A comprehensive scoring system to evaluate patient-centered risk factors regarding lower extremity amputation
Abstract: Care of the patient with a presumed life- or limb-threatening lower extremity wound poses many challenges. The mindset regarding potential outcomes of such conditions is mostly driven by the experiences and expertise of those providing the care. This mindset generally appears as two primary actions presented to the afflicted patient: attempted resolution of the problem via medical, surgical or combination treatment, with the hope of low recurrence risk, or exacerbation and amputation—amputations at a level sufficient to, at least in the mind of the surgeon, eliminate the problem. Achieving the former outcome is dependent on a number of factors associated with both patient and caregiver. If healing is achieved, the secondary goal of prevention of recurrence may be no less arduous, with failure most likely resulting in amputation. Clearly, these considerations appear to be based more on the health professionals perception, of the patient’s physical and medical status rather than on patient-centered considerations. This article will review considerations and recommendations for lower extremity amputation, and the short- and long-term implications. Based on our research, there is clear need for a set of criteria against which to weigh not just the medical issues, but also definitive patient-centered issues when considering a lower extremity amputation. We offer a set of patient-centered, easily verified and recognized criteria that we believe addresses this need. The goal of the Miller-Newgent Amputation Scale (MENACE) is to provide a decision base from which to consider and evaluate all factors in determining the need for a lower extremity amputation. This involves identification of patient-centered issues, which are likely to produce satisfactory short- and long-term physical and quality-of-life outcomes if the amputation does proceed.
Declaration of interest: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare. The lead author, as a Board Certified general surgeon with 23 years’ experience in the field of advanced wound care, has been involved in the different aspects to amputation and its considerations and a common thread my colleagues and I have identified is that the expertise of those attempting to heal and salvage limbs was largely ineffectual. More often than not, the progression of high-risk conditions mandated lower extremity amputation. The progression of technology, science and products to promote healing is thought to improve limb salvage rates; however, there has not been an appreciable reduction in amputations. The thought is that those possessing the skill, knowledge and desire to promote limb salvage (which entails greater time and effort with considerably lower compensation) are few and far between. Despite advances in medical care, the rates of lower extremity amputation are unchanged at best or are even increasing.
Despite educational programmes touting the newest technologies for vascular intervention and advanced wound healing to mitigate those conditions commonly leading to amputation, there has been minimal change in the willingness of health professionals to consider limb salvage and indications for amputation have changed minimally. There is a clear need for a matrix against which to compare and contrast the clinical and non-clinical considerations for amputation. Since the patient is the one undergoing this potentially horrific procedure, it is only fair that all aspects of the procedure must be considered as an integral part of the decisionmaking process. The Miller-Newgent Amputation Scale (MENACE) scale was created to provide a patientcentred guide using simple, easily identified information that directly impacts on all aspects of the amputation decision process.
Background Considerations for the intentional removal of a body part have their roots in antiquity. Matthew 5:29–30, 18:8–9 and Mark 9:43–47 are commonly recognised biblical references to amputation. Lower extremity amputation is one of the oldest known surgical practices with Hippocrates among others providing insights.
In the US, 30,000–40,000 amputations are performed annually. In 2005, there were an estimated 1.6 million individuals living with the loss of a limb; by 2050, this figure is expected to rise to 3.6 million.
In 1954, Silbert and Hamiovici published an article recommending that lower extremity amputation be avoided, preferring more conservative surgeries such as supracondylar amputations as opposed to mid-leg amputations. In the paper they cited the Handbook on Amputations, published in 1942 by the Council on Physical Therapy of the American Medical Association, which expressed the opinion of most surgeons, when it advised the use of supracondylar amputations and warned against mid-leg amputations: an opinion justifiable at the time before the advent of antibiotics.
The Netherlands Society of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine in October 2012 published its guideline on Amputation and Prosthetics of the Lower Extremities in which it recommended that the interventional radiologist, vascular internist and rehabilitation physician collectively identify and resolve those clinical issues before proceeding with a lower extremity amputation. Further, the guidelines state that treatment by a multidisciplinary team (MDT) involving a surgeon, anaesthesiologist, pain specialist, rehabilitation specialist, and possibly an internist is necessary for treatment of pain, cardiovascular risks, comorbidity and the co-determination of the level of amputation. The article identified many of the clinical indications for lower extremity amputation found in the literature; however, there is the same omission of any patient-centred, non-clinical concerns.
