standard clinical techniques like the colony forming unit (CFU) assay to detect infection may not detect biofilm infection. Thus, biofilm infection may be viewed as a silent maleficent threat in wound care … read more
The healing of bilateral chronic VLUs using medical grade honey in an end of life patient with polymorbidity
Palliative care provides holistic, person-centred care by managing symptoms, preventing suffering by treating pain and other problems, and providing physical, psychosocial and spiritual support (Chaplin, 2004; Grocott and Gray, 2010; Dale and Emmons, 2014). Palliative wound care should focus upon relieving wound-related suffering and improving the quality of life of patients and their families when facing life-threatening illness (Grocott and Gray, 2010; Dale and Emmons, 2014). Patients requiring palliative wound care can present with any type of wound, particularly those common in older people, such as venous leg ulcers (VLUs), pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers and malignant wounds … read more
New Clinical Study Finds MolecuLight i:X® Point-of-Care Imaging Improved Sensitivity
of Detecting Bacterial Burden in Surgical Site Wounds by 11-Fold
Authors Suggest that Fluorescence Imaging of Bacterial Burden is Positioned to Change
Contemporary Paradigms of Post-Surgical Wound Management
TORONTO, Jan. 18, 2022 /PRNewswire/ – MolecuLight Inc., the leader in point-of-care fluorescence imaging for real-time detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial loads, announced the publication of “Uncovering the high prevalence of bacterial burden in surgical site wounds with point-of-care fluorescence imaging“1 in International Wound Journal. The publication reports on the results of an analysis of 58 imaged and biopsied surgical site wounds from the 350-patient multi-centre FLAAG (fluorescence imaging assessment and guidance) clinical trial2.
Key findings of the study include:
- 76% of surgical sites that reach the stage of referral to a wound specialist had clinically significant bacterial loads (104 to 109 CFU/g), however only 6.8% exhibited symptoms of infection, resulting in delayed infection management.
- Point-of-care fluorescence imaging (using the MolecuLight i:X device) for detecting high bacterial loads improved sensitivity by 5.7-fold compared to clinical signs and symptoms alone.
- Clinician experience with fluorescence imaging and interpretation (>200 imaging sessions) increased sensitivity of fluorescence imaging to 11.3-fold higher than clinical signs and symptoms alone, and accuracy to 2.6-fold higher.
The incidence of surgical wound complications, including surgical site infections (“SSI”), continue to rise and the development of an SSI is associated with a marked increase in morbidity, a 2-to 11-fold increase in mortality rate, and prolonged hospital stays3. Approximately 2-5% of surgical wounds in the US develop an SSI7-10 at an annual cost of up to $10 billion4-7. This includes extended hospital stays, readmissions, and more resources required to manage complications.
“While early identification and management of high bacterial burden is critical for the prevention of surgical site infections, this study shows that pathogenic bacterial burden is present in most (>75%) surgical wounds that are referred to a wound specialist, but is largely asymptomatic and therefore goes undetected, delaying bacterial management strategies”, says lead author Associate Professor Sandy-Hodgetts, Centre for Molecular Medicine & Innovative Therapeutics, Murdoch University & Senior Research Fellow, School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Western Australia and the Founder and inaugural President of the International Surgical Wound Complications Advisory Panel (ISWCAP). “Due to its ability to quickly and reliably detect bacterial burden at the point-of-care, fluorescence imaging using the MolecuLight device is positioned to change contemporary paradigms of post-surgical wound management”.
These findings are part of an important initiative by the International Surgical Wound Complications Advisory Panel (ISWCAP) to study surgical site infections on a global scale and highlight the need for more objective diagnostic techniques to support the early and accurate detection of clinically concerning bacterial burden in surgical wounds. The authors note that this is the first study reporting the use of an advanced diagnostic device for the visualisation and diagnosis of bacterial burden in surgical wounds.
“MolecuLight fluorescence imaging technology allows clinicians to see into the wound. The point-of-care imaging device enables clinicians to detect and manage elevated levels of bacteria to inform our decision-making,” says Dr. Thomas Serena, the publication’s contributing author, Founder and Medical Director of The SerenaGroup®, and Vice President of ISWCAP. “Management of bacterial burden should always begin with wound hygiene strategies (e.g., cleansing, debridement), and only escalate to antibiotics when essential.”
|
References: |
|
1 Sandy Hodgetts, K. et al., Int Wound J. 2021;1–11 |
|
3Hatch MD et al. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(3):472-477 |
|
4 Badia JM, et al. J Hosp Infect. 2017;96(1):1-15 |
|
5 McLaws ML et al. J Hosp Infect. 2003;53(4):259-267 |
|
6 Sullivan E et al. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2017;18(4):451-454 |
|
7 Ban KA et al. J Am Coll Surg. 2017;224(1):59-74 |
|
8 Berrios-Torres SI et al. JAMA Surg. 2017;152(8):784-791 |
|
9 Institute CPS. Canadian Surgical Site Infection Prevention Audit. 2016 |
|
10 Si D et al. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:318 |
About MolecuLight Inc.
MolecuLight Inc. is a privately-owned medical imaging company that has developed and is commercializing its proprietary fluorescent imaging platform technology in multiple clinical markets. MolecuLight’s suite of commercially released devices, including the MolecuLight i:X® and DX™ fluorescence imaging systems and their accessories, provide point-of-care handheld imaging devices for the global wound care market for the real-time detection of wounds containing elevated bacterial burden (when used with clinical signs and symptoms) and for digital wound measurement. The company is also commercializing its unique fluorescence imaging platform technology for other markets with globally relevant, unmet needs including food safety, consumer cosmetics and other key industrial markets.
Coverage, Payment, and the Impact of Advocacy
Decisions about which wound care products and services are (or are not) covered under Medicare are made at the national level by the CMS or regionally by Medicare contractors that each make local coverage determinations (LCDs) for the parts of the country they cover. The impact of these policies is significant. If something is not covered by Medicare, you cannot be reimbursed for it. As a result, many clinical treatment decisions are guided by Medicare coverage decisions rather than best clinical practices … read more
Utilizing Disposable, Mechanical NPWT Devices to Aid Wound Management at Home: Cost Savings Considerations
In this clinical case presentation, Dr. Napolitano describes 3 cases using mechanically powered, disposable negative pressure wound therapy. The cases covered in this presentation include an open wound after hematoma excision, Charcot foot deformity presenting with a diabetic foot ulcer, and an open wound after ankle fusion surgery. Data from this poster were presented at the SAWC Fall in Las Vegas, Nevada (October 29-31, 2021) … read more
Nutrition Interventions in Adults with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- Diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) are chronic wounds in the foot or feet associated with neuropathy and/or peripheral artery disease (PAD) of the lower limb in patients with diabetes mellitus.
- Reports from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show that in the United States there are nearly one in four adults living with diabetes, which indicates that a large number of Americans are at risk of DFU.
- DFUs will develop in up to 34% of patients with diabetes at some time in their lives, and of those, approximately 15%–25% will require an amputation.
- Moderate or severe malnutrition has been identified in over half of patients with DFU, and malnutrition in DFU is correlated with increased lower-extremity amputation.
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection of the Forearms in a Patient Using Intravenous Heroin
Case Report of Advanced Wound Management Improving Dressing Tolerance and Expediting Skin Graft
Necrotizing soft tissue infection (NSTI) is rare and characterized by rapid onset and spread of inflammation and necrosis. The infection starts within the fascia but can rapidly progress to include musculature, subcutaneous fat, and overlying skin. Its presentation is considered a surgical emergency. Persons who use intravenous or subcutaneous opioids are at higher risk of NSTIs. PURPOSE: The purpose of this case report is to describe the positive clinical outcome after consulting with wound specialists and using a dressing regimen to expedite more rapid wound healing, shortened time to skin graft, and improved pain tolerance in a patient with a history of intravenous and subcutaneous heroin use. CASE REPORT: The patient presented with an NSTI that required extensive debridement of the bilateral upper extremities. The acute surgical wound service was consulted. A dressing regimen consisting of hypochlorous acid–preserved wound cleansing, followed by carboxymethylcellulose fiber with 1.2% ionic silver covered by hydrocellular foam… read more
Diabetic Foot Surgery: An Overview
Procedures have assumed an increasingly important role in patient care
During their lifetime, up to 30% of people with diabetes will develop a foot ulcer. Diabetes-related foot ulcers and lower extremity amputations result in a major burden for patients, their family, and the healthcare system. Interest in this complex and challenging specialty has been growing and, in recent decades, there has been acceptance of a shift towards operative correction of diabetic foot deformities. Surgical management of diabetic foot deformities has now become an integral part of the overall care … read more
Maceration Mitigation: Recognition, Prevention, and Management of Overhydrated Wounds
Maceration is a common clinical complication that poses challenges in chronic wound treatment.1 Excessive moisture can be trapped on the wound surface, especially when occlusive dressings are overused or when nonbreathable cover dressings are applied for extended periods. Maceration as part of the broader umbrella of moisture-associated skin damage (MASD) occurs as a cascade of events that stem from an impaired microclimate and increased humidity on the wound’s surface. The increased moisture level causes overhydration and the stratum corneum to swell, resulting in decreased tensile strength of this epidermal layer … read more
ESVS publishes 2022 guidelines on management of chronic venous disease of the lower limb
The European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) has released 2022 clinical practice guidelines on the management of chronic venous disease (CVD) of the lower limb to update its 2015 recommendations. The document, authored by Marianne G De Maeseneer (Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, The Netherlands) and colleagues, was published online ahead of print in the European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery (EJVES) … read more
New method may help make immunomodulation more effective in individuals with Type 1 diabetes
Pancreatic islets control insulin production when blood sugar levels change, and in Type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks and destroys such insulin-producing cells. Islet transplantation has emerged over the past few decades as a potential cure for Type 1 diabetes. With healthy transplanted islets, Type 1 diabetes patients may no longer need insulin injections, but transplantation efforts have faced setbacks as the immune system continues to eventually reject new islets… “At my past program, I worked on wound healing for diabetic foot ulcers, which are a complication of Type 1 diabetes,” Burke said. “As someone who’s 26, I never really want to get there, so I felt like a better strategy would be to focus on how we can treat diabetes now in a more succinct way that mimics the natural occurrences of the pancreas in a non-diabetic person.” … read more
India uses 4D bioprinting for diabetic foot ulcer management
Indian pharmaceutical firm Alkem Laboratories has announced to launch a unique patented technology for the treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU). The solution would be based on disruptive 4D Bioprinting technology, which would be used to treat deep, non-healing chronic wounds and is expected to be launched in the Indian market in the latter half of 2022 post regulatory approval … This advanced technology for DFU management has a high scope of preventing amputations in diabetic patients. This technology will be available at affordable rates to Indian patients at a time when there is no definitive treatment for DFU in India … read more
LinkedIn:
Alkem Laboratories
LimFlow System a ‘cost-effective and high-value alternative’ to traditional therapies
Percutaneous Deep Vein Arterialisation (pDVA) with the LimFlow System offers a cost-effective and high-value alternative to traditional therapies or amputation, according to a recent study published in the Journal of Critical Limb Ischemia … Peter Schneider, professor of surgery at the University of California (San Francisco, USA) and co-author of the published article, said: “The cost-effectiveness analysis builds on recently published 12-month data from the PROMISE I study by showing that pDVA with the LimFlow System can be a high-value therapy alternative to the status quo for no-option CLTI patients … “This research highlights the health economic benefits of reducing amputations and the need to offer patients a better alternative worldwide.” … read more
LinkedIn:
LimFlow SA
Healogics Launches Healing Can’t Wait Program For 2022
JACKSONVILLE, Fla., Jan. 13, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — Healogics®, the nation’s leading provider of world-class wound care, is announcing their “Healing Can’t Wait” program for the millions of people struggling with a non-healing wound. Chronic wounds affect seven million Americans, limiting their quality of life, as well as life expectancy … With the 2022 Healing Can’t Wait program, Healogics looks to address the significant increase in amputations observed in recent years due to the impact of COVID-19 on patient treatment schedules. It is critical that patients understand the urgency and importance of treatment. Through the 2022 Healing Can’t Wait program and resources, Healogics Wound Care Centers will focus on educating the underserved chronic wound population … “Treatment delays and the staggering increase in amputations drive us to work even harder to improve awareness and access to advanced wound care. Any untreated wound is at risk for complications such as infection, hospitalization or amputation,” explains David Bassin, Chief Executive Officer of Healogics. “This is why the Healogics Healing Can’t Wait program is so critical.” … People living with diabetes, heart disease or peripheral artery disease (PAD) are at an even greater risk for health complications that stem from an untreated wound … read more
LinkedIn:
Healogics, Inc.
Intensive glycemic control may prevent diabetic foot ulcers
medwireNews: Early intensive glycemic control may reduce the long-term risk for foot ulcers in people with type 1 diabetes, suggest data from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) and Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study … The DCCT included 1408 people with type 1 diabetes who completed an average of 6.5 years of intensive (target glycated hemoglobin [HbA1c] <6.05% [42.6 mmol/mol]) or conventional (no specific glycemic target) diabetes treatment and subsequently underwent 23 years of follow-up in the EDIC study … During this period, 195 participants developed at least one diabetic foot ulcer (48 people had multiple events) and 36 needed lower extremity amputation … read more
Cryotherapy Treatment of Cutaneous Kaposi Sarcoma in a Patient With B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
A Case Report and Short Review of the Literature
Kaposi sarcoma (KS) is a low-grade mesenchymal tumor involving the blood and the lymphatic vessels that primarily effaces the skin and is mediated by human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) in more than 90% of patients. There are 4 distinct types of KS. Compared with the classic and AIDS-related variants, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) associated with KS is a relatively rare clinical condition; thus, only a few cases have been reported. Case Report. This report presents a case study of an 87-year-old patient with B-cell CLL and cutaneous KS managed with cryotherapy, along with a short review of the literature. Conclusions. Considering that the method is relatively simple and with few adverse effects, cryotherapy may represent a simple and safe treatment method for cutaneous KS. However, more studies should be conducted … read more
Silver in Wound Care: Clinical Outcomes | webinar
Thursday, January 27, 2022
Health care professionals should consider silver nanoparticle dressings to decrease healing times and improve the quality of life of their patients.
