
Category: Articles











































































































































































































































































Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2019
The Medscape Physician Compensation Report is the most comprehensive and widely used physician salary survey in the United States. This year’s report represents almost 20,000 physicians in more than 30 specialties who responded to Medscape’s salary survey, providing their salary information, number of hours worked, amount of time spent seeing patients, what they find most rewarding and challenging about their jobs, and more … read more
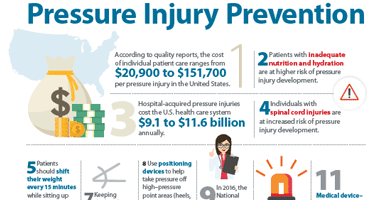
Skin Injury and Chronic Wounds: Shear, Pressure, and Moisture
Wound healing is a complex process that is highly dependent on many skin cell types interacting in a defined order. With chronic wounds, this process is disrupted, and healing does not normally progress. Although there are different types of chronic wounds, those occurring from injury, such as skin tears or pressure injuries, are some of the most common. These injuries are a result of repeated mechanical irritation. Moisture-associated skin damage is another condition that can contribute to chronicity.1 Understanding the causes and contributors to these injuries can help to minimize patients’ risk of developing them. It can also aid in the formation of an optimal treatment plan for when injuries do occur, which reduces the healing time and leads to better patient outcomes … read more
Legal Perils and Pitfalls of Wound Care: Risk Factors for Unavoidable Ulcers
According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality,1 more than 17,000 lawsuits related to pressure ulcers are filed annually in the United States, second only to wrongful death lawsuits. One of the greatest gifts to defense attorneys was when the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) published F-Tag 314, finally acknowledging that some ulcers can occur despite best care. The facility essentially can maintain, “Hey, we did everything we were supposed to, and despite that, the patient developed that pressure ulcer”—that is, the ulcer was unavoidable. To prove unavoidability, proper documentation (proof) of best care needs to be in place, as well as documentation that all proper prevention and treatment measures were implemented … read more
Healing glove reaches major milestone, earns national recognition
The revolutionary bioengineered healing glove created by researchers at the University of Texas at Arlington Research Institute (UTARI) and the University of Washington has completed another key step on the road toward commercialization … Empowered by a $227,000 award from the Medical Technology Enterprise Consortium (MTEC), the REHEAL Glove team at UTARI and REHEAL LLC has successfully developed a manufacturing process for the technology. The MTEC agreement, awarded in October 2017, funded the development of this low volume manufacturing process, which has created 100 flexible polymeric gloves for early stage clinical trials … read more
Vet Gets His Leg Cut Off Because Veteran Affairs Made Administrative Errors: Report
Improper management at the Department of Veterans Affairs office in Indianapolis led to one man having a below-the-knee amputation, federal officials said … The U.S. Office of Special Counsel said that management at the office directed social workers to stop entering home health care consults into a computerized patient record system …The decision was coupled without properly implementing a change. The visits weren’t properly logged … “As a direct result, one veteran had to have his leg amputated after he was not provided timely wound care,” the Office of Special Counsel stated in a press release … read more
Skin Injury and Chronic Wounds: Shear, Pressure, and Moisture