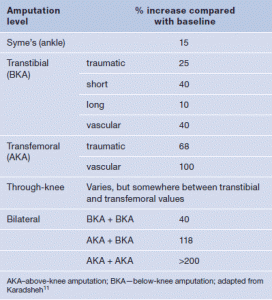
Table 1. Estimated change in metabolic energy expenditure based on level of amputation
Reyzelman and Kim presented their idea of acceptable considerations for partial tissue removal (digital amputation) based on presenting conditions including: osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, gas gangrene, ischaemia/ gangrene and an advancing soft tissue infection. The authors concluded that early digital amputation in the appropriate patient allowed patients a return to normal activity with minimal disability.
Kalapatapu attempted to provide a compendium of indications for lower extremity amputation by providing an exhaustive listing of essentially all lower extremity morbidities. He stated:
‘Primary amputation may be the only option for
patients without an anatomic option for
revascularisation or those with medical risk factors that
contraindicate revascularisation.’
Recognising that the spectrum of surgical and medical skills is considerable, and that there are an almost limitless number of non-medical factors, even attempting to define specific conditions as the basis for amputations is extremely problematic and potentially precludes the surgeon and thus the patient from any consideration of limb salvage.
A patient presenting with a condition prompting even the slightest consideration for lower extremity amputation likely has other issues related directly or indirectly to the presenting condition itself. It is a small leap of faith to recognise that an increase in metabolic demand places greater stress systemically on the patient with a concurrent risk of exacerbating current comorbidities as well as promoting new ones. These increased energy expenditures clearly mandate the highest scrutiny of a patient’s physical condition, both pre- and postoperatively, before undertaking any surgical consideration including lower extremity amputation. Recognising that the loss of an extremity means a dramatic change in the metabolic as well as mental status of the body, the failure to include these considerations potentially impacts on the ability of the patient to engage in activities of daily living. Estimates of the changes in metabolic energy expenditure based on the level of the amputation are shown in Table 1.
However, the definitive consideration must be the effect of survival from a lower extremity amputation since this takes all factors together under a single irreversible endpoint. Survival rates for individuals with dysvascular pathology undergoing major lower extremity amputations including (above the knee amputation) AKA and BKA (below the knee amputation) have been reported as 69.7% and 34.7% at 1 and 5 years, respectively.12 Mortality was found to be significantly higher for patients who underwent AKA (50.6% and 22.5% at 1 and 5 years) as compared with BKA (74.5% and 37.8% at 1 and 5 years).
Although amputation can be considered a failure of treatment, the actual considerations must be based on a number of factors, even when the initial impression is that salvage of the limb is untenable. There are still general categories of lower extremity conditions in which limb salvage is not appropriate. These would include traumatic limb loss or significant tissue deformation from motor vehicle or industrial accidents, malignancies whose location or dissemination precluded salvage, and congenital malformations precluding use of prosthetics or achieving a functional end result. Excluding the majority of these still leaves a considerable number of lower extremity conditions, in which the end result, amputation, unquestionably puts the patient at a higher risk of morbidity and mortality than before the decision to perform the procedure.
At present, the decision to recommend lower extremity amputation appears to be universally based on objective medical issues. Without recognising and attending to the equally important and pervasive, nonclinical, patient-centred issues, the decision is usually made based on the surgeon’s tunnel vision. The most basic tenet becomes that of removing the problem as the key to resolving the problem. As Ertl aptly stated:
‘The only contraindication for amputation is poor
health that impairs the patient’s ability to tolerate
anaesthesia and surgery. However, the diseased limb is
often at the centre of the patient’s illness, leading to a
compromised medical status. The removal of the
diseased limb is necessary to eliminate systemic toxins
and save the patient’s life.’
Unfortunately, the mere removal of an afflicted lower extremity under the guise of resolving the issue takes on a ‘low-hanging fruit’ mentality as it fails to address equally important patient-centred issues that often define the progress and ultimate outcome.
The identification of any criteria regarding the appropriateness of a lower extremity amputation based on patient-centered, non-clinical criteria has been found to be nonexistent despite an exhaustive literature search. This covered 70 years and approximately 200 citations. Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston uses a Pre-Amputation Assessment Checklist that, while comprehensively identifying specific patient expectations and information, does not consider any patient-centered criteria for amputation. Therefore, the Brigham tool does not recognize the potential issues and ultimate outcomes surrounding amputation. In contrast, the MENACE SCALE and its patent-centered components focus the attention on those issues related to non-clinical outcomes when lower extremity amputation is considered.