Registrants attending this session will learn:
- The history of silver usage
- The problem of antimicrobial resistance
- Indications and contraindications for the use of medicinal silver
- Variations of medical silver in dressings and their clinical outcomes
Technology in Wound Care | webinar
On Wednesday, January 19 at 8:00 PM ET, AAWC will host “Technology in Wound Care,” a webinar presented by Olamide Alabi, MD, RPVI, FACS. Dr. Alabi is an Assistant Professor of Surgery, Division of Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy, Department of Surgery, Emory University School of Medicine. She was also the keynote speaker at our 2021 Pressure Ulcer Summit.
… register
Enzymatic Debridement in Chronic Wounds and Severe Burns | webinar
Treating chronic dermal ulcers and severe burns can be challenging. This webinar will discuss the phases of wound healing and overview wound bed preparation using enzymatic debridement.
… register
Kathleen D. Schaum, MS, Named World Expert in Reimbursement Health Insurance
Congratulations to TWC’s own Kathleen D. Schaum, MS, who recently received recognition as an Expertscape World Expert in Reimbursement Health Insurance.
Expertscape tweeted the news on Dec. 12 as part of International Universal Health Coverage Day. Expertscape ranks and lists the world’s top experts in Clinical and Research Medicine and calls itself “the objective, current, global resource for patients and referring physicians.” … read more
All Edema Is Lymphedema: Progressing Lymphedema and Wound Management to an Integrated Model of Care
Chronic edema affects millions of people in the United States and worldwide. Edema can result from a variety of diseases, trauma, medications, and other contributing factors; however, all edema is related to lymphatic fluid dysregulation. Additionally, lymphatic impairment and integumentary dysfunction are interrelated, leading to complex clinical presentations that require an integrated medical model of care to maximize outcomes. PURPOSE: This narrative review article will highlight the current evidence that details lymphatic physiology, fluid regulation by the endothelial glycocalyx layer, and the interconnectedness of the vascular and integumentary systems leading to a paradigm shift in our understanding of edema, lymphedema, and chronic wounds. Traditional pedagogy remains siloed with respect to the body systems, whereas current evidence indicates a certain interdependence, particularly between and among the venous, lymphatic, and integumentary systems … read more
LinkedIn:
Wound Management & Prevention
Biofilm-Innate Immune Interface: Contribution to Chronic Wound Formation
Delayed wound healing can cause significant issues for immobile and ageing individuals as well as those living with co-morbid conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. These delays increase a patient’s risk for infection and, in severe cases, can result in the formation of chronic, non-healing ulcers (e.g., diabetic foot ulcers, surgical site infections, pressure ulcers and venous leg ulcers). Chronic wounds are very difficult and expensive to treat and there is an urgent need to develop more effective therapeutics that restore healing processes. Sustained innate immune activation and inflammation are common features observed across most chronic wound types. However, the factors driving this activation remain incompletely understood. Emerging evidence suggests that the composition and structure of the wound microbiome may play a central role in driving this dysregulated activation but the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying these processes require further investigation. In this review, we will discuss the current literature on: 1) how bacterial populations and biofilms contribute to chronic wound formation … read more
Maceration Mitigation: Recognition, Prevention, and Management of Overhydrated Wounds
Maceration is a common clinical complication that poses challenges in chronic wound treatment.1 Excessive moisture can be trapped on the wound surface, especially when occlusive dressings are overused or when nonbreathable cover dressings are applied for extended periods. Maceration as part of the broader umbrella of moisture-associated skin damage (MASD) occurs as a cascade of events that stem from an impaired microclimate and … read more
LinkedIn:
Alex M. Aningalan
WoundSource
Limb Loss… Who Is Really to Blame?
The Patient? The Physician? The System?—Part 1
The discipline of limb preservation and salvage has spawned extraordinary innovations in both scientific and clinical applications, offering new hope for those seeking the benefits of the burgeoning state-of-the-art lower extremity amputation prevention platforms. Wound treatment complexes are flourishing as well as access to them; research studies abound; extensive data is amassed; myriad public relations campaigns stimulate public awareness; training programs … read more
Optimising wound care through patient engagement
Patient engagement is a crucial and timely topic, both in terms of wound healing (and, in some cases, symptom management), and in improving individuals’ experiences of the process. This document aims to provide clear guidance in listening and engaging with individuals, and thus optimising the care experience for all key stakeholders, of which the patient is the most important. The document was developed with input from both healthcare professionals and individuals using healthcare services Kathleen D. Schaum … read more
LinkedIn:
Wounds International
Have You Revised Your EHR Screens/Templates and Charging System?
At the 2021 SAWC Fall a team (medical director, program director, and clinical nurse manager) from a hospital owned outpatient wound/ulcer management provider-based department (PBD) asked many questions after my main session reimbursement presentation and during my interactive reimbursement session post-conference … When I returned to my office the next week, this same team called me and requested teleconsultation services as soon as possible … As a reimbursement consultant … read more
LinkedIn:
Kathleen D. Schaum
Today’s Wound Clinic
Single cell transcriptomic landscape of diabetic foot ulcers
Diabetic foot ulceration (DFU) is a devastating complication of diabetes whose pathogenesis remains incompletely understood. Here, we profile 174,962 single cells from the foot, forearm, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells using single-cell RNA sequencing. Our analysis shows enrichment of a unique population of fibroblasts overexpressing MMP1, MMP3, MMP11, HIF1A, CHI3L1, and TNFAIP6 and increased M1 macrophage polarization in the DFU patients with healing wounds. Further, analysis of spatially separated samples from the same patient and spatial transcriptomics reveal preferential localization of these healing associated fibroblasts toward the wound bed as compared to the wound edge or unwounded skin … read more
Healthy.io achieves HITRUST CSF® certification for Information Security
BOSTON, Jan. 11, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — Healthy.io, the global leader in transforming the smartphone camera into a medical device, today announced its at-home Minuteful Kidney test and Minuteful for Wound services have earned Certified status for information security by HITRUST, which follows a standardized framework to measure HIPAA compliance … HITRUST CSF Certified status demonstrates that Healthy.io has met key federal and state regulations and industry-defined requirements and is appropriately managing risk. This achievement places Healthy.io in an elite group of organizations worldwide that has earned this certification … Healthy.io’s business case is simple: smartphone-powered technology can help health systems and insurance providers improve patient health, reduce costs across the healthcare system, and improve access to care. Early results are tremendous: In the US, health plans can more than double their current adherence rates. A recent rollout in the United Kingdom showed that Healthy.io test kits raised test adherence from 0% to 50% among patients who had not done a urine test for kidney disease in the previous year … read more
LinkedIn:
Healthy.io
Is Your Wound Bioburdened? Case 2
• 50-year-old male with morbid obesity visiting the outpatient wound care center for bilateral lower extremity wounds and lymphedema. Click here for a photo.
• The wound on his leg was present for several months and previously treated with broad spectrum oral antibiotics for cellulitis. Click here for photo.
• Pain, odor and erythema detected from wound, prompting the clinician to perform a fluorescence scan. Click here for photo
LinkedIn:
Today’s Wound Clinic
2021 Prime Minister’s prize for improving the repair of human tissue, a beacon for wound research in Australia
The broad purpose of laboratory-based wound research is to obtain a scientific understanding of the mechanistic processes that underpin normal and abnormal wound healing. Translation of this knowledge can lead to the development of new tools, technologies, therapeutics diagnostics and sensors that ultimately will lead to improved wound management and patient care. While this process may seem far removed from the day-to-day challenge of dealing with patients with impaired healing, occasionally we see breakthroughs and achievements that encourage both researchers and clinicians alike … read more
Effective Wound Management For Arterial Ulcers
Lower extremity ulcers are a common occurrence in individuals aged over 60. A combination of risk factors and disease processes in these individuals impact the wound healing stages, which leads to the development of chronic, non-healing ulcers. Arterial ulcers account for 8-10% of all lower extremity ulcers. However, the prevalence might be significantly underreported due to the failure to recognize the etiology of leg ulcers. Wound care specialists need to be aware of the differences between arterial ulcers and other ulcer types to provide effective wound care … read more
Wound Week 2022 – February 24-27, 2022 Philadelphia, PA
Wound Week™ 2022 is an innovative, unparalleled educational opportunity that will feature superior content delivered by multidisciplinary faculty with true clinical expertise. This conference will allow clinician driven training and education in wound care, vascular and hyperbaric medicine. In addition to education and training, this meeting will offer unmatched clinician networking … brochure (PDF)
Can Smartphone Apps Enrich Wound Care?
Access to healthcare has enhanced by leaps and bounds with the arrival of mobile technology The most interesting trends in the healthcare industry now comprise flexible and efficient wound care, among others. Extensive smartphone penetrations, along with cost-effective internet connectivity, have committed to taking wound care to the next level. Today, one can have the greatest of wound care facilities through smartphone apps. Traditionally, the healthcare industry had to offer services at dedicated wound care facilities. This required an appropriately-skilled workforce, maintenance of facilities, and important overheads, which occurred in higher costs for patients. With smartphone apps, many of these difficulties have been overcome … read more
Survey on Wound Hygiene
An article in the Journal of Wound Care surveyed participants on awareness, implementation, barriers, and outcomes of wound hygiene
Data from a survey created to better understand wound care awareness, implementation, barriers, and outcomes was recently published in the Journal of Wound Care. The survey, which was created by the Journal of Wound Care projects team with consultation from ConvaTech, was 26 questions long and featured a variety of multiple and open-ended questions. It was sent out by email and online, being open for a little over 12 weeks. Nonprobability sampling was used and authors of the survey reviewed the outputs to help analyze the data with the support of a medical writer … read more
CPD Accredited 5th International Conference on Wound Care, Tissue Repair and Regenerative Medicine
Paris, France – April 15-16, 2022
This year with the refreshing theme on “Emerging and Innovative Approaches for Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration”.
Wound Care Congress is all set to bring together the eminent scholars from the wound care and tissue regeneration community presenting the unsurpassed opportunities to present and explore the future wound healing and tissue science medicine.
Witness the gathering the world-leading and renowned academicians, business delegates, principal investigators, nurses, homeopathists, researchers, students to witness the futuristic ideologies put forth by the experts.
This integrative 2-day event deliberates the new strategies, convictions that will impact the process of your professional development. Join us with your research and business tactics which will direct to the optimistic approach to the advancements of the future wound care & tissue regeneration.
Connect with us to Socialize, Interact, Network, and Collaborate at Wound Care Conference 2022.
… read more
Embedding Predictive Analytics Into Your Wound Care Workflow | Webinar
This webinar, presented by Matt Berezo, Joshua Budman, Abbey Cooper, and Cathy Thomas Hess will discuss how wound care-specific analytics can impact a practice’s workflow. Specifically, the presenters will discuss several clinical analytics models, how they are validated, and how clinicians can use them to improve their clinical and operational outcomes … register
A prospective, randomized, controlled, clinical study on the effectiveness of a single-use negative pressure
wound therapy system, compared to traditional negative pressure wound therapy in the treatment of diabetic ulcers of the lower extremities
A systematic review of multidisciplinary teams to reduce major amputations for patients with DFUs
Multiple single-center studies have reported significant reductions in major amputations among patients with diabetic foot ulcers after initiation of multidisciplinary teams. The purpose of this study was to assess the association between multidisciplinary teams (ie, two or more types of clinicians working together) and the risk of major amputation and to compile descriptions of these diverse teams … read more
THE JWC WUWHS AWARDS ARE OPEN FOR ENTRY
The awards are ‘The Olympics of Wound Care’ and will culminate in an evening which will celebrate excellence in practicing research internally. This will be the first celebration of its kind in the UAE, recognising the fantastic work clinicians in the world and across the region have undertaken. There will be fourteen categories covering a range of wild therapy areas.
Nominations are open to individuals, teams, organisations, societies, companies, charities, and government organisations whose work has made a huge impact based on work carried out over the last year.
The deadline has been extended! You have until the 17th of January to enter … read more
Use of a purified reconstituted bilayer matrix in the management of chronic diabetic foot ulcers
improves patient outcomes vs standard of care: Results of a prospective randomized controlled multi-center clinical trial
The prevalence of diabetes in the United States continues to rise, with the disease now affecting 34.2 million, with an estimated additional 84 million at risk of progressing to diabetes in the coming years.1 The lifetime incidence of DFUs among diabetics is 19% to 34%, with recurrent ulceration reported as approximately 40% at 1 year and 60% at 3 years.2 Management is challenging and associated with substantial socio-economic burden approaching $40 billion annually in direct costs.3 Approximately 70% of DFUs resolve with standard wound care therapies. However, the natural healing cascade is arrested in the remaining 30%, which ultimately become chronic wounds.4, 5 Patients with chronic wounds typically suffer loss of function, recurrent infection, and significant morbidity.6 Amputations are reported in up to 20% of cases with an associated mortality of 70% at 5 years post-amputation … read more
New Level-1 Evidence Finds Geistlich Derma-Gide® Closes Significantly More Diabetic Foot Ulcers
in Appreciably Shorter Time and at Lower Costs
Demonstrates Superiority Compared to Standard of Care in Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial
PRINCETON, N.J.–(BUSINESS WIRE)–The Geistlich Medical business unit of Geistlich Pharma AG, a family owned, Swiss-based global leader in regenerative solutions, is proud to announce the results from their clinical study of the Geistlich Derma-Gide® Advanced Wound Matrix. The study, “Use of a Purified Reconstituted Bilayer Matrix (PRBM) in the Management of Chronic Diabetic Foot Ulcers Improves Patient Outcomes vs Standard of Care – Results of a Prospective Randomized Controlled Multi-Center Clinical Trial,” was peer-reviewed and published in the International Wound Journal – Wiley Online Library … The paper was authored by David G. Armstrong, DPM, MD, PhD; Dennis P. Orgill, MD, PhD; Robert D. Galiano, MD; Paul M. Glat, MD; Jarrod P. Kaufman, MD; Marissa J. Carter, MA, PhD; Lawrence A. DiDomenico, DPM; and Charles M. Zelen, DPM, FACFAS. The paper is now available in the Wiley Online Library at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/iwj.13715 … In a 40-patient, prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter clinical trial comparing a purified reconstituted bilayer matrix (PRBM, Geistlich Derma-Gide) vs. Standard of Care (SOC – collagen alginate dressing), Geistlich Derma-Gide was found to be superior relative to healing rates and time to wound closure … read more
Moisture-Associated Skin Damage | A Historic Step Forward
Every WOC nurse is aware of how often we encounter patients with conditions that are prevalent and clinically relevant but their management falls outside of available guidelines that provide direction for the care of we provide. As a result, we sometimes find ourselves managing disorders supported by scant evidence regarding epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, prevention, and treatment. Fortunately, WOC nurses and there are allies, along with the WOCN Society and its official journal, have a rich history of purposely drawing attention to these disorders, supporting and epidemiologic and clinical research expanding our knowledge of these conditions, and influencing public policies regulating care of these conditions … read more
Journal of Wound Management | October 2021
Welcome to the October 2021 issue of the Journal of Wound Management. Official journal of the European Wound Management Association
This issue of the Journal of Wound Management includes seven original manuscripts. the full issue can be accessed here: Journal of Wound Management. No 22, vol. 3, October 2021
What is the practice and understanding of podiatrists towards patient-centred consultations regarding diabetic foot care?