Wound healing is a complex process that is highly dependent on many skin cell types interacting in a defined order. With chronic wounds, this process is disrupted, and healing does not normally progress. Although there are different types of chronic wounds, those occurring from injury, such as skin tears or pressure injuries, are some of the most common. These injuries are a result of repeated mechanical irritation. Moisture-associated skin damage is another condition that can contribute to chronicity. Understanding the causes and contributors to these injuries can help to minimize patients’ risk of developing them. It can also aid in the formation of an optimal treatment plan for when injuries do occur, which reduces the healing time and leads to better patient outcomes … read more
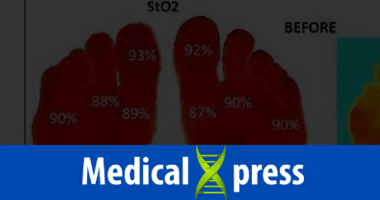
Circularity Healthcare Presenting D’OXYVA Diabetic Wound Healing
Microcirculation Therapy Clinical Evidence & Sponsoring the 3rd International Microcirculation Conference
he conference focuses on advancing scientific research and medicine in all areas of vascular biology/medicine. Biennially, the ESM-EVBO hosts a four-day conference, where vascular enthusiasts from biology, preclinical and clinical research groups, and opinion leaders gather to share new fundamental scientific insights and current pre-clinical advances. Its network now has over 500 members worldwide, including representation in over 30 countries … read more
Urgostart for treating diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers
putting the NICE guidance into practice
NICE supports the case for adopting UrgoStart dressings to treat diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers in the NHS, because they are associated with increased wound healing compared with non-interactive dressings. UrgoStart dressings are therefore recommended as an option for people with diabetic foot ulcers or venous leg ulcers after any modifiable factors such as infection have been treated … read more
Weekly Debridement Leads to Faster Healing in Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers debridement should be part of the standard of care, and repetitive weekly debridement may be beneficial … Written by Kristin Della Volpe … Frequent debridement of chronic wounds is associated with improved healing, according to James Wilcox, RN, lead author of a retrospective study of more than 300,000 wounds. Diabetic foot ulcers accounted for a large percentage of these wounds … “An effective healing strategy for chronic wounds should include an early and accurate diagnosis of wound etiology, as well as the appropriate application of debridement and advanced healing modalities in an effort to achieve optimal outcomes,” said Mr. Wilcox, who is Director of Research and Quality for Medical Affairs at Healogics in Jacksonville, FL, and Immediate Past President of the Baromedical Nurses Association … read more
Prototype ‘smart bandage’ can detect infections and auto-apply antibiotics
Here at Digital Trends we have covered a surprising number of fascinating high-tech wound dressings, such as one made of spider silk and a futuristic Star Trek-style patch, which uses cold plasma as part of the healing process. Adding to this growing subgenre of stories is a new smart bandage developed by researchers at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln. Not only is it capable of checking whether a wound is infected, but it can also proactively treat it with medication if it deems this to be the case … read more
Immunity as a continuum of archetypes
The immune system has long been recognized for its importance in eliminating pathogens. Recently, it has become appreciated for additional distinct roles in normal tissue biology, contributing to tissue development and maintenance. Further, it is being revealed as a major force in diseases as diverse as fibrosis, type 2 diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as cancer. The immune system is exquisitely selective; more than a billion different adaptive immune lymphocytes (T cells and B cells) survey the body. These can individually be sensitized to antigens … Perhaps the best-developed exemplar for an immune response that is neither focused on destruction nor tolerance, but rather on achieving tissue homeostasis, is in wound healing and tissue repair. In early wounds, infiltration of inflammatory neutrophils and monocytes provides wound sterilization. In late wound-healing responses … read more
Medical News Today: Can we heal wounds by printing skin?
