 Chronic Wounds and Technology
Chronic Wounds and Technology
Chronic wounds can be notoriously difficult for many clinicians to manage. It is only natural, then, that we are always looking for the newest, most technologically advanced dressings and treatments to help … Let’s use the example of pressure injuries, a relatively common type of chronic wound. Despite our best efforts, to date, no advanced wound dressings have been shown to be any better than any other dressings. It can be quite difficult to assess whether chronic wounds are infected. We found that the presence of increasing pain may make infection of a chronic wound more likely. It is still unclear what, if any, blood tests or quantitative swab cultures are most diagnostic …
Guidance on device-caused ulcers coming
Global experts seeking to reduce the risk of medical device-related pressure injuries and influence the design of new prevention technologies will issue their first consensus document this fall …
The guidelines will look at device use among older people with fragile skin, according to an editorial published recently in the Journal of Wound Care.
Bioinspired mechanically active adhesive dressings to accelerate wound closure
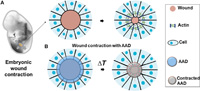 Wound management remains a central concern in clinical care because of the constant incidence of traumatic injuries, the rising prevalence of chronic wounds such as diabetic ulcers and pressure sores, and aging populations that exhibit diminished wound healing ability (1–3). Skin injuries are painful and can compromise the integrity and protective function of the skin, resulting in infections. Current treatment options involve gauzes, cotton wools, and dressings, which aim to primarily maintain the moisture at wound sites, manage exudates, and protect the wound from pathogenic infections …
Wound management remains a central concern in clinical care because of the constant incidence of traumatic injuries, the rising prevalence of chronic wounds such as diabetic ulcers and pressure sores, and aging populations that exhibit diminished wound healing ability (1–3). Skin injuries are painful and can compromise the integrity and protective function of the skin, resulting in infections. Current treatment options involve gauzes, cotton wools, and dressings, which aim to primarily maintain the moisture at wound sites, manage exudates, and protect the wound from pathogenic infections …
Bioinspired mechanically active adhesive dressings to accelerate wound closure
Inspired by embryonic wound closure, we present mechanically active dressings to accelerate wound healing. Conventional dressings passively aid healing by maintaining moisture at wound sites. Recent developments have focused on drug and cell delivery to drive a healing process, but these methods are often complicated by drug side effects, sophisticated fabrication, and high cost. Here, we present novel active adhesive dressings consisting of thermoresponsive tough adhesive hydrogels …
Bioinspired wound dressing contracts in response to body heat
uts, scrapes, blisters, burns, splinters, and punctures — there are a number of ways our skin can be broken. Most treatments for skin wounds involve simply covering them with a barrier (usually an adhesive gauze bandage) to keep them moist, limit pain, and reduce exposure to infectious microbes, but they do not actively assist in the healing process …
Fish skin acellular dermal matrix: potential in the treatment of chronic wounds
The role of cellular and tissue-based therapies (CTPs) in the treatment of chronic wounds continues to grow. However, the utility of these is only partially investigated and very few head-to-head studies exist. In general, the ideal CTP would provide a structural matrix which would allow for dermal and epidermal regeneration with a single application. At present, this Holy Grail is very far from where we are. However, new CTPs continue to be designed with the goal of wound closure in mind. Acellular fish skin (AFS) is one such therapy. The histologic features make it amenable to cellular modulation, and its ability to provide omega-3 fatty acids to the local tissue makes it an unprecedented anti-inflammatory
Laser therapy for onychomycosis in patients with diabetes at risk for foot ulcers: A randomized, quadruple-blind, sham-controlled trial
Researchers conducted this randomized, quadruple-blind, sham-controlled trial to assess the effectiveness and safety of the treatment of onychomycosis with local laser therapy. For this investigation, patients with diabetes mellitus microbiological confirmation at risk of developing diabetic foot ulcers (Sims classification score 1, 2) and a clinical suspicion on onychomycosis were randomized to either 4 sessions neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd-YAG) 1064 nm laser or sham therapy. The most detected pathogen was Trichophyton rubrum. No difference was found in the primary outcome between laser and sham treatment.
Topical Fluoxetine as a Novel Therapeutic That Improves Wound Healing in Diabetic Mice
3D Bioprinting of Self-Standing Silk-Based Bioink
Xiaoquin Wang at Soochow University and David Kaplan at Tufts University report on the preparation of a new silk based bioink for 3D printing of tissue constructs. The ink is composed of silk fibroin protein and PEG, which can be printed with high resolution and shape fidelity. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can printed together with the ink and are growing in vitro and in vivo implanted in mice for more than 6 weeks …
Smart bandage covering your wound and healing progress looks to 5G tech
(Tech Xplore)—Some technology watchers this week are talking about “smart” bandages, and the question is, why are they smart, and what can they do?