Table 2
The MENACE scale
It is not enough to objectively quantify only the clinical considerations for lower extremity amputation. The resulting amputation and the effect on quality-oflife must be taken into account. For that reason, there must be a combination of clinical factors together with non-clinical factors. The impact of these patientcentred, non-clinical factors cannot be overstated. The loss of all or part of a limb has a major psychological impact on the patient’s mental status. The psychological effects of amputation can be related to postoperative pain, cosmetic appearance, cultural and social effects, all potentially causing or exacerbating anxiety and depression.
We believe that any initial consideration for lower extremity amputation, regardless of the presenting issues, can be based on two primary factors. Those two factors are intractable pain and functionality in the presence of a potentially life- or limb-threatening condition. While these factors may at first appear to be objective they are equally dependent on the patient’s subjective impressions of their condition.
In considering the issues that ‘open the door’ to amputation, the authors felt that this process is analogous to ‘looking through a keyhole’ from which only a narrowed view is possible. We chose the term ‘keyhole criteria’ to represent this process as initial consideration regarding amputation. The two criteria (Table 2) establish a platform that forms the basis for the critical decision of amputation. These criteria move the decision from one that is based solely on the surgeon’s experience to a more germane one that encompasses considerations of the patient as a whole.
Criterion 1 is significant in that there are lower extremity conditions including neurologic, musculoskeletal or other deficits where attempted preservation would offer no benefit to the patient. When these presentations are associated with debilitating pain, then this criterion would be met and consideration for an amputation at some level would be appropriate. This criterion would require that all attempts be made to mitigate the pain. Thus, an acute presentation (following traumatic accident, postoperative complications from prosthetic implantation, etc.) would arguably require some time to be allowed to pass before accepting these criteria.
The issues regarding criterion 2 include preservation of the patient’s functionality and assumed morbidity and mortality of the presenting condition and that of the procedure. The goal of MENACE is to assure full consideration of all aspects of limb salvage versus amputation. Recognising that lesser procedures may provide both short- and long-term satisfactory outcomes, the issue of when to perform a lesser procedure and what that procedure may be, must be based on preservation of maximum functionality. For these reasons, attention must be directed to the patientspecific issues since information obtained provides the necessary elements required for a successful outcome. For example, the presence of distal pedal gangrenous changes in a diabetic neuropathic ulcer with a history of osteomyelitis poses a daunting problem. Not surprisingly, these findings would, in the vast majority of cases, lead to a strong recommendation for amputation. However, the usual discussion of potential complications and progression of disease state will generally lead to at least a discussion of the ‘benefits’ of simply removing the entire problem-containing lower limb. In contrast, the consideration of functionality is integral because it changes the discussion from one that obviates a potential progression of the presenting problem to one that recognises that retained maximum functionality allows ongoing quality-of-life based on retaining the limb. In simplest terms, if the extremity is still used to bear weight, provide propulsion in a wheelchair, transfer from chair to bed to commode, or even ambulate for any distance, then maintenance of that functionality takes on the highest priority. The goal becomes maximising the longevity and functionality of that extremity.
The authors believe that the two keyhole criteria represent a mandatory check step for medical providers who either perform or refer to those performing lower extremity amputation. These two criteria need to be used to ascertain the appropriateness of amputation for a given patient. This represents a marked departure from the practice that the decision be based on the perception of perceived benefit of amputation.
Initial evaluation of the patient’s presenting status with respect to the keyhole criteria should be undertaken. If the result is a decision to amputate, the MENACE scale assures that patient-centred factors are considered in the decision to amputate. Those factors placing the patient at risk for quality-of-life issues after surgery should be addressed well before amputation.
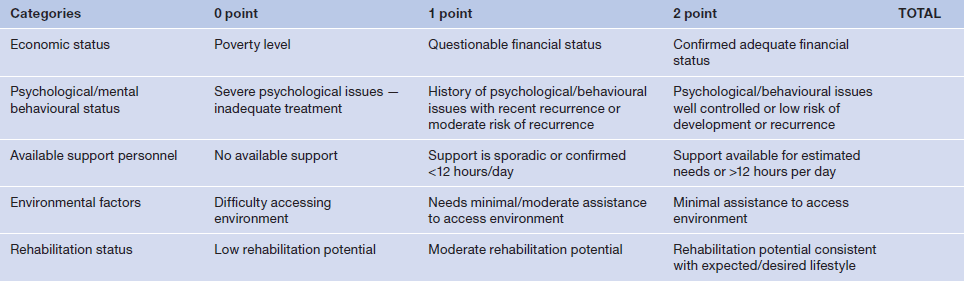
Table 3
The initial tool used by the authors was the 1–2 point scale to assess patient-centred factors. However, we recognised that the keyhole criteria were needed to focus the attention of the surgeon on what the authors felt were the two critical issues: pain and functionality.
With the focus now placed on the patient, those factors that impact on their lives both pre- and postoperatively need to be considered. While there are an infinite number of both specific and general categories to be considered, we believe that those factors identified in Table 3 represent the most salient, recognising the interrelationship of these factors and others not specifically identified.
The social status of the patient is integral to mental and physical wellbeing. Considerations must include: Who else is in the home? What will be the patient’s functional capacity both before and after the amputation? What is the expected effect on the family after amputation? Is the patient the primary breadwinner/caretaker for the family? Are there others who will be affected by the patient’s amputation status in the same environment (young children, teenagers, young adults, middle-agers)?
Habitation factors must include: where does the patient live (both geographically and in terms of the actual residence)? The geographic location, including changes in elevation (mountainous, or San Francisco hills), whether there are stairs to navigate, or consistently functioning lifts, and old versus new construction (ADA, Standards for Accessible Design related to the Americans With Disabilities Act)15 are all considerations that must be addressed before amputation.
Economic factors are the underpinning of what transpires with the patient and their direct family and friends. How will the patient’s economic status change after the amputation? Financial considerations are the bedrock on which much of the other issues achieve stability. Are they ready for retirement? Are they employable after amputation? Is there another breadwinner? Are they financially able to withstand loss of leg? What about the costs of treatment, prosthetics, devices? Are there accessible and available sources available to provide external financial support and can the patient access them (social security, disability insurance, etc.)? Is there adequate and sustained financial means either through a health insurance or other entity to pay for ongoing care including rehabilitation, care for any complications, medications, therapies, home health care, and if so for how long?
Interpersonal support and functional issues have the potential to create effects that reverberate throughout the entire recuperative period and beyond. What other intrinsic/extrinsic factors do they have to contend with? Do they live with conditions such as a small cluttered house (hoarder), ‘bad’ neighbourhood, difficulty getting to the grocery store, doctors, and social events? Is there inter-family stress such as abusive or uncaring children or relatives?
What psycho-emotional and self-perception issues are present? Do they already have body-centred issues (too fat, too skinny, too old, too sick …)? Is there a history of behavioural or mental health issues (depression, anxiety, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, etc.)? How are they dealing with the potential amputation? Do they consider the recommendation for amputation a ‘death sentence’? Is there the opportunity to do something besides see the wound specialist all the time? How will they deal with the resultant disfigurement? The ultimate question is clearly: how important is that toe, foot, or leg to their life?
An exhaustive online search of the available literature identified definitive criteria/guidelines for removal of the gallbladder, appendix and performance of caesarean sections as well as numerous other surgeries. However, regarding amputation of a lower extremity, the overwhelming majority of articles that even entertain the rationale for performing the procedure present surgeon-based clinical considerations as the primary decision criteria and mention patient-centred factors only in passing.
Based on the experiences of the authors, there clearly needs to be a set of patient-centred criteria to juxtapose with the experiences of the surgeon and other providers integral to the decision-making process. We recognise that there are a myriad of compounding factors that affect provider and patient considerations that are easily overlooked and so a set of guidelines for evaluation such as the MENACE scale identifies those factors that can be easily evaluated and rectified.
The MENACE scale including the keyhole criteria has been used by the primary author for 23 years in one form or another. Explanation and review of the MENACE critera has been undertaken with our patients for whom amputation was the only alternative offered before coming to our clinics. In clinical practice, numerous encounters have occurred with patients marked for amputation in which their presenting condition was clearly (and ultimately) salvageable. Based on extensive clinical use, we believe that the appropriate use of this tool can balance the patient’s presentation using both the accepted medical/surgical objective criteria and the less often considered patientcentred criteria. In those situations the decision for amputation gains more credence as evaluation progresses, for those MENACE scale categories in which the highest score (2 points) is not present, appropriate actions and interventions are taken to maximise that score. For example, the patient who lives in an upperfloor apartment with an unreliable lifts should have their residence changed to one with greater accessibility even if this is to occur immediately after the surgery. The planned change allows for the full score for that category to be considered as accomplished despite its implementation postoperatively. The same holds for caregivers needed in the home following surgery. The key to MENACE is to recognise that maximising a successful outcome after the elective performance of a lower extremity amputation must be based on resolving as many patient-centred stumbling blocks as possible. We recognise that the act of doing so may not be appropriate for the surgeon themselves but believe strongly that it can be appropriately achieved by other entities including social workers, local, state and federal entities.