Printing layers of skin to help treat chronic wounds or burns may be on the horizon, thanks to a newly developed mobile skin bioprinting system … The skin bioprinter at work … Scientists at the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) in Winston-Salem, NC, have created a bioprinter that uses a person‘s own skin cells to create layers of new skin and apply them directly to the wound … A new paper, which now in the journal Scientific Reports, details the development of this new technology … The procedure involves harvesting major skin cells called dermal fibroblasts and epidermal keratinocytes from a biopsy of a person‘s normal skin tissue … read more
Investigational Gene Therapy KB103 Receives Priority Designation
in Europe for Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa
The topical gene therapy candidate KB103 to treat dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) has been granted PRIME (PRIority MEdicines) designation by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) … KB103 is a gene therapy candidate developed by Krystal Biotech to deliver a functional COL7A1 gene directly to skin cells using a modified and safe herpes simplex virus. Mutations in the COL7A1 gene are the underlying cause of DEB and lead to a defective production of COL7 protein, causing layers of the skin to separate and form blisters … read more
The Effect of Natrox® Oxygen Wound Therapy on the Healing Rate of
Chronic Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Approximately 150 patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers will be enrolled into the trial at fifteen Wound Care Centers and Hospitals across the United States of America. Patients will be selected to receive standard wound care or standard wound care plus Natrox Oxygen Wound Therapy for their wounds. Patients will be monitored for 12 weeks. The primary comparator between the groups will be complete wound healing at 12 weeks, but other parameters will be assessed, such as pain, wound size reduction and infection status … read more
Vitamin D deficiency increases risk for diabetic foot ulcer
Adults with diabetes and severe vitamin D deficiency are three times more likely to develop a diabetic foot ulcer than similar patients with sufficient vitamin D levels, according to findings from a meta-analysis published in Nutrition & Diabetes … “Vitamin D has been suggested to play an important role in many chronic diseases, such as diabetes,” Yimin Chai, MD, PhD, professor in the department of orthopedic surgery at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China, and colleagues wrote. “Low serum vitamin D levels are associated with insulin resistance, impaired beta-cell function and the development of [diabetes]. There is also ongoing interest in the association between lower level of vitamin D and diabetic complications.” … read more
Operate Like a DPM with Today’s Podiatrist
The American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA) announced today the launch of a spring campaign featuring Today’s Podiatrist, in conjunction with April’s National Foot Health Awareness Month. The campaign will educate the public about the wide range of capabilities of Doctors of Podiatric Medicine (DPMs), with a particular emphasis on their surgical expertise .. Today’s Podiatrist is a foot and ankle expert, specially trained to treat and evaluate patients based on individual needs. Whether that evaluation necessitates surgical intervention or conservative care, Today’s Podiatrist will provide the appropriate treatment … “There is no foot and ankle injury beyond the capabilities of Today’s Podiatrist,” said APMA President David G. Edwards, DPM. “We keep patients on their feet by recommending and executing the right treatment for that specific condition and individual. From performing complex ankle reconstructions to caring for diabetic foot ulcers, we are at the forefront of foot and ankle medicine and surgery … “No matter the severity of your condition, when you have a foot or ankle issue you should turn to Today’s Podiatrist. In some cases, surgery may be the most appropriate treatment to alleviate discomfort or restore the function of your foot. Individual factors determine the length and kind of rehabilitation required to ensure a successful recovery … read more
Virus that Infects Bacteria Turns Immune Response Away
from P. aeruginosa, Study Shows
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the most common bacteria found in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients, uses a virus to go unnoticed by the host immune system, a new study shows … Treatment with a vaccine designed to help the immune system detect the virus was found to significantly reduce P. aeruginosa’s ability to infect mice, suggesting it might represent a new way to treat CF patients … The study, “Bacteriophage trigger antiviral immunity and prevent clearance of bacterial infection,” was published in the journal Science … P. aeruginosa, dangerous for CF patients, is also common in diabetic ulcers, bedsores, and burn wounds. At the moment there is no approved vaccine against these bacteria, and they are increasingly becoming resistant to antibiotics …The World Health Organization categorized P. aeruginosa as one of the most dangerous pathogens to human health … “I see this every day in my clinical practice,” Paul Bollyky, MD, PhD … read more
Clinical Outcomes Data on SkinTE™ from Lower Extremity Chronic
Wounds to be Presented at Diabetic Limb Salvage (DLS) Conference