Background: Patient education is an integral part of diabetes management, yet research shows that increased knowledge alone does not translate into behaviour change. Behaviour change techniques (BCTs) have the potential to increase foot self-care and reduce the incidence of diabetic foot disease. Aims: The aim of this study was to explore the practice and understanding of podiatrists towards patient-centred support versus prescriptive instruction in consultations regarding diabetic foot care. Methods: The study was a cross-sectional design with a web-based questionnaire distributed to members of the College of Podiatry in the UK. Descriptive statistics, conceptual content analysis and the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient were used to analyse the data. Results: Most respondents reported using BCTs in their consultations “often” or “very often” and that they “strongly agree” or “agree” that their consultations were patient-led … read more
Physician Coaching Explained
Did I choose the right path? How can I accomplish my professional goals? Do I have any career options outside of clinical practice? How can I decrease stress? I’m sure many reading this blog have asked one or more of these questions of themselves. The work we do as physicians is unique, and often many do not completely “get it,” except fellow physicians. So, whether one desires to be happier or advance in their current professional path, or seeks an entirely different trajectory, physician coaching could be a vital tool to pursue … Coaching has no definitive definition, but the concepts it entails are empowering. Thinking, listening, and verbalizing … read more
Today is National Human Trafficking Awareness Day
We invite you to join us in spreading awareness about our mission. During the month of January, share your personal message of #WhyIFight on social media using up-to-date and accurate statistics. Included below are a few resources we’ve put together to help you share the message of anti-trafficking.
Skin Manifestations with COVID-19
The Purple Skin and Toes that you are seeing may not be Deep Tissue Pressure Injury
Many reports are occurring concerning areas of purpuric/purple skin and purple toe lesions in patients diagnosed with COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2). Wound care providers are being asked if these skin lesions are forms of Deep Tissue Pressure Injury and/or “skin failure”. Early reports of COVID-19 related skin changes included rashes, acral areas of erythema with vesicles or pustules (pseudo-chilblain), other vesicular eruptions, urticarial lesions, maculopapular eruptions, and livedo or necrosis.1-4 The pattern and presentation of skin manifestations with COVID-19 is more than rashes … read more (PDF)
No Surprises Act – What it Means for Your Practice
Bob Jasak, VP of Coverage and Payment Policy with Hart Health Strategies will present on the recently implemented No Surprises Act and address recently released rules related to it and what it means for your practice.
This content is available to APMA members only. If you are a member, please log in to see the full content
Umbilical Cord Blood Mononuclear Cell Gel in the Treatment of Refractory Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Actual Study Start Date: March 30, 2021
Estimated Primary Completion Date: December 2022
Estimated Study Completion Date: December 2023
Umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells (MNC) may improve the wound repair ability. This study aims to investigate the role of MNC in refractory diabetic foot ulcer by comparing the combination of PRP and MNC with PRP alone … read more
Wound Care Today 2022 conference and exhibition 28-29 March, Marshall Arena, Milton Keynes
Wound Care Today 2022 offers delegates a unique learning platform, FREE of charge, to enhance their delivery of care through clinical updates, personal development, practical learning zones and networking in a friendly, open and above all else safe environment … read more
Periwound health: new definition, new recommendations
I’m delighted to have been invited to present the best practice recommendations on the Prevention and Management of Periwound Skin Complications at this year’s Wounds UK conference (LeBlanc et al, 2020). These recommendations were devised by the International Skin Tear Advisory Panel (ISTAP) based on existing evidence and reviewed externally by 14 health professionals from seven different countries including Canada, UK, Brazil, Republic of Ireland, Switzerland, South Africa, and Indonesia. Consensus statements, of which there are 13, had to reach a level of 80% agreement to be included. The statements are summarised and discussed here for information … read more (PDF)
Custom-Molded Offloading Footwear Effectively Prevents Recurrence and Amputation …
and Lowers Mortality Rates in High-Risk Diabetic Foot Patients: A Multicenter, Prospective Observational Study
Recurrence of high-risk diabetic feet, after wound, healing is a common challenge among diabetic patients. Continuous use of an offloading device significantly prevents recurrence of high-risk diabetic feet, although patient adherence is imperative to ensuring this therapy’s clinical efficacy. In this study, we explored clinical outcomes of patients with a high-risk diabetic foot who had been prescribed with custom-molded offloading footwear under different adherence conditions … read more
Scientists map skin cells that contribute to diabetic foot ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcerations—open sores or wounds that refuse to heal—are a devastating complication affecting more than 15 percent of people with diabetes and resulting in more than 70,000 lower extremity amputations per year in the United States alone. Notably, more than half of patients undergoing amputations due to diabetic foot ulcerations are expected to die within five years—a mortality rate higher than most cancers. Yet, the biological processes at work in diabetic foot ulcerations are poorly understood … read more
Wound Care Research & the Imperative for Funding
Though wound care is a robust evidence-driven field with a broad variety of treatments for chronic wounds that have been proven safe and effective, more research must be done to determine how to best optimize healing for painful, life-threatening wounds. With the anticipated rise in chronic wounds, the Federal government needs to provide more funding for wound care research so patients can get back on their feet, literally, as quickly as possible. The longer a patient suffers from a chronic wound, the more likely they are to contract potentially fatal infections … read more
Molecular Biomarkers of Oxygen Therapy in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Alisha R. Oropallo 1,*, Thomas E. Serena 2, David G. Armstrong 3 and Mark Q. Niederauer 4
1 Comprehensive Wound Healing Center and Hyperbarics, Department of Vascular Surgery, Zucker School of Medicine Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, NY 11549, USA
2 Serena Group Research Foundation, Cambridge, MA 02140, USA; serena@serenagroups.com
3 Limb Preservation Program, Department of Surgery, Keck School of Medicine of University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90033, USA; armstrong@usa.net
4 EO2 Concepts, San Antonio, TX 78249, USA; m.niederauer@eo2.com
* Correspondence: aoropallo@northwell.edu; Tel.: +1-516-233-3780
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) and topical oxygen therapy (TOT) including continuous diffuse oxygen therapy (CDOT) are often utilized to enhance wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcerations. High pressure pure oxygen assists in the oxygenation of hypoxic wounds to increase perfusion. Although oxygen therapy provides wound healing benefits to some patients with diabetic foot ulcers, it is currently performed from clinical examination and imaging. Data suggest that oxygen therapy promotes wound healing via angiogenesis, the creation of new blood vessels. Molecular biomarkers relating to tissue inflammation, repair, and healing have been identified. Predictive biomarkers can be used to identify patients who will most likely benefit from this specialized treatment. In diabetic foot ulcerations, specifically, certain biomarkers have been linked to factors involving angiogenesis and inflammation, two crucial aspects of wound healing. In this review, the mechanism of how oxygen works in wound healing on a physiological basis, such as cell metabolism and growth factor signaling transduction is detailed. Additionally, observable clinical … read more
Diabetes-Related Amputations Kept at Bay During Pandemic in Canada
Shift to virtual care and prioritization of certain procedures key, researchers say
Despite delays in screening and care during the COVID-19 pandemic, there wasn’t a spike in diabetes-related foot amputations, a Canadian study found … In an analysis of nearly 1.5 million adults with diabetes living in Ontario, rates for nearly all diabetes-related services took quite a nosedive in 2020, noted Charles de Mestral, MDCM, PhD, of St. Michael’s Hospital in Toronto, and colleagues … For starters, comprehensive in-person diabetes care assessment immediately dropped down from March to May, averaging only 28% of the 2019 level, they reported in JAMA Network Open … read more
Battling ‘the Pandemic within the Pandemic’
RedDress Addresses Wound Care Challenges in the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ponte Vedra Beach, FL, Jan. 05, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Patients suffering with non-healing wounds continue to experience challenges accessing treatment two years after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic … As new variants of COVID-19 emerge, wound care providers across the United States are reporting a more than 50 percent increase in the severity of wounds. If left unaddressed, these non-healing wounds can have severe consequences including infection, sepsis, amputation, and even death. RedDress is battling this compounding issue researchers have dubbed “the pandemic within the pandemic” utilizing cutting-edge technology … read more
Anastassia Johnson Tapped as Senior Manager at The Wound Pros
LOS ANGELES, Jan. 6, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — The Wound Pros (https://thewoundpros.com/) today announced Anastassia Johnson as a Senior Manager at the company. The Wound Pros specializes in the treatment and management of chronic non-healing wounds at long-term care facilities. It also partners with facilities to provide advanced wound care dressings for acute and chronic wounds as well as education for staff … Anastassia Johnson joined The Wound Pros in December 2020. She holds a Diploma and an Associate of Science Degree in Computer Systems Technology and a Bachelor of Science Degree in Information and Communication Technology. As senior manager at The Wound Pros, she brings over a decade of experience in project management, administration, customer support, quality assurance, training, and analytical decision-making … read more
Can we go from scarface to scarless?
Researchers examined skin regeneration over two years in various body parts of the adult newt, Cynops pyrrhogaster. Their wounds were very quickly healed over several days without prolonged inflammation. Because of this rapid healing, granulation/dermal fibrosis, and therefore scarring, did not occur. The skin was able to fully regenerate. These findings provide evidence that this newt species may be an ideal model system to study and prevent scar formation in human skin … read more
Newly developed injectable, adhesive surgical gel to prevent scar tissue
Up to 90% of patients who undergo open abdominal or pelvic surgery develop postoperative adhesions, or scar tissue. Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgical approaches can reduce the severity of the adhesions, but the scar tissue still forms. The cellular response to injury—even intentional injury, such as surgery to repair a problem—results in a cascade of molecules pouring to the site to heal the tissue. But the molecules, working quickly to close the wound, often go too far and bind the wound to nearby healthy tissue. Depending on the location, the resulting scar tissue can cause chronic pain, bowel obstruction and even death … read more
Wound Dehiscence After Achilles Tendon Trauma and Repair
Treatment With Ultraportable Negative Pressure Wound Therapy and Compression Therapy
Achilles tendon rupture is a common injury requiring surgical repair. Re-ruptures, infections, delayed wound healing, and hematomas have been reported postoperatively. Objective. This case series described the use of ultraportable negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) and compression bandaging following postoperative dehiscence of Achilles tendon repair. Materials and Methods. Retrospective records were reviewed to identify patients who underwent wound management for Achilles tendon dehiscence between January 2014 and January 2018. Patient demographics, wound size at first and last visit, number of visits, and previous treatment data were extracted. Wound management included wound irrigation, surgical debridement, and application of silver dressings, as needed. Therapy was transitioned to ultraportable NPWT with twice-weekly dressing changes. When possible, patients with an ankle-brachial index greater than 0.8 received multilayer, multicomponent compression … read more
Mechanical Negative Pressure Wound Therapy: Real-World Effectiveness in Challenging Patient Presentations
When used for wound management, negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) delivers subatmospheric pressure at the wound site, exerting multiple beneficial effects, including microstrain, macrostrain, edema management, granulation tissue formation, drainage management, and wound stabilization. Comparative effectiveness research has demonstrated similar wound healing and adverse event outcomes between traditional NPWT (tNPWT) and mechanical NPWT (mNPWT). Therefore, considerations for patient selection for mNPWT vs tNPWT are in alignment with current recommendations, including therapeutic goals, wound-related factors, patient satisfaction, quality of life, care setting, economic-related factors, and product design. Case Reports. The 3 complex patient cases in the present report describe the routine use of mNPWT between December 18, 2020, and June 7, 2021 … read more
Reflections on the Extraordinary Life of Norma N. Gill-Thompson, ET
In June 1986, I was a relatively new certified enterostomal therapy (ET) nurse. I was standing in line for an industry-sponsored lunch at my first International Association of Enterostomal Therapy (now the Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nurses Society) meeting at Caesar’s Palace in Las Vegas, NV, when someone around me said, “Look, there’s Norma Gill!” Sure enough, she was a few spots ahead of me in line. I got so excited—it felt like I was in the presence of Florence Nightingale! I went over and introduced myself as a new ET nurse, saying how honored I was to meet her. In her down-home, humble way, she threw her arm around my shoulder and said, “Honey, come sit next to me at lunch.” So began my long and special relationship with this extraordinary pioneer of ET/wound ostomy continence … read more
INTERNATIONAL ALLIANCE OF WOUND CARE SCHOLARSHIP FOUNDATION AND HEALIANT …
Announces partnership to award wound care scholarships
The International Alliance of Wound Care Scholarship Foundation® is proud to announce a partnership with Healiant Training Solutions™ to bring hundreds of wound care scholarships to the nurse community. It is the purpose of IAWCSF® to provide financial aid in the form of scholarships to those individuals pursuing an education and certification in wound care. Healiant Training Solutions™ will match up to 100 scholarships that will be donated by sponsors from the wound care product community to be awarded to deserving healthcare providers. Accordingly, the funds will be used specifically for advanced education and subsequent certification in wound care. Our passion is wound care and our mission is to help decrease the rising costs and loss of limbs and life throughout the world. We cannot accomplish this without the help from benefactors such has Healiant. “Partnering with Healiant Training Solutions is just the beginning of what is to come for the future of wound care education and certification,” said Angela Weathersby, Ph.D., Executive Director of IAWCSF … read more
DIAGNOSTIC ACCURACY OF POINT-OF-CARE FLUORESCENCE IMAGING FOR THE DETECTION OF ….
bacterial burden in wounds
This excellent work from Le and coworkers strongly suggests that using a point of care diagnostic device (Moleculight) can identify elevated bacterial load and influence medical decision making … High bacterial load contributes to chronicity of wounds and is diagnosed based on assessment of clinical signs and symptoms (CSS) of infection, but these characteristics are poor predictors of bacterial burden. Point-of-care fluorescence imaging (FL) can improve identification of wounds with high bacterial burden (>104 CFU/g). FL detects bacteria, whether planktonic or in biofilm, but does not distinguish between the two … read more
The Role of Internal Offloading and Rotational Flap Closure of Charcot Arthropathy-Related Midfoot Ulcers
The patient with Charcot foot is seldom studied for their body’s ability to heal an open diabetic foot ulcer. These patients are usually excluded from all prospective randomized trials. Over a 5-year period, patients with Charcot arthropathy (CA) have been shown to have a 63% chance of developing a CA foot ulcer (CAFU), and those with a foot ulcer have a 37% mortality within the same timeframe.¹ To the authors’ knowledge, a correlation between healing a CAFU and mortality reduction has not been indicated. It is well-known that healing such ulcers improves quality of life and reduces the chance of hospitalization. The primary modality to heal such an ulcer is maintaining or creating a plantar grade foot.1 In a retrospective study of 106 patients with CAFU, Schmidt and Holmes² reported that 44% of the patients’ ulcers had healed, 11% had received a minor amputation, and only 9% had undergone major amputation … read more

Paracrine to Present at Biotech Showcase™ 2022
Paracrine, Inc. announced today that it is presenting virtually at the Biotech Showcase™ 2022 conference with an online presentation which is now accessible. This year, registered attendees to Biotech Showcase can access Paracrine’s recorded company presentation on-demand.
Paracrine is an emerging biotechnology company developing a first-in-class, device-based, autologous cell therapy. Paracrine’s cell therapy platform bears the promise of cost-effectively addressing common, underlying pathology of several debilitating chronic diseases due to its unique multi-prong mechanisms of action. The company has an FDA approved IDE for the pivotal ASCEND Trial in patients with non-healing diabetic foot ulcers, the STAR II pivotal trial IDE is currently under review at FDA for hand dysfunction due to scleroderma and an IDE is being prepared for submission later this year for the ATHENA III trial in patients with chronic heart failure … read more
Safe and effective wound healing preparation reaches Clinical Phase II
APO-2 (Aposec) is a secretome-based trial preparation derived from stressed peripheral blood mononuclear cells. APO-2 was shown to be safe and effective in a multinational Phase I study in patients with diabetic foot ulcers (non-healing foot ulcers). The Data Safety Monitoring Board has therefore recommended continuation into a Phase II clinical trial. This represents a major success for the wound healing preparation developed at MedUni Vienna … read more
The Disconnect with Diabetic Foot Ulcers | Video
During the last 10 years, the United States FDA has approved only a few new treatments for diabetic foot ulcer (DFU). Amarex’s Kazem Kazempour, PhD, believes careful study design is required to demonstrate efficacy of new wound healing treatments. In this video, Kazempour explains the disconnect between the FDA’s definition of wound healing and the reality of DFUs … watch
New Technology in Identifying Wound Infections Helping to Deprescribe Antibiotics with Martha Kelso
In this podcast, Amy Stewart, MSN, RN, DNS-MT, QCP-MT, RAC-MT, RAC-MTA, vice president of education and certification strategy for AAPACN (American Association of Post-Acute Care Nursing) and Martha Kelso, RN, LNC, HBOT, CEO of Wound Care Plus, a mobile wound care provider, discuss new point-of-care technology (MolecuLight i:X) to help identify wound infections and the impact this has on deprescribing antibiotics
Adding Wound Care Specialist to Proning Team Reduces Pressure Injury Risks
Newswise — The addition of a certified wound and skin care nurse to a multiprofessional prone-positioning team at Penn Medicine Princeton Health significantly reduced the odds of patients with COVID-19 developing pressure injuries, according to a study published in American Journal of Critical Care … The development of healthcare-associated pressure injuries is a significant complication of placing patients prone, and prolonged prone positioning for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is associated with higher rates of new pressure injuries, specifically on the face, cheekbones and thorax and over bony prominences … Although many studies have reported the development of pressure injuries in patients with ARDS who are placed prone for prolonged periods, “Pressure Injury Outcomes of a Prone-Positioning Protocol in Patients with COVID and ARDS” is one of the first to explore specific treatment-related strategies for preventing pressure injuries … read more
Prioritizing Diabetic Foot Care During Pandemic Pays Off
The COVID-19 pandemic was not associated with increased limb loss among people with diabetes in Ontario, Canada, new research suggests.
The findings, which contrast with those from several other locales worldwide, were published online January 5 in JAMA Network Open by Charles de Mestral, MDCM, PhD, of the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St. Michael’s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, and colleagues.
Despite limited in-person visits with physicians, hospital avoidance, and non-emergency surgical procedure restrictions, excess leg amputations were not seen among people with diabetes during the first 11 months of the COVID-19 pandemic. The authors postulate several reasons for this, including prioritization of foot care … read more
UK MP highlights efforts to improve care landscape for lower limb wound patients
This country is facing a crisis in vascular disease made worse by the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, there is a potential answer in the recommendations of the National Wound Care Strategy Programme, being implemented in places like Hull University Teaching Hospitals Trust, but for it to succeed it needs the full commitment and backing of government … read more
Foot Sparing Amputations in Diabetics
These techniques can save limbs and lives.
The recent global SarsCoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic significantly disrupted the delivery of healthcare across many disciplines and the effect of the pandemic has had an especially detrimental effect on people with diabetes-related foot complications, resulting in more amputations. Major level lower extremity amputation is one of the most feared complications of diabetes. One study found that patients with diabetes and lower extremity complications were more in fear of major amputation than death.1 In many cases, major level amputations can result in loss of function, decline in quality of life, and even death … read more
Hope for Health and Healing in 2022
One year ago, this page contained a message of hope and a wish that 2021 would bring an increased appreciation for the science we desperately need.1 That wish remains as heartfelt now as it was then because the end of this pandemic remains elusive and because the millions of health care providers who have worked behind a mask to provide care deserve all the help they can get. When we think about science, our minds usually ponder new technologies, medications, or expansive, expensive, or complicated treatments or interventions. However, some of the most critical and enduring innovations to help us help patients are neither high-tech nor fancy and expensive … read more
Welcome to APWH: The Academy of Physicians in Wound Healing
APWH, the Academy of Physicians in Wound Healing, originally formed in 2011 specifically for physicians (MD,DO,DPM) now includes advanced practice providers (Nurse Practitioners-NP and Physician Assistants-PA). The organization provides information and support in three subject areas: clinical and operations-focused education, compensation advocacy, and legislative action on healthcare issues. Additionally, the organization provides this information specifically to and for the benefit of providers that are responsible for diagnosis and management of patient care which defines the demographic of our membership … read more
3D Printed Skin? Potential New Treatment For Chronic Wounds
Wounds come in many shapes and sizes. Some are small and heal quickly, causing few problems. Others are larger and slower to heal. Deep wounds that take especially long to go through the normal healing process, called chronic wounds, are of particular concern; these have a tendency to reopen and are often accompanied by infection and, eventually, scarring. Add to this the fact that chronic wounds are difficult to treat with currently available therapies, and you end up with a serious healthcare challenge … read more
Combined Regenerative Approach for a Complex Lower Extremity Wound: A Case Report
More than 400 million patients worldwide are affected by diabetes; over their lifetime, at least 25% will develop foot ulcers that often result in high rates of nonhealing wounds and amputation. The authors present the case of a 43-year-old female patient with multiple comorbidities who presented with a large (8 cm x 4 cm), noninfected, hindfoot plantar ulcer that extended down to the bone and calcaneus. Over 2 weeks, the patient was successfully treated using a combination of an acellular dermal matrix, nanofat grafting, and negative pressure wound therapy, lessening the effects of the ulcer on the patient’s quality of life and achieving limb salvage … read more
The Scientist: Robert Kirsner, MD, PhD
Dr. Kirsner is Chairman and the endowed Harvey Blank Professor in the Dr. Phillip Frost Dermatology in the Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Surgery at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. He is Chief of Dermatology at the University of Miami Hospital and Clinics and Jackson Memorial Hospital and directs the University of Miami Hospital Wound Center. Dr. Kirsner received his undergraduate degree from Texas A&M University, his medical degree from the University of Miami and a PhD in epidemiology from the University of Miami, after he completed his clinical training. His clinical training included internal medicine, a clinical and research fellowship in wound healing and dermatology at the University of Miami … listen
Retrospective Analysis Using Viable Placental Membrane Allografts in Chronic Wounds
Introduction. Viable placental membrane (vPM) has been shown to decrease time to healing, adverse wound events, and wound-related infections. Wound research exclusion criteria commonly exclude wound types other than diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers (VLUs), comorbidities including peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM), and wounds with exposed bone or tendon. Objective. This retrospective research study evaluated the clinical use and outcomes of the vPM with living mesenchymal stem cells used in chronic wound management in the community hospital outpatient department setting with the goal of comparing real-world use and outcomes of the product with use and outcomes described in the chronic wound literature … read more
Silver in Wound Care: Clinical Outcomes | Webinar
Since as early as ancient (1850 BCE) Egypt, silver has been used in wound care owing to its antimicrobial properties. Although its popularity dwindled in 1928 with the discovery of penicillin, medicinal silver has recaptured wound care professionals’ attention with the rise of antimicrobial-resistant microbes. In modern dressings, the incorporation of silver nanoparticles decreases the risk of infection while allowing the dressing to continue the facilitation of a moist wound bed environment. In nanoparticle form, silver deconstructs the cell membrane of microbes, passes into their cell body, and causes internal damage … Register
All Edema Is Lymphedema: Progressing Lymphedema and Wound Management to an Integrated Model of Care
Chronic edema affects millions of people in the United States and worldwide. Edema can result from a variety of diseases, trauma, medications, and other contributing factors; however, all edema is related to lymphatic fluid dysregulation. Additionally, lymphatic impairment and integumentary dysfunction are interrelated, leading to complex clinical presentations that require an integrated medical model of care to maximize outcomes. PURPOSE: This narrative review article will highlight the current evidence that details lymphatic physiology, fluid regulation by the endothelial glycocalyx layer, and the interconnectedness of the vascular and integumentary systems leading to a paradigm shift in our understanding of edema, lymphedema, and chronic wounds. Traditional pedagogy remains siloed with respect to the body systems, whereas current evidence indicates a certain interdependence, particularly between and among the venous, lymphatic, and integumentary systems … read more
Is Weight Loss or Physical Activity More Important for Preventing Type 2 Diabetes?
Ever since the US Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) multicenter trial was completed nearly two decades ago (1), we have known that it is possible to prevent, or at least delay, prediabetes (an insulin–resistant state) from progressing into full-blown type 2 diabetes. Why? Diabetes risk was reduced by 58% in the “intensive lifestyle“ (ILS) participant group and by 31% in the metformin (an oral glucose-lowering medication) participants compared to no intervention (“placebo“ group). For 60 years or older participants, lifestyle changes worked much better to prevent diabetes than taking metformin … read more
Moisture Management in Neonatal Pressure Injury Prevention: A Survey
Neonates are widely known as a vulnerable patient population—especially critically ill and premature infants. This vulnerability has limited clinicians’ knowledge of moisture management products in the neonatal population that prevent pressure injuries. Recently, a survey of neonatal nurses from across the United States was conducted to find out what is being used for moisture management … This study was designed as a cross-sectional survey with a convenience sample of neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) nurses. A survey link was distributed electronically through websites, listservs, discussion boards, and newsletters to the National Association of Neonatal Nurses (NANN), the Academy of Neonatal Nurses (AAN), and WoundSource. There were 252 NICU nurses who completed the survey … read more
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer in France
Platelet-Rich Plasma vs Standard of Care
Introduction: Diabetic chronic foot ulcers (DFU) lead to pain, reduced quality of life and represent a severe economic burden for patients and health systems. The clinical results of PRP effectiveness in the treatment of DFU are promising; on the other hand, the costs associated with treating DFUs with PRP are higher than those using standard therapy. Therefore, this study aims to determine the cost-effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy compared to standard therapy from the French healthcare system perspective.
Methods: A cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) was performed using a decision Markov model with a cohort of patients with chronic DFU (duration of > 3 weeks) with high orthopaedic risk and with ulcers graded 3A according to University of Texas classification … read more
Chronic Wounds: Innovations in Diagnostics and Therapeutics
A major global health issue is the existence of chronic wounds. Appropriate diagnosis and treatment is essential to promote wound healing and prevent further complications. Traditional methods for treatment and diagnosis of chronic wounds have shown to be of limited effectiveness. Therefore, there is a need for the development of diagnostic and therapeutic innovations in chronic wound care.
Objective: This mini-review aims to provide insight in the current knowledge of the wound healing process and the deficiencies encountered in chronic wounds, which provides a basis for the development of innovations in chronic wound care. Furthermore, promising diagnostic and therapeutic innovations will be highlighted … read more
Wound hygiene survey: awareness, implementation, barriers and outcomes
In light of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has resulted in changes to caseload management, access to training and education, and other additional pressures, a survey was developed to understand current awareness and implementation of the wound hygiene concept into practice one year on from its dissemination. Barriers to implementation and outcomes were also surveyed … read more
Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
at Siriraj Hospital – Thailand’s Largest National Tertiary Referral Center
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is one of the most common chronic complications of diabetes mellitus (DM). DR is characterized by gradually progressive alterations in the retinal microvasculature, leading to areas of retinal non-perfusion, increased vascular permeability, and pathologic intraocular proliferation of retinal vessels. The complications are associated with macular edema, and uncontrolled neovascularization, termed proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), resulting in severe and permanent vision loss if not treated in a timely and appropriate manner. DR is the leading cause of blindness among working-aged adults worldwide. However, with appropriate medical and ophthalmologic care, more than 90% of vision loss from PDR can be prevented.1 Unfortunately, in many cases, presenting symptoms may go unnoticed or unheeded and the damage caused by the disease becomes irreparable … By 2045, it is estimated that approximately 700 million people worldwide will have diabetes2 and that approximately 103 millions of those will have DR … read more
Theories of Skin Aging and Wound Care
Theories of Aging
One theory of aging is the free radical theory and mitochondrial DNA damage. Mitochondria are organelles within cells that are responsible for respiration, which promotes energy production using oxygen and simple sugars to produce adenosine triphosphate, the article explains. The DNA is located in a place with little protection and cannot repair itself which can lead to aging skin. The free radicals are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons that initiate a damaging chain reaction resulting in DNA crosslinking that leads to aging and may contribute to cancer genesis, the article continues … read more
Expanding horizons to upskill wound practice and research
With our horizons limited by Covid-related travel restrictions, it is more important than ever to experience and learn about our multicultural world through reading about wound-related research and practice in other jurisdictions and countries. Two such articles provide this important international insight and are included in this issue of the journal. The first by Obilor and colleagues describes the assessment of nurses’ knowledge, attitude and competence in wound assessment in a tertiary healthcare facility in southwest Nigeria. Here they found that many of the nurses surveyed were lacking in wound assessment competence, suggesting an important continuing need for education and skills development. The second internationally focused paper, by Yigit and Tas, describes the demography and injuries related to chemical burns in the southeastern Anatolia region of Turkey. The burn centre at the core of this study serves 10 million people in Diyarbakir and the surrounding 300km and is the only centre with an intensive care unit in southeast Turkey, a very different experience from what we would see in an Australian context … read more

AAN Updates Painful Diabetic Neuropathy Guidance
Four medication classes have been shown to help, plus topical and other treatments Gabapentinoids, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants, and sodium channel blockers were more likely than placebo to improve diabetic neuropathy pain, according to a new practice guideline from the American Academy of Neurology (AAN). Those classes typically had comparable effect sizes…
Therapy Delayed is Therapy Denied: A Case Report of Melanoma Misdiagnosed as Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Malignant melanoma is a deadly form of skin cancer, and prompt diagnosis is a key factor in providing adequate, life-saving therapy. A 75-year-old man, with long-standing type 2 diabetes mellitus, presented with a 2- to 3-year history of right heel ulcer. He had received various therapies for a diagnosis of diabetic foot ulcer, to no avail. Physical examination showed a black, fungating ulcerated lesion on his right heel, with minimal bleeding. No inguinal lymphadenopathy was palpated. A biopsy was done, which revealed BRAF-negative malignant melanoma, with a vertical growth phase, Breslow 3.1 mm, ulceration, 11 mitoses/mm2, Clark level IV, no lymphatic or vascular invasion observed. Right inguinal lymph node sampling suggested no involvement, but PET-CT suggested pulmonary, right inguinal lymph node and bone involvement. The patient was referred to the oncologists. Written informed consent for publication was given by the patient. Diabetic foot ulcers are a frequently encountered, but serious complication of diabetes mellitus. Delayed healing is often seen, despite adequate therapy. The differential diagnosis of diabetic foot ulcers is vast and includes neoplasia. When a foot ulcer fails to heal, other differential diagnoses must be considered, in order for the patient to receive adequate therapy. Here specialist consultations, including dermatology consultations, could improve chances of delivering the right therapy promptly. This is a factor underlying the emphasis on a multidisciplinary approach to foot ulcer therapy. Our presentation – reported according to the CARE guidelines – also illustrates the fact that failure to reach a timely diagnosis may deny the patient the opportunity to receive adequate treatment … read more
Advances in Skin & Wound Care | January 2022 – Volume 35 – Issue 1
BIDE-NADEP-PWGDF collaborates with Ferozsons Laboratories to end avoidable foot amputations
The Country wide health initiative “Fast Track Pathway” was launched at a simple but dignified ceremony held at a local Hotel in Lahore on Dec 20, 2021 … An MOU signing ceremony was held between BIDE and Ferozsons Laboratories Limited for the implementation of this project … Addressing the ceremony, the Project Director, Dr ZahidMiyan, from Baqai Institute of Diabetology and Endocrinology, told that; Foot involvement is one of the major and devastating complications of diabetes. It is estimated that approximately 3,000,000 people with diabetes in Pakistan have foot ulcers while approximately 300,000 people loose their limbs to diabetes, every year, he told further … The huge burden of diabetic foot and the high frequency of avoidable amputations strongly necessitate consolidated and unified efforts. Dr Zahid highly appreciated the leading role of Prof Abdul Basit, the Director of BIDE, who always emphasized on nationwide improvement in diabetic foot care. In that context the “Fast Track pathway” has been launched in Pakistan, Dr Zahid declared … read more
International Alliance of Wound Care Scholarship Foundation® & Healiant™️
to award hundreds of Wound Care Scholarships
Healiant Training Solutions™ and IAWCSF® partner to make 100+ scholarships available to clinicians who desire to become wound care trained and certified.
TAMPA, FL, UNITED STATES, December 21, 2021 /EINPresswire.com/ — Healiant Training Solutions™ and the International Alliance of Wound Care Scholarship Foundation® (IAWCSF®) come together to make scholarships available to passionate clinicians who desire to become wound care trained and certified. Healiant Training Solutions™ will match up to 100 scholarships that will be donated by sponsors from the wound care product community to be awarded to deserving healthcare providers … read more
New Screening Tool to Prevent Mortality from Complications of Foot Ulcers
Individuals with diabetes have around a 34% chance of developing a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU). This debilitating condition may lead to severe complications, including hospitalization, infection, and amputation. A recent study reported grim data on DFU, finding a five-year survival rate of just 29%. Any delay in treatment has been associated with worsened clinical outcomes. The researchers of this study were interested in identifying risk factors for DFU in patients with T2D. Early detection might one day reduce the number of diabetic foot ulcers … read more
Foot ulceration associated with increased risk for amputation or death
Using the Scottish Care Information – Diabetes database, Graham Leese (Ninewells Hospital, Dundee, UK) and co-authors observed that out of 23,395 individuals with type 1 diabetes and 210,064 with type 2 diabetes included in the study, a total of 13,093 had a previous foot ulceration and among these, 34.3% developed a further foot ulcer during the follow‑up period (2012–2017). In addition, a total of 9023 people developed a first ulcer during follow-up… read more
Biomechanical and musculoskeletal changes after flexor tenotomy to reduce the risk of diabetic
neuropathic toe ulcer recurrence
OBJECTIVE: To assess the effect of flexor tenotomy in patients with diabetes on barefoot plantar pressure, toe joint angles and ulcer recurrence during patient follow-up.
METHODS: Patients with a history of ulceration on the toe apex were included. They underwent minimally-invasive needle flexor tenotomy by an experienced musculoskeletal surgeon. Dynamic barefoot plantar pressure measurements and static weight-bearing radiographs were taken before and 2-4 weeks after the procedure … read more
History of Foot Ulcer & Risk for Limb Amputation or Death
Since care for diabetic foot ulcers is delivered by a wide range of healthcare professionals, from nurses working in primary care to specialized diabetes foot clinics, collecting population-based data on diabetic foot ulceration is notoriously difficult. Furthermore, epidemiological data on populations with diabetic foot ulceration collected from selected subpopulations is open to bias, hence the importance of unselected population-based data … To address this issue, my colleagues and I conducted a national, population-based, cohort study of people with diabetes, with the aim of describing the incidence of foot ulceration and amputation-free survival associated with foot ulceration status … read more
In Vitro and In Vivo Studies on the Antibacterial Activity and Safety
of a New Antimicrobial Peptide Dermaseptin-AC
Antimicrobial resistance has been an increasing public health threat in recent years. Antimicrobial peptides are considered as potential drugs against drug-resistant bacteria because they are mainly broad-spectrum and are unlikely to cause resistance. In this study, a novel peptide was obtained from the skin secretion of Agalychnis callidryas using the “shotgun” cloning method. The amino acid sequence, molecular weight, and secondary structure of Dermaseptin-AC were determined … The skin safety of Dermaseptin-AC was evaluated on wounds on the back skin of a rat … it was applied to skin wounds. Chronic wounds are often accompanied by high bacterial burdens and, at the same time, antimicrobial resistance is more likely to occur during repeated infections and treatments. Therefore, developing Dermaseptin-AC to treat chronic wound infection may be an … read more
Technology And Innovation Power Wound Care’s Ongoing Evolution – Marketplace Experts
Like all nurses who specialize in wound care, I have seen many changes in our profession over the years. Perhaps most significant are the influences that breakthrough technologies and products have had on our profession … In order to fully appreciate its scope, we must recall recent history. Not so long ago, a non-healing diabetic foot ulcer often resulted in complications and possible amputation. In addition, to follow the healing process of a wound, the measurements had to be taken manually with rulers, a subjective measurement process that is prone to variation between institutions and even individuals … read more
A year of international growth and product advancement
KEELE, England, Dec. 15, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Biocomposites, an international medical devices company that engineers, manufactures and markets world leading products for use in infection management in bone and soft tissue, is pleased to provide the following business update … Enhanced approval for STIMULAN in Canada and Saudi Arabia … In 2021, STIMULAN® products gained a new approval in Canada for mixing with antibiotics: vancomycin, gentamicin and tobramycin, for use in treating bacterial infection in soft tissue surrounding bone. This was followed by a new approval in Saudi Arabia for STIMULAN® to be mixed with antibiotics for use in bone and soft tissue … STIMULAN® is the only calcium matrix antibiotic carrier with an EU approval for use in bone and soft tissue and offers surgeons the flexibility to apply broad spectrum ‘off-the-shelf’ antibiotics at concentrations that will support their patient-specific treatment plans – dramatically improving patient outcomes and redefining standard of care … read more
BioPhotonics Preview – March/April 2022
The measurement of oxygen levels in the blood commonly referred to as blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) is a critical medical diagnostic. The condition of below normal levels (<95%) is termed hypoxemia and is associated with patients who have asthma, heart disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease … SpO2 levels are also of interest for brain and other surgical procedures (i.e. flap surgery), peripheral vascular disease (PVD), tumor development, the healing of wounds from conditions such as diabetic foot ulcer, systemic rheumatic disease, neuropathy and sepsis2–5. Pulse oximeters, a simple optical device that measures the ratios of two critical band-passes of light through an appendage … read more
Novel therapeutic targets for diabetes-related wounds: An update on pre-clinical and clinical research
Diabetes-related wounds, particularly diabetes-related foot ulceration, is mainly caused by lack of foot sensation and high plantar tissue stress secondary to peripheral neuropathy, ischemia secondary to peripheral artery disease and dysfunctional wound healing. Current management of diabetes-related wounds involves the offloading high foot pressures and the treatment of ischemia through revascularisation. Despite these treatments, the global burden of diabetes-related wounds is growing, and thus novel therapies are needed. The normal wound healing process is a coordinated remodelling process orchestrated by fibroblasts, endothelial cells, phagocytes and platelets, controlled by an array of growth factors. In diabetes-related wounds this coordinated process is dysfunctional. Past animal model and human research suggests that prolonged wound inflammation, failure to adequately correct ischemia and impaired wound maturation are key therapeutic targets to improve diabetes-related wound healing … read more
Extracellular Vesicles from HIF-1α-Overexpressing Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
Restore Diabetic Wounds Through Accelerated Fibroblast Proliferation and Migration
Inhibition of cellular adaptation to hypoxia can cause persistent inflammation, thereby increasing tissue damage and complicating wound healing in diabetes patients. Regulating cellular adaptation to hypoxic environments can help in effective wound repair. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α is a key regulator of cell hypoxia. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) regulate wound repair. This study investigated the mechanism of HIF-1α overexpression in adipose-derived stem cell extracellular vesicles (ADSCs-hEVs) in the repair of diabetic wounds … read more
Evolving Survivor: Wound Care From the Patient’s Perspective | Podcast
Having survived flesh eating bacteria, septic episodes, and pulmonary embolisms, one patient discusses his experience as an “evolving survivor,” explaining how hyperbaric oxygen therapy and integrative care helped him … listen
What Is All This Swelling About? An Update on Lymphedema for Healthcare Providers and Patients
Swelling or edema is common. It can result from certain diseases, infections, conditions, trauma, or injury, and even medication.1 Typically, the swelling goes away on its own. Sometimes, however, the swelling continues and can worsen over time … This article serves as a guide to help patients and caregivers understand what swelling is and when medical help is necessary. We will educate patients and their caregivers about lymphedema including common risks and contributing factors. This article will also provide general treatment recommendations for lymphedema and provide general and disease-specific resources for individuals affected by lymphedema … read more
Get Up to Speed With Recent Wound Care Policy Updates
The Fall is a busy time in the policy world, as government agencies such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) finalize policies for the fiscal year ahead such as the CY 2022 Physician Fee Schedule and more. Get up to speed on the latest payment and coverage policies that can impact wound care with this update from the Alliance of Wound Care Stakeholders … Real world evidence: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is opening up the door to more real-world evidence (RWE) in 2022 and beyond with two new draft guidance documents issued: Real-World Data: Assessing Electronic Health Records and Medical Claims Data To Support … read more
Frank & Lizzie Show: Episode 010, Dr. Mark Melin, Wound Week 2022
Frank & Lizzie host Dr. Mark Melin on this episode as they discuss Dr. Melin’s sessions during Wound Week 2022. This includes their courses Diagnosing & Treating Chronic Venous Insufficiency (Friday, February 25 2:45 PM – 3:45 PM EST) and Management of Lower Extremity Edema (Saturday, February 26 2:30 PM – 3:30 PM EST). To find out more information about Wound Week 2022 in Philadelphia February 24-27, go to WoundWeek.com! We hope to see you there.
From baker to wound care innovator – my HS story
Suzanne Moloney, the founder of HidraWear, first experienced the painful symptoms of Hidradenitis suppurativa as a young teen … At the time was a Suzanne a typical teenager who loved sports and running. She kept quiet about what was happening – she was embarrassed, as any 13-year-old would be. By her mid-teens, the lumps were bigger and harder to manage. Suzanne finally mustered up the courage to speak to a GP when they became infected … Suzanne was prescribed antibiotics every time new lumps flared up, which helped but didn’t stop the painful growths coming back. This cycle continued for years as more lumps appeared under her arms and at the tops of her legs … read more
sanaFactur – An Innovative Player in Wound Care Launches a ….
Novel Food Supplement to Support Tissue Regeneration
GRÄFELFING, Germany–(BUSINESS WIRE)– suppliDerm, a new brand by sanaFactur, represents a science based range of food supplements supporting tissue regeneration the immune system, and energy metabolism. All of these are critical for wound patients. ‘Our team of pharmacists, biochemists and nutritional specialists have combined carefully selected micro- and macro nutrients to support the body’s regenerative processes. Many older people and wound patients are suffering from nutritional deficiencies, also impacting their wound healing.’ says Dr. Alexander Maassen, CEO Scientific. A patent has been filed.
sanaFactur is an established brand in Wound Care, currently focusing on antimicrobial products. ‘suppliDerm will perfectly complement our existing portfolio, enabling patients to actively support wound therapy by supporting their regenerative metabolism. We do look forward to launch our food supplement with several flavors internationally, like the US and UK as leading markets for wound care.’ says Olaf Ohm CEO Commercial … read more
A 57-Year-Old Man with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and a Chronic Foot Ulcer Successfully Managed
with a Remote Patient-Facing Wound Care Smartphone Application
BACKGROUND Wounds affect millions of people world-wide, with care being costly and difficult to deliver remotely. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic highlights the urgent need for telehealth solutions to play a larger role as part of remote care strategies for patient monitoring and care. We describe our findings on the use of a patient-facing wound care app (Swift Patient Connect App, Swift Medical, Canada) as an innovative solution in remote wound assessment and management of a diabetic patient’s wound. CASE REPORT In February 2020, a 57-year-old man with type I diabetes and peripheral arterial disease presented with osteomyelitis in the left foot at the fifth metatarsal, arising from a chronic ulcer … read more
Skin Bioprinter for Wound Care on Latest NASA SpaceX Resupply Mission
a German Aerospace Center study centers on bioprinting—using viable cells and biological molecules to print tissue structures. The German Aerospace Center study Bioprint FirstAid demonstrates a portable, handheld bioprinter that uses a patient’s own skin cells to create a tissue-forming patch to cover a wound and accelerate the healing process. On future missions to the Moon and Mars, bioprinting such customized patches could help address changes in wound healing that can occur in space and complicate treatment. Personalized healing patches also have potential benefits on Earth, providing safer and more flexible treatment anywhere needed … read more
Related:
The 3D bioprinting process in the Bioprint FirstAid Handheld Bioprinter
MediWound offers hope for chronic wound treatment – study
In a phase II study, EscharEx demonstrated safe and effective debridement of diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers.
A phase II pharmacology study has found positive initial data of EscharEx, a bioactive therapy for rapid debridement in chronic and hard-to-heal wounds, Israeli biopharmaceutical company MediWound announced on Monday … The US-based study, which is ongoing, examined the treatment of seven patients with either diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) or venous leg ulcers (VLUs) … read more
Biogenic Nanoparticles Synthesized from African Medicinal Plants for Wound Healing
Wounds are described as damage to living tissue that disrupts its normal anatomical structure and function. They develop as a result of tissue damage caused by physical, chemical, thermal, microbiological, or immunological factors … The damage can compromise the skin’s epithelial surface and spread into the surrounding tissues, disturbing other systems such as ligaments, muscles, and nerves … Chronic wounds develop when wounds fail to heal properly and claim the lives of countless people around the world … read more
Ankle-Brachial Index Is Independently Associated With Cardiovascular Outcomes
and Foot Ulcers in Asian Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
BACKGROUND AND AIMS: The ankle-brachial index (ABI) is an efficient tool for objectively documenting the presence of lower-extremity peripheral arterial disease (PAD). The predictive factors of cardiovascular events and diabetic foot ulcer were not clear from the ABI examination in Taiwanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM).
METHODS: We enrolled 482 patients with type 2 DM who regularly visited the outpatient department of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and received ABI as well as brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity … read more
Nano-Silver Medical Antibacterial Dressing Combined with High-Flow Oxygen
Therapy Facilitates Ulcer Wound Healing of Superficial Malignant Tumors
Malignant tumors (cancer cells) are metastatic and invasive, and cancer cells can spread throughout the body through hematogenous, lymphatic and implantation metastases. Clinically, the most common tumor metastasis sites are lung, liver, brain, bone, etc. Some patients will have metastasis on the body surface, while in some cases, the tumor directly spreads or invades the body surface.1 The appearance of superficial malignant tumor usually indicates that the tumor is in the middle and late stage. However, many patients seek medical treatment only after the superficial tumor has grown, ruptured, and become infected. The ulceration of superficial malignant tumors can lead to wound bleeding, exudation, pain, infection, and scar hyperplasia, which makes the wound unhealed for a long time, greatly reducing the quality of life of patients.2 At present, surgical resection, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are the mainstays of treatment for superficial malignant tumors.3 Clinically, such patients are required to maintain local dryness of the wound, but frequent dressing changes and large surgical wound make it difficult to keep the wound dry; Moreover, chemotherapy is easy to cause a large amount of exudate in the wound to be in a moist state, coupled with the skin damage aggravation resulted from radiotherapy, leading to the susceptible to wound bleeding and infection and consequently delayed wound healing … read more
Is Your Wound Bioburdened? Case 1
CASE
• 22-year-old male with paraplegia following a fall from a balcony presented with large presacral and buttock pressure injuries that continued to increase in size since last visit >3 months prior. Click here for photo.
• Although the ulcers were large with areas of increased depth, there were minimal clinical signs of bioburden.
• A fluorescence scan revealed red fluorescence indicative of significant bioburden that could not be removed with cleansing or debridement.
• A point-of-care fluorescence scan (MolecuLight i:X) revealed a pattern of scattered red fluorescence (white arrows) indicating elevated bacterial burden (>104 CFU/g) extending beyond … read more
EWMA Podcasts Season 1
- EP07: Personal protective equipment
This podcast episode will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the prevention and management of skin injuries related to the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).This is a follow-up to the EWMA webinar we ran on the 30th April devoted to this topic. Due to a high volume of questions and level of interest that we have received during the webinar we have decided to follow-up with this podcast. In this episode we will be answering some of the questions raised from the webinar. - EP06: Wound Care Essentials during COVID-19
In this short special edition of the EWMA podcasts, Julie Jordan O’Brien talks about how to help wound care patients during COVID-19 and how a healthcare professional (HCP) can change a dressing in a home care setting. - EP05: AMS in Wound Management
In this episode, Samantha Holloway, Chair of the EWMA Education Committee and Teacher Network, speaks to Karen Ousey, Professor of Skin Integrity and Director for the Institute of Skin Integrity and Infection Prevention at the University of Huddersfield, about antimicroabial stewardship in wound management. - EP04: Atypical Wounds
In this episode, Samantha Holloway and Kirsi Isoherranen briefly discuss the best clinical practices and challenges related to the management of atypical wounds. By listening to this podcast you can learn more about how to suspect an atypical wound and will get more information about the diagnostic criteria and available tools - EP03: Person-centred Wound Care
Georgina Gethin discusses with the podcast’s host, Julie Jordan O’Brien, what person-centred care is and why it is so important in wound management. By listening to this episode, you can learn more about the benefits of shared decision-making between the patient and clinicians in wound management and get some practical support in implementing it - EP02: Standardisation Wound Education in EU
Samantha Holloway, Chair of the EWMA Education Committee and Teacher Network, speaks to Sebastian Probst and Ida Verheyen-Cronau about the standardisation of the wound education in Europe. Both podcast guests shares their experience in implementation of the EWMA level 5 and 6 post-registration curricula for nurses in Switzerland and Germany - EP01: Understanding Diabetic Foot
In this episode of the EWMA podcasts, Julie Jordan O’Brien and David G. Armstrong discuss current challenges and opportunities in the management and prevention of diabetic foot ulcers. Jordan O’Brien is a former EWMA Council member who works as anadvanced nurse practitioner in plastic surgery at Beaumont Hospital, in Ireland. Armstrong is Professor of Surgery and Director of the Southwestern Academic Limb Salvage Alliance (SALSA) at the Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California
Evidence for Person-centred Care in Chronic Wound Care
Chronic wounds affect an estimated 2.21 per 1000 population. They are a significant source of morbidity and affect individuals physically, psychologically, socially and financially. Person-centered care is one approach to improve patient outcomes in wound care as it values patients’ perspectives, beliefs and autonomy and considers the person as a whole within the cultural context in which care is provided … read more
Best Practice Statement – Addressing complexities in the management of venous leg ulcers
This document builds on the Best Practice Statement: Holistic Management of Venous Leg Ulcers to address complexities in the management of venous leg ulcers.
The aim of this document is to help ensure consistent clinical practices in relation to the assessment and management of people with VLUs who are outside the scope of the leg ulcer treatment pathway developed by Atkin and Tickle (2016). It will provide guidance based on relevant evidence and the experiences and opinions of clinicians, with a focus on practical, holistic and patient-centred strategies … read more
Researchers develop novel 3D printing technique to engineer biofilms
Anne S. Meyer, an associate professor of biology at the University of Rochester, and her collaborators at Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands recently developed a 3D printing technique to engineer and study biofilms—three-dimensional communities of microorganisms, such as bacteria, that adhere to surfaces. The research provides important information for creating synthetic materials and in developing drugs to fight the negative effects of biofilms … read more
Anti-biofilm Wound Dressing Market: High Prevalence of Diabetes to Drive Growth of the Market in Near Future
The rise in the occurrence of chronic illnesses such as diabetes and cancer throughout the world is driving expansion of the global anti-biofilm wound dressing market. Non-communicable illnesses are becoming more prevalent due to various factors such as smoking, alcohol usage, antibiotic resistance, and unhealthy and sedentary lifestyles.
Healthcare facilities, such as hospitals, have been overburdened as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic … read more
Payers Continue to Release Pertinent Coverage Policies
At the 2021 SAWC Fall, this reimbursement consultant/educator/author was honored to provide a main session reimbursement presentation, as well as a 3-hour interactive reimbursement post-conference workshop. The attendees at both venues were very attentive and asked many excellent questions. On the plane ride home, this author reflected on the questions that were asked at both sessions and came to the conclusion that many wound/ulcer management professionals either 1) have not implemented a process for monitoring and reviewing pertinent payers’ coverage policies or 2) have not incorporated these important “playbook guidelines” into their wound/ulcer management assessments, care plans, coding selections (diagnosis, evaluation & management, procedure, and product), and documentation … read more
Wound Care Technology: Advanced Tissue Therapeutics
Human knowledge is growing exponentially. This explosion is clearly evident in the field of Medicine. We hear almost daily about advances in cardiovascular and oncologic treatments. Medicine appears to be on the verge of extending human life well beyond 100 years. Fortunately, Wound Care physicians and their patients are also reaping the benefits of this rapid knowledge advancement. In the last decade, key elements in the body’s cellular healing processes have been elucidated. A major thrust has been in the development of human tissue therapies … read more
Expecting The Unexpected: When A Small Wound Has Big Implications
Acral lentiginous melanoma only accounts for only two to 10 percent of all reported melanoma types.1 Although the term “lentiginous” often refers to the typical dark coloration of the pathology, the dark coloration is not always a clinical finding, as multiple studies report amelanotic lesions, as well.2,3,4 Therefore, it is pertinent for every practitioner to give due diligence to any suspicious lesion and to know the key findings that may help differentiate a serious lesion from one that is more benign … read more
Compassionate and Versatile Brush-Biopsy for Histologic Wound Sampling
Soft K-Biopsy® – SFT-1000
SoftBiopsy® is a sterile single-use brush-curette is designed to be both minimally invasive and clinically effective for tissue sampling. The plastic applicator tip is coated with Kylon®, a patented medical fabric which dislodges and collects wound base tissue post-debridement, efficiently and effectively.
The SoftBiopsy® is designed with a trumpet shaped brush tip to easily press into the wound base surface and remove and trap a biopsy sample for anatomic pathology as curettings (tangential biopsy sample). When used post-debridement, it is optimal for molecular (PCR) or microbiological culture.
Organism ID Sampling Method
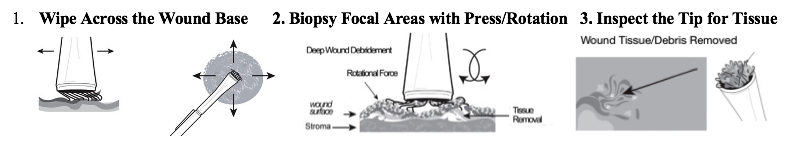
Once the biopsy is obtained, tissue samples for analysis are easily collected in the KYLON® hook tapered tip head and snapped off and placed into the vial to preserve tissue for organism (culture, PCR) or anatomic pathology lab analysis.
Request that your pathology lab that performs wound related tests contact us to become a Kylon® device “Center of Excellence”.
Benefits:
- Fabric pad on tapered applicator tip is designed for visible surface wounds that are visible on the body surface
- Versatile use, Ergonomic, and minimally invasive design facilitates user tactile control for targeting and guiding the brushing, sweeping and rotational movements – modulating tactile pressure and method allows for tissue. removal and trapping using a pressure-twisting motion of the wound surface
- Kylon® medical fabric hooks gently, yet substantially obtain abundant tissue samples that are trapped in the hook array, snapped free from the handle, and transported for laboratory analysis
- Designed for compassionate patient experience and compliance
Clinical Scenarios: (Refer to Instructions for Use)
The SoftBiopsy® is indicated for tangential biopsy of wounds on visual surfaces in order to obtain a sterile biopsy sample. Once the tissue filled tip is detached and placed in a vial, it is transported for histological analyses and further laboratory evaluation regarding infection or other pathology
Contraindications:
SoftBiopsy® is contraindicated for use with patients with known bleeding disorders or those on anticoagulant therapy, patients with an acute wound infection or condition that is not amenable to biopsy, patients with a known allergy to nylon or acrylic plastic, or patients who are pregnant or suspected to be pregnant when a wound biopsy would not be indicated
Warnings and Precautions:
Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician or other licensed practitioner.
Storage Requirements:
Consult manufacturer on special storage requirements outside of normal room temperatures.
How Supplied/Sizing:
Box of 25 minimum order
Recommended Use:
- Burns
- Chronic Wounds
- Diabetic Foot
- Graft Bed Preparation
- Non/Minimally Exudating Wounds
- Palliative Wounds
- Pressure Ulcers
- Non-Eschar/Solid/Fibrotic Wounds
- Sloughy Wounds
- Surgical Wounds
- Venous Ulcers
Mode of Use/Application:
See manufacturer’s website for detailed instructions for use (IFU)
Clinically Tested:
Latex-friendly
Product features:
- Single Use
- Disposable
- Instrument
- Sterile
Other features:
- Educational Material Available
- Free Samples/Trials Available
- Published Clinical Study Available
Manufacturer: Histologics LLC – www.histologicswc.com
Histologics LLC’s primary objective is to advance a compassionate approach to debridement and wound biopsy sampling with devices using Kylon®, a medical fabric enabling biopsy with tissue capture, or frictional tissue cleaning, and debridement.
Website:
Email:
Phone:
(888) 235-2275
Toll-free:
(888) 235-2275
Fax:
(888) 738-9757
A Challenging Case Of Limb Preservation For A Patient With Neuropathic Pedal Dislocation
In the summer of 2020, an 82-year-old male presented to the emergency department to evaluate right foot pain and swelling over the past week. He saw his primary care physician earlier in the morning, who referred him for more emergent evaluation. He states he fell at home one week ago, injuring his right foot. This initially resulted in minimal pain, but over one week, the pain and swelling continued to worsen. He notes that he had no open wounds or active bleeding at the time of the initial injury. However, over that week, in addition to the escalating pain and swelling, he developed a bleeding ulcer on the dorsal aspect of the right foot. He could stand and ambulate … read more
Impact of repeated remote ischemic conditioning on diabetic foot ulcers: A proof-of-concept study
The WHS Communications Committee is pleased to launch the WRR Fireside Chat video series to feature groundbreaking research in Wound Repair and Regeneration (WRR).
Each video Drs. Mitch Sanders, PhD and Kyle Quinn, PhD will feature a recent article in WRR.
Impact of repeated remote ischemic conditioning on diabetic foot ulcers: A proof-of-concept study
Author: Matthew Regulski, DPM
Technology in Wound Care
In all fields of medicine, technology is changing and improving how we treat our patients. Wound care is no exception. From improved charting with electronic medical records to new treatment options to expanding access with the use of telemedicine, in wound care offices, technology plays an increasing role in our day to day interactions with patients.
The majority of physicians use an electronic medical record (EMR) for documentation, and in wound care, the way we use EMR’s to document is changing. New imaging technologies improve the accuracy of documentation and facilitate the process. For example, many wound centers still measure wounds with a ruler to document the length x width x depth and describe the type of tissue present in the wound. This opens up the possibility of user error, which may ultimately affect the way the wound is treated and the healing outcome overall. With newer imaging systems like the one from Tissue Analytics, the provider can picture, measure, and analyze the wound in one step, allowing for faster and more accurate documentation … read more
Is There An Optimal Metatarsal Length To Prevent Reulceration After Ray Amputations?
The podiatric surgeon frequently utilizes partial ray amputations aiming to remove infection while preserving bipedal ambulatory status and preventing further morbidity or mortality. An estimated 50 to 70 percent of lower extremity amputations take place due to diabetic complications, most commonly diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) formed in the setting of peripheral neuropathy. Patients with diabetes often face additional comorbidities, including peripheral vascular disease and a diminished immune response, both of which increase the risk for ulcer development and complicate healing potential. Although amputation is an effective method of eradicating osseous infection, removing pedal anatomy will alter normal biomechanics and increase pressure distribution to surrounding structures. Furthermore, amputation of pedal structures involved in the gait cycle will require increased metabolic expenditure during ambulation. One hypothesis … read more
Roles of Oxidative Stress and Raftlin in Wound Healing Under Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy
Negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is an effective way to promote wound healing. However, its mechanisms have not been investigated thoroughly. Growing evidence suggests that oxidative stress and Raftlin levels play important roles in wound healing. However, whether NPWT promotes wound healing through this mechanism remains unclear.
Purpose: Our study focuses on the different levels of oxidative stress and antioxidant response between wounds treated by NPWT and routine dressing change. The objective of this study was to measure the differences in Raftlin levels between the two groups, which is a new biomarker related to wound healing … read more
Preventing complications at wound dressing changes
This module aims to make clinicians aware of:
- The importance of skin health and what makes it vulnerable to damage.
- The damage that can occur when using medical adhesives and improper removal techniques.
- The impact that MARSIs (medical adhesive-related skin injuries) can have on patients.
- Ways to reduce the risk of MARSIs by providing appropriate treatment for at-risk patients groups.
Executive Summary: Debridement
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Nurses Developed by Nurses Specialized in Wound, Ostomy and Continence Canada (NSWOCC)
Debridement is described in the literature as having a high level of clinical risk and may result in patient harm when performed by untrained nurses. As a result, specialized knowledge, skills, and competencies are required to initiate, direct, and perform safe and effective debridement. This executive summary provides an overview of Debridement: Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Nurses from the Nurses Specialized in Wound, Ostomy and Continence Canada (NSWOCC). The primary objective of these recommendations is to positively influence patient outcomes and enhance safety. The 12 recommendations place the safety of the patient and nurse at the forefront and highlight the educational, competency, certification, preceptor/mentorship, and legal requirements for nurses to initiate, direct, and perform all methods of debridement. We designed these recommendations to be circulated and implemented widely by … read more
Determining Amputation Level To Optimize Functional Outcomes
Diabetes is the leading cause of non-traumatic amputations in the lower extremity.1 Around 15 percent of all patients with diabetes will develop a lower extremity ulceration, with these patients being 17 to 40 times more likely to require an amputation.1 Unfortunately for most, the decision to amputate is not always clear cut and the determination of where to make a definitive amputation is not always as it seems on plain films or advanced imaging, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT). There are several factors to consider when performing limb salvage procedures for these patients with diabetes … read more
APMA’s 2021 Diabetes Campaign, “Es Hora,” Focuses on Hispanic Males
November is Diabetes Awareness Month, and APMA’s Communications Committee is launching a new public education campaign designed to reach one of our most at-risk patient populations: Hispanic males. The campaign, “Es Hora,” offers a wealth of educational materials for you to use in your practice.
This content is available to APMA members only. If you are a member, please log in to see the full content … read more
Coding and Billing for the Foot and Ankle Surgeon
Take the first few steps to coding and billing by joining us for a comprehensive workshop covering the fundamentals of coding and billing for foot and ankle surgeons. Learn the foundation of the coding and billing process from expert colleagues before taking the ACFAS Coding and Billing for the Foot and Ankle Surgeon course. This course is for residents, fellows, new practitioners, office staff of foot and ankle surgeons or anyone who wants to learn more of the basic coding and billing terminology and process. Plus, if you’re a resident and attending Residents Day in the morning the day of the event, this course is a great next step to learning more about coding and billing for your future practice and can be bundled in your pricing … read more
Getting Back to Basic Wound Care
Author: Bill Richlen PT, WCC, DWC
My 25 years in the wound care field has been an incredible journey. Over the years I have been witness to better understanding of wound healing, better research and improved products and technology that has changed the way wounds are managed. At the same time, I regularly hear my students and colleagues share some of the practices being implemented today, along with many myths still being perpetuated, and it makes me wonder “what happened to the basics?”. I once learned from a colleague and now include it my teaching that there are 2 fundamentals to heal all wounds: 1) healthy patient; and 2) healthy wound. As long as those fundamentals are achieved, a wound is likely going to heal despite what you do it … read more
Evidence in wound care
There is an ever-growing variety of products and devices available to practitioners to improve healing rates and patient outcomes, but practitioners should be able to critically appraise evidence to make appropriate evidence-based changes to practice. This position document reviews the available evidence in wound care, looking especially at the critical appraisal of level 1 evidence, before considering the steps required to translate evidence to practice … read more
Printing technique creates effective skin equivalent, heals wounds
Chronic wounds are deep and difficult to repair. Often, the top of the injury heals before the bottom, so the wound collapses in on itself. Over time, this can result in scar tissue and reduced skin function … The technique is the first of its kind to simulate three layers of skin: the hypodermis, or fatty layer, the dermis, and the epidermis … “You effectively have three different cell types. They all grow at different speeds,” said author Alan Smith. “If you try to produce tri-layered structures … read more
MolecuLight Announces Availability of its MolecuLight i:X® Platform on Epic’s App Orchard
Save MolecuLight i:X fluorescence wound images and measurements in Epic
Toronto, CANADA – (August 12, 2020) MolecuLight Inc., the leader in point-of-care fluorescence imaging for real-time detection of bacteria in wounds, announces the availability of its MolecuLight i:X® platform on the Epic App Orchard Marketplace and the integration of its platform with Epic’s leading EMR (electronic medical record) platform.
Users who use Epic for the treatment of wounds can upload standard and fluorescence images, and measurements captured with the MolecuLight i:X device at the point-of-care to the patient’s record. The integrated platforms allow clinicians to optimize their workflow and document their patients’ wounds digitally. The MolecuLight i:X application – iX Imaging – is available on the App Orchard.
“We are proud to announce the inclusion of our MolecuLight i:X platform in the Epic App Orchard Marketplace to allow customers to generate and access documentation of patients’ wounds”, says Anil Amlani, MolecuLight’s CEO. “The MolecuLight i:X is the only point-of-care device enabling clinicians to capture wound images showing clinically significant bacteria, information that improves clinical decision making to ensure the fastest path to healing. The integration of this additional information into existing documentation protocols will provide clinicians with a more complete wound dataset.” … read more
NHS Resolution reviews medical negligence claims by patients with diabetes and lower limb complications
The NHS’s defence organisation, NHS Resolution, are reviewing past medical negligence claims against the NHS by patients with diabetes who suffered lower limb complications. Most of these cases relate to patients with non-healing foot ulcers, who then needed major lower limb amputations. The aim of the review is to identify and report on the themes which are common in these cases to help the NHS learn from its mistakes. NHS Resolution hope that by raising awareness of the risks and need for consistent, correct treatment of diabetes-related lower limb problems, both the number of amputations and the cost to the NHS can be reduced. The key message of the review will be that lower limb amputations are often preventable, but this requires NHS organisations to work together to improve care for these patients. The review will be published within the next few months … read more
Wound photography for evaluation of surgical site infection and wound healing after lower limb trauma
AIMS: Deep surgical site infection (SSI) is common after lower limb fracture. We compared the diagnosis of deep SSI using alternative methods of data collection and examined the agreement of clinical photography and in-person clinical assessment by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) criteria after lower limb fracture surgery … read more
Wound Healing Gets a Boost from 3D Printed Platelet-Rich Plasma
Researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences report replicating a crucial component of our blood may aid wound healing … The findings are published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials in a paper titled, “3D Printed Scaffolds Incorporated with Platelet-Rich Plasma Show Enhanced Angiogenic Potential while not Inducing Fibrosis,” and led by researchers at the Tissue Engineering Research Group (TERG) and SFI AMBER Centre based at RCSI’s department of anatomy and regenerative medicine … read more
3 Steps For Turning Wound Care Into Staff Inspiration
Staffing was a challenge in skilled nursing care prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, and like all segments of health care, the problem has only worsened for SNFs since March 2020. But new figures from the Bureau of Labor Statistics are nevertheless a shock to the system … Since the start of the pandemic, the industry lost a startling 221,000 jobs — or 14% of its workforce — from March 2020 to October 2021. This is a significantly greater loss than any other health care segment, well ahead of the 8.2% drop in assisted living staff … read more
ZZ Biotech Announces First Patients Dosed in Phase 2 Clinical Trial of 3K3A-APC for
Treatment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
HOUSTON–(BUSINESS WIRE)–ZZ Biotech, a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company developing the experimental drug 3K3A-APC for some of the biggest unmet needs in stroke, neurodegenerative disease and chronic wound healing, today announced that the first patients have been dosed in a Phase 2 clinical trial evaluating 3K3A-APC for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease. The study is being conducted at Macquarie University, in Sydney, Australia, and seeks to investigate whether 3K3A-APC is safe and potentially effective in patients with ALS. The Firies Climb for Motor Neurone Disease provided an AU$1 million donation to support this clinical trial … The Phase 2 open label trial (NCT05039268) will enroll a total of 16 patients with ALS into two dose cohorts. The primary study outcomes are to ensure the safety and tolerability of 3K3A-APC in ALS patients and to determine whether 3K3A-APC is able to reduce the pathological changes that are thought to cause ALS. The study will evaluate biomarkers of microglial and monocyte activation and should provide evidence as to whether microglial activation is a major pathogenic contributor to ALS … read more
Singapore tests out ‘smart bandage’ for remote recovery
SINGAPORE – Researchers in Singapore have developed a smart bandage to enable patients to have chronic wounds monitored remotely via an app on a mobile device, potentially saving them visits to the doctor … A research team at the National University of Singapore has created a wearable sensor attached to a transparent bandage to track progress in healing, using information like temperature, bacteria type, and levels of pH and inflammation … “Traditionally when someone has a wound or ulcer, if it’s infected, the only way to examine it is through looking at the wound itself, through visual inspection … read more
Stem cell memories may drive wound repair, and also chronic disease
A trifling paper cut is a site of frenzied activity. Within it, a squad of epidermal stem cells briskly regenerate to patch up the wound. A closer inspection of this war-torn swath of epidermis will reveal that while some of the stem cells are native to the area, others are newcomers—former hair-producing stem cells, that—upon sensing nearby injury—migrated from the hair follicle to the wound bed, where they transformed to resemble indigenous epidermal stem cells … read more
Novel Plasma Gas-Based Strategy Kills Resistant Bacteria, COVID-19 Virus
A novel, antibiotic-free strategy for fighting antimicrobial-resistant bacteria using cold plasma ionized gas to activate key molecules has shown early efficacy in eradicating bacteria commonly found in chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers. The gas also killed the SARS-CoV-2 virus on surfaces … read more
A Comparative Study of Efficacy of Povidone Iodine Versus Super Oxidized Solution in Lower Limb Ulcers
BACKGROUND Wounds and their management are important in the practice of surgery. Super oxidised solution is a recent concept in wound management. It is an aqueous solution which is electrochemically processed which is non-toxic, non-irrigating and is having a neutral pH. Povidone iodine is the most common topical wound care product used in surgical practice. Both are affordable solutions for the patients. There are very few studies comparing the efficacy. In this study, we wanted to compare the efficacy of super oxidised solution and povidone iodine in the management of lower limb ulcers. METHODS A prospective study was conducted on 100 patients who were randomized into two groups. Group A was treated with super oxidized solution and Group B were treated with povidone iodine. Assessments of wounds were done on various days (1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21). Various outcomes of data were analysed using statistical analysis. RESULTS The average percentage reduction in wound size on day 21 was 47 % in Group A compared to 24 % in Group B. Early appearance of granulation tissue, disinfection, decrease in wound size, and less duration of hospital stay was achieved in Group A. CONCLUSIONS The results were more favourable towards super oxidised solution than povidone iodine. In this comparative study, super oxidized solution had faster efficacy and wound healing … read more
Sherlock Holmes and the Case of the Missing Evidence
Diversity and Pressure Injury Prevention: Important Terms to Know
Erythema: A result of injury or irritation that causes dilation of blood capillaries and manifests as patchy reddening of the skin. Occurs after a patient/resident is exposed to unrelieved pressure for 2 hours. It can be identified as a deep, localized redness; can also be blue or purple.
Hyperemia: The condition of having excess blood in vessels that supply an organ or area of the body. Occurs after patient/resident is exposed to 30 minutes of unrelieved pressure. It can be identified as a localized, non-blanchable redness.
Perfusion: The passage of blood through arteries and capillaries into tissues or organs. When insufficient, there is an increased chance that the patient may have complications.
… more
Wound Care Search Engine
Beyond being a great source for news, Wound Care Weekly is also an effective search engine for wound care related content. Google searching will reflect results targeted toward the general public where our search results will be derived from thousands of articles written almost exclusively for medical professionals.
Use italics for more focused search results “foot ulcer”
Smart wound dressing provides suture-free closure of surgical incisions
It is a staple of science fiction to mock sutures as outdated. The technique has, after all, been in use for at least 5,000 years. Surely medicine should have advanced since ancient Egypt. Professor Hossam Haick from the Wolfson Department of Chemical Engineering at the Technion has finally turned science fiction into reality. His lab succeeded in creating a smart sutureless dressing that binds the wound together, wards off infection … read more
Research holds promise of new information about skin injuries
Biomedical engineering professor Kyle Quinn has received a four-year, $1.6 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to develop non-invasive, real-time “optical biopsies” of chronic skin wounds.
The goal of Quinn and researchers in his lab is to provide digital histopathology images — the microscopic examination of tissue to study the manifestation and progression of disease — and other quantitative information without the need for an invasive biopsy, tissue processing and staining with histology dyes … read more
‘Death is a greater risk’ than amputation after diabetic foot ulcer
People with diabetes and a history of foot ulcer are more likely to die than undergo amputation during 6 years of follow-up, a potential measure of effectiveness of diabetes care, registry data from Scotland show.
In an analysis of real-world data comparing people with diabetes with and without foot ulcer, researchers also found amputation or death occurred for approximately one in two of those with a prior foot ulcer … read more
Frank & Lizzie Show: Episode 009, Dr. Jeffrey Lehrman and Moira Sykstus, Wound Week 2022
On this episode, Frank & Lizzie’s guests Dr. Jeffrey Lehrman and Moira Sykstus share insight on their upcoming “Coding, Compliance, and Documentation in Wound Care” course held during the American Professional Wound Care Association’ s (APWCA) Wound Week 2022 conference in Philadelphia. This course will be held on Thursday, February 24, 2022 at the Loews Hotel. The conference will be held Feb 24-27, 2022. For more information about Early Bird Discounts, New Member deals, and more, visit woundweek.com.
The role of non-medicated dressings for the management of wound infection
There is growing concern regarding the treatment of infection, caused by the rise of antimicrobial resistance. This position document looks at current treatment approaches to identifying and treating biofilm in wounds, focusing on the mechanism of action and role of non-medicated wound dressings (NMWDs) within antimicrobial stewardship practices and evidence that supports their effectiveness … read more
Strategies to reduce practice variation in wound assessment and management
The T.I.M.E. Clinical Decision Support Tool
This document seeks to help clinicians support those who do not have specialist wound training to accurately assess patients and their wounds and arrive at a broad-based, systematic rationale that will ultimately help reduce variations in clinical decision-making. The T.I.M.E. Clinical Decision Support Tool provides a structured approach to wound bed preparation … read more
Development and Implementation of an Individualized Turning Program for Pressure Injury Prevention
Using Sensor Technology in Nursing Homes: A Quality Improvement ProgramA Quality Improvement Program
Turning nursing home residents every 2 hours has been a long-held standard for pressure injury (PrI) prevention in individuals with mobility impairments although evidence to substantiate this practice is limited. New guidelines recommend personalizing turning schedules to support person-centered care but lack specific recommendations about which turning frequencies are appropriate for various risk levels. PURPOSE: This quality improvement program aimed to determine the feasibility and outcomes of using individualized turn schedules for newly admitted nursing home residents. METHODS: An expert panel of wound clinicians developed, tested, and implemented a turn frequency tool that allowed staff in 2 nursing homes to select a turning schedule of 1, 2, 3, or 4 hours based on resident risk factors. Turning schedules were operationalized using a wearable sensor-based visual cueing technology that alerted staff to resident repositioning needs. Nonparticipating resident data were collected for comparison of PrI incidence. Descriptive statistics were calculated for all covariates. Significance of differences tests were performed as … read more
A Review: Matrix Metallopeptidase-9 Nanoparticles Targeted for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetes foot ulcers are a leading cause of death in diabetic individuals. There are very few medicines and treatments that have received regulatory clearance for this indication, and numerous compounds from various pharmacological classes are now in various stages of clinical studies for diabetic foot ulcers treatment. Multiple risk factors contribute to diabetic foot ulcers, including neuropathy, peripheral artery disease, infection, gender, cigarette smoking, and age. The present difficulties in diabetic foot ulcers treatment are related to bacterial resistance to currently utilized antibiotics. Inhibition of the quorum sensing (QS) system and targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9 (MMP-9) are promising. This study focuses on the difficulties of existing treatment, current treatment technique, and novel pharmacological targets for diabetic foot ulcer. The electronic data base search diabetic for literature on foot ulcers treatment was carried out using Science Direct, PubMed, Google-Scholar, Springer Link, Scopus, and Wiley up to 2021. Becaplermin, a medication that targets MMP-9, glyceryl trinitrate, which inhibits the bacterial quorum sensing system, probiotic therapy, and nano technological solutions are just a few of the novel pharmaceuticals being developed for diabetic foot ulcers … read more
Study shows how management of serious diabetic foot ulcers was possible during the COVID-19 lockdown
New research being presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), held online this year (27 Sept-1 Oct), reveals how Belgium’s efforts to maintain a diabetic foot care program during the COVID-19 pandemic can offer valuable lessons to the rest of the world … “Thanks to the great efforts of diabetic foot clinics, continued availability of diabetic foot ulcer services during lockdown, although in a limited capacity, were really helpful, and may be the reason why we didn’t see late presentation and the impact on the severity of ulcers was limited to slightly larger wounds”, says lead author Dr. An-Sofie Vanherwegen from Sciensano … read more
WoundSource Upcoming Webinars

Presenter: Robert J. Klein, DPM, FACFAS, CWS; Catherine T. Milne, MSN, APRN, CWOCN-AP and Dot Weir, RN, CWON, CWS

Presenter: Naz Wahab, MD, FAAFP, FAWPCA

Presenter: Neesha Oozageer Gunowa MSc, PGCert, BSc, SPT, DN, RN, QN
Efficacy of Hydromechanical Therapy in Nonhealing, Chronic Wounds
as a Cost- and Clinically Effective Wound Care Modality
Chronic wounds pose a widespread challenge to health care, with many new, costly wound care modalities introduced in recent years with varying degrees of success. Bacterial biofilms have been postulated as one of the main culprits of the stagnation of chronic wound healing. For years, surgical fields have used pressurized irrigation for cleansing surgical wounds, but its utility in managing nonhealing chronic wounds has often been overlooked. Objective. In this case series, the authors aimed to demonstrate that hydromechanical therapy with pressurized irrigation can be a cost-effective and clinically effective wound care modality … read more
Trends in Wound Care Audits & Denials, with Dr. Caroline Fife and Dr. Helen Gelly
Last week I (Dr. Caroline Fife) enjoyed a relaxed, unscripted conversation with Dr. Helen Gelly about trends in wound care audits and charge denials, with a live audience Q&A. You can watch the recording of the conversation and Q&A below.
You can also find the audio of this event on Google Podcasts by searching for the Intellicure Wound Care Podcast.
Cold plasma ionised gas as new treatment for diabetic foot ulcers could also kill COVID-19 virus indoors
A new formulation developed by University of South Australia scientists to treat antimicrobial-resistant bacterial infections in diabetic foot ulcers could also be used to kill the COVID-19 virus circulating in air conditioning systems … Enhancing cold plasma ionized gas with peracetic acid eradicates bacteria in wounds and substantially reduces SARS-CoV-2 viral loads, Australian and UK scientists claim in a paper published in Applied Physics Letters … read more
The FDA’s Take on Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatments
This is fairly complex issue. There are many factors in responding to your question. Really, it’s multi-factor issue. Part of the challenge is that the regulatory agency, FDA, has a very clear, and at the same time, very narrow definition of wound healing. That is 100% wound closure with no drainage or no need for any dressing … read more
Embedding Predictive Analytics Into Your Wound Care Workflow Webinar
This webinar, presented by Matt Berezo, Joshua Budman, Abbey Cooper, and Cathy Thomas Hess will discuss how wound care-specific analytics can impact a practice’s workflow. Specifically, the presenters will discuss several clinical analytics models, how they are validated, and how clinicians can use them to improve their clinical and operational outcomes … register
Resolving Patient and Provider Concerns: Overcoming Another Year of Disruption
As 2021 comes to a close, it marks 2 full years that the US, Canada, and other parts of the world have endured the effects of COVID-19 on our personal and professional lives. The pandemic continues to force our hands in so many ways that were unimaginable just a short time ago and has had innumerable unforeseen consequences for patients and providers. In this issue, articles on provider- and patient-centered concerns speak to the social, psychological, and physical components that determine quality-of-life scores and impact activities of daily living … read more
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces thermal wound complications and length of stay in hospitals, study finds
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can reduce thermal wound complications, length of stay in hospitals due to thermal burns, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) mRNA gene expression, and ICAM-1 serum level, a case-control study published in Annals of Medicine and Surgery concludes.
“The damaging effects of thermal burns need to be managed holistically in order to create a suitable environment for wound healing,” study author Mendy Hatibie Oley (University Sam Ratulangi; R D Kandou Hospital; Hyperbaric Centre Siloam Hospital; all Manado, Indonesia) et al write … read more
Workflow Strategy Snapshots: Fresh Focus for the New Year
Kicking off any new year allows us to pause and reflect on the previous year’s actions and results. When you work within wound care, perhaps your first action this year was to review your schedule of patients to ensure they were provided the proper time to be seen, or review your staffing matrix to ensure you are you are meeting the needs of the scheduled patients, or dig into your supply cabinets to ensure inventory is abundant. Each action is vital to maintain your business and is interconnected to your unique process … read more
Where Are We With Point-Of-Care Testing For PAD In Patients With Diabetes?
How reliable are our screening tools for peripheral arterial disease (PAD)? A recently published meta-analysis suggests that while our current diagnostic testing measures are promising, one should be wary of relying upon any one tool in isolation in patients with diabetes.
In their 2020 study in the Journal of Vascular Surgery, Normahani and coworkers reviewed and analyzed studies to evaluate the accuracy of bedside testing for PAD in patients with diabetes.1 In examining the diagnostic accuracy of the ankle-brachial pressure index (ABPI), the toe brachial pressure index (TBPI) and the tibial waveform assessment, these authors reviewed 11 studies (including a total of 1,543 limbs) … read more