Based on our use of the MENACE scale in our own practices, we believe that a score of less than seven strongly suggests the highest potential for postoperative issues that will have an impact on the patient’s shortand long-term recovery and status. The failure to address identified issues both individually and collectively in the preoperative/perioperative periods may preclude a safe and complication-free recovery. MENACE was created to fill an unmet need. We understand that MENACE will require ‘real-life’ testing and validation. It is our expectation that when used alongside other criteria, it will provide a basis for expansion, revision, confirmation or deletion of the considerations we have proposed when a lower extremity amputation is considered.
Conclusion
The recommendation for, and performance of, a lower extremity amputation appears to be based primarily on criteria that remain undefined despite advances in all aspects of medicine. Although certain lower extremity presentations preclude safe attempts at limb salvage, there is clearly a trend towards performance based more on subjective criteria of the attending health-care providers than on clear objective patient-based criteria.
Lower extremity amputation does not merely remove all or part of the lower extremity. The interdependence of structure and function, both before and after amputation, and the potentially catastrophic consequences of failing to consider these factors, mandates that there be a specific and definitive categorical assessment of patient-centred factors rather than the current criteria, which are based solely on the skill, education and experience of the medical providers. When these decisions are based solely on their own criteria rather than those of the patient—who represents the primary consideration regarding a successful outcome—then failure to identity and resolve potential patient-centred issues means that the patient is not truly the focus of the intended procedure, although they will suffer any untoward effects. The loss of a lower extremity does not merely mean that a pending problem has been resolved but that the potential loss of the limb now presents its own life-affecting challenges well beyond the time that the surgical incision heals.
References
1 Quality Improvements Organization. Strategies to Help Reduce
Diabetes-Related Lower Extremity Amputations Among Minority
Populations. April 2017, https://tinyurl.com/yd3hcgrn (accessed 7
September 2017)
2 Murdoch G, Bennett-Wilson A Jr, Amputation: Surgical Practice and
Patient Management. Butterworth-Heinemann Medical, 1996.
3 Tooms RE. Amputations. In: Crenshaw AH (ed). Campbell’s Operative
Orthopedics (7th edn) Mosby-Year Book,1987: 597–637
4 Ertl JP. Amputations of the lower extremity. Medscape. 2016. http://bit.
ly/2uUFuEv (accessed 14 August 2011)
5 Zeigler-Graham K, Mackenzie EJ, Ephraim PL et al. Estimating the
prevalence of limb loss in the United States: 2005 to 2050. Arch Phys
Med Rehabil 2008; 89(3): 422-429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.
apmr.2007.11.005
6 Silbert S., Haimovici H. Criteria for the selection of the level of
amputation for ischemic gangrene. JAMA 1954; 155(18): 1554–1558.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1954
7 Book Notices: Handbook on Amputations JAMA 1942; 120(9):724.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1942.02830440066028
8 Netherlands Society of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine
(Nederlandse Vereniging van Revalidatieartsen – VRA). Guideline: amputation and prosthetics of the lower extremities. Utrect. 2012. http://bit.ly/2uCbGRM |
9 Reyzelman A, Kim J. A guide to digital amputations in patients with
diabetes. Podiatry Today. 2011; 24(9). http://bit.ly/2wX6Ew2 (accessed 14
August 2011)
10 Kalapataku V. Lower extremity amputations. UpToDate. 2017. http://
www.uptodate.com/contents/lower-extremity-amputation (accessed 14
August 2017)
11 Karadsheh M. Amputations. Orthobullets.com. 2017. http://www.
orthobullets.com/trauma/1052/amputations (accessed 14 August 2017)
12 Brigham And Women’s Hospital Department of Rehabilitation
Services. Physical therapy standard of care: lower extremity amputation.
2011. http://bit.ly/2vwFFct (accessed 14 August 2011)
13 Hakami, K. Pre-operative rehabilitation evaluation of the dysvascular
patient prior to amputation. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2009; 20(4):
677-688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmr.2009.06.015
14 Bhuvaneswar CG, Epstein LA, Stern TA. Reactions to amputation:
recognition and treatment. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry 2007;
9(4): 303–308
15 ADA. Information and technical assistance. standards for accessible
design related to the Americans With Disabilities |