SALT LAKE CITY, March 27, 2019 /PRNewswire/ — PolarityTE, Inc. (Nasdaq: PTE), a biotechnology company developing and commercializing regenerative tissue products and biomaterials, announced today that two clinical outcomes abstracts on SkinTE™ for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) will be presented at the Diabetic Limb Salvage (DLS) Conference in Washington, DC being held on April 4-6, 2019. SkinTE is a first-of-its-kind autologous, homologous human cellular and tissue-based product designed to regenerate full-thickness, functional skin for the repair, reconstruction and replacement of patient’s own skin … One of the abstracts, which includes data from the pilot study for a randomized controlled trial evaluating SkinTE for DFUs, has been recognized with a Top Abstract Special Designation. The abstracts are being presented by investigators, independent providers and users of the Company’s SkinTE product …Charles M. Zelen, DPM, Foot and Ankle Associates of Southwest Virginia and Director of Professional Education and Research Institute, will present an abstract on the use of SkinTE for treatment of DFUs. This abstract was selected as one of only three abstracts for a Top Abstract Special Designation. The abstract presentation will detail the status of healing of eleven patients treated with SkinTE as part of the pilot study … read more
Cura Surgical’s Silverlon® Antimicrobial Dressing Line
Receives Contract from Premier Inc., a Leading Healthcare Improvement Company
Cura Surgical has been awarded a contract with Premier Inc., a leading healthcare improvement company. This agreement enables Cura Surgical to provide a comprehensive line of unique silver-plated nylon dressings in both Silverlon® and TheraBond® product ranges … Premier Inc., is a healthcare improvement company utilizing an alliance of approximately 4,000 U.S. hospitals and health systems and approximately 165,000 other providers and organizations … “Silverlon has been included in numerous studies that have clearly demonstrated that silver nylon dressings can offer advantages that help to improve patient care,” said Raul Brizuela, president and CEO of Cura Surgical and Argentum Medical, provider of Silverlon. “We are grateful for this opportunity and look forward to working with Premier member hospitals providing improved patient care, enhanced savings, and creating exceptional value through clinical excellence.” …Silverlon® antimicrobial silver-plated dressings provide 50-100xs more silver than other silver-based antimicrobial dressings, and Silverlon’s efficacy is supported by multiple independent, peer-reviewed and published clinical studies. These studies suggest Silverlon® Dressings can be an important element in wound care and that control of wound bacteria within the dressing may help reduce the risk of infection … read more
World first 3D printed feet
It’s gory, sticky and undoubtedly on the nose, but a blend of icing sugar, chicken stock and flexible resin is proving to be the just the right recipe for creating realistic foot ulcers as part of a world-first podiatric training initiative at the University of South Australia … Concocted by UniSA’s Dr Helen Banwell and Dr Ryan Causby the gooey mixture is being added to newly printed 3-dimensional feet and is designed to mimic infected and non-infected diabetic foot wounds …The 3D printed feet are created with wound-like cavities in place. Made from thermoplastic polyurethane (a plastic with many properties, including elasticity, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease … read more
Wearable sensors mimic skin to help with wound healing process
Researchers at Binghamton University, State University of New York, have developed skin-inspired electronics to conform to the skin, allowing for long-term, high-performance, real-time wound monitoring in users … “We eventually hope that these sensors and engineering accomplishments can help advance healthcare applications and provide a better quantitative understanding in disease progression, wound care, general health, fitness monitoring and more,” said Matthew Brown, a PhD student at Binghamton University … Biosensors are analytical devices that combine a biological component with a physiochemical detector to observe and analyze a chemical substance and its reaction in the body. Conventional biosensor technology, while a great advancement in the medical field, still has limitations to overcome and improvements to be made to enhance their functionality. Researchers at Binghamton University’s Intimately Bio-Integrated … read more
HydroCision® Announces Global Licensing Agreement with PROCEPT
BioRobotics, Providing Access to its Proprietary Pump Cartridge Technology
BOSTON and REDWOOD SHORES, Calif., March 26, 2019 /PRNewswire/ — HydroCision, a pioneer in the use of high velocity water jet technology for the minimally invasive treatment of musculoskeletal, spine and wound care conditions, today announced it has provided an exclusive worldwide license of its pump cartridge technology to PROCEPT BioRobotics for use in Urology … The agreement provides PROCEPT BioRobotics with the rights to use HydroCision’s innovative means of pumping high pressure fluids with their AquaBeam® Robotic System, the world’s first surgical robot providing autonomous tissue removal for the safe and effective treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) … “This global agreement with PROCEPT BioRobotics is another significant and strategic step to bring the value of our differentiated technology into new surgical applications affecting millions of people around the world,” commented recently appointed HydroCision CEO, Alain Tranchemontagne. “This is yet another important validation of the value of our proprietary technology.” … read more
Venous Leg Ulcers: Frequently Asked Questions
In my recent WoundSource webinar on management strategies of venous leg ulcers (VLU), I discussed the complex pathophysiology of VLUs and procedural interventions that can help them reach closure … VLUs comprise the majority of lower extremity ulcers. These wounds are costly to treat and have a high rate of recurrence. Sequelae of VLUs include infection or sepsis risk, pain, loss of mobility, and possible amputation. Healing of VLUs requires an understanding of their multifactorial etiology, consideration of patient-specific risk factors, careful assessment, and best practice management for optimal clinical outcomes … The following categories of VLU prevention, management and treatment can help to answer some of the most frequently asked questions about VLU … read more
Neurovascular Response to Pressure in Patients With Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is a problem worldwide, and prevention is crucial. We hypothesized that the inability of the skin to respond to pressure is involved in DFU pathogenesis and could be an important predictive factor to take into account. We included 29 patients with DFU and 30 patients with type 2 diabetes without DFU. Neuropathy and skin blood flow at rest were assessed in response to acetylcholine, sodium nitroprusside, local heating (42°C), and to nonnoxious locally applied pressure. Results were compared with those obtained from 10 healthy age-matched control subjects. Vasodilatation in response to pressure was significantly impaired in both groups with diabetes compared with healthy subjects. The vasodilator capacity to pressure was significantly lower in patients with DFU compared … read more
Mechanism of impaired wound healing in diabetes identified
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have identified a mechanism that can explain the impaired wound healing in diabetes which can lead to diabetic foot ulcers. The study is published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In diabetic mice, wound healing improved when the identified signalling pathway was blocked … Diabetic foot ulcerations are a common complication of diabetes that constitute a major medical, social and economic issue. The lifetime risk of a person with type 1 or type 2 diabetes developing a foot ulcer is around fifteen percent. The treatment options are currently … read more
Bacteria partners with virus to cause chronic wounds
A virus that infects a dangerous bacteria helps it thrive in wounds, according to a study by Stanford researchers. But a vaccine against the virus dramatically cuts the bacteria’s infectivity … A common bacterial pathogen called Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces a virus that substantially increases the pathogen’s ability to infect us, according to a study by investigators at the Stanford University School of Medicine … P. aeruginosa weaponizes its resident virus to exploit the immune system’s distinct responses to bacterial versus viral infections … read more
Janssen Submits Supplemental New Drug Application to U.S.
FDA for INVOKANA® (canagliflozin) for the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
The Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson announced today the submission of a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) seeking a new indication for INVOKANA® (canagliflozin) to reduce the risk of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), the doubling of serum creatinine, which is a key predictor of ESKD, and renal or cardiovascular (CV) death in adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). The submission is based on results from the Phase 3 CREDENCE (Canagliflozin and Renal Events in Diabetes with Established Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation) study, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of INVOKANA® versus placebo in this high-risk patient population when used in addition to standard of care.
Primary investigators will present the CREDENCE data during a late-breaking clinical trials session at the International Society of Nephrology (ISN) World Congress of Nephrology (WCN) Annual Meeting in Melbourne, Australia on April 15 at 8:30 am AEST (April 14 at 6:30 pm EDT in the U.S.). An open access live-stream of the late-breaking presentation can be accessed here (registration is required).
“Today, millions of people living with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease are at high risk of experiencing kidney failure, and unfortunately, we have not seen treatment innovation for these patients in almost 20 years. Janssen’s application is a significant step toward bringing a much-needed, new standard of care for those living with these serious conditions,” said James List, M.D., Ph.D., Global Therapeutic Area Head, Cardiovascular & Metabolism, Janssen Research & Development, LLC. “We look forward to presenting the CREDENCE data at the ISN World Congress of Nephrology and working closely with the FDA to bring this important medicine as quickly as possible to people living with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.” … read more