Closure of Refractory DFUs and Venous Stasis Leg Ulcers Using an Autologous Homologous Skin Construct
Dr. David Armstrong reports the results of a pilot study evaluating 11 patients with diabetic foot ulcers and 5 with venous stasis leg ulcers (all being refractory to at least 1 month of conservative care) that were treated with an autologous homologous skin construct; these results were presented as a poster (“Closure of Refractory Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Venous Stasis Leg Ulcers Using a Single Application of an Autologous Homologous Skin Construct in the Clinic Setting”) at the Symposium on Advanced Wound Care Spring 2019 in San Antonio, Texas.
How a certified wound care nurse improves outcomes, reduces costs
Having a certified wound care nurse on staff makes a positive difference for both patient care and the bottom line.
Researchers have found reducing pressure injury rates saves money, with individual organizations that prevent even just one stage 3 or stage 4 pressure injury saving $20,000 in direct costs or up to $120,000 in total cost …
Relias now Offers Wound Care Education Institute® (WCEI®) Online Wound Care Curriculum as Part of the Relias Family of Solutions
Course content designed to help clinicians identify, prevent, treat and document clinically sound wound care, as well as prepare for wound care certification
Morrisville, NC, July 30, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Relias, a trusted partner to more than 10,000 healthcare organizations around the world, today announced the addition of online wound care curriculum and certification exam prep education from the Wound Care Education Institute (WCEI), originally co-founded by registered nurses, Nancy Morgan and Donna Sardina …
Spectral MD Gets $27M to Advance Trials of AI-Powered Wound, Burn Care Device
 Dallas-based biotech startup Spectral MD has received $27 million from the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority for an expanded proof-of-concept clinical trial of its AI-powered Deepview system that targets wound and burn care assessment in pediatric patients … Spectral MD’s work could benefit the everyday treatment of wounds and burns as well as be a tool in the response to mass burn casualties in a national emergency. “During a radiological or nuclear emergency, surgeons could have thousands of patients …
Dallas-based biotech startup Spectral MD has received $27 million from the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority for an expanded proof-of-concept clinical trial of its AI-powered Deepview system that targets wound and burn care assessment in pediatric patients … Spectral MD’s work could benefit the everyday treatment of wounds and burns as well as be a tool in the response to mass burn casualties in a national emergency. “During a radiological or nuclear emergency, surgeons could have thousands of patients …
The Effects of Ultraviolet C Irradiation in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds: A Retrospective, Descriptive Study
Although there is evidence supporting the bactericidal effects of ultraviolet C (UVC) in chronic wounds, clinical studies examining the effects of UVC on wound healing are limited. Purpose: The objective of this single-center, retrospective, descriptive study was to evaluate the effect of UVC as an adjunct modality to standard wound care. Methods: Data from January 1, 2015, through August 30, 2015, from all patients receiving UVC treatment and wound etiology-appropriate standard care provided twice …
Cost of treating diabetic foot ulcers in five different countries
Most estimates in the literature for the economic cost of treating a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) are from industrialized countries. There is also marked heterogeneity between the complexity of cases considered in the different studies. The goal of the present article was to estimate treatment costs and costs to patients in five different countries (Chile, China, India, Tanzania, and the United States) for two hypothetical, but well-defined, DFUs at the extreme ends of the complexity spectrum.
Diabetic Wound Care: New Discovery Points Toward Possible Treatment for Non-Healing Wounds
A new mouse and human tissue study identifies an enzyme critical for normal wound healing
For the average person, getting a cut or scrape on the foot may not be cause for immediate concern. However, for people with type 2 diabetes, these wounds can be life-threatening. According to a 2016 study, one-third of the cost of type 2 diabetes treatment is related to non-healing diabetic foot wounds and ulcers, which are the leading cause of amputation in the United States.
 New EWMA Document: Atypical wounds – Best clinical practices and challenges
New EWMA Document: Atypical wounds – Best clinical practices and challenges
The new EWMA Document Atypical Wounds – Best Clinical Practices and Challenges addresses the wounds that are creating the most challeging situations for clinicians and/or patients from a prevention, treatment and organisational perspective.
Diabetic foot care providers’ perspectives on barriers and facilitators to delivering patient-focused foot care services: A qualitative descriptive study
What are health care providers’ perspectives on the barriers and solutions to delivery of evidence-informed, patient-focused foot care and foot wear services? This study examined health care professionals – foot care providers’ perspectives on the barriers and solutions to delivery of evidenceinformed, patient-focused foot care services.
Biomaterial-based regenerative approaches would allow cost-effective off-the-shelf solution for the treatment of wounds. Dmitri. A. Ossipov et al. from Uppsala University in Sweden report a facile chemical strategy to generate “ready-to-use” HA supramolecular hydrogel that is uniquely adapted for the clinical applicability of wound treatment as it can fill irregularly shaped wound defects without the need for premolding …

Nexodyn Wound Care Solution Launched in the U.